文章目录
1. 万能计算器的实现以及源码分析
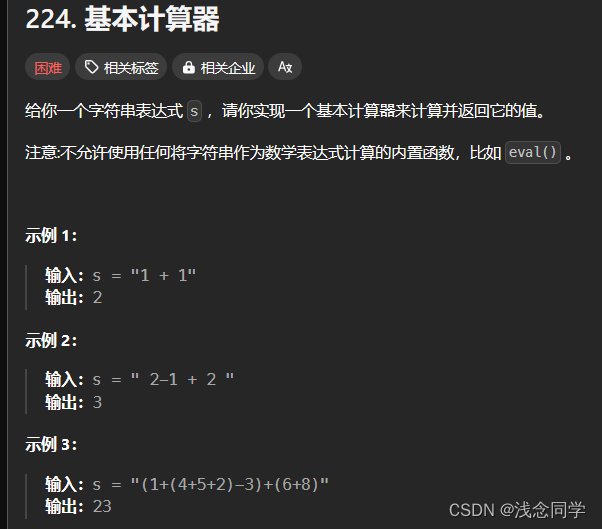
/**
* 我们尝试写一个完整版的计算器,由于计算机不能很好的识别括号,所以一般要转换为逆波兰表达式求解
* 思路解析 :
* 1. 输入一个 中缀表达式
* --> 使用repleaceAll函数将所有的空格处理,
* 2. 中缀表达式转化为list存储
* -->> 补充一下,在转化为list存储的时候我们要注意一些细节,比如如果是 (- 要转化为 (0-
* 3. 把list转换为一个逆波兰表达式
* 规则如下 首先准备两个栈,stack1 , list2(stack2)
* 如果是数字直接装入 list2
* 如果是括号 分为左括号跟右括号
* 如果是左括号直接进入stack1
* 如果是右括号 stack1 弹栈 ,弹出的元素进入stack2,直到出现 ')' ,抵消掉一个右括号
* 如果是操作符
* 如果stack1 为空 或者是 栈顶为左括号,那么直接入栈 <---------------------------
* 如果操作符的优先级大于 栈顶 操作符的优先级,直接入栈 *
* 如果操作符的优先级小于等于 栈顶操作符 ,那么就弹出栈顶元素入stack2,然后进入第一条比较 --------
* <p>
* 4. 利用逆波兰表达式进行求值
*/
class MyCalculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String initexp = "1-( -( -2))";
String newexp = processInitexp(initexp);
List<String> infixexperssion = toList(newexp);
System.out.println(infixexperssion);
List<String> suffixexpression = toSuffixexpression(infixexperssion);
System.out.println(suffixexpression);
//int ret = calculate(suffixexpression);
//System.out.println(ret);
}
/**
* 该方法的作用是初始化我们的基本操作串,包括去掉空格,处理单目运算的-或者+问题
*
* @param initexp
* @return
*/
public static String processInitexp(String initexp) {
String temp = initexp.replaceAll(" ", "");
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
int len = temp.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
char ch = temp.charAt(i);
if ((ch == '-' && (i == 0 || temp.charAt(i - 1) == '('))) {
stringBuilder.append("0-");
} else if ((ch == '+' && (i == 0 || temp.charAt(i - 1) == '('))) {
stringBuilder.append("0+");
}else{
stringBuilder.append(ch);
}
}
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
/**
* 该方法的作用就是把一个字符串转换为一个中缀表达式的list
*
* @param infixexpression : 中缀表达式
* @return
*/
public static List<String> toList(String infixexpression) {
List<String> ret = new ArrayList<>();
int count = 0;
while (count < infixexpression.length()) {
if (infixexpression.charAt(count) == ' ') {
count++;
continue;
}
if (infixexpression.charAt(count) < '0' || infixexpression.charAt(count) > '9'
&& infixexpression.charAt(count) != ' ') {
ret.add(infixexpression.charAt(count) + "");
count++;
} else {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
while (count < infixexpression.length() && infixexpression.charAt(count) >= '0'
