一、分析stl源码中map和set对应的头文件<map>,<set>
#ifndef __SGI_STL_MAP
#define __SGI_STL_MAP#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_TREE_H
#include <stl_tree.h>
#endif
#include <stl_map.h>
#include <stl_multimap.h>#ifndef __SGI_STL_SET
#define __SGI_STL_SET#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_TREE_H
#include <stl_tree.h>
#endif
#include <stl_set.h>
#include <stl_multiset.h>
可以发现都包含了stl_tree这个头文件,而这个stl_tree中,本质是一个红黑树的模板。
分析:set和map通过组合的方式,将一颗红黑树封装成队友的map和set。第一个参数传的都是键值Key的类型,第二个参数传的是节点的数据的类型,对于set来说有些多余,毕竟都是Key,但对于map来说是必要的,否则不知道pair<const Key,value>,不知道value的类型。
二、使用红黑树封装map和set,实现插入和迭代器
因此对于红黑树的节点的设计如下:
//T为节点的数据类型 template<class T> struct RBTreeNode { // 这里更新控制平衡也要加入parent指针 T _data; RBTreeNode<T>* _left; RBTreeNode<T>* _right; RBTreeNode<T>* _parent; Colour _col; RBTreeNode(const T& data) :_data(data) , _left(nullptr) , _right(nullptr) , _parent(nullptr) , _col(RED) {} };但是如果仅按照第一个参数传Key,第二个参数传节点的数据类型。由于无法区分到底是T到底是Key还是pair<const Key,value>,插入的时候拿到的只是T,指针也是指向T类型,无法区分,因此要在map和set处传一个仿函数来方便insert时获取对应的Key值,以便于比较。
仿函数实现在map和set的内部(存疑)
set的仿函数
private: struct KeyOfT { const K& operator()(const K& key) const { return key; } };map的仿函数:
private: struct KeyOfT { const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv) const { return kv.first; } };
RBTree_iterator设计:
为了同时支持iterator和const_iterator,可以通过以下方式:
typedef RBTree_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator; typedef RBTree_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator和const_iterator唯一区别就是operator*和operator->的返回值类型不同,可以通过传const T&和constT*的方式使得返回值类型不同,只需在RBTree_iterator处接受即可。
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr> class RBTree_iterator { typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node; typedef RBTree_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self; public: RBTree_iterator(Node* cur, Node* root) :_cur(cur) , _root(root) {} Ref operator*() { return _cur->_data; } Ptr operator->() { return &(_cur->_data); } //... };
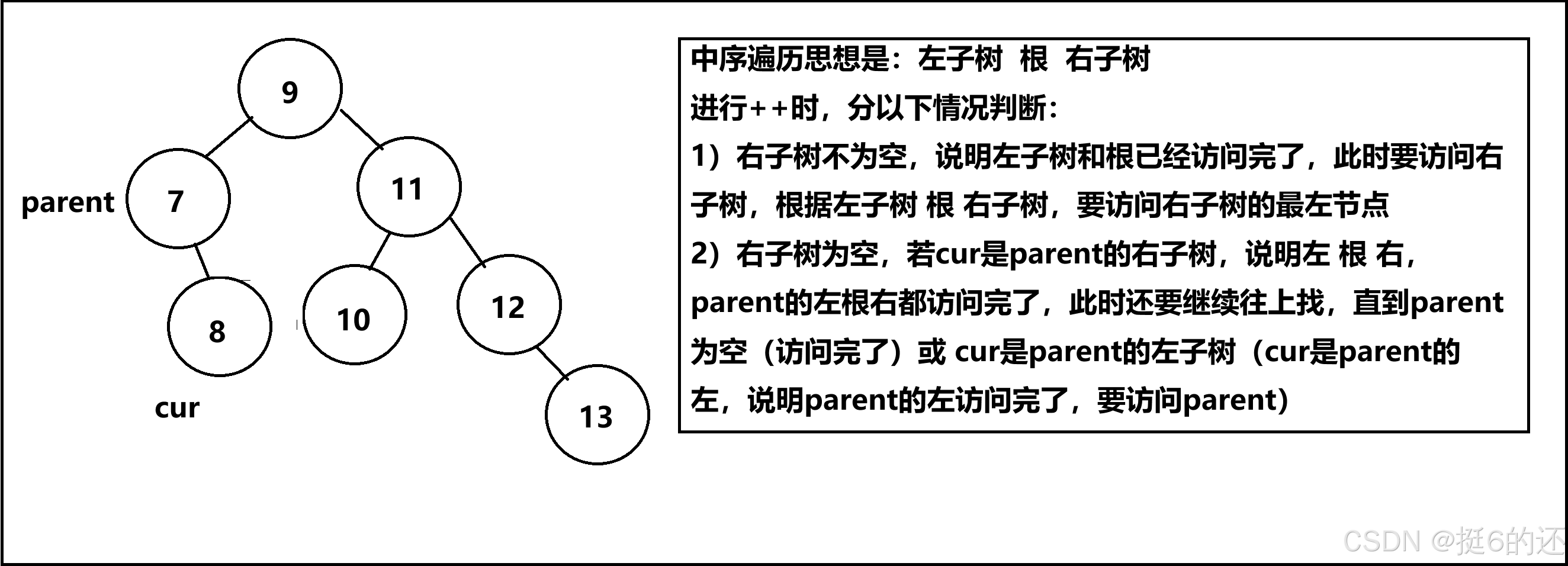
map和set是双向迭代器,设计时包含++和--,具体设计按以下分析
如上图所述。
需要注意的是:为什么能确定cur是parent左子树的根时parent的左访问完了?
