目录

1.预备知识
我们要了解一下map和set这两个容器,可以到C++官网中搜索map和set进行了解,以下是C++官网链接:
如果想了解更多,可以去看我写的两篇关于map和set的博客:
C++进阶-set-优快云博客文章浏览阅读608次,点赞23次,收藏17次。本文系统介绍了C++ STL中的set容器的特性与使用方法。set作为关联式容器,基于红黑树实现,具有自动去重和排序功能,增删查效率为O(logN)。文章详细讲解了set的构造函数、常用成员函数(如emplace_hint、key_comp等)以及边界查找函数(lower_bound、upper_bound等),并通过代码示例演示了其具体用法。同时对比了set与multiset的差异,指出后者允许重复元素。最后通过两个力扣编程题(查找数组交集和环形链表入口)展示了set的实际应用场景,体现了其在数据去重和快https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/2401_86446710/article/details/149322360?spm=1011.2415.3001.10575&sharefrom=mp_manage_linkC++进阶-map-优快云博客文章浏览阅读835次,点赞26次,收藏14次。本文介绍了C++ STL中的map容器。map是基于二叉搜索树实现的键值对容器,具有自动排序特性。文章详细讲解了map的声明方式、构造函数、operator[]操作符(可查找/插入元素)、at方法(安全访问)、emplace_hint高效插入等核心功能。特别强调了map与set的区别在于存储键值对,以及operator[]的独特行为(找不到键时会自动插入)。还介绍了辅助类pair的用法,以及key_comp/value_comp比较函数的使用。通过多个代码示例演示了map的基本操作,包括元素访问、修改和异常
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/2401_86446710/article/details/149344636?spm=1011.2415.3001.10575&sharefrom=mp_manage_link非常建议去了解一下C++的红黑树的内容,以方便我们实现map和set:
map和set的iterator和list差不多,建议各位参考一下list的模拟实现,可以见以下博客:
2.初步代码
该代码是实现红黑树的实现时,去掉注释后的代码:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <assert.h>
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
enum Color
{
Red,
Black
};
template<class K,class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
Color _col;
RBTreeNode(const pair<K,V>& kv)
:_kv(kv)
,_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
{ }
};
template<class K,class V>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
assert(parent != nullptr);
Node* subL = parent->_left;
assert(subL != nullptr);
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
subL->_right = parent;
if (subLR)
{
subLR->_parent = parent;
}
Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parent == _root)
{
subL->_parent = nullptr;
_root = subL;
}
else
{
if (parentParent->_left == parent)
{
parentParent->_left = subL;
}
else
{
parentParent->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = parentParent;
}
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
assert(parent != nullptr);
Node* subR = parent->_right;
assert(subR != nullptr);
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
{
subRL->_parent = parent;
}
subR->_left = parent;
Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (parent == _root)
{
subR->_parent = nullptr;
_root = subR;
}
else
{
if (parentParent->_left == parent)
{
parentParent->_left = subR;
}
else
{
parentParent->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = parentParent;
}
}
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = Black;
return true;
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(kv);
cur->_parent = parent;
if (parent->_kv.first > kv.first)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_col = Red;
while (parent && parent->_col == Red)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
{
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur->_col = Black;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = Black;
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Check(Node* root, int blackNum, const int refNum)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
if (refNum != blackNum)
{