&& infixexpression.charAt(count) <= '9') {
stringBuilder.append(infixexpression.charAt(count));
count++;
}
ret.add(stringBuilder.toString());
}
}
return ret;
}
/**
* 该方法的作用是将我们的中缀表达式转化为逆波兰表达式
*
* @param infixexpression : 传入的中缀表达式
* @return
*/
public static List<String> toSuffixexpression(List<String> infixexpression) {
//首先创建两个栈,因为第二个栈不涉及弹栈操作,所以我们可以创建为顺序表
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (String elem : infixexpression) {
if (elem.equals("(")) {
stack.push(elem);
} else if (elem.equals(")")) {
while (stack.size() != 0 && !stack.peek().equals("(")) {
list.add(stack.pop());
}
stack.pop();
} else if (isOperator(elem)) {
if (stack.size() == 0 || stack.peek().equals("(") || priority(elem) > priority(stack.peek())) {
stack.push(elem);
continue;
}
while (stack.size() != 0 && priority(elem) <= priority(stack.peek()) && !stack.peek().equals("(")) {
list.add(stack.pop());
}
stack.push(elem);
} else {
list.add(elem);
}
}
while (stack.size() != 0) {
list.add(stack.pop());
}
return list;
}
//判断是否是操作符
public static boolean isOperator(String elem) {
if (elem.equals("+") || elem.equals("-") || elem.equals("*") || elem.equals("/")) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
//判断优先级的大小
public static int priority(String elem) {
if (elem.equals("+") || elem.equals("-")) {
return 1;
} else {
return 2;
}
}
/**
* 最后收一下尾巴,用我们所得到的逆波兰表达式求出值
* 求值的基本思路应该比较好理解
* 如果是数字直接入栈,如果不是,弹出两个数字,然后进行运算结果入栈
*/
public static int calculate(List<String> sufferixexperssion) {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
for (String elem : sufferixexperssion) {
if (isOperator(elem)) {
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int num1 = 0;
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
}
switch (elem) {
case "+":
stack.push((num1 + num2) + "");
break;
case "-":
stack.push((num1 - num2) + "");
break;
case "*":
stack.push((num1 * num2) + "");
break;
case "/":
stack.push((num1 / num2) + "");
break;
}
} else {
stack.push(elem);
}
}
return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
}
}
2. leetcode 150 逆波兰表达式求值
逆波兰表达式又叫做后缀表达式,因为计算机是好辨认出中缀表达式的计算顺序的,所以有时候要用后缀表达式进行求解
题目描述

思路分析:
1.如果是数字,直接入栈
2.如果是操作符,弹出两个数字分别作为右操作数跟左操作数运算,结果入栈
3.最后弹出栈内的最后一个元素
代码实现如下
public static int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < tokens.length; ++i) {