原因:因为右不为空是优先访问右的最左节点的,正因为这个前提条件,可以确定当cur的右为空时,且cur为parent的右子树时,当前parent已经访问完了,需要向上找,直到作为parent左或parent为空。cur为parent左时,parent的左访问完了,要访问parent的根就是parent;parent为空时,在向上找之前,cur就是整颗树的最右节点,此时截止了。
代码实现:Self& operator++() { assert(_cur); Node* cur = _cur; //cur的右不为空,左 根 右, // 说明左和根已经访问完了 //现在要访问右子树的最左节点(最小节点) if (cur->_right) { Node* minRight = cur->_right; while (minRight->_left) { minRight = minRight->_left; } _cur = minRight; } else { Node* parent = cur->_parent; //如果当前节点是父亲的右 // 说明父亲的左子树 父亲的根 父亲的右子树 都访问完了 //此时还要继续向上找,直到cur为父亲的左 //cur为父亲的左代表父亲的左子树访问完了,访问父亲的根 while (parent && parent->_right == cur) { cur = parent; parent = cur->_parent; } //不论是 空 或是 非空,都是_cur等于parent _cur = parent; } return *this; }operator--与++类似,只不过是右 根 左的顺序。
但若要实现--end()达到反向遍历的效果,可以特殊处理,只不过要传root根节点的指针,当_cur为nullptr即end()时,让_cur等于中序遍历的最后一个(即根的最右节点的指针)
//中序左 根 右 //与++逻辑类似,不过是右 根 左 Self& operator--() { //若要实现能反向遍历, //--到中序的最后一个,即根的最右节点 if (_cur == nullptr) { Node* cur = _root; while (cur && cur->_right) { cur = cur->_right; } _cur = cur; return *this; } Node* cur = _cur; // 右 根 左 //cur的左不为空, // 说明右访问完了,根也访问完了, // 上一个需要访问的就是左子树的最右节点 if (cur->_left) { Node* maxLeft = cur->_left; while (maxLeft->_right) { maxLeft = maxLeft->_right; } _cur = maxLeft; } else { //--也会走到空,与++走到空含义不同 //--是右根左的空,++是左根右的空 Node* parent = cur->_parent; //右 根 左 //如果cur是parent的左, // 说明parent已经访问完了,要向上找 //直到cur为parent的右 while (parent && parent->_left == cur) { cur = parent; parent = cur->_parent; } //不论是 空 或是 非空,都是_cur等于parent _cur = parent; } return *this; }
封装RBTree时注意事项:
stl源码中把map中的RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, KeyOfT>类型重命名为repe_type,这种方式很好,因为在map和set中为了使用的方便,且为了让重命名iterator时不用写那么多。
重命名如下:
set
public: typedef typename RBTree<K,const K, KeyOfT> tree_type; typedef typename tree_type::iterator iterator;map
public: typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, KeyOfT> tree_type; typedef typename tree_type::iterator iterator;
最后就是map的operator[]的实现:
operator[],本质就是调用insert。若不存在,则插入,返回对应迭代器位置的value的引用。若存在,则不插入,返回对应迭代器位置的value的引用。
实现如下:
V& operator[](const K& key) { pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert({ key,V() }); iterator it = ret.first; return (*it).second; }
以下就是所以实现的源码:
RBTree.h
#pragma once #include<assert.h> // 枚举值表示颜色 enum Colour { RED, BLACK }; //T为节点的数据类型 template<class T> struct RBTreeNode { // 这里更新控制平衡也要加入parent指针 T _data; RBTreeNode<T>* _left; RBTreeNode<T>* _right; RBTreeNode<T>* _parent; Colour _col; RBTreeNode(const T& data) :_data(data) , _left(nullptr) , _right(nullptr) , _parent(nullptr) , _col(RED) {} }; template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr> class RBTree_iterator { typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node; typedef RBTree_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self; public: RBTree_iterator(Node* cur, Node* root) :_cur(cur) , _root(root) {} Ref operator*() { return _cur->_data; } Ptr operator->() { return &(_cur->_data); } bool operator==(const Self& it) const { return _cur == it._cur; } bool operator!