问题引入

设编号为1,2,…,的n个人围坐一圈,约定编号为k(1<=k<=n)的人从1开始报数,数到m的那个人出列,他的下一位又从1开始报数,数到m的那个人再次出列,以此类推,直到所有人出列为止,由此产生一个出队编号的序列。
解决思路
用一个不带头节点的循环链表来解决约瑟夫环问题,先构建一个有n个节点的单循环链表,然后由k节点起从1开始计数,计到m时,对应节点从链表删除,然后从被删除的节点的下一个节点又从1开始计数,直到最后一个节点从链表中被删除,则算法结束。
代码实现
首先构建关于每一个孩子的节点
//创建一个boy类,表示一个节点
class Boy{
private int no;
private Boy next; //指向下一个节点,默认为null
public Boy(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public Boy getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Boy next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
接下来创建单向循环链表
基本思路:
链表的构建:
开始有第一个孩子,让一个first指针指向它,然后再有一个临时指针,指向链表的最后一个节点,当然,现在它指向first节点,因为当前第一个孩子就是最后一个节点,这个指针我们把它命名为curBoy。
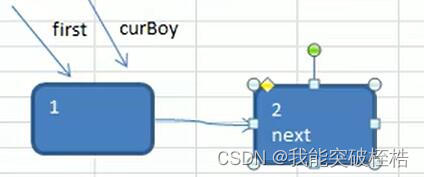
因为要构成环状,所以第一个孩子被创建时,first指针的next域要指向自己,而以后的孩子则是用以下方法来解决:
curBoy指针的next域指向下一个孩子,此孩子的next域指向first节点,然后将curBoy指针后移一位。
结果如下:
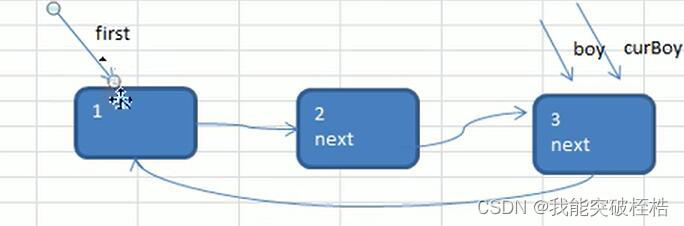
链表的遍历,实现解决约瑟夫环问题:
此时我们需要两个指针,一个指针指向first节点,次指针我们已经拥有,还需要一个指针,指向最后一个节点。我们把它命名为helper。
此时用while循环来遍历单向循环链表,结束条件为first != helper,因为当first == helper时,链表内只有一个节点了,结束循环再次打印链表即可得到最后一个孩子节点。
循环过程中,我们让first节点移动到要开始的那个孩子节点,让helper移动到开始那个孩子节点前面的那个节点。之后开始循环。
用first指针打印出该孩子节点的信息,然后移动first指向其下一个节点,让helper的next域指向first节点达到删除此节点的效果。
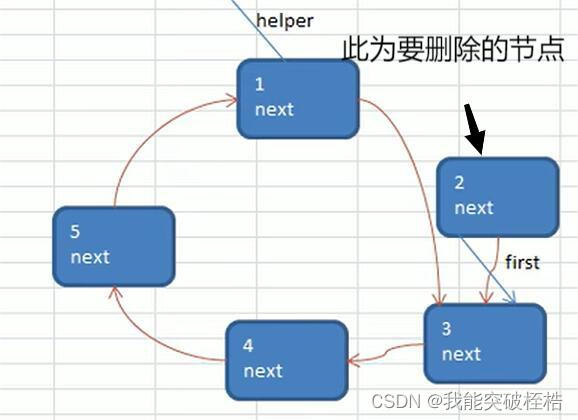
接下来就是不停的while循环,打印出一个个孩子节点,也就是我们需要的孩子的输出序列。
当然之前也提到过跳出while循环条件是first != helper,那就使最后一个节点并为被打印出来,在while循环之外在打印最后一个节点即可。
以下是代码的实现:
//创建一个环形的单向链表
class CircleSingleLinkedist{
//创建一个first节点,当前没有编号
private Boy first = null;
//添加小孩节点,构建一个环形链表
public void addBoy(int nums){
//对nums做数据校验
if(nums < 1){
return;
}
int n = 1;
//辅助指针,帮助构建环形链表
Boy curBoy = null;
while(n <= nums){
Boy boy = new Boy(n);
if(n == 1){
first = boy;
first.setNext(first);
curBoy = first;
}else {
curBoy.setNext(boy);
boy.setNext(first);
curBoy = boy;
}
++n;
}
}
//根据用户的输入,计算用户出圈的顺序
/**
*
* @param startNo 表示从第几个小孩开始数数
* @param countNum 表示数几下
* @param nums 表示最初有几个小孩在圈中
*/
public void countBoy(int startNo,int countNum,int nums){
//判断链表是否为null,开始的孩子数是否有误
if(first == null || startNo < 1 || startNo > nums){
System.out.println("参数输入有误!");
return;
}
//创建辅助指针,帮助小孩出圈
Boy helper = first;
//helper指向环形链表的最后一个节点
while (helper.getNext() != first){
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//小孩报数前,先让first和helper移动k - 1次
for (int i = 0; i < startNo - 1; i++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//当小孩报数时,让first和helper指针同时移动m - 1 次,然后出圈
