C#进阶
- 复杂数据类型
- 泛型
- 常用泛型数据结构类
- 委托和事件
- 匿名函数
- Lambad表达式
- List排序
- 协变逆变
- 多线程
- 预处理器指令
- 反射和特性
- 反射
- 什么是程序集
- 元数据
- 反射的概念
- 反射的作用
- 语法相关
- 总结
- 特性
- 迭代器
- 特殊语法
- 排序进阶
复杂数据类型
ArrayList
ArrayList的本质
ArrayList是C#为我们封装好的类,它的本质是一个object类型的数组,ArrayList类帮助我们实现了很多方法,比如数组的增删查改
ArrayList的申明
命名空间:using System.Collections;
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
ArrayList的增删查改
增
- 增加一个 Add
list.Add(1);
list.Add("hello");
list.Add(true);
list.Add(new object());
- 两个ArrayList拼接 AddRange
ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList();
list.AddRange(list2);
- 插入一个元素 Insert
只能在ArrayList的中间或者末尾插入,如果一个ArrayList的长度为1,执行Insert操作传入的位置是2,则会报错。
例如:list.Insert(0, 1);表示在第一个元素的后面插入1
// 在第4个位置插入元素1
list.Insert(3, 1);
- 插入一组元素 InsertRange
ArrayList list3 = new ArrayList();
list3[0] = "a";
list.InsertRange(1, list3);
删
- 移除指定元素 Remove
原理:从头开始找,找到第一个符合的元素,删掉,然后把后面的元素往前挪。如果找不到元素就不会有任何效果。
如果list中有两个1,只会移除掉第一个1
list.Remove(1);
- 移除指定位置的元素 RemoveAt
如果list中找不到指定的位置,会报错。
// 删除第一个位置的元素
list.RemoveAt(0);
- 清空 Clear
list.Clear();
查
- 得到指定位置的元素
var item = list[1];
- 查看元素是否存在 Contains
```csharp
bool exist = list.Contains(1);
- 正向查找元素位置,返回的值是第一个符合条件的元素的位置。-1表示没有找到元素 indexOf
int index = list.indexOf(1);
- 反向查找元素位置,返回的值是从后面开始第一个符合元素的位置(位置是从头计数的),-1表示没有找到元素 LastIndexOf
int index = list.LastIndexOf(1);
改
list[0] = 111;
如果list中只有一个元素,只能修改第一个元素,如果执行list[1] = XXX,则会报错。
遍历
- for遍历
for(int i = 0; i < list.Count; i ++)
{
}
- foreach遍历
foreach(var item in list)
{
}
装箱拆箱
由于ArrayList装载object,当往ArrayList中存值类型时,是在装箱(将值类型转化为引用类型,将栈上的元素转到堆上),当将值类型从ArrayList中取出时,是在拆箱(将引用类型转化为值类型,将堆上的元素转到栈上)。
Stack 栈
Stack的本质
Stack,栈存储容器,是一个C#为我们封装好的类,它的本质也是object[]数组,只是封装了特殊的存储规则。
Stack是一种先进后出的数据结构,先存入的数据后获取,后存入的数据先获取。
Stack的申明
命名空间:System.Collections;
Stack s = new Stack();
增取查改
增 压栈 push
s.Push(object);
取 弹栈 Pop
// 栈遵循先进后出的原则,执行Pop即栈顶开始取,取出的数据自动从栈中删除,当栈中没有元素了,执行Pop操作,会报错
object o = s.Pop();
查
栈是不能查看指定位置的元素,只能查看栈顶的元素。
查看栈顶元素,但是不会删除 Peek
object o = s.Peek();
查看元素是否在栈中 Contains
if(s.Contains(object))
{
}
改
栈无法改变其中的元素,只能压栈和弹栈,如果实在要改,只能清空 (Clear)栈。
遍历
长度 Count
int len = s.Count;
foreach遍历
// 从栈顶开始
foreach(object item in s)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
将Stack转化为数据 再遍历 ToArray
object[] ary = s.ToArray();
for(int i = 0; i < ary.Length; i ++)
{
Console.WriteLine(ary[i]);
}
循环弹栈 while + Pop
while(s.Count > 0)