cout << "存在⿊⾊结点的数量不相等的路径" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
if (root->_col == Red && root->_parent->_col == Red)
{
cout << root->_kv.first << "存在连续的红⾊结点" << endl;
return false;
}
if (root->_col == Black)
{
blackNum++;
}
return Check(root->_left, blackNum, refNum)
&& Check(root->_right, blackNum, refNum);
}
bool IsBalance()
{
if (_root == nullptr)
return true;
if (_root->_col == Red)
return false;
int refNum = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == Black)
{
++refNum;
}
cur = cur->_left;
}
return Check(_root, 0, refNum);
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_kv.first << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};以上代码将会放到RBTree.h文件中。
3.对红黑树实现的代码进行改造
改造红黑树代码是为了实现我们的set和map两个容器。
由于set是只存放了一个值,故我们要把红黑树的结点结构改成key结构:
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
T _data;//存放数据,可以传递T为pair类型
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
Color _col;
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
{
}
};我们还需要把RBTree.h中改一部分:
template<class K,class T>
class RBTree
{
public:
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
bool Insert(const T& kv)
{//……
}
//……
};Insert函数里面结构我们先不要改,之后再进行集中改变。
4.对map和set的改造
首先我们需要把map和set的基本结构写出来,这里map的模拟实现放到mymap.h中,set的模拟实现放到myset.h中:
//myset.h
#include"RBTree.h"
template<class K>
class myset
{
public:
//以后代码增加的地方
bool insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K, K> _t;
};为了不破坏太多的RBTree结构,我们这里的set就构造成key-key结构,保持和set的源码的方式一样(源码各位可以自行搜索,如果想改造成一个参数的结构就把RBTree第二个模板参数置为缺省参数,缺省值为K)。
//mymap.h
#include"RBTree.h"
template<class K,class V>
class mymap
{
public:
//以后代码增加的地方
bool insert(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<K,V>> _t;
};这样写的原因是:我们的RBTree的第二个模板参数是T,相当于我们的键值对,这样写主要是为了适应RBTree的insert函数。
5.对RBTree::insert的改造
改造该函数之前的代码:
bool Insert(const T& kv)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = Black;
return true;
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(kv);
cur->_parent = parent;
if (parent->_kv.first > kv.first)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_col = Red;
while (parent && parent->_col == Red)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
{
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur->_col = Black;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = Black;
return true;
}由于参数改变,我们需要把_kv.first直接变成_data,所以有:
bool Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = Black;
return true;
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_data > data)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_data < data)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
cur->_parent = parent;
if (parent->_data > data)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_col = Red;
while (parent && parent->_col == Red)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
{
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur->_col = Black;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = Black;
return true;
}这里主要是要注意一下:如果我们是插入一个键值对即pair类型时,如果我们直接用parent->_data<data能不能比较出正确的结果,实际上,我们在C++官网中也很容易得到结论:
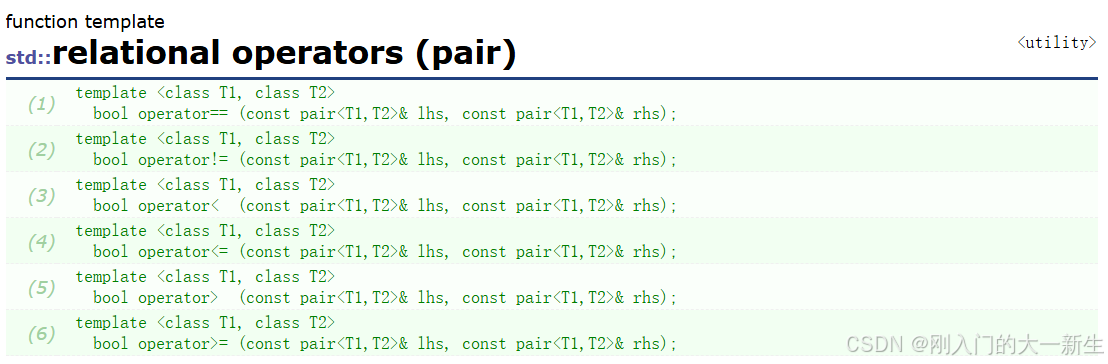

但是我们就想要只用first进行比较,所以我们不能直接这样写。
如果我们使用仿函数来进行比较逻辑,那么在这个时候也是不行的,因为如果用仿函数的话,我们要Find,而Find是用key来比较的,如果用仿函数,我们如何取得map的key值从而使比较逻辑正确?
