前言
学习的underscore.js 源码版本为1.13.1(文章修改于2021-12-06日)
为什么会有这两个玩意?
先看以下场景:
- window对象的resize、scroll事件;
- DOM元素的拖拽事件(mousemove);
- 射击游戏中的mousedown、keydown事件;
- 文字输入搜索联想提示等操作的keyup事件;
- ...
以上场景往往由于事件频繁被触发,因而频繁执行DOM操作、资源加载等行为,导致UI停顿甚至浏览器崩溃。我们需要做的是降低触发回调的频率,提高用户体验。因此根据不同的处理模式(一种是停止n毫秒后执行,一种是以一定的频率执行),就出现了函数去抖和函数节流两种解决办法。
函数去抖(debounce)
如果用手指一直按住一个弹簧,它将不会弹起直到你松手为止。
也就是说当调用动作n毫秒后,才会执行该动作,若在这n毫秒内又调用此动作则将重新计算执行时间。
防抖常用于搜索框/滚动条的监听事件处理,如果不做防抖,每输入一个字/滚动屏幕,都会触发事件处理,造成性能浪费。
第一版实现
underscore.js1.1.3 版本 --- debounce方法
解决了this指向、传参问题
var debounce = function (func, wait) {
var timeout;
return function () {
var context = this, args = arguments;
var throttler = function () {
func.apply(context, args);
};
clearTimeout(timeout);
timeout = setTimeout(throttler, wait);
};
}
第二版实现
underscore.js1.3.3 版本 --- debounce方法
新增参数immediate: 是否立即执行,会影响到达时间间隔后执行的是最先的函数调用还是最后的函数调用
var debounce = function (func, wait, immediate) {
var timeout;
return function () {
var context = this, args = arguments;
var later = function () {
timeout = null;
if (!immediate) func.apply(context, args);
};
// immediate 参数为 true,并且 timeout 还没设置就立即执行
if (immediate && !timeout) func.apply(context, args);
clearTimeout(timeout);
timeout = setTimeout(later, wait);
};
};
第三版实现
underscore.js1.4.0 版本 --- debounce方法
考虑返回值
var debounce = function(func, wait, immediate) {
var timeout, result;
return function() {
var context = this, args = arguments;
var later = function() {
timeout = null;
if (!immediate) result = func.apply(context, args);
};
var callNow = immediate && !timeout;
clearTimeout(timeout);
timeout = setTimeout(later, wait);
// func 可能是有返回值的
if (callNow) result = func.apply(context, args);
return result;
};
};
最终版
underscore.js1.13.1 版本 --- debounce方法
区别:
- 加入
.cancel()方法,可用于取消调用 - 使用通过递归启动计时器来代替通过调用clearTimeout来调整调用func函数的延时执行(关于这点具体可以看https://github.com/jashkenas/underscore/pull/1269)
function debounce (func, wait, immediate) {
var timeout, previous, args, result, context;
var later = function () {
var passed = new Date().getTime() - previous;
// 当wait指定的时间间隔期间多次调用debounce返回的函数,则会不断更新previous的值,导致wait > passed一直为true,从而不断启动新的计时器延时执行func
if (wait > passed) {
timeout = setTimeout(later, wait - passed);
} else {
// 到了可以触发的时间点
// 将 timeout 值置为空,使之不影响下次连续事件的触发
