1、文件权限管理
自我塑造的过程很疼,但终将遇见更好的自己.
Linux用户权限解析
我们linux服务器上有严格的权限等级,如果权限过高导致误操作会增加服务器的风险。所以对于了解linux系统中的各种权限及要给用户,服务等分配合理的权限十分重要
1.基本权限 UGO
=====================================================
文件权限设置: 可以赋于某个用户或组 能够以何种方式 访问某个文件

- rw- r-- r--. 1 root root 2103 5月 5 15:10 /etc/passwd u g o 权限对象: 属主------->u 属组------->g 其他人------>o
基本权限类型: 读(read):r ---->4 写(write):w ---->2 执行(exec):x ---->1
案例:
r w x rw- r-- alice hr file1.txt 属主权限 属组权限 其他人权限 属主 属组 文件 #前提条件:jack属于hr组 一 alice对file1.txt文件有什么权限? 二 jack对file1.txt文件有什么权限? a. jack是所有者吗? b. jack属于hr组吗? 三 tom对file1.txt文件有什么权限? a. tom是所有者吗? b. tom属于hr组吗? c. tom为其他人吗?
1.1.设置权限
chown:改变文件或目录的所属主以及所属组 chmod:为文件或目录设置访问权限
更改文件的属主(拥有者)、属组 (所属组)
chown:
[root@linux-server ~]# chown 用户.组 文件或目录 [root@linux-server ~]# chown alice.hr file1.txt #修改属主、属组 [root@linux-server ~]# chown tom file1.txt #修改属主 [root@linux-server ~]# chown .it file1.txt #只改属组 [root@linux-server ~]# chown -R alice.hr dir1 #递归修改---针对目录
更改权限
a. 使用符号

[root@linux-server ~]# chmod u+x file1.txt #属主增加执行 [root@linux-server ~]# chmod a=rwx file1.txt #所有人等于读写执行 [root@linux-server ~]# chmod a=- file1.txt #所有人都没有权限 [root@linux-server ~]# chmod ug=rw,o=r file1.txt #属主属组等于读写,其他人只读 [root@linux-server ~]# ll -rw-rw-r--. 1 tom it 0 Nov 1 15:30 file1.txt
b.使用数字
[root@linux-server ~]# chmod 644 file1.txt [root@linux-server ~]# ll file1.txt -rw-r--r--. 1 tom it 0 Nov 1 15:30 file1.txt [root@linux-server ~]# chmod 755 file1.txt [root@linux-server ~]# ll -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 0 Jul 23 22:40 file1.txt [root@linux-server ~]# chmod 521 file1.txt [root@linux-server ~]# ll -r-x-w---x 1 root root 0 Jul 23 22:40 file1.txt
2 .权限案例 UGO
r、w、x权限对文件和目录的意义
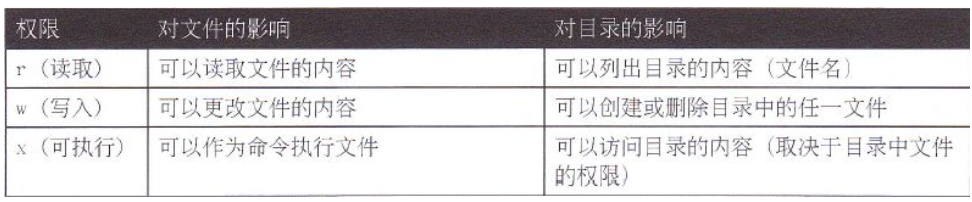
对文件: r ----cat w ---vi、vim x ---- bash /dir/file 对目录: r ---ls w -----touch、rm x ---- cd
实战
rwx对文件的影响
实战案例1:rwx对文件的影响
[root@linux-server ~]# vim /home/file1 date [root@linux-server ~]# ll /home/file1 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 Nov 3 15:19 /home/file1 [root@linux-server ~]# su - alice #切换普通用户 [alice@linux-server ~]$ cat /home/file1 date [alice@linux-server ~]$ /home/file1 #执行文件 -bash: /home/file1: Permission denied [alice@linux-server ~]$ exit logout [root@linux-server ~]# chmod o+x /home/file1 [alice@linux-server ~]$ /home/file1 Sun Nov 3 15:26:21 CST 2019 [root@linux-server ~]# chmod o+w /home/file1 [alice@linux-server ~]$ vim /home/file1 date 123 ls
rwx对目录的影响
实战案例2:对目录没有w,对文件有rwx