=(const Self& it) const { return _cur != it._cur; } Self& operator++() { assert(_cur); Node* cur = _cur; //cur的右不为空,左 根 右, // 说明左和根已经访问完了 //现在要访问右子树的最左节点(最小节点) if (cur->_right) { Node* minRight = cur->_right; while (minRight->_left) { minRight = minRight->_left; } _cur = minRight; } else { Node* parent = cur->_parent; //如果当前节点是父亲的右 // 说明父亲的左子树 父亲的根 父亲的右子树 都访问完了 //此时还要继续向上找,直到cur为父亲的左 //cur为父亲的左代表父亲的左子树访问完了,访问父亲的根 while (parent && parent->_right == cur) { cur = parent; parent = cur->_parent; } //不论是 空 或是 非空,都是_cur等于parent _cur = parent; } return *this; } //中序左 根 右 //与++逻辑类似,不过是右 根 左 Self& operator--() { //若要实现能反向遍历, //--到中序的最后一个,即根的最右节点 if (_cur == nullptr) { Node* cur = _root; while (cur && cur->_right) { cur = cur->_right; } _cur = cur; return *this; } Node* cur = _cur; // 右 根 左 //cur的左不为空, // 说明右访问完了,根也访问完了, // 上一个需要访问的就是左子树的最右节点 if (cur->_left) { Node* maxLeft = cur->_left; while (maxLeft->_right) { maxLeft = maxLeft->_right; } _cur = maxLeft; } else { //--也会走到空,与++走到空含义不同 //--是右根左的空,++是左根右的空 Node* parent = cur->_parent; //右 根 左 //如果cur是parent的左, // 说明parent已经访问完了,要向上找 //直到cur为parent的右 while (parent && parent->_left == cur) { cur = parent; parent = cur->_parent; } //不论是 空 或是 非空,都是_cur等于parent _cur = parent; } return *this; } private: Node* _cur; Node* _root; }; //第一个参数传key,第二个参数传节点的数据类型 //第三个参数传仿函数,以便插入时获取节点的Key进行比较 template<class Key, class T,class KeyOfT> class RBTree { public: typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node; typedef RBTree_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator; typedef RBTree_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator; public: iterator Begin() { Node* cur = _root; while (cur && cur->_left) { cur = cur->_left; } return iterator(cur, _root); } iterator End() { return iterator(nullptr, _root); } ~RBTree() { destory(_root); } pair<iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data) { if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(data); _root->_col = BLACK; return { iterator(_root,_root),true }; } KeyOfT kot; Node* parent = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { //比cur小,往左走 if (kot(cur->_data)> kot(data)) { parent = cur; cur = parent->_left; } //比cur大,往右走 else if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)) { parent = cur; cur = parent->_right; } else { return { iterator(cur,_root),false }; } } Node* newnode = new Node(data); cur = newnode; //比parent小,链接在左边,否则链接在右边 if (kot(data) < kot(parent->_data)) { parent->_left = cur; } else { parent->_right = cur; } cur->_parent = parent; //调整部分 //parent不为空 且 parent的颜色为红色就还要继续调整 while (parent && parent->_col==RED) { //grandparent一定非NULL, // 因为如果parent如果是根节点,parent就是黑色的 //parent是黑色的进不来循环 Node* grandparent = parent->_parent; if (parent == grandparent->_left) { // g g // p u 或 p u // c c Node* uncle = grandparent->_right; //无论cur在左还是右都不影响 //uncle存在且为红 if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) { parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK; grandparent->_col = RED; //还要向上处理 cur = grandparent; parent = cur->_parent; } //uncle不存在 或者 uncle存在且为黑 else { // g // p u // c //cur为parent的左 if (cur == parent->_left) { rotateR(grandparent); parent->_col = BLACK; grandparent->_col = RED; //旧的parent现在的grandparent // 已经为黑色了,不需要向上处理 break; } //cur为parent的右,不是单纯一边高 //双旋加变色 else { // g // p u // c rotateL(parent); rotateR(grandparent); cur->_col = BLACK; grandparent->_col = RED; //旧的cur现在的grandparent //已经变为黑色了,不需要向上处理 break; } } } else { // g // u p // c Node* grandparent = parent->_parent; Node* uncle = grandparent->_left; //无论cur在左还是右,不影响 if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) { grandparent->_col = RED; uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK; //此时grandparent为红色,需要向上更新 cur = grandparent; parent = cur->_parent; } // uncle存在且为黑 或者 uncle为空 else { // g // u p // c //单纯一边高,单旋加变色 if (cur == parent->_right) { rotateL(grandparent); parent->_col = BLACK; grandparent->_col = RED; //旧parent新grandparent //此时已经为黑,停止更新 break; } // g // u p // c //不是单纯一边高,双旋加变色 else { rotateR(parent); rotateL(grandparent); cur->_col = BLACK; grandparent->_col = RED; //旧cur新grandparent //此时已经为黑,停止更新 break; } } } } _root->_col = BLACK; return { iterator(newnode, _root), true }; } private: //右单旋 void rotateR(Node* parent) { Node* grandparent = parent->_parent; Node* subL = parent->_left; Node* subLR = subL->_right; //1.判断parent是否是根,链接grandparent与subL if (grandparent == nullptr) { _root = subL; } else { if (grandparent->_left == parent) { grandparent->_left = subL; } else { grandparent->_right = subL; } } subL->_parent = grandparent; //2.链接subL和parent subL->_right = parent; parent->_parent = subL; //3.链接subLR和parent,subLR不为空,subLR的parent要链接parent parent->_left = subLR; if (subLR) subLR->_parent = parent; } //左单旋 void rotateL(Node* parent) { Node* grandparent = parent->_parent; Node* subR = parent->_right; Node* subRL = subR->_left; //1.判断parent是否是根,链接grandparent与subR if (grandparent == nullptr) { _root = subR; } else { if (grandparent->_left == parent) { grandparent->_left = subR; } else { grandparent->_right = subR; } } subR->_parent = grandparent; //2.链接subR和parent subR->_left = parent; parent->_parent = subR; //3.链接subRL和parent parent->_right = subRL; if (subRL) subRL->_parent = parent; } void destory(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) return; destory(root->_left); destory(root->_right); delete root; root = nullptr; } private: Node* _root = nullptr; };
Myset.h
#pragma once #include"RBTree.h" namespace quiteSix { //template<class K> //struct KeyOfT //{ // const K& operator()(const K& key) const // { // return key; // } //}; template<class K> class set { private: struct KeyOfT { const K& operator()(const K& key) const { return key; } }; public: typedef typename RBTree<K,const K, KeyOfT> tree_type; typedef typename tree_type::iterator iterator; public: pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& data) { return _t.Insert(data); } iterator begin() { return _t.Begin(); } iterator end() { return _t.End(); } private: tree_type _t; }; }
Mymap.h
#pragma once #include"RBTree.h" namespace quiteSix { //template<class K, class V> //struct KeyOfT //{ // const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv) const // { // return kv.first; // } //}; template<class K, class V> class map { private: struct KeyOfT { const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv) const { return kv.first; } }; public: typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, KeyOfT> tree_type; typedef typename tree_type::iterator iterator; public: pair<iterator,bool> insert(const pair<const K, V>& _data) { return _t.Insert(_data); } iterator begin() { return _t.Begin(); } iterator end() { return _t.End(); } V& operator[](const K& key) { pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert({ key,V() }); iterator it = ret.first; return (*it).second; } private: tree_type _t; }; }























 1582
1582

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










