Android系统进程Zygote启动过程分析
标签(空格分隔): 开关机流程
- Android系统进程Zygote启动过程分析
- Step 1. app_main.cpp
- Step 2. AndroidRuntime.start
- Step 3. ZygoteInit.main
- Step 4. ZygoteInit.registerZygoteSocket
- Step 5. ZygoteInit.startSystemServer
- Step 6. ZygoteInit.handleSystemServerProcess
- Step 7. RuntimeInit.zygoteInit
- Step 8. AndroidRuntime.com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit_nativeZygoteInit
- Step 9. SystemServer.main
- Step 10. SystemServer.startBootstrapServices
- Step 11. startCoreServices
- Step 12. startOtherServices
- 总结:
我们知道,Android系统是基于Linux内核的,而在linux系统中,所有的进程都是init进程的子孙进程,也就是说,所有的进程都是直接或者间接地由init进程fork出来的。Zygote进程也不例外,它是在系统启动的过程,由init进程创建的。在系统启动脚本system/core/rootdir/init.rc文件中,我们可以看到启动Zygote进程的脚本命令(MSM8937平台启动Zygote进程的脚本命令放在system/core/rootdir/init.zygote32.rc):
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
class main
priority -20
user root
group root readproc
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart cameraserver
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
onrestart restart wificond
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks- 关键字
service: 告诉init进程创建一个名为”zygote”的进程,这个zygote进程要执行的程序是/system/bin/app_process,后面是要传给app_process的参数。
Zygote进程可以执行文件是app_process。app_process模块的源文件在frameworks/base/cmds/app_process下,只有一个文件app_main.cpp
// 详见frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp:
// arguments :
//
// --zygote : Start in zygote mode
// --start-system-server : Start the system server.
// --application : Start in application (stand alone, non zygote) mode.
// --nice-name : The nice name for this process.- -Xzygote是传递给虚拟机的参数
- /system/bin 是 parent dir(程序运行目录)
- –zygote表示以zygote模式启动
class main: It belongs to the main class and will start along with any other service that belongs with that classOnrestart: Execute a command when service restarts
最后的一系列onrestart关键字表示这个zygote进程重启时需要执行的命令。
关于init.rc文件的更多信息,请参考system/core/init/readme.txt文件。
了解了这个信息之后,我们就知道Zygote进程要执行的程序便是system/bin/app_process了,它的源代码位于frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp文件中,入口函数是main。在继续分析Zygote进程启动的过程之前,我们先来看看它的启动序列图:
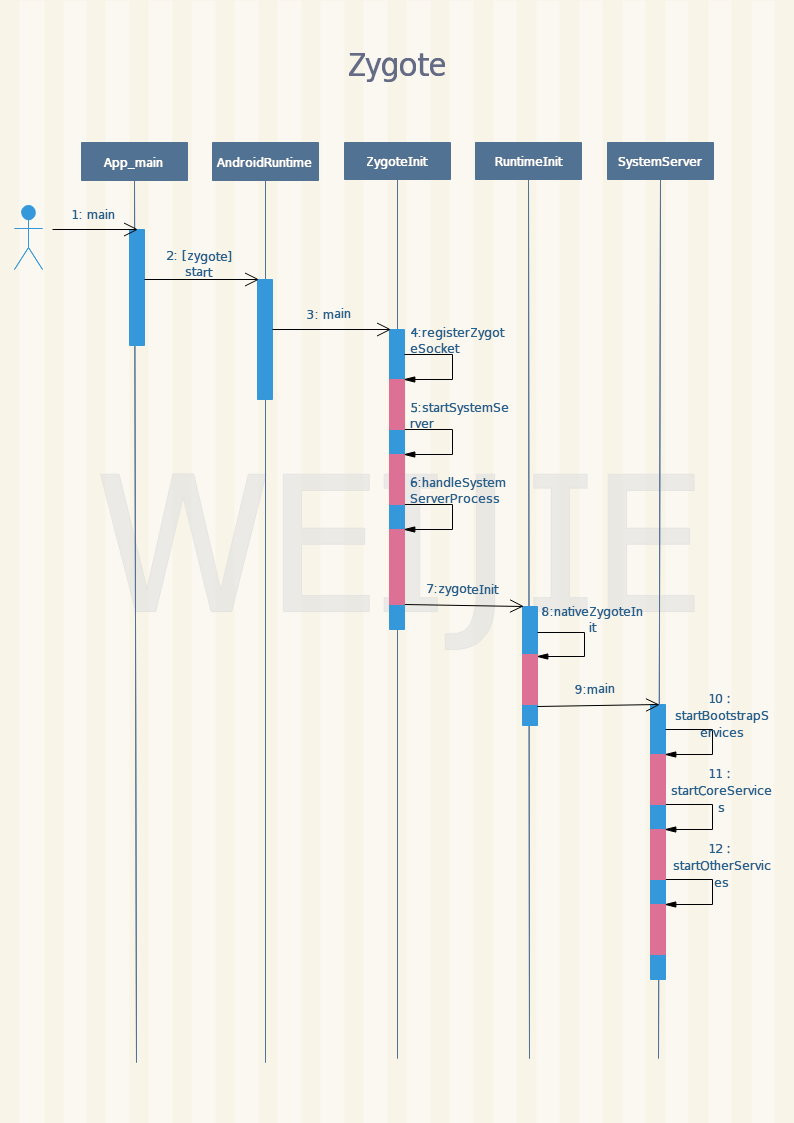
本文源码版本为Android7.1
进入Zygote启动的C篇
Step 1. app_main.cpp
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp文件中:
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
...