timeout = null;
// 如果不是立即执行,随即执行 func 方法
if (!immediate) result = func.apply(context, args);
if (!timeout) args = context = null;
}
};
var debounced = function () {
context = this;
args = arguments;
// 每次触发函数,更新时间戳
previous = new Date().getTime();
if (!timeout) {
// 在wait指定的时间间隔内首次调用该方法,则启动计时器定时调用func函数
timeout = setTimeout(later, wait);
// 第一次调用该方法时,且immediate为true,则调用func函数
// func 可能是有返回值的
if (immediate) result = func.apply(context, args);
}
return result;
}
debounced.cancel = function () {
clearTimeout(timeout);
// 解除引用
timeout = args = context = null;
};
return debounced;
}
够用版
function debounce (func, wait, immediate) {
var timeout, result;
var debounced = function () {
var context = this, args = arguments;
if (timeout) clearTimeout(timeout);
if (immediate) {
var callNow = !timeout;
timeout = setTimeout(function () {
timeout = null;
}, wait);
if (callNow) result = func.apply(this, args);
} else {
timeout = setTimeout(function () {
func.apply(context, args);
}, wait);
}
return result;
}
debounced.cancel = function () {
clearTimeout(timeout);
timeout = null;
}
return debounced;
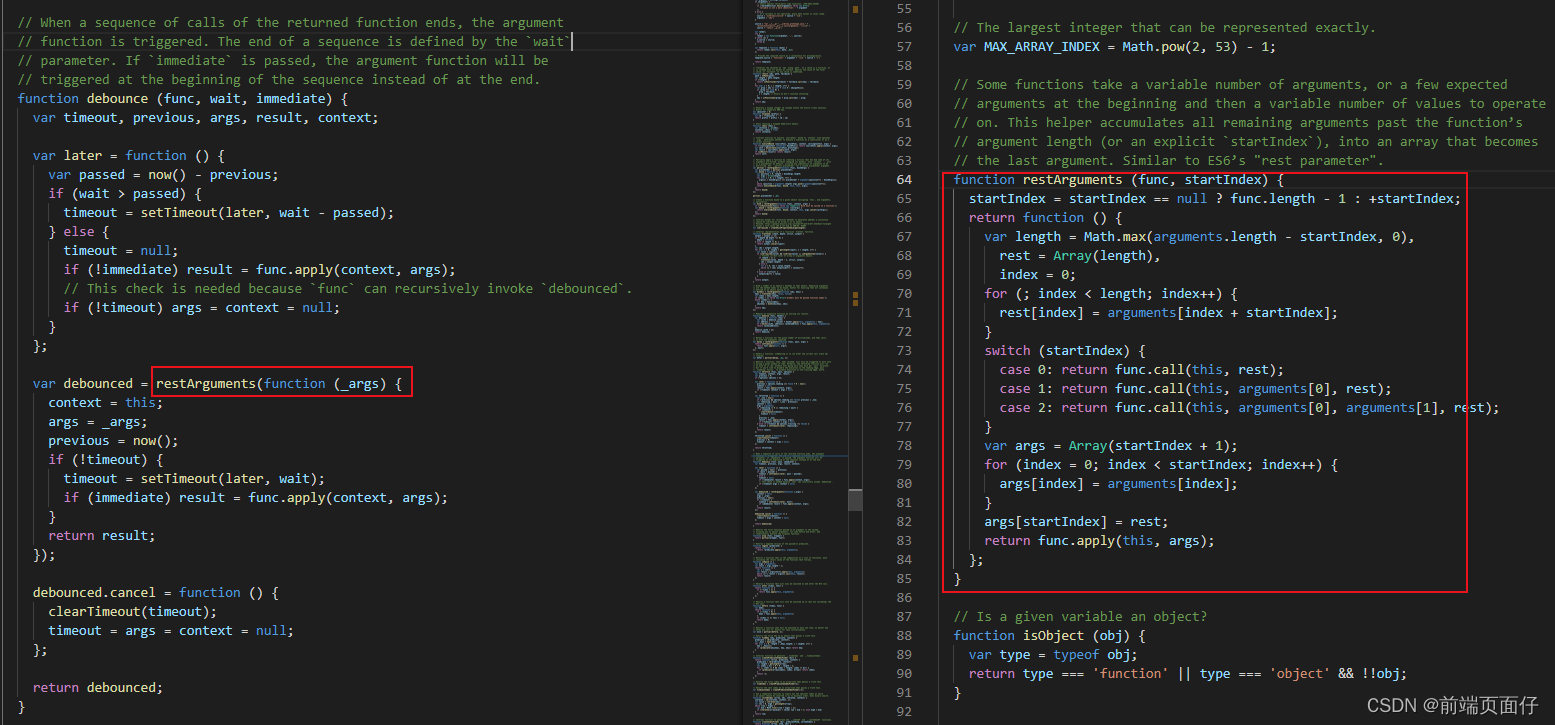
}注: 实际源码中debounced函数被内部函数restArguments包裹起来
关于内部函数restArguments我们后面再讲。
函数节流(throttle)
如果将水龙头拧紧直到水是以水滴的形式流出,那你会发现每隔一段时间,就会有一滴水流出。
也就是会说预先设定一个执行周期,当调用动作的时刻大于等于执行周期则执行该动作,然后进入下一个新周期。
防抖是延迟执行,而节流是间隔执行,函数节流即每隔一段时间就执行一次,实现原理为设置一个定时器,约定xx毫秒后执行事件,如果时间到了,那么执行函数并重置定时器,和去抖的区别在于,去抖每次触发事件都重置定时器,而节流在定时器到时间后再清空定时器
第一版实现
underscore.js1.1.3 版本 --- throttle方法
var throttle = function (func, wait) {
var timeout;
return function () {
var context = this, args = arguments;
var throttler = function () {
timeout = null;
func.apply(context, args);
};
if (!timeout) timeout = setTimeout(throttler, wait);
};
}
第二版实现
underscore.js1.4.3 版本 --- throttle方法
跟第一版区别在于立即执行
var throttle = function(func, wait) {
var context, args, timeout, result;
var previous = 0;
var later = function() {
// 重置为当前时间戳
previous = new Date;
timeout = null;
result = func.apply(context, args);
};
return function() {
var now = new Date;
// 距离下次触发 func 还需要等待的时间
var remaining = wait - (now - previous);
context = this;
args = arguments;
if (remaining <= 0) {
clearTimeout(timeout);
timeout = null;
// 重置前一次触发的时间戳
previous = now;
// 触发方法并考虑有返回值