实际上,我们可以用仿函数进行,但是这个仿函数不能单单用来比较大小,还要取得key,这个时候,我们可以这样写:
//RBTree.h
template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{};通过给RBTree增加一个模板参数来接收仿函数进行比较的逻辑,同时要改:
//myset.h
template<class K>
class myset
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};//mymap.h
template<class K,class V>
class mymap
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
private:
RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};同时,我们还需要把比较逻辑改成二者key的比较,所以可以这样写:
bool Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = Black;
return true;
}
KeyOfT kot;
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
cur->_parent = parent;
if (kot(parent->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
//……
}6.对RBTree::Find函数的改造
和insert函数类似,我们也可以对Find函数进行改造:
//RBTree.h
bool Find(const K& key)
{
KeyOfT kot;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}7.实现iterator(最重要)
实现iterator的思路:
(1)iterator实现的⼤框架跟list的iterator思路是⼀致的,⽤⼀个类型封装结点的指针,再通过重载运算符实现,迭代器像指针⼀样访问的⾏为。
这里我先把iterator基本结构写出来:
//RBTree.h
template<class T>
struct _TreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef _TreeIterator<T> Self;
Node* _node;
_TreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{ }
T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
T* operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node!=s._node;
}
};我们这里主要要理解一下如何实现operator++和operator--。
首先map和set走的是中序遍历,所以返回的第一个结点的iterator是begin()。
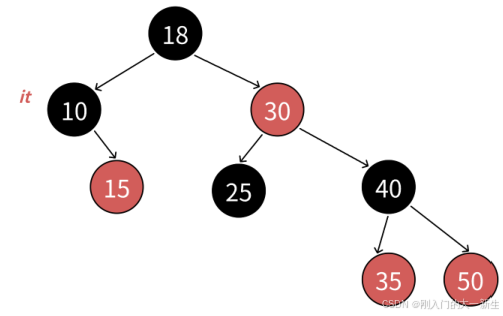
第一个结点就是10这个结点,也就是说我们需要从根结点开始走起,一直往左子树遍历,直到左子树为空时。
(2)迭代器++的核⼼逻辑就是不看全局,只看局部,只考虑当前中序局部要访问的下⼀个结点。
我们不用管其他结点,就看这个子树,如果这棵子树遍历到左孩子,就看根;如果遍历到根,就看右孩子。
(3)迭代器++时,如果it指向的结点的右⼦树不为空,代表当前结点已经访问完了,要访问下⼀个结点是右⼦树的中序第⼀个,⼀棵树中序第⼀个是最左结点,所以直接找右⼦树的最左结点即可。
(4)迭代器++时,如果it指向的结点的右⼦树空,代表当前结点已经访问完了且当前结点所在的⼦树也访问完了,要访问的下⼀个结点在当前结点的祖先⾥⾯,所以要沿着当前结点到根的祖先路径向上找。
(5)如果当前结点是⽗亲的左,根据中序左⼦树->根结点->右⼦树,那么下⼀个访问的结点就是当前结点的⽗亲;
(6)如果当前结点是⽗亲的右,根据中序左⼦树->根结点->右⼦树,当前结点所在的⼦树访问完了,当前结点所在⽗亲的⼦树也访问完了,那么下⼀个访问的需要继续往根的祖先中去找,直到找到孩⼦是⽗亲左的那个祖先就是中序要访问的下⼀个结点。
这上面都是有些难以理解的,我这里就直接用画图的方式加以讲解:
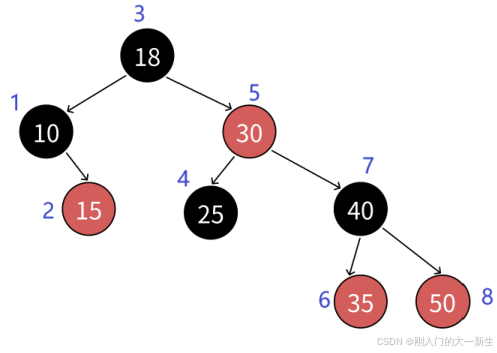
我按照中序遍历的顺序进行讲解。
首先从根结点开始往左子树遍历,发现18的左孩子不为空,则10作为左子树的根结点继续遍历,然后发现10没有左孩子,这个时候就遍历到10这个结点。
遍历到10结点后,++,我们发现10为根结点,所以要继续遍历右子树,遍历到15结点,发现15结点没有左孩子,所以直接返回到15这个结点。
遍历到15结点后,++,我们发现15结点没有右子树,所以往上递归,然后发现10为18的左孩子,所以是一定遍历过的,所以就继续往上;发现18是根结点,这个时候就返回18这个结点了。
遍历到18结点后,++,发现30为右孩子,而且30还有左孩子,所以遍历到25,发现25没有左孩子,所以返回25。
遍历到25结点后,++,发现25没有右孩子,所以返回到25的父亲,到30结点,返回30。
遍历到30结点后,………………
直到到达50结点(已经被访问过),如果++,发现没有右孩子,然后往上,发现父亲都为爷爷的右孩子,证明该子树遍历完,所以继续往上访问,直到没有父亲或者该孩子为父亲的左结点为止。这个时候我们发现父亲为空,则这个时候返回nullptr,所以这个时候直接就是用nullptr构造一个结点进行返回。
//_TreeIterator
Self& operator++()
{
//中序遍历,这个时候就需要访问右孩子
if (_node->_right)
{
//找右子树的最左结点
_node = _node->_right;
while (_node->_left)
{
_node = _node->_left;
}
}
else
{
//右子树为空
//对应15结点或者50结点
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
//当parent不为空,且cur为parent的右孩子是继续往上
//因为这代表该子树已经遍历完了
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//要么cur是parent的左孩子,这个时候就可以直接用_node=parent
//这两种情况都可以这样写
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}以上逻辑需要结合画图理解,最重要的是我们要理解为什么当右孩子没有时要往上递归,因为这个时候该子树都遍历完了(如:15结点,为10的右孩子,根据左根右的遍历方式,右孩子都被遍历完了,那么也就代表根也被遍历完了,所以我们需要往上,此外,如果cur(当前结点)是父亲的左孩子,代表父亲(根)还没有被遍历,所以直接用父亲作为结点返回)。