// 1. 隐式创建一个AppRuntime对象:runtime
AppRuntime runtime(argv[0], computeArgBlockSize(argc, argv));
// Process command line arguments
// ignore argv[0]
argc--;
argv++;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < argc; i++) {
if (argv[i][0] != '-') {
break;
}
if (argv[i][1] == '-' && argv[i][2] == 0) {
++i; // Skip --.
break;
}
runtime.addOption(strdup(argv[i]));
}
// Parse runtime arguments. Stop at first unrecognized option.
bool zygote = false;
bool startSystemServer = false;
bool application = false;
String8 niceName;
String8 className;
// 2. 处理输入参数
++i; // Skip unused "parent dir" argument.
while (i < argc) {
const char* arg = argv[i++];
if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) {
zygote = true;
niceName = ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0) {
application = true;
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--nice-name=", 12) == 0) {
niceName.setTo(arg + 12);
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--", 2) != 0) {
className.setTo(arg);
break;
} else {
--i;
break;
}
}
...
if (zygote) {
// 3. 最终走到这里
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
} else if (className) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
return 10;
}
}1.AppRuntime
AppRuntime继承了AndroidRuntime
class AppRuntime : public AndroidRuntime
{
......
}; 由于AppRuntime没有实现自己的start函数,它继承了父类AndroidRuntime的start函数,因此,最终会执行AndroidRuntime类的start函数
2.处理输入参数
以-Xzygote /system/bin –zygote –start-system-server为例,结果如下:
- parentDir 等于/system/bin
- niceName 等于 zyoget
- startSystemServer 等于 true
- zygote 等于 true
3.启动ZygoteInit
Step 2. AndroidRuntime.start
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp文件中:
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote)
{
ALOGD(">>>>>> START %s uid %d <<<<<<\n",
className != NULL ? className : "(unknown)", getuid());
// 1. 启动SystemServer
static const String8 startSystemServer("start-system-server");
// 2. 调用函数startReg注册JNI方法
/*
* Register android functions.
*/
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
/*
* We want to call main() with a String array with arguments in it.
* At present we have two arguments, the class name and an option string.
* Create an array to hold them.
*/
jclass stringClass;
jobjectArray strArray;
jstring classNameStr;
stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
assert(stringClass != NULL);
strArray = env->NewObjectArray(options.size() + 1, stringClass, NULL);
assert(strArray != NULL);
classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
assert(classNameStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
jstring optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options.itemAt(i).string());
assert(optionsStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, i + 1, optionsStr);
}
/*
* Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
* not return until the VM exits.
*/
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className);
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
/* keep going */
} else {
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
/* keep going */
} else {
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
...
}这个函数的作用是启动Android系统运行时库,它主要做了三件事情,一是调用函数startVM启动虚拟机,二是调用函数startReg注册JNI方法,三是调用了com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit类的main函数。
进入Zygote启动的java阶段
Step 3. ZygoteInit.main
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/Java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java文件中:
public static void main(String argv[]) {
...
