一、概念
ArrayList 类是一个可以动态修改的数组,与普通数组的区别就是它是没有固定大小的限制,我们可以添加或删除元素。
二、创建方式
import java.util.ArrayList; // 引入 ArrayList 类
ArrayList<E> objectName =new ArrayList<>(); // 初始化
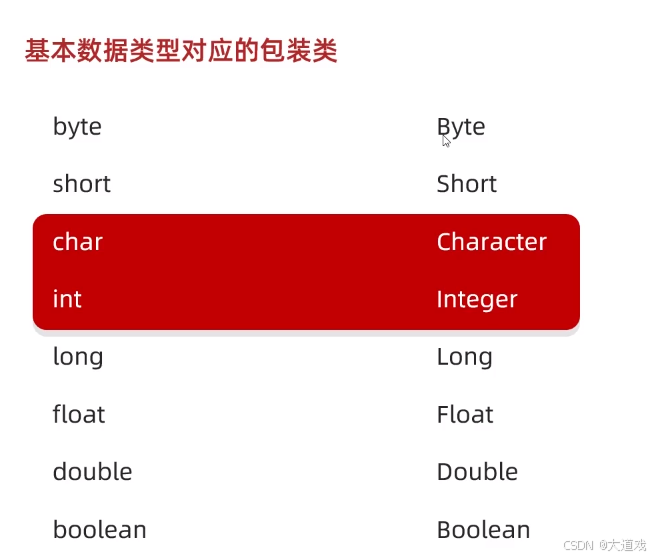
- E: 泛型数据类型,用于设置 objectName 的数据类型,只能为引用数据类型。
- objectName: 对象名。
三、使用方法

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class CollectionExample {
private List<String> items;
// 构造函数,初始化集合
public CollectionExample() {
items = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 添加元素
public void addItem(String item) {
items.add(item);
System.out.println(item + " has been added.");
}
// 删除元素
public void removeItem(String item) {
if (items.remove(item)) {
System.out.println(item + " has been removed.");
} else {
System.out.println(item + " not found.");
}
}
// 访问元素
public String getItem(int index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < items.size()) {
return items.get(index);
} else {
return "Index out of bounds.";
}
}
// 更改元素
public void updateItem(int index, String newItem) {
if (index >= 0 && index < items.size()) {
items.set(index, newItem);
System.out.println("Item at index " + index + " has been updated to " + newItem + ".");
} else {
System.out.println("Index out of bounds.");
}
}
// 打印所有元素
public void printItems() {
System.out.println("Current items in the collection: " + items);
}
// 主方法用于测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
CollectionExample collection = new CollectionExample();
// 添加元素
collection.addItem("Apple");
collection.addItem("Banana");
collection.addItem("Orange");
// 打印当前元素
collection.printItems();
// 访问元素
System.out.println("Item at index 1: " + collection.getItem(1));
// 更新元素
collection.updateItem(1, "Mango");
// 打印更新后的元素
collection.printItems();
// 删除元素
collection.removeItem("Apple");
collection.printItems();
}
}
运行结果:
Apple has been added.
Banana has been added.
Orange has been added.
Current items in the collection: [Apple, Banana, Orange]
Item at index 1: Banana
Item at index 1 has been updated to Mango.
Current items in the collection: [Apple, Mango, Orange]
Apple has been removed.
Current items in the collection: [Mango, Orange]
四、 示例
1、添加字符串,并进行遍历
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArraylistDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("点赞");
list.add("收藏");
list.add("转发");
System.out.print("[");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if(i==list.size()-1){
System.out.print(list.get(i));
}else{
System.out.print(list.get(i)+",");
}
}
System.out.println("]");
}
}
[点赞,收藏,转发]
2、添加数字,并进行遍历
package week6_String;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArraylistDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建元素
ArrayList<Integer> list2 =new ArrayList<>();
//2.添加元素
list2.add(1);
list2.add(2);
list2.add(3);
list2.add(4);
list2.add(5);
System.out.print("[");
for (int i = 0; i < list2.size(); i++) {
if(i==list2.size()-1){
System.out.print(list2.get(i));
}else{
System.out.print(list2.get(i)+",");
}
}
System.out.println("]");
}
}
[1,2,3,4,5]
3、添加学生对象并遍历
package week5_class_test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test_student {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建集合
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
//2.创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("zhangsan",23);
Student s2 = new Student("andy",34);
Student s3 = new Student("lyla",24);
Student s4 = new Student("tina",26);
Student s5 = new Student("bella",27);
//3.添加元素
list.add(s1);
list.add(s2);
list.add(s3);
list.add(s4);
list.add(s5);
//4.遍历集合
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
Student stu =list.get(i);
System.out.println(stu.getName()+","+stu.getAge());
}
}
}
zhangsan,23
andy,34
lyla,24
tina,26
bella,27

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