//当圈中只有一个节点就结束循环
while (first != helper){
//让first和helper指针同时移动countNum - 1 次,然后出圈
for (int i = 0; i < countNum - 1; i++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//这时first指向的节点,就是要出圈的小孩节点
System.out.println("小孩" + first.getNo() + "出圈");
//清除这个小孩
first = first.getNext();
helper.setNext(first);
}
System.out.println("留在圈中的小孩编号为:" + first.getNo());
}
}
总结
以下是代码的总题实现:
public class Josepfu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircleSingleLinkedist c = new CircleSingleLinkedist();
c.addBoy(25);
c.countBoy(1,2,25);
}
}
//创建一个环形的单向链表
class CircleSingleLinkedist{
//创建一个first节点,当前没有编号
private Boy first = null;
//添加小孩节点,构建一个环形链表
public void addBoy(int nums){
//对nums做数据校验
if(nums < 1){
return;
}
int n = 1;
//辅助指针,帮助构建环形链表
Boy curBoy = null;
while(n <= nums){
Boy boy = new Boy(n);
if(n == 1){
first = boy;
first.setNext(first);
curBoy = first;
}else {
curBoy.setNext(boy);
boy.setNext(first);
curBoy = boy;
}
++n;
}
}
//根据用户的输入,计算用户出圈的顺序
/**
*
* @param startNo 表示从第几个小孩开始数数
* @param countNum 表示数几下
* @param nums 表示最初有几个小孩在圈中
*/
public void countBoy(int startNo,int countNum,int nums){
if(first == null || startNo < 1 || startNo > nums){
System.out.println("参数输入有误!");
return;
}
//创建辅助指针,帮助小孩出圈
Boy helper = first;
//helper指向环形链表的最后一个节点
while (helper.getNext() != first){
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//小孩报数前,先让first和helper移动k - 1次
for (int i = 0; i < startNo - 1; i++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//当小孩报数时,让first和helper指针同时移动m - 1 次,然后出圈
//当圈中只有一个节点就结束循环
while (first != helper){
//让first和helper指针同时移动countNum - 1 次,然后出圈
for (int i = 0; i < countNum - 1; i++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//这时first指向的节点,就是要出圈的小孩节点
System.out.println("小孩" + first.getNo() + "出圈");
//清除这个小孩
first = first.getNext();
helper.setNext(first);
}
System.out.println("留在圈中的小孩编号为:" + first.getNo());
}
}
//创建一个boy类,表示一个节点
class Boy{
private int no;
private Boy next; //指向下一个节点,默认为null
public Boy(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public Boy getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Boy next) {
this.next = next;
}
}























 5988
5988

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