// 1. 调用registerZygoteSocket函数创建了一个socket接口,用来和ActivityManagerService通讯
registerZygoteSocket(socketName);
// 2. 加载公共java类和部分framework资源
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
// 3. 调用startSystemServer函数来启动SystemServer组件
if (startSystemServer) {
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName);
}
// 4. 调用runSelectLoopMode函数
runSelectLoop(abiList);
}- 调用registerZygoteSocket函数创建了一个socket接口,用来和ActivityManagerService通讯。
- 调用preload函数加载公共java类和部分framework资源
- 调用startSystemServer函数来启动SystemServer组件。
- 调用runSelectLoopMode函数进入一个无限循环在前面创建的socket接口上等待ActivityManagerService请求创建新的应用程序进程。
Step 4. ZygoteInit.registerZygoteSocket
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java文件中:
public class ZygoteInit {
......
/**
* Registers a server socket for zygote command connections
*
* @throws RuntimeException when open fails
*/
private static void registerZygoteSocket() {
if (sServerSocket == null) {
int fileDesc;
try {
String env = System.getenv(ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV);
fileDesc = Integer.parseInt(env);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
......
}
try {
sServerSocket = new LocalServerSocket(
createFileDescriptor(fileDesc));
} catch (IOException ex) {
.......
}
}
}
......
} 这个socket接口是通过文件描述符来创建的,这个文件描符代表的就是我们前面说的/dev/socket/zygote文件了。这个文件描述符是通过环境变量ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV得到的。
Step 5. ZygoteInit.startSystemServer
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java文件中:
private static boolean startSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName)
throws MethodAndArgsCaller, RuntimeException {
...
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
String args[] = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1032,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--nice-name=system_server",
"--runtime-args",
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try {
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
/* Request to fork the system server process */
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) {
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
return true;
}这里我们可以看到,Zygote进程通过Zygote.forkSystemServer函数来创建一个新的进程来启动SystemServer组件,返回值pid等0的地方就是新的进程要执行的路径,即新创建的进程会执行handleSystemServerProcess函数。
Step 6. ZygoteInit.handleSystemServerProcess
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java文件中:
public class ZygoteInit {
......
private static void handleSystemServerProcess(
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
closeServerSocket();
/*
* Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
* "--nice-name=system_server com.android.server.SystemServer"
*/
RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
/* should never reach here */
}
......
} 由于由Zygote进程创建的子进程会继承Zygote进程在前面Step 4中创建的Socket文件描述符,而这里的子进程又不会用到它,因此,这里就调用closeServerSocket函数来关闭它。这个函数接着调用RuntimeInit.zygoteInit函数来进一步执行启动SystemServer组件的操作。
Step 7. RuntimeInit.zygoteInit
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java文件中:
public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "RuntimeInit");
redirectLogStreams();
commonInit();
nativeZygoteInit();
applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
}nativeZygoteInit()是一个Native函数,实现在frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp文件中。
Step 8. AndroidRuntime.com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit_nativeZygoteInit
Step 9. SystemServer.main
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java文件中:
/**
* The main entry point from zygote.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}private void run() {
try {
...
// Here we go!
Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
...
// Initialize the system context.
createSystemContext();
// Create the system service manager.
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
mSystemServiceManager.setRuntimeRestarted(mRuntimeRestart);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
}
// Start services.
try {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER, "StartServices");
startBootstrapServices();
startCoreServices();
startOtherServices();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
}
...
// Loop forever.
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}里面主要涉及了是三个方法:
startBootstrapServices() 主要用于启动系统Boot级服务
startCoreServices() 主要用于启动系统核心的服务
startOtherServices() 主要用于启动一些非紧要或者是非需要及时启动的服务
Step 10. SystemServer.startBootstrapServices
private void startBootstrapServices() {
// 1. start Installer
Installer installer = mSystemServiceManager.startService(Installer.class);
// 2. start ActivityManagerService
// Activity manager runs the show.
mActivityManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager);
mActivityManagerService.setInstaller(installer);
// 3. start PowerManagerService
mPowerManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerManagerService.class);
// 4. initialize power management features.
mActivityManagerService.initPowerManagement();
// 5. start LightsService
mSystemServiceManager.startService(LightsService.class);
// 6. start DisplayManagerService
// starts up.
mDisplayManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(DisplayManagerService.class);
// 7. Start the package manager.
mPackageManagerService = PackageManagerService.main(mSystemContext, installer,
mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_OFF, mOnlyCore);
mFirstBoot = mPackageManagerService.isFirstBoot();
mPackageManager = mSystemContext.getPackageManager();
...