{
object o = s.Pop();
Console.WriteLine(o);
}
在这里插入代码片
装箱拆箱
由于Stack装载object,所以也存在装箱拆箱的问题。
Queue 队列
Queue的本质
Queue,队列容器,是一个C#为我们封装好的类,它的本质也是object[]数组,只是封装了特殊的存储规则。
Queue是一种先进先出的数据结构,先存入的数据先取出,后存入的数据后取出。
Queue的申明
命名空间:System.Collections;
Queue q = new Queue();
增取查改
增 Enqueue
q.Enqueue(object);
取 Dequeue
// 队列遵循先进先出的原则,执行Dequeue即从头开始取,取出的数据自动从队列中删除,当队列中没有元素了,执行Dequeue操作,会报错
q.Dequeue(object);
查
队列是不能查看指定位置的元素,只能查看列队头部的元素。
查看队列头部元素,但不会删除 Peek
object o = q.Peek();
查看元素是否存在于队列中 Contains
if(q.Contains(object))
{
}
改
队列无法改变其中的元素,只能进出队列,如果实在要改,只有清空(Clear)队列。不能使用[]来访问元素
遍历
长度 Count
int len = q.Count;
foreach遍历
// 从队列第一个开始
foreach(object item in q)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
将Queue转化为数据 再遍历 ToArray
object[] ary = q.ToArray();
for(int i = 0; i < ary.Length; i ++)
{
Console.WriteLine(ary[i]);
}
循环出列 while + Dequeue
while(q.Count > 0)
{
object o = q.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine(o);
}
装箱拆箱
由于Queue装载object,所以也存在装箱拆箱的问题。
Hashtable
Hashtable的本质
Hashtable(又称散列表),是基于键的哈希代码组织起来的键值对。它主要作用是提高数据查询的效率,主要使用键来访问表中的元素。
Hashtable的键值都是object类型,即Hashtable可以包含所有类型的元素。
Hashtable的申明
Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable();
Hashtable的增删查改
增 Add
hashtable.Add(1, "ABC");
hashtable.Add("ABC", 1);
注意:使用Add添加元素时,不能重复出现相同的键
删 Remove
只能通过Remove来删除
删除不存在的键,没反应
hashtable.Remove(1);
hashtable.Remove(2);
清空 Clear
hashtable.Clear();
查
通过键查看值
通过键查看值,找不到返回null
判断是否存在
- 通过键判断 Contains或者ContainsKey
if (hashtable.Contains(1))
{
Console.WriteLine("存在键为1的键值对");
}
- 通过值判断 ContainsValue
if (hashtable.ContainsValue("ABC"))
{
Console.WriteLine("存在值为ABC的键值对");
}
改
只能改键对应的值内容,无法修改键
没有该键则为新增,有该键则为修改
hashtable["ABC"] = 100;
Hashtable的遍历
遍历所有键
foreach (object key in hashtable.Keys)
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0}={1}", key, hashtable[key]));
}
遍历所有值
foreach (object value in hashtable.Values)
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
键值对一起遍历
foreach (DictionaryEntry item in hashtable)
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0}={1}", item.Key, item.Value));
}
迭代器遍历法
IDictionaryEnumerator enumerator = hashtable.GetEnumerator();
while (enumerator.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0}={1}", enumerator.Key, enumerator.Value));
}
装箱拆箱
由于Hashtable是使用object来储存数据,自然存在装箱拆箱操作。当在存值时,装箱,取值时拆箱。
泛型
泛型
什么是泛型