相似的逻辑我们还可以写出--,其逻辑和++完全相反,不过还有特殊处理一下当_node==nullptr的情况,这个时候就是end(),我们需要得到root以遍历子树:
//_TreeIterator
Node* _root;
_TreeIterator(Node* node,Node* root)
:_node(node)
,_root(root)
{ }
Self& operator--()
{
if (_node == nullptr) // end()
{
// --end(),特殊处理,⾛到中序最后⼀个结点,整棵树的最右结点
Node* rightMost = _root;
while (rightMost && rightMost->_right)
{
rightMost = rightMost->_right;
}
_node = rightMost;
}
else if (_node->_left)
{
//代表该子树还没遍历完
//找左子树的最右结点
_node = _node->_left;
while (_node->_right)
{
_node = _node->_right;
}
}
else
{
//该子树被遍历完
//向上查找,直到查找到根或者该孩子为父亲的右孩子
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}我们的目的是为了得到Bgein和End,所以在RBTree中加:
//RBTree
public:
typedef _TreeIterator<T> Iterator;
Iterator Begin()
{
Node* minleft = _root;
while (minleft && minleft->_left)
{
minleft = minleft->_left;
}
//调用_TreeIterator
//相当于_TreeIterator(minleft)
return Iterator(minleft, _root);
}
Iterator End()
{
return Iterator(nullptr, _root);
}同样,我们还需要在mymap和myset中进行修改:
//myset
public:
typedef RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}//mymap
public:
typedef RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}这个时候要注意:我们现在在测试文件中随便写一个主函数都会报错:
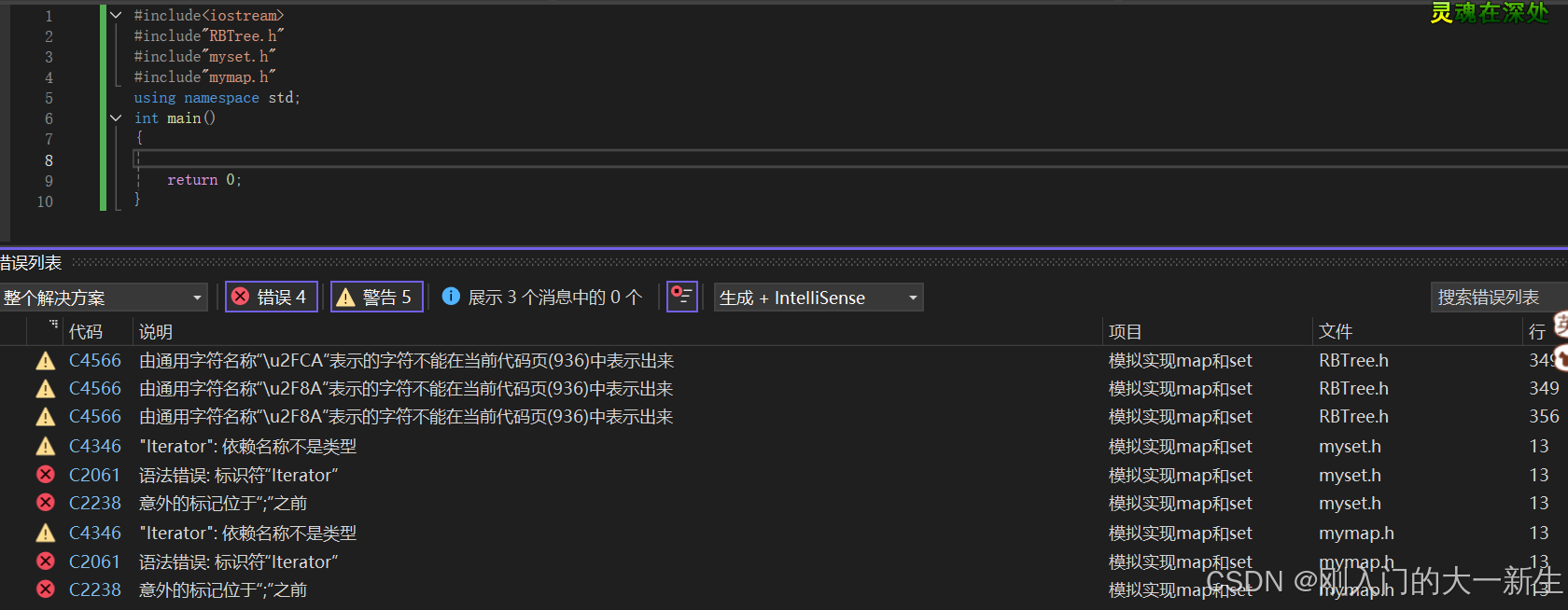
这主要是因为:如果我们要取模板里面的类型(含内嵌类型、内部类)都要加typename,因为取模板里的东西,现在的模板可能还没有实例化,此时取的模板里面的类型编译器分不清楚它是静态成员变量还是内嵌类型,而我们这样写:
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;那个typename就是告诉编译器这是一个类型,是合乎语法的,而确定这个类型要等到类模板被实例化后就可以了,这样就没问题了。
不过我们也可以改造成这样也是没问题的:
using iterator = typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator;
using iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator;这种写法更好一些,以后见到这种写法也不要奇怪。
以上是iterator基本的实现,不过如果你觉得可以再进行完善功能的话也可以,以下代码可以选择性加到_TreeIterator中:
//_TreeIterator
bool operator==(const Self& s)
{
return _node == s._node;
}
//后置++
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp = *this; // 保存当前状态
++(*this); // 调用前置++实现
return tmp; // 返回旧值
}
//后置--
Self operator--(int)
{
Self tmp = *this; // 保存当前状态
--(*this); // 调用前置--实现
return tmp; // 返回旧值
}8.实现const_iterator
和list一样,我们最好还是不要增加一个一样的类来实现const_iterator,可以在_TreeIterator模板参数后加两个模板参数,以下是_TreeIterator的改造:
//_TreeIterator
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct _TreeIterator
{
typedef _TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;//Ref:引用,Ptr:指针
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
};以下是对RBTree的改造:
template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
public:
typedef _TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;
typedef _TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> ConstIterator;
ConstIterator Begin() const
{
Node* minleft = _root;
while (minleft && minleft->_left)
{
minleft = minleft->_left;
}
return ConstIterator(minleft, _root);
}
ConstIterator End() const
{
return ConstIterator(nullptr, _root);
}
};同理,我们还需要在mymap和myset中进行改造:
//myset
public:
//下面两种随意选:
//typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.End();
}//mymap
//下面两种随便选一种
//typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.End();
}9.完成set和map的key不能修改
这个是改造代码比较少的部分,但是还是需要注意,我们不支持key修改不是代表value不支持修改,所以需要改造成这样:
//myset
public:
//下面两种随意选
//typedef typename RBTree<K,const K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
using iterator = typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator;