[root@linux-server ~]# mkdir /dir10 [root@linux-server ~]# touch /dir10/file1 [root@linux-server ~]# chmod 777 /dir10/file1 [root@linux-server ~]# ll -d /dir10/ drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 19 Nov 3 15:37 /dir10/ [root@linux-server ~]# ll /dir10/file1 -rwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Nov 3 15:37 /dir10/file1 [root@linux-server ~]# vim /dir10/file1 jack [root@linux-server ~]# su - alice Last login: Sun Nov 3 15:28:06 CST 2019 on pts/0 [alice@linux-server ~]$ cat /dir10/file1 jack [alice@linux-server ~]$ rm -rf /dir10/file1 #权限不够 rm: cannot remove ‘/dir10/file1’: Permission denied [alice@linux-server ~]$ touch /dir10/file2 #权限不够 touch: cannot touch ‘/dir10/file2’: Permission denied
实战案例3:对目录有w,对文件没有任何权限
[root@linux-server ~]# chmod 777 /dir10/ [root@linux-server ~]# chmod 000 /dir10/file1 [root@linux-server ~]# ll -d /dir10/ drwxrwxrwx. 2 root root 19 Nov 3 15:38 /dir10/ [root@linux-server ~]# ll /dir10/file1 ----------. 1 root root 5 Nov 3 15:38 /dir10/file1 [root@linux-server ~]# su - alice #切换普通用户 Last login: Sun Nov 3 15:38:53 CST 2019 on pts/0 [alice@linux-server ~]$ cat /dir10/file1 cat: /dir10/file1: Permission denied #没有权限 [alice@linux-server ~]$ rm -rf /dir10/file1 [alice@linux-server ~]$ touch /dir10/file2 #小结 对目录有w权限,可以在目录中创建新文件,可以删除目录中的文件(跟文件权限无关)
注意事项 文件: x 权限小心给予 目录: w 权限小心给予
grep: 文件内容过滤
[root@qfedu.com ~]# grep 'root' /etc/passwd #从/etc/passwd文件中过滤root字段 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin # grep 查找关键字 # -v 取反 # 查找的是包含root内容的行 # grep "root" /etc/passwd # 查找以root开头的行 # grep "^root" /etc/passwd # 查找以root结尾的行 # grep "root$" /etc/passwd # 查找空行"^$" # grep "root$" /etc/passwd # 查找不包含root的行 # grep -v "root" /etc/passwd # 查看命令所在的位置 [root@localhost opt]# which ls alias ls='ls --color=auto' /usr/bin/ls [root@localhost opt]# which grep alias grep='grep --color=auto' /usr/bin/grep [root@localhost opt]# which useradd /usr/sbin/useradd [root@localhost opt]# which chown /usr/bin/chown [root@localhost opt]# /usr/sbin/useradd wanger [root@localhost opt]# id wanger uid=10093(wanger) gid=10093(wanger) groups=10093(wanger) # 设置别名 alias 别名='命令' # 取消别名 unalias 别名 # 查看当前系统中有哪些别名 # alias # 查询命令所在位置及配置文件 # whereis ls # umask root用户默认是0022,普通用户默认是0002 权限掩码 # root用户创建文件默认权限是0644 #最大0666 rw # root用户创建目录默认权限0755 # 最大0777 # umask 0666 # 控制创建的文件或者目录的默认权限 # 用户创建出的文件或者目录的默认权限加上umask值等于可以给这个文件或者目录的最大权限
查找命令
[root@qfedu.com ~]# which ls alias ls='ls --color=auto' /usr/bin/ls [root@qfedu.com ~]# which cd /usr/bin/cd [root@qfedu.com ~]# which rm alias rm='rm -i' /usr/bin/rm
查询命令和配置文件的位置
[root@qfedu.com ~]# whereis rpm rpm: /usr/bin/rpm /usr/lib/rpm /etc/rpm /usr/share/man/man8/rpm.8.gz [root@qfedu.com ~]# whereis passwd passwd: /usr/bin/passwd /etc/passwd /usr/share/man/man1/passwd.1.gz
find详解: 文件查找,针对文件名
语法: # find 路径 条件 跟条件相关的操作符 [-exec 动作] 路径: 1.默认不写路径时查找的是当前路径. 2.加路径。 条件: 1.指定的名称 -name 2.文件类型 -type 3.时间