String s = tokens[i];
if (toolOperator(s)) {
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
switch (s) {
case "+":
stack.push((num2 + num1) + "");
break;
case "-":
stack.push((num2 - num1) + "");
break;
case "*":
stack.push((num2 * num1) + "");
break;
case "/":
stack.push((num2 / num1) + "");
break;
}
} else {
stack.push(s);
}
}
return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
}
//判断是不是操作符
public static boolean toolOperator(String s) {
if (s.equals("+") || s.equals("-") || s.equals("*") || s.equals("/")) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
3.牛客 JZ31 栈的压入弹出序列
题目描述如下
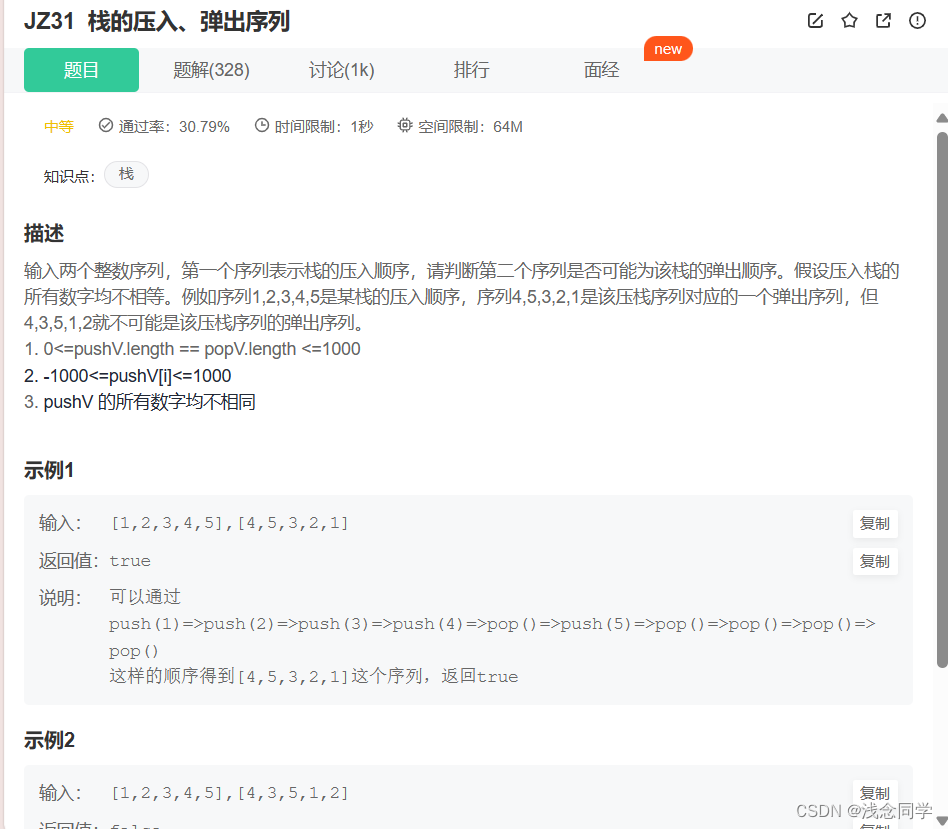
思路分析
- 首先创建一个栈用来保存我们的压入的数字
- 创建两个指针分别指向两个数组的初始位置( i , j )
- 遍历我们的pushV数组,压入进栈,在压入之后判断我们的popV[j]是不是与pushV[i]一致
如果一致就弹栈, j++ , 如果不是继续压栈判断重复,最后看一看栈是否为空
代码实现如下
/**
* 栈的应用,正确的出栈顺序,给两个数组,一个是入栈的顺序的数组,一个是出栈的顺序的数组,请你判断该出栈序列是否是合理的
* @param pushV : 入栈序列
* @param popV : 出栈序列
* @return
*/
public static boolean trueOrderPop(int[] pushV,int[] popV){
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < pushV.length; ++i) {
stack.push(pushV[i]);
while(!stack.empty() && stack.peek() == popV[j]){
stack.pop();
j++;
}
}
return stack.empty();
}
4. leetcode 155 最小栈
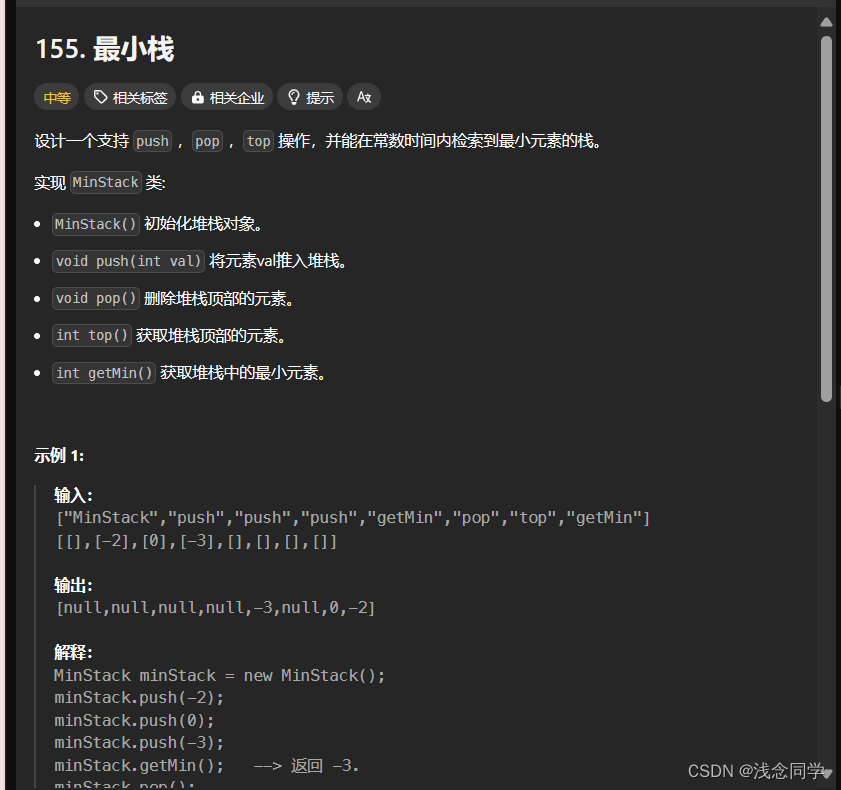
思路分析
如果仅仅利用一个栈就想让查询复杂度达到O(1)级别是做不到的,所以我们需要引入另外一个栈,所以本题的基本思路就是,存在两个栈,一个普通栈,一个最小栈来保存最小值
本题的坑点就是由于我们的Integer是引用数据类型,进行比较的时候要用equals方法来进行比较,如果比较的双方有一方是基本数据类型,那就会进行基本的拆箱工作,就不用使用equals方法了
还有就是我们入栈的时候如果是与minStack栈顶相等的时候要一起入栈,stack与minstack栈顶元素一致的时候要一起出栈
代码实现如下
/**
* 栈的应用 : 实现一个最小栈
*/
class MinStack {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> minStack = new Stack<>();
public MinStack() {
}
public void push(int val) {
stack.push(val);
if(minStack.empty()){
minStack.push(val);
return;
}
if(minStack.peek() >= val){
minStack.push(val);
}
}
public void pop() {
if(minStack.peek().equals(stack.peek())){
minStack.pop();
stack.pop();
}else{
stack.pop();
}
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack obj = new MinStack();
* obj.push(val);
* obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* int param_4 = obj.getMin();
*/
还有另外一种解法,我们的LinkedList类既可以当作链表,又可以当作栈(链式栈,底层为双向链表),还可以当作双端队列
/**
* 请注意,我们之前写的那个Stack栈底层用的是数组,也就是传说中的顺序栈
