平常存在问题:当需要一个业务类突然需要在原来的基础上扩展的时候,==需要修改源代码,耦合强==
动态代理:代理程序中的某个类的功能,为该功能增强,当清楚目的,学习就不会吃力
而使用场景:为方法前后需要增加功能的情况,使用
![![[Pasted image 20250228110440.png]]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/3c12fba25fd844c79756d6d91bc537d5.png)
本质上更像是加了一个中间层,然后在执行中间层的时候再去调用被代理对象
而Java中提供了动态代理对象 : Proxy
重点:被代理类得需要实现接口
二、使用
1.先保证被代理类有实现接口
2.创建被代理类对象
3.使用JDK提供的Proxy对象来代理被代理类 -> 格式如下
proxy.newProxyInstace(
//参数1:类加载器
//参数2:接口数组 -> 被代理类所继承的所有接口 -> 为了保证代理和被代理类实现同父接口
//参数3:处理器(关键)
)
通过源码
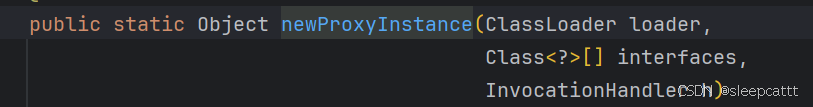
可以得到
第一个参数类加载器 ClassLoader
第二个参数有个新成员方法,Class.getInterfaces() 来得到全部接口
第三个参数为处理器 但是InvocationHandler是一个接口,所以需要一个实现类,所以这填实现类
三、案例分析
场景:在原有的接口实现类功能上,扩展一个统计运行时间的功能
提前准备好一个接口和一个实现类,然后接下来就是test类
他的思路是这样的:
1.首先要知道,Proxy的三个组成结构,都需要被代理对象的字节码文件,所以第一步,就是创建被代理对象
UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();
2.之后开始填写前两个Proxy的参数
UserService proxyObj = (UserService)Proxy.newProxyInstance(
userService.getClass().getClassLoader(), // 类加载器
userService.getClass().getInterfaces(),// 接口数组
// 处理器对象
);
3.当写到处理器对象InvokeHandler的时候发现是接口,所以需要创建实现类,并调用Method方法,和写我们的增加功能,再回去new一个处理器对象,然后强转类型为接口,这样能保证可以使用实现类的方法,并调用被代理类的方法add()
class MyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler{
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 使用method对象,执行原有被代理类的功能
Object result = method.invoke(userServiceImpl,args);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("执行使用了:"+(end-begin)+"ms");
return result;
}
}
......
UserService proxyObj = (UserService)Proxy.newProxyInstance(
userService.getClass().getClassLoader(), // 类加载器
userService.getClass().getInterfaces(),// 接口数组
new MyInvocationHandler()
);
proxyObj.add();
4.以上操作后运行会发现,NullPointerException,是因为处理器对象中,Method的invoke没有对象调用,这个时候就需要创建一个带参构造,将实现类传进去,来调用方法,而为了全局,则在成员变量定义好变量,在带参构造赋值,并在Proxy对象第三个参数添加实现类对象
class MyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler{
// 创建被代理类对象
private UserServiceImpl userServiceImpl = null;
// 在构造方法中给被代理类对象赋值,因为invoke需要被代理类对象调用方法
public MyInvocationHandler(UserServiceImpl userServiceImpl) {
this.userServiceImpl = userServiceImpl;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 使用method对象,执行原有被代理类的功能
Object result = method.invoke(userServiceImpl,args);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("执行使用了:"+(end-begin)+"ms");
return result;
}
}
.......
// 强转类型来保证代理对象可以使用被代理对象的方法
UserService proxyObj = (UserService)Proxy.newProxyInstance(
userService.getClass().getClassLoader(), // 类加载器
userService.getClass().getInterfaces(),// 接口数组
new MyInvocationHandler(userService) // 处理器对象
);
通过以上步骤 可以得到整体
package testProxy3;
import jdk.nashorn.internal.ir.CallNode;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
// 因为InvocationHandler是一个接口,直接创建一个实现类来调用
class MyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler{
// 创建被代理类对象
private UserServiceImpl userServiceImpl = null;
// 在构造方法中给被代理类对象赋值,因为invoke需要被代理类对象调用方法
public MyInvocationHandler(UserServiceImpl userServiceImpl) {
this.userServiceImpl = userServiceImpl;
}
/**
* @param proxy 代理对象(没用)
* @param method 方法对象(被代理类所书写的每一个成员方法)
* @param args 成员方法中的参数0
* @return 成员方法执行后的结果
* @throws Throwable
*/ @Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 使用method对象,执行原有被代理类的功能
Object result = method.invoke(userServiceImpl,args);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("执行使用了:"+(end-begin)+"ms");
return result;
}
}
public class testMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();
// 强转类型来保证代理对象可以使用被代理对象的方法
UserService proxyObj = (UserService)Proxy.newProxyInstance(
userService.getClass().getClassLoader(), // 类加载器
userService.getClass().getInterfaces(),// 接口数组
new MyInvocationHandler(userService) // 处理器对象
);
proxyObj.add();
}
}
四、原理
![![[Pasted image 20250228151416.png]]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/bbca6ab0dfba4c8b83dd57b64778b271.png)
本质就是Proxy创建了和被代理类一模一样的子类
- 接口数组是为了实现和被代理类一模一样的接口
- 类加载器是为了将class加载到内存中,创建子类
方法执行的时候,会被处理器拦截,而method.invoke是调用原方法,而前后则是我们可以扩展的内容
























 1125
1125

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