1.1.按文件名
从根开始找文件 [root@qfedu.com ~]# find / -name “file2” #从根开始找文件 /root/file2 /var/tmp/file2 [root@qfedu.com ~]# find /etc -name "ifcfg-ens33" #以名字的方式查找 [root@qfedu.com ~]# find /etc -iname "Ifcfg-ens33" #-i忽略大小写
熟用*通配符
[root@qfedu.com ~]# find /etc -iname "*.txt" 参数解释: *:表示所有字符
1.2.按文件大小 -size
[root@qfedu.com ~]# find /etc -size +5M #大于5M [root@qfedu.com ~]# find /etc -size 5M #等于5M [root@qfedu.com ~]# find /etc -size -5M #小于5M [root@qfedu.com ~]# find / -size +3M -a -size -5M #查找/下面大于3M而且小于5M的文件 -a:and [root@qfedu.com ~]# find / -size -1M -o -size +80M #查找/下面小于1M或者大于80M的文件 -o:or [root@qfedu.com ~]# find / -size -3M -a -name "*.txt" #查找/ 下面小于3M而且名字是.txt的文件
1.3按时间查找
按时间找(atime,mtime,ctime) -atime = access访问时间 -mtime = modify改变时间 内容修改时间会改变 -ctime = change修改时间 属性修改时间会改变 -amin #分钟 -mmin -cmin
[root@qfedu.com ~]# find /opt -mtime +5 #修改时间5天之前 [root@qfedu.com ~]# find /opt -atime +1 #访问时间1天之前 [root@qfedu.com ~]# find . -mtime -2 #修改时间2天之内 [root@qfedu.com ~]# find . -amin +1 #访问时间在1分钟之前 [root@qfedu.com ~]# find /opt -amin -4 #访问时间在4分钟之内 [root@qfedu.com ~]# find /opt -mmin -2 #修改时间在2分钟之内
1.4按文件类型
[root@qfedu.com ~]# find /dev -type f #f普通文件 [root@qfedu.com ~]# find / -type f -size -1M -o -name "*.txt" [root@qfedu.com ~]# find /dev -type d #d目录 [root@qfedu.com ~]# find /etc/ -type d -name "*.conf.d" [root@qfedu.com ~]# find /etc -type l #l链接
案例1: 分别找出test5 和除了test5的文件
[root@qfedu.com ~]# find /home/ -name *test5* [root@qfedu.com ~]# find /home/ ! -name "test5*" # !--取反
# find 查找文件在什么位置
# find $PATH 条件
# -name 按照文件名称查找
# 从/etc目录开始查找,查找/etc目录及子目录中所有文件名叫'passwd'的
# find /etc -name "passwd"
# 从/etc目录开始查找,查找/etc目录及子目录中所有文件名最后是"ens33" [模糊查询]
# find /etc/ -name "*ens33"
# -iname 忽略文件名称大小写
# fine /etc -iname "iFCfg-ens33"
# -size 按照文件的大小查找[bcwKMG]
# 查找一个大于10M,并且小于20M的文件,两个条件要同时成立
# find / -size +10M -a -size -20M
# 查找一个文件小于3M或者大于10M,两个条件只需要符合一个即可
# find / -size -3M -o -size +10M
# 查找一个文件,文件名为“test.txt” 并且文件大小大于5M【-a 可以忽略】
# find / -name "test.txt" -size +5M
# 按照时间去查找文件
# stat $filename # 查看文件的详细信息
Access: 2024-10-21 14:09:21.514325992 +0800 # 访问时间
Modify: 2024-10-21 14:09:21.514325992 +0800 # 修改时间 文件内容修改时间
Change: 2024-10-21 14:09:21.514325992 +0800 # 修改时间 文件属性的修改时间(属主、属组)
[root@localhost ~]# stat Inode.txt
File: ‘Inode.txt’
Size: 0 Blocks: 0 IO Block: 4096 regular empty file
Device: fd00h/64768d Inode: 108568324 Links: 1
Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root)
Context: unconfined_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0
Access: 2024-10-21 14:09:21.514325992 +0800
Modify: 2024-10-21 14:09:21.514325992 +0800
Change: 2024-10-21 14:09:21.514325992 +0800