* 但是我们java中 , LinkedList(双向链表) 和 Deque(双端队列) 也可以当作栈来使用,其中前者是链式栈
*/
class LinkedStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.peek();
stack.pop();
Deque<Integer> stack1 = new LinkedList<>();
stack1.push(1);
stack1.push(1);
stack1.push(1);
}
}
剩下的就不多说了
5. leetcode 225 用队列实现栈
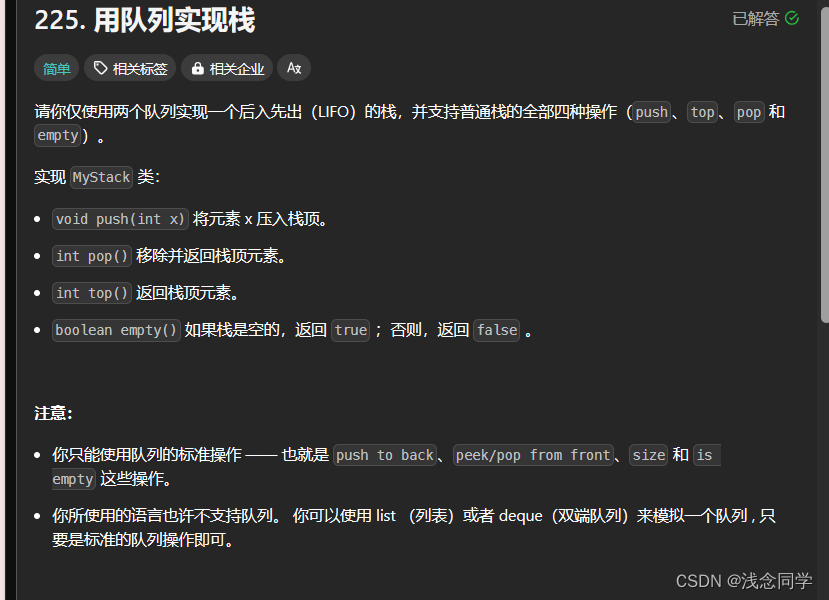
基本思路就是申请两个队列
代码如下
class MyStack {
public Queue<Integer> queue1;
public Queue<Integer> queue2;
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
if(queue2.isEmpty()){
queue1.offer(x);
return;
}
if(queue1.isEmpty()){
queue2.offer(x);
return;
}
}
public int pop() {
if(queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
if(queue2.isEmpty()){
int size = queue1.size() - 1;
while(size != 0){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
size--;
}
return queue1.poll();
}else{
int size = queue2.size() - 1;
while(size != 0){
queue1.offer(queue2.poll());
size--;
}
return queue2.poll();
}
}
public int top() {
if(queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
if(queue2.isEmpty()){
int size = queue1.size() - 1;
while(size != 0){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
size--;
}
int val = queue1.poll();
queue2.offer(val);
return val;
}else{
int size = queue2.size() - 1;
while(size != 0){
queue1.offer(queue2.poll());
size--;
}
int val = queue2.poll();
queue1.offer(val);
return val;
}
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue2.isEmpty() && queue1.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
6. leetcode 232 用栈实现队列
基本思路也是使用两个栈
代码实现如下
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stack1;
Stack<Integer> stack2;
public MyQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<>();
stack2 = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(stack2.empty()){
while(!stack1.empty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(stack2.empty()){
while(!stack1.empty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stack1.empty() && stack2.empty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/







 本文介绍了如何实现万能计算器,重点讨论了中缀表达式到逆波兰表达式的转换,逆波兰表达式的求值,以及使用栈和队列解决LeetCode中的相关问题,如最小栈和用队列实现栈的功能。
本文介绍了如何实现万能计算器,重点讨论了中缀表达式到逆波兰表达式的转换,逆波兰表达式的求值,以及使用栈和队列解决LeetCode中的相关问题,如最小栈和用队列实现栈的功能。
















 1018
1018

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