//下面两种随意选
//typedef typename RBTree<K,const K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K,const K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;
private:
RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;需要注意的是RBTree的第二个参数才是所存储的东西,所以是第二个参数加const,第一个参数代表的是类型,第二个参数代表的是所存储的值。
类似,我们还可以对mymap进行改造:
//mymap
public:
//下面两种随便选一种
//typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
using iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator;
//下面两种随便选一种
//typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;10.实现map的operator[]
首先,实际上,map的Insert函数返回值是pair<Iterator,bool>类型,map的operator[]会根据insert的返回值的bool来判断是否需要插入,当insert成功时,第一个参数是为新插入位置的结点地址,当insert失败时,第一个参数是为原结点的地址。
而这个时候operator[]就返回了该结点对应的值(value)。
所以关键是对Insert的改造,我们可以改造成这样:
//RBTree
pair<Iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = Black;
return { Iterator(_root,_root),true };//隐式类型转换
}
KeyOfT kot;
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return { Iterator(cur,_root),true };
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newnode = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
if (kot(parent->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_col = Red;
while (parent && parent->_col == Red)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
{
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur->_col = Black;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = Black;
return { Iterator(newnode,_root),true };
}再对myset和mymap进行改造:
//myset
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}如果对于mymap则不仅需要改造insert函数,还需要完成operator[]的实现这个时候我们需要返回值的类型是V&,我们需要接收一下insert的返回值,如:pair<iterator,bool> ret=_t.Insert({key,V()});我们这样写的目的是mymap对RBTree的模板参数T实例化为pair<const K,V>了,所以需要构造一个pair对象进行传入,然后我们需要返回这个返回值的iterator里的值,因为iterator实际上存储的还是一个pair对象,所以要返回的是值,为second,所以写成了如下奇怪的形式:
ret.first->second;
再解释一遍是Insert返回的是插入的值的迭代器作为键,是否插入成功的结果作为值,我们想得到的是键,所以用对象.first访问到,而iterator本质上是存储了一个键值对的,而访问只能通过迭代器->second或者->first进行,(也可以*(对象).first和*(对象).second进行),但是为了方便理解,这里就用->形式了。
总之我们用operator[]的结果就是为了得到键对应的值,而我们调用Insert的目的是避免重复插入并且返回最终该值对应的迭代器,而该迭代器是存储了一个键值对的,我们要得到传入的键所对应的值,所以要这样写,所以在mymap中:
//mymap
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert({ key,V() });//调用V对应的类型的构造函数初始化该键对应的值
return ret.first->second;
}11.代码汇总
在map和set中重要的函数已经实现了,像什么:
剩余的函数感兴趣的可以自行实现一下,掌握到这个地步已经可以了。
以下是三个文件的代码:
//myset.h
#include"RBTree.h"
template<class K>
class myset
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
//typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
//using iterator = typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator;
//下面两种随意选
//typedef typename RBTree<K,const K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
using iterator = typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator;
//下面两种随意选:
//typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
//using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;
//下面两种随意选
//typedef typename RBTree<K,const K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K,const K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.End();
}
private:
//RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};//mymap.h
#include"RBTree.h"