泛型实现了类型参数化,达到代码重用的目的。通过类型参数化来实现一份代码上操作多种类型。
泛型相当于类型占位符,定义类或者方法时使用替代符代表变量类型,当真正使用类或者方法时再具体指定类型。
泛型的分类
- 泛型类和泛型接口
基本语法:
class 类名<泛型占位符>
interface 接口名<泛型占位符> - 泛型函数
基本语法:函数名<泛型占位符>(参数列表)
泛型占位符可以有多个,使用逗号隔开。
泛型类和接口
- 泛型类
class TClass<T, M>
{
public T t;
public M m;
}
// 使用时指定泛型占位符所表示的类型
TClass<int, string> tc = new TClass<int, string>();
tc.t = 100;
tc.m = "Hello";
- 泛型接口
interface TInterface<T>
{
T t
{
get;
set;
}
}
// 实现接口时需要指定泛型占位符代表的类型
class TInterfaceClass : TInterface<int>
{
public int t
{
get;
set;
}
}
泛型方法
普通类中的泛型方法
class TestClass
{
// 方法的参数使用泛型
public void TestFunc<T>(T p)
{
Console.WriteLine(p);
}
// 泛型不作为方法的参数,用于方法的逻辑中
public void TestFunc<T>()
{
T t = default(T);
// 逻辑
}
// 泛型作为方法的返回值
public T TestFunc1<T>()
{
return default(T);
}
}
泛型类中的泛型方法
class TClass<T>
{
// 这个不是泛型方法,因为这是定义泛型类时就定义好的,只能传入实例化TClass时指定的类型作为参数
public void Func(T t)
{
}
// 这个是泛型方法,可以接受任何类型的参数
public void Func<K>(K k)
{
}
}
TClass<int> tc = new TClass<int>();
// 这里只能传入int类型的参数
tc.Func(10);
// 泛型方法可以传入任何类型的参数
tc.Func<string>("Hello");
泛型的作用
- 不同类型对象的相同逻辑处理就可以选择泛型
- 使用泛型可以一定程度避免装箱拆箱
泛型约束
什么是泛型约束
泛型约束就是限制泛型占位符所表示的数据类型
关键字是where
各种泛型约束
泛型约束总共有6种:
- 值类型:where 泛型占位符:struct
class TClass<T> where T:struct
{
}
- 引用类型:where 泛型占位符:class
class TClass<T> where T:class
{
}
- 存在公共无参构造函数的非抽象类型:where 泛型占位符:new()
class TClass<T> where T:new()
{
}
- 某个类本身或者其他派生类:where 泛型占位符:类名
class BaseClass
{
}
class CustomClass:BaseClass
{
}
class TClass<T> where T:BaseClass
{
}
TClass<BaseClass> tc = new TClass<BaseClass>();
TClass<CustomClass> tc1 = new TClass<CustomClass>();
- 某个接口的派生类型:where 泛型占位符:接口名
interface TestInterface
{
}
interface CustomInterface : TestInterface
{
}
class CustomClass : CustomInterface
{
}
class TClass<T> where T:TestInterface
{
}
TClass<CustomClass> tc = new TClass<CustomClass>();
TClass<CustomInterface> tc1 = new TClass<CustomInterface>();
TClass<TestInterface> tc2 = new TClass<TestInterface>();
- 另一个泛型类型本身或者派生类型:where 泛型占位符:另一个泛型字母
class BaseClass
{
}
class CustomClass : BaseClass
{
}
// T与K是同一种类型或者T是K的派生类型
class TestClass<T, K> where T:K
{
}
TestClass<CustomClass, BaseClass> tc = new TestClass<CustomClass, BaseClass>();
泛型约束的组合使用
约束之间可以组合起来一起使用,各个约束之间使用都好隔开
// 约束T是引用类型且有公共的无参构造函数
class TestClass<T> where T:class, new()
{
}
多个泛型有约束
where关键字并列写
// 约束T是引用类型且有公共的无参构造函数 约束K是值类型