Birth: -
[root@localhost ~]# chown wanger Inode.txt
[root@localhost ~]# ll
total 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 wanger root 2 Oct 21 15:39 inode.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 wanger root 0 Oct 21 14:09 Inode.txt
[root@localhost ~]# stat Inode.txt
File: ‘Inode.txt’
Size: 0 Blocks: 0 IO Block: 4096 regular empty file
Device: fd00h/64768d Inode: 108568324 Links: 1
Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: (10093/ wanger) Gid: ( 0/ root)
Context: unconfined_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0
Access: 2024-10-21 14:09:21.514325992 +0800
Modify: 2024-10-21 14:09:21.514325992 +0800
Change: 2024-10-21 15:41:37.583304873 +0800
Birth: -
[root@localhost ~]# echo 123456v >> Inode.txt
[root@localhost ~]# ll Inode.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 wanger root 8 Oct 21 15:45 Inode.txt
[root@localhost ~]# stat Inode.txt
File: ‘Inode.txt’
Size: 8 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file
Device: fd00h/64768d Inode: 108568324 Links: 1
Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: (10093/ wanger) Gid: ( 0/ root)
Context: unconfined_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0
Access: 2024-10-21 14:09:21.514325992 +0800
Modify: 2024-10-21 15:45:27.089303998 +0800
Change: 2024-10-21 15:45:27.089303998 +0800
Birth: -
[root@localhost ~]# cat Inode.txt
123456v
[root@localhost ~]# stat Inode.txt
File: ‘Inode.txt’
Size: 8 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file
Device: fd00h/64768d Inode: 108568324 Links: 1
Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: (10093/ wanger) Gid: ( 0/ root)
Context: unconfined_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0
Access: 2024-10-21 15:46:12.993303823 +0800
Modify: 2024-10-21 15:45:27.089303998 +0800
Change: 2024-10-21 15:45:27.089303998 +0800
Birth: -
# 级别:天
-atime
-mtime
-ctime
# 分钟级别
-amin
-mmin
-cmin
# 查找5分钟之内被修改过的文件
# find /opt -mmin -5
# 查找10天之前被访问过的文件
# find /opt -atime +10
# 查找15天之前被修改过的文件,并且文件名以".txt"结尾
# find /opt -mtime +15 -a -name "*.txt"
# 按照文件类型查找
# f
# 查找当前目录下的文件
# find ./ -type f
# d
# 查找当前目录下的目录
# find ./ -type d
# 查找/opt/dir001/目录下所有的目录,及子目录下的目录
# find /opt/dir001/ -type d
# 查找/opt/dir001/目录下所有的文件,及子目录下的文件
# find /opt/dir001/ -type f
# 查找/opt/dir001/十分之前被修改过的目录
# find /opt/dir001/ -mmin +10 -a -type d
# 查找/opt/dir001/除了十分之前被修改过的目录 【! 取反】
# find /opt/dir001/ ! -mmin +10 -a -type d
# 查找/opt/dir001/十分之内被除了修改过的目录 【! 取反】
# find /opt/dir001/ -mmin -10 -a ! -type d
# 按照文件名查找
# 按照文件大小查找
# 按照文件时间查找
# 按照文件类型查找
# ! 取反

























 627
627

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