// 8. start UserManagerService
mSystemServiceManager.startService(UserManagerService.LifeCycle.class);
// 9. Initialize attribute cache used to cache resources from packages.
AttributeCache.init(mSystemContext);
// 10. Set up the Application instance for the system process and get started.
mActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess();
// 11. start SensorService
startSensorService();
}可见,BootstrapServices中启动了:
1. ActivityManagerService
2. PowerManagerService
3. LightsService
4. DisplayManagerService
5. UserManagerService
6. SensorService
Step 11. startCoreServices
/**
* Starts some essential services that are not tangled up in the bootstrap process.
*/
private void startCoreServices() {
// Tracks the battery level. Requires LightService.
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BatteryService.class);
// Tracks application usage stats.
mSystemServiceManager.startService(UsageStatsService.class);
mActivityManagerService.setUsageStatsManager(
LocalServices.getService(UsageStatsManagerInternal.class));
// Tracks whether the updatable WebView is in a ready state and watches for update installs.
mWebViewUpdateService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(WebViewUpdateService.class);
}CoreServices中启动了:
- BatteryService
- UsageStatsService
- WebViewUpdateService
Step 12. startOtherServices
try {
// 1. add SchedulingPolicyService
ServiceManager.addService("scheduling_policy", new SchedulingPolicyService());
// 2. start TelecomLoaderService
mSystemServiceManager.startService(TelecomLoaderService.class);
// 3. add telephonyRegistry
telephonyRegistry = new TelephonyRegistry(context);
ServiceManager.addService("telephony.registry", telephonyRegistry);
if (!disableCameraService) {
// 4. start CameraService
mSystemServiceManager.startService(CameraService.class);
}
// The AccountManager must come before the ContentService
// 5. start AccountManager
mSystemServiceManager.startService(ACCOUNT_SERVICE_CLASS);
// 6. start ContentService
mSystemServiceManager.startService(CONTENT_SERVICE_CLASS);
// 7. InstallSystemProviders
mActivityManagerService.installSystemProviders();
// 8. start VibratorService
vibrator = new VibratorService(context);
ServiceManager.addService("vibrator", vibrator);
if (!disableConsumerIr) {
// 9. start ConsumerIrService
consumerIr = new ConsumerIrService(context);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.CONSUMER_IR_SERVICE, consumerIr);
}
// 10. start AlarmManagerService
mSystemServiceManager.startService(AlarmManagerService.class);
// 11. init InitWatchdog
final Watchdog watchdog = Watchdog.getInstance();
watchdog.init(context, mActivityManagerService);
// 12. start InputManagerService
inputManager = new InputManagerService(context);
// 13. start WindowManagerService
wm = WindowManagerService.main(context, inputManager,
mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL,
!mFirstBoot, mOnlyCore);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE, wm);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.INPUT_SERVICE, inputManager);
if (!disableVrManager) {
// 14. start VrManagerService
mSystemServiceManager.startService(VrManagerService.class);
}
mActivityManagerService.setWindowManager(wm);
inputManager.setWindowManagerCallbacks(wm.getInputMonitor());
inputManager.start();
// 15. start BluetoothService
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BluetoothService.class);
// 16. start MetricsLoggerService
mSystemServiceManager.startService(MetricsLoggerService.class);
// 17. start IpConnectivityMetrics
mSystemServiceManager.startService(IpConnectivityMetrics.class);
// 18. start PinnerService
mSystemServiceManager.startService(PinnerService.class);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
...
}// TODO
可以看出,otherServices中启动了大量的Services,后续再详细分析。
1. CameraService
2. ContentService
3. AlarmManagerService
4. InputManagerService
5. WindowManagerService
6. BluetoothService
…
总结:
SystemServer进程是android中一个很重要的进程由Zygote进程启动;
SystemServer进程主要用于启动系统中的服务;
SystemServer进程启动服务的启动函数为main函数;
SystemServer进程将系统服务分为三类:boot服务,core服务和other服务,并逐步启动
当我们需要启动一个Android应用程序时,ActivityManagerService会通过Socket进程间通信机制,通知Zygote进程为这个应用程序创建一个新的进程。





















 1870
1870

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