class TestClass<T, K> where T:class, new() where K:struct
{
}
常用泛型数据结构类
List
List的本质 对应ArrayList
List是C#为我们封装好的类,它的本质是一个可变类型的泛型数组,List类帮助我们实现了很多方法,比如泛型数组的增删查改
List的申明
命名空间:System.Collections.Generic
List<int> list = new List<int>();
List<string> list1 = new List<string>();
增删查改
增
增加一个元素 Add
list.Add(1);
list.Add(2);
拼接两个List
List<int> list2 = new List<int>();
list2.Add(100);
list2.Add(200);
遍历
Dictionary
Dictionary的本质
可以将Dictionary理解为拥有泛型的Hashtable。它也是基于键的哈希代码组织起来的键值对。键值对类型从Hashtable的object变为了可以自己定义的泛型。
Dictionary的申明
Dictionary<int, string> dict = new Dictionary<int, string>();
Dictionary的增删查改
增 Add
注意:使用Add添加元素时,不能重复出现相同的键
// 键不能有相同的,值可以有相同的
dict.Add(1, "ABC");
dict.Add(10, "ABC");
dict.Add(100, "ABCD");
删 Remove
只能通过键来删除
删除不存在的键,没反应
dict.Remove(1);
dict.Remove(99);
清空 Clear
dict.Clear();
查
通过键查
通过键查看值,找不到直接报错(与Hashtable不同)
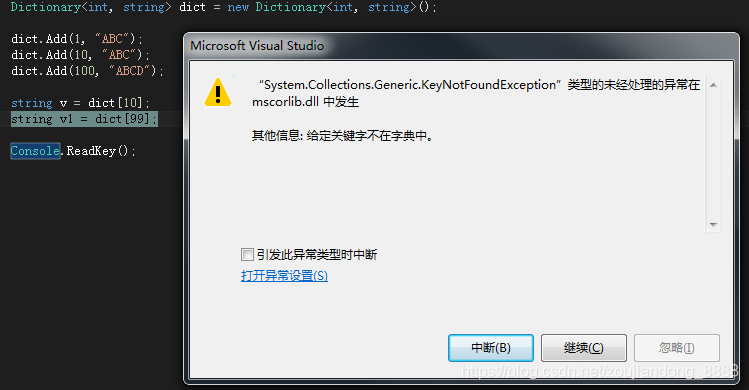
可以通过TryGetValue方法,来避免报错。
string v;
if (dict.TryGetValue(10, out v))
{
Console.WriteLine("存在键为10的键值对");
}
判断是否存在
- 通过键判断 ConainsKey
if (dict.ContainsKey(99))
{
Console.WriteLine("存在键为99的键值对");
}
- 通过值判断 ContainsValue
if (dict.ContainsValue("ABC"))
{
Console.WriteLine("存在值为ABC的键值对");
}
改
通过键来修改,没有该键则为新增,有该键则为修改
dict[99] = "Hello";
Dictionary的遍历
遍历所有键
foreach (int key in dict.Keys)
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0}={1}", key, dict[key]));
}
遍历所有值
foreach (string value in dict.Values)
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
键值一起遍历
foreach (KeyValuePair<int, string> item in dict)
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0}={1}", item.Key, item.Value));
}
迭代器遍历法
Dictionary<int, string>.Enumerator dictEnumerator = dict.GetEnumerator();
while (dictEnumerator.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0}={1}", dictEnumerator.Current.Key, dictEnumerator.Current.Value));
}
顺序存储与链式存储
Linedlist
委托和事件
委托
事件
什么是事件
事件是基于委托的存在,事件是委托的安全包裹,让委托的使用更具安全性,事件也是一种特殊的变量类型
事件的使用
语法:访问修饰符 event 委托类型 事件名
事件的使用方法跟委托基本一样,主要有以下几个区别:
- 事件只能作为类、接口、结构体的成员变量,不能在方法中定义为局部变量;委托可以
- 事件在类外部不能使用=赋值。 = null、= 方法都不行。但是可以使用+=、-=复合运算符;委托在类内部和外部的是方式没有区别
- 不能在类外部调用事件;委托在任何地方都可以调用。
class TestClass
{
public Action myDelegate;
public event Action myEvent;
public TestClass()
{
// 委托
myDelegate += MyFunc;
myDelegate += MyFunc1;
// 执行委托
myDelegate();
//myDelegate.Invoke();
// 清空委托
myDelegate = null;
// 事件
myEvent += MyFunc;
