P1216 数字三角形
题目描述
观察下面的数字金字塔。
写一个程序来查找从最高点到底部任意处结束的路径,使路径经过数字的和最大。每一步可以走到左下方的点也可以到达右下方的点。
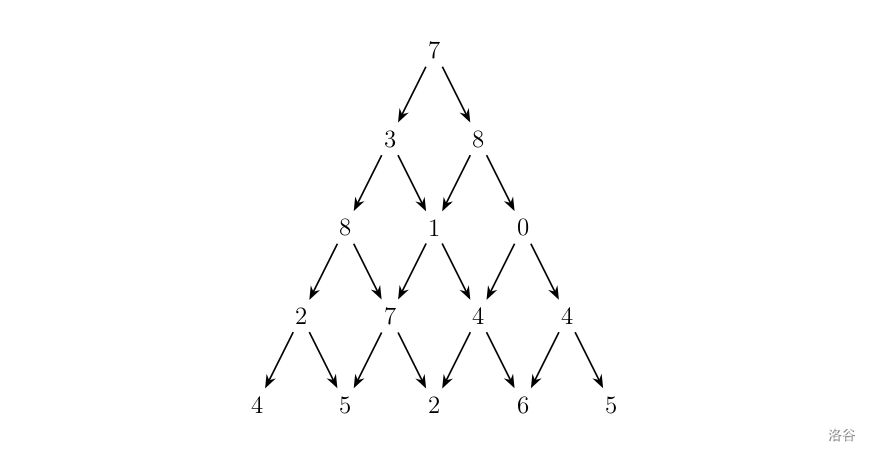
在上面的样例中,从 7 → 3 → 8 → 7 → 5 7 \to 3 \to 8 \to 7 \to 5 7→3→8→7→5 的路径产生了最大权值。
输入格式
第一个行一个正整数 r r r ,表示行的数目。
后面每行为这个数字金字塔特定行包含的整数。
输出格式
单独的一行,包含那个可能得到的最大的和。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
5
7
3 8
8 1 0
2 7 4 4
4 5 2 6 5
样例输出 #1
30
提示
【数据范围】
对于
100
%
100\%
100% 的数据,
1
≤
r
≤
1000
1\le r \le 1000
1≤r≤1000,所有输入在
[
0
,
100
]
[0,100]
[0,100] 范围内。
题目翻译来自NOCOW。
USACO Training Section 1.5
IOI1994 Day1T1
题解
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define Int __int128
#define pb push_back
#define eb emplace_back
#define ff first
#define ss second
#define M1 20
#define M2 1010
#define M3 5005
#define RI register int
#define ull unsigned long long
#define isc ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef pair<int, int>pii;
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
while ((a %= b) && (b %= a));
return a + b;
}//最大公约数函数
int spid(int a, int b, int p = mod)
{
int ans = 1;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1)ans = ans * a % p;
b >>= 1;
a = a * a % p;
}
return ans;
}//快速幂函数
int r;
int a[M2][M2], f[M2][M2],ans = 0;
void dfs1(int x, int y, int c) {//从下向上
if (x == r+1) { if (ans < c)ans = c; return; }
dfs1(x + 1, y, c + a[x][y]);
dfs1(x + 1, y + 1, c + a[x][y]);
}
//在此处记得要初始化f数组的值为-1,不然若a数组的值全为0与dfs1()并无区别,也会超时
int dfs2(int x,int y){
if(f[x][y]!=-1)return f[x][y];//记忆化搜索的关键
if(x==r){f[x][y]=a[x][y];}
else f[x][y]=a[x][y]+max(dfs2(x+1,y),dfs2(x+1,y+1));
return f[x][y];
}
void solve() {
cin >> r;
for (int i = 1; i <= r; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= i; ++j)
cin >> a[i][j];
dfs1(1, 1, 0);
//在此处记得要初始化f数组的值为-1,不然若a数组的值全为零与dfs1()并无区别,也会超时
memset(f,-1,sizeof(f));
dfs2(1,1);
//还有一个递推从下方向上a[x][y]+=max(a[x+1][y],a[x+1][y+1])
for(int x=r-1;x>=1;x--)
for(int y=1;y<=x;y++)
a[x][y]+=max(a[x+1][y],a[x+1][y+1]);
cout << ans << endl;
cout<<f[1][1]<<endl;
cout<<a[1][1]<<endl;
}
int main() {
int t = 1;
//cin>>t;
while (t--)solve();
}
cout<<f[1][1]<<endl;
cout<<a[1][1]<<endl;
}
int main() {
int t = 1;
//cin>>t;
while (t–)solve();
}
























 780
780

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