result = func.apply(context, args);
} else if (!timeout) {
// 间隔 remaining 毫秒后触发 later 方法
timeout = setTimeout(later, remaining);
}
return result;
};
};
最终版
underscore.js1.13.1 版本 --- throttle方法
区别:
- 加入
.cancel()方法,可用于取消调用 - 加上options参数,其中{leading: false}表示不会马上触发,{trailing: false}表示最后一次回调不会被触发
var now = Date.now || function () {
return new Date().getTime();
};
// 如果 options 参数传入 {leading: false}, 那么不会马上触发(等待 wait 毫秒后第一次触发 func)
// 如果 options 参数传入 {trailing: false}, 那么最后一次回调不会被触发
// options 不能同时设置 leading 和 trailing 为 false
function throttle(func, wait, options) {
var timeout, context, args, result;
var previous = 0;
if (!options) options = {};
var later = function() {
// 如果 options.leading === false,则每次触发回调后将 previous 置为 0,否则置为当前时间戳
previous = options.leading === false ? 0 : now();
timeout = null;
result = func.apply(context, args);
if (!timeout) context = args = null;
};
var throttled = function() {
// 记录当前时间戳
var _now = now();
// 第一次执行回调(此时 previous 为 0,之后 previous 值为上一次时间戳)
// 并且如果程序设定为不是立即执行的(options.leading === false)
// 则将 previous 值(表示上次执行的时间戳)设为 now 的时间戳(第一次触发时)
// 表示刚执行过,这次就不用执行了
if (!previous && options.leading === false) previous = _now;
var remaining = wait - (_now - previous);
context = this;
args = arguments;
// 如果没有剩余的时间了或者你改了系统时间
if (remaining <= 0 || remaining > wait) {
if (timeout) {
clearTimeout(timeout);
timeout = null;
}
// 重置前一次触发的时间戳
previous = _now;
result = func.apply(context, args);
// 解除引用,防止内存泄露
if (!timeout) context = args = null;
} else if (!timeout && options.trailing !== false) {
// 定时器不存在且options.trailing !== false 则触发最后一次回调
// 间隔 remaining 毫秒后触发 later 方法
timeout = setTimeout(later, remaining);
}
return result;
};
// 取消方法
throttled.cancel = function() {
clearTimeout(timeout);
previous = 0;
timeout = context = args = null;
};
return throttled;
}
参考资料:








 本文详细剖析underscore.js中函数去抖(debounce)和节流(throttle)的实现原理,从基础版本到最终版本,探讨它们在性能优化中的应用,如搜索框监听、滚动事件处理等。同时,介绍了underscore.js 1.13.1版本中去抖和节流函数的改进,包括`.cancel()`方法的添加以及不同选项的影响。
本文详细剖析underscore.js中函数去抖(debounce)和节流(throttle)的实现原理,从基础版本到最终版本,探讨它们在性能优化中的应用,如搜索框监听、滚动事件处理等。同时,介绍了underscore.js 1.13.1版本中去抖和节流函数的改进,包括`.cancel()`方法的添加以及不同选项的影响。
















 704
704

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