myEvent += MyFunc1;
// 执行事件
myEvent();
//myEvent.Invoke();
// 清空事件
myEvent = null;
}
private void MyFunc()
{
Console.WriteLine("MyFunc");
}
private void MyFunc1()
{
Console.WriteLine("MyFunc1");
}
}
// 类的外部委托和事件的区别
class TestClass1
{
public TestClass1()
{
TestClass tc = new TestClass();
// 正确!委托可以在类外部调用
tc.myDelegate();
// 正确!委托可以在类外部使用+=、-=等复合运算符
tc.myDelegate += MyFunc;
// 正确!委托可以在类外部使用赋值运算符
tc.myDelegate = null;
// 错误!事件不能在类外部调用
tc.myEvent();
// 正确!事件可以在类外部使用+=、-=等复合运算符
tc.myEvent += MyFunc;
// 错误!事件在类外部不能使用赋值运算符,虽然等价于tc.myEvent += MyFunc
tc.myEvent = tc.myEvent + MyFunc;
// 错误!事件在类外部能使用赋值运算符
tc.myEvent = null;
}
private void MyFunc()
{
}
}
为什么有事件
- 防止外部随意置空委托
- 防止外部随意调用委托
- 事件相当于对委托进行了一次封装,让其更加安全
匿名函数
什么是匿名函数
没有名字的函数叫匿名函数,匿名函数主要是配合委托和事件进行使用,脱离委托和事件,是不会使用匿名函数的。
基本语法
delegate(参数列表)
{
// 函数逻辑
};
在定义匿名函数的时候,必须使用委托变量来承接,不能直接定义,否则会报错。
// 正确写法
Action act = delegate(){
Console.WriteLine("Hello");
};
// 错误写法
delegate(){
Console.WriteLine("Hello");
};
无参无返回值的匿名函数
Action act = delegate() {
Console.WriteLine("Hello");
};
有参数无返回值的匿名函数
Action<string, int> act1 = delegate(string name, int age)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{name}的年龄为{age}");
};
无参有返回值的匿名函数
Func<int> rt = delegate()
{
return 100;
};
有参有返回值的匿名函数
// 两个参数,一个返回值
Func<int, int, int> sum = delegate(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
};
匿名函数使用场景
- 当作函数的参数传递
- 作为函数返回值
class UnnameFuncTest
{
// 当作函数的参数传递
public void DoFunc(Action func)
{
func?.Invoke();
}
// 作为函数返回值
public Action GetFunc()
{
return delegate ()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello!");
};
}
}
匿名函数的缺点
因为匿名函数没有名字,当一个委托中存有多个匿名函数,如果这些匿名函数没有被记录,无法从委托中删除指定的匿名函数。
Action act = null;
Action act1 = delegate()
{
Console.WriteLine("Action1");
};
Action act2 = delegate()
{
Console.WriteLine("Action2");
};
Action act3 = delegate()
{
Console.WriteLine("Action3");
};
act += act1;
act += act2;
act += act3;
act.Invoke();
Console.WriteLine("-------------------------");
// 只有匿名函数有被记录的情况下,才可以从委托中指定删除
act -= act2;
act.Invoke();
Lambad表达式
什么是Lambad表达式
可以将lambad表达式理解为匿名函数的简写,除了语法不同,使用上和匿名函数一模一样,都是和委托和事件配合使用的
Lambad表达式的语法
(参数列表) => {
// 函数逻辑
};
*lambad表达式的使用与匿名函数相同
闭包
内层的匿名(闭包)函数可以引用包含它外层的函数的变量,即使外层函数执行已经终止。该变量提供的值并非变量创建时的值,而是在父函数范围内的最终值。
class ClosedFuncTest
{
private event Action func;
public ClosedFuncTest()
{
int index = 10;
