文章目录
线性表介绍
线性表是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。线性表在逻辑结构上一定是连续的,但物理结构不一定连续。
顺序表介绍
顺序表是在计算机内存中以数组的形式保存的线性表。
创建顺序表
在创建顺序表之前要先创建3个项目,为什么要创建多个项目呢?这是为了方便我们管理。
test.c用于测试函数。
SeqList.c函数实现。
SeqList.h函数声明和顺序表的定义。
顺序表需要有指向动态数组指针,有效数据个数和容量。
这就要用结构体来定义了:
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* arr;//指向动态数组的指针
int size;//有效数据个数
int capacity;//容量
}SL;typedef函数是用来重命名的。
为了方便后续修改顺序表数据类型,我们可以用 typedef重新给数据类型命名为 SLDataType。
同理在这里把结构体类型重命名为SL。
初始化
初始化就是把arr置为空指针,其余为0。
//初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);//检查是否为空指针
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}assert是判断传过来的参数是否为NULL,如果是则退出,否则继续执行。在后面的函数中都会涉及到它。
销毁
为什么要销毁呢?顺序表是动态开辟在堆区的,如果不销毁会造成内存泄漏。销毁用到的是free函数,把其余置为0即可。
//销毁
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->arr)//判断arr是否为NULL
{
free(ps->arr);
}
ps->arr = NULL;//防止出现野指针
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}扩容
先检查是否要开辟。在确定开辟多大容量后(我写的是上一次容量的1倍),用realloc函数开辟一块空间,开辟完后要检查一下是否开辟失败。然后再把它的值赋给arr。
//扩容
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->capacity == ps->size)//判断是否要扩容
{
ps->capacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? ps->capacity = 2 : ps->capacity * 2;//扩后容量大小
SLDataType* new = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, ps->capacity * sizeof(SLDataType));//创建一片空间
if (new == NULL)//判断创建是否失败
{
perror("realloc:");
exit(1);
}
ps->arr = new;
}
}打印
遍历一遍即可。
//打印
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}增加数据
在增加数据前要检查容量是否满了。增加完数据后,size要加一。
尾插
在最后的位置插入数据即可。
//尾插
void SLpushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
ps->arr[ps->size++] = x;
}演示:

头插
把原数据依次向后移一位,挪动数据的时候应从后向前依次挪动,若从前向后挪动,会导致后一个数据被覆盖。然后在首位置插入数据。
//头插
void SLpushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
for (int i = ps->size; i > 0; i--)//把原数据向后移一位
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];
}
ps->arr[0] = x;//插入数据
ps->size++;//有效数据个数加一
}演示:

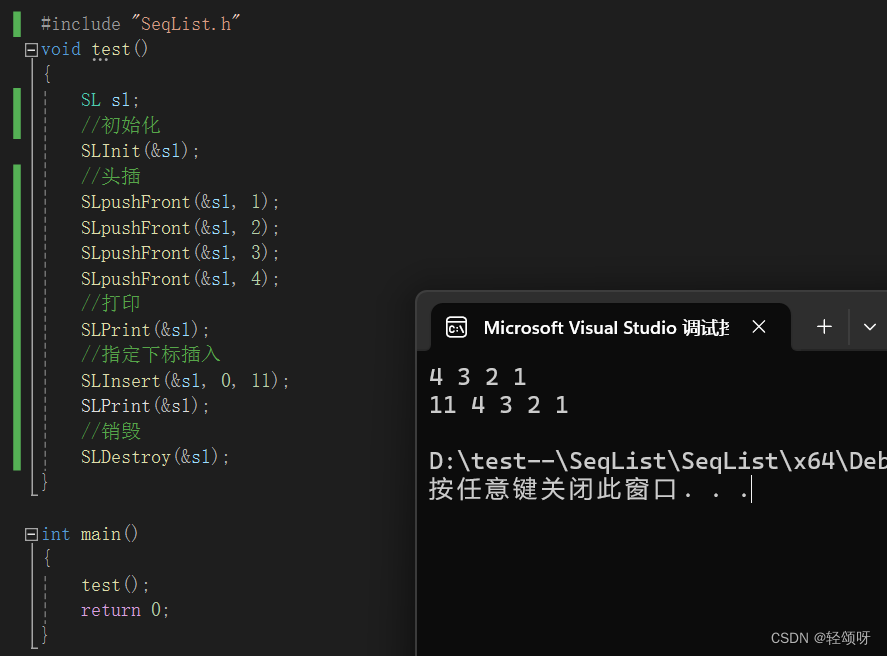
指定下标插入
要检查下标是否合理,然后把下标之后的数据依次向后移一位,挪动数据的时候要从后向前依次挪动。然后在把数据插入。
//指定下标插入数据
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);//检查下标是否合理
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
for (int i = ps->size; i > pos; i--)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];
}
ps->arr[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}演示:
删除数据
删除数据前要判断顺序表中是否有数据。在删除完数据后,size要减一。
尾删
size减一即可。
//尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);//判断顺序表中是否有数据
ps->size--;
}演示:

头删
把所有数据依次向前移一位即可,挪动数据的时候应从前向后依次挪动,若从后向前挪动,会导致后一个数据被覆盖。
//头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
for (int i = 1; i < ps->size; i++)//所有数据向前移一位
{
ps->arr[i - 1] = ps->arr[i];
}
ps->size--;//有效数据减一
}演示:

指定下标删除
要检查下标是否合理,再把下标之后的数据依次向前移一位,挪动数据的时候应从前向后依次挪动。
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
assert(ps->size);
for (int i = pos; i < ps->size - 1; i++)//把下标pos之后的数据向前移
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}演示:

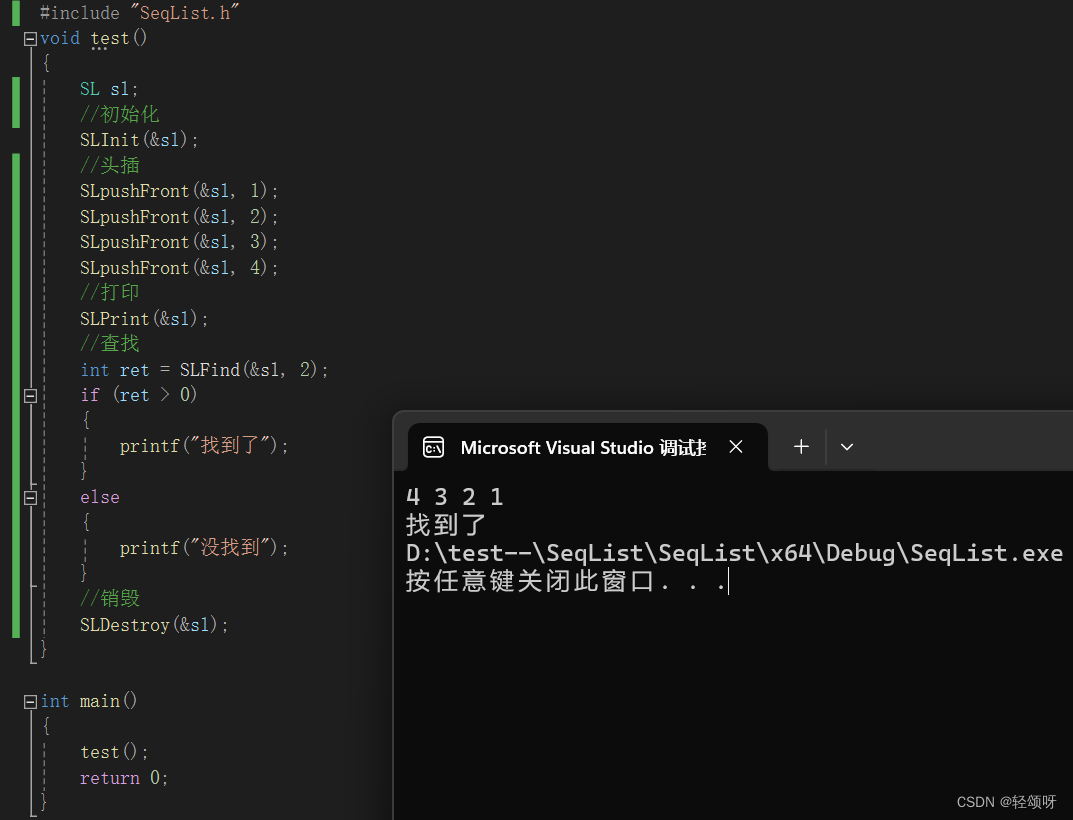
查找
在遍历一遍时判断有无相等若有返回下标,否则返回-1。
//查找
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->arr[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}演示:
整体代码
SeqList.h
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* arr;
int size;
int capacity;
}SL;
//初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps);
//扩容
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps);
//打印
void SLPrint(SL* ps);
//尾插
void SLpushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
//头插
void SLpushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
//尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);
//头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps);
//指定下标插入数据
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);
//指定下标删除数据
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos);
//查找
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
//销毁
void SLDestroy(SL* ps);SeqList.c
#include "SeqList.h"
//初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}
//扩容
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->capacity == ps->size)
{
ps->capacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? ps->capacity = 2 : ps->capacity * 2;
SLDataType* new = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, ps->capacity * sizeof(SLDataType));
if (new == NULL)
{
perror("realloc:");
return;
}
ps->arr = new;
}
}
//打印
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//尾插
void SLpushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
ps->arr[ps->size++] = x;
}
//头插
void SLpushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
for (int i = ps->size; i > 0; i--)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];
}
ps->arr[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
ps->size--;
}
//头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
for (int i = 1; i < ps->size; i++)
{
ps->arr[i - 1] = ps->arr[i];
}
ps->size--;
}
//指定下标插入数据
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
for (int i = ps->size; i > pos; i--)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];
}
ps->arr[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//指定下标删除数据
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
assert(ps->size);
for (int i = pos; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
//查找
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->arr[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//销毁
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->arr)
{
free(ps->arr);
}
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}
好了讲到这儿就差不多讲完了,希望你能有所收获。如果存在错误地方请及时指出,如果还有什么不懂的地方可以私信我,如果觉得不错那就点点赞吧!








 本文详细介绍了如何在C语言中使用结构体和动态数组实现顺序表,包括初始化、销毁、扩容、打印、数据插入和删除操作,以及查找功能的实现。
本文详细介绍了如何在C语言中使用结构体和动态数组实现顺序表,包括初始化、销毁、扩容、打印、数据插入和删除操作,以及查找功能的实现。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