template<class K,class V>
class mymap
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
//typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
//using iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator;
//下面两种随便选一种
//typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
using iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator;
//下面两种随便选一种
//typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
//using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;
//下面两种随便选一种
//typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator;
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert({ key,V() });//调用V对应的类型的构造函数初始化该键对应的值
return ret.first->second;
}
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.End();
}
private:
//RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};//RBTree.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <assert.h>
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
enum Color
{
Red,
Black
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
T _data;//存放数据,可以传递T为pair类型
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
Color _col;
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
{
}
};
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct _TreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef _TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;//Ref:引用,Ptr:指针
Node* _node;
Node* _root;
_TreeIterator(Node* node,Node* root)
:_node(node)
,_root(root)
{ }
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s)
{
return _node == s._node;
}
//后置++
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp = *this; // 保存当前状态
++(*this); // 调用前置++实现
return tmp; // 返回旧值
}
//后置--
Self operator--(int)
{
Self tmp = *this; // 保存当前状态
--(*this); // 调用前置--实现
return tmp; // 返回旧值
}
//前置++
Self& operator++()
{
//中序遍历,这个时候就需要访问右孩子
if (_node->_right)
{
//找右子树的最左结点
_node = _node->_right;
while (_node->_left)
{
_node = _node->_left;
}
}
else
{
//右子树为空
//对应15结点或者50结点
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
//当parent不为空,且cur为parent的右孩子是继续往上
//因为这代表该子树已经遍历完了
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//要么cur是parent的左孩子,这个时候就可以直接用_node=parent
//这两种情况都可以这样写
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
//前置--
Self& operator--()
{
if (_node == nullptr) // end()
{
// --end(),特殊处理,⾛到中序最后⼀个结点,整棵树的最右结点
Node* rightMost = _root;
while (rightMost && rightMost->_right)
{
rightMost = rightMost->_right;
}
_node = rightMost;
}
else if (_node->_left)
{
//代表该子树还没遍历完
//找左子树的最右结点
_node = _node->_left;
while (_node->_right)
{
_node = _node->_right;
}
}
else
{
//该子树被遍历完
//向上查找,直到查找到根或者该孩子为父亲的右孩子
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
};
template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
public:
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef _TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;
typedef _TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> ConstIterator;
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
assert(parent != nullptr);
Node* subL = parent->_left;
assert(subL != nullptr);
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
subL->_right = parent;
if (subLR)
{
subLR->_parent = parent;
}
Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parent == _root)
{
subL->_parent = nullptr;
_root = subL;
}
else
{
if (parentParent->_left == parent)
{
parentParent->_left = subL;
}
else
{
parentParent->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = parentParent;
}
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
assert(parent != nullptr);
Node* subR = parent->_right;
assert(subR != nullptr);
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
{
subRL->_parent = parent;
}
subR->_left = parent;
Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (parent == _root)
{
subR->_parent = nullptr;
_root = subR;
}
else
{
if (parentParent->_left == parent)
{
parentParent->_left = subR;
}
else
{
parentParent->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = parentParent;
}
}
pair<Iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = Black;
return { Iterator(_root,_root),true };//隐式类型转换
}
KeyOfT kot;
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return { Iterator(cur,_root),true };
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newnode = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
if (kot(parent->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_col = Red;
while (parent && parent->_col == Red)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
uncle->_col = parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
{
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = Red;
cur->_col = Black;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = Black;
return { Iterator(newnode,_root),true };
}
Iterator Begin()
{
Node* minleft = _root;
while (minleft && minleft->_left)
{
minleft = minleft->_left;
}
//调用_TreeIterator
//相当于_TreeIterator(minleft)
return Iterator(minleft, _root);
}
Iterator End()
{
return Iterator(nullptr, _root);
}
ConstIterator Begin() const
{
Node* minleft = _root;
while (minleft && minleft->_left)
{
minleft = minleft->_left;
}
return ConstIterator(minleft, _root);
}
ConstIterator End() const
{
return ConstIterator(nullptr, _root);
}
bool Find(const K& key)
{
KeyOfT kot;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool Check(Node* root, int blackNum, const int refNum)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
if (refNum != blackNum)
{
cout << "存在⿊⾊结点的数量不相等的路径" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
if (root->_col == Red && root->_parent->_col == Red)
{
cout << root->_kv.first << "存在连续的红⾊结点" << endl;
return false;
}
if (root->_col == Black)
{
blackNum++;
}
return Check(root->_left, blackNum, refNum)
&& Check(root->_right, blackNum, refNum);
}
bool IsBalance()
{
if (_root == nullptr)
return true;
if (_root->_col == Red)
return false;
int refNum = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == Black)
{
++refNum;
}
cur = cur->_left;
}
return Check(_root, 0, refNum);
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_kv.first << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};12.总结
map和set和红黑树在C++进阶中都算比较重要的知识,如果能学会这些就比较厉害了,封装红黑树实现map和set的逻辑性比较强,建议各位加以理解。
好了,该讲内容就到这里,下讲将讲解C++进阶-哈希(非常重要),哈希理解起来不是很难,但是实现的时候可能难度比较高,所以各位做好心理准备哦。
喜欢的可以一键三连哦,下讲再见!


























 802
802

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