// 正常情况下,index变量在执行完ClosedFuncTest的构造函数后会被回收,由于index变量被一个匿名函数包裹,在该匿名函数没有被销毁之前,index也不会销毁
func = () =>
{
Console.WriteLine(index);
};
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++)
{
// 当执行func时,输出的i的值为10个10,而不是从0-9
// 因为for循环中,i变量是变化的,当执行完for循环时,i的最终值为10
func += () => {
Console.WriteLine(i);
};
// 要想打印出0-9,可以这样处理。执行for循环会创建10个ii变量,交给闭包函数,每个ii变量是不同的。
int ii = i;
func += () => {
Console.WriteLine(ii);
};
}
}
public void ExecuteAction()
{
func();
}
}
ClosedFuncTest closedFuncTest = new ClosedFuncTest();
closedFuncTest.ExecuteAction();
List排序
List自带排序方法
使用List自带的Sort()方法,可以对int、float、double等List进行升序排序
List<int> list = new List<int>();
list.Add(1);
list.Add(100);
list.Add(-20);
list.Add(50);
// -20、1、50、100
list.Sort();
对自定义类的排序
如果List中的元素是自定义的类型,则不能直接使用Sort()方法进行排序,否则会报错。
之所以对于int这些List可以直接使用Sort进行排序,是因为int等这些结构体都实现了IComparable、IComparable接口,这些接口中的CompareTo方法实现了排序规则。因此,想要使用Sort()方法直接进行排序,只需将自定义类也实现这两个接口中的一个或多个,重写CompareTo方法即可。
class Item : IComparable<Item>
{
public int count;
public Item(int count)
{
this.count = count;
}
// 实现排序逻辑,返回-1排在前面,返回0位置不变,返回1排在后面。这里的逻辑实现的是升序排序。
public int CompareTo(Item other)
{
return this.count > other.count ? 1 : -1;
}
}
List<Item> list = new List<Item>();
list.Add(new Item(1));
list.Add(new Item(99));
list.Add(new Item(100));
list.Add(new Item(20));
list.Add(new Item(50));
// 升序排序
list.Sort();
通过委托进行排序
对于盛放自定义类的List,除了对自定义类实现IComparable接口外,还可以调用List的Sort重载,传入一个比较函数。
public void Sort(Comparison<T> comparison);
Comparison是一个两个参数一个返回值的委托:
public delegate int Comparison<in T>(T x, T y);
class Item
{
public int count;
public Item(int count)
{
this.count = count;
}
}
List<Item> list = new List<Item>();
list.Add(new Item(1));
list.Add(new Item(99));
list.Add(new Item(100));
list.Add(new Item(20));
list.Add(new Item(50));
// 匿名函数方式
list.Sort(delegate(Item a, Item b)
{
return a.count > b.count ? 1 : -1;
});
// Lambad表达式的方式
//list.Sort((a, b) => a.count > b.count ? 1 : -1);
协变逆变
什么是协变逆变
- 协变
协变:和谐的变化,自然的变化,因为里氏替换原则,父类可以装子类,所以子类变父类比如string变成object,感觉是和谐的。 - 逆变
逆常规的变化,不正常的变化。因为里氏替换原则,父类可以装子类,但是子类不能装父类,所以父类变为子类比如object变为string,感受是不和谐的。
协变和逆变是用来修饰泛型委托和泛型接口的,协变使用out关键字修饰泛型字符,逆变使用in关键字修饰泛型字符。
协变逆变的应用
规范泛型字母的作用
- 使用out修饰的泛型只能用作返回值
delegate T TestDelegateOut<out T>();
// !!!!!!错误
// delegate T TestDelegateIn<out T>(T t);
interface TestInterfaceOut<out T>
{
void T TestFunc();
// !!!!!!错误 T被out修饰,不能作为参数
// void T TestFunc(T t);
}
- 使用in修饰的泛型只能用作参数
delegate void TestDelegateIn<in T>(T t);
// !!!!!!错误
// delegate T TestDelegateIn<in T>(T t);
interface TestInterfaceIn<in T>
{
void TestFunc(T t);
// 错误,T被in修饰,不能作为返回值
// T TestFunc(T t);
}
父类、子类委托的承接
class Father
{
}
class Son : Father
{
}
// 协变
TestDelegateOut<Son> son = () =>
{
return new Son();
};
// 协变 父类委托承接子类委托(把子类当父类用)
TestDelegateOut<Father> father = son;
// 逆变 子类委托承接父类委托(把父类当子类用)
TestDelegateIn<Father> father1 = (Father f) =>
{
};
TestDelegateIn<Son> son1 = father1;
多线程
预处理器指令
反射和特性
反射
什么是程序集
程序集就是我们写的代码的一个集合,我们所写的所有代码最终都会被编译器翻译为一个程序集供别人使用。比如一个代码库文件(.dll)或者一个可执行文件(.exe)
元数据
程序中的类、类中的变量、属性、方法等信息就是程序的元数据。元数据保存在程序集中。
反射的概念
在程序运行时,通过反射可以得到其他程序集或者自己的程序集代码中的元数据,可以实例化他们、执行他们或者操作他们。
反射的作用
因为反射可以在程序编译后获得元数据信息,所以它提高了程序的拓展性和灵活性
- 在程序运行时可以获得所有的元数据,包括元数据的特性
- 程序运行时可以通过反射实例化对象、操作对象
- 程序运行时可以通过反射创建新对象,用这些对象执行任务
语法相关
Type
什么是Type
Type:表示类的信息类,它是反射功能的基础,是访问元数据的主要方式。使用Type的成员可以获取对应类型声明的信息,如构造函数、变量、属性、方法、事件等。
获取Type
// 方式1 通过对象的GetType方法获取Type 所有的对象都有GetType方法
int a = 100;
Type type = a.GetType();
// 方式2 通过typeof(类)方法获取Type
Type type2 = typeof(int);
// 方式3 通过Type.GetType(类名)的方式获取Type 注意需要带命名空间
Type type3 = Type.GetType("System.Int32");
通过这三种方式获取的同一个类型的Type指向的是同一个堆内存(即每一种类型的Type是唯一的)
通过Type获取元数据
通过Type获取类的程序集信息(Assembly) [type.Assembly]
int a = 100;
Type type = a.GetType();
Assembly assembly = type.Assembly;
通过Type获取类中所有的公共成员(MemberInfo) [type.GetMembers()]
public class ReflectionTestClass
{
private int i = 100;
public string j = "sss";
public ReflectionTestClass()
{
}
public ReflectionTestClass(int i)
{
this.i = i;
}
public ReflectionTestClass(int i, string j) : this(i)
{
this.j = j;
}
public void Speek()
{
Debug.Log("Speek");
}
public void Speek(string content)
{
Debug.Log($"Speek {content}");
}
}
// 获取ReflectionTestClass类的所有公共成员
Type type = typeof(ReflectionTestClass);
MemberInfo[] memberinfoList = type.GetMembers();
for(int i = 0; i < memberinfoList.Length; i ++)
{
Debug.Log(memberinfoList[i]);
}
通过Type获取类的所有构造函数(ConstructorInfo) [type.GetConstructors()]
Type type = typeof(RefrectionTestClass);
ConstructorInfo[] constructorList = type.GetConstructor();
通过Type获取类的其中一个构造函数并执行(ConstructorInfo)[type.GetConstructor(param)]
获取构造函数需要传入Type数组,数组中的内容是要获取的构造函数各个参数对应的类型
执行构造函数需要传入Object数组,数组中的内容是对应构造函数的各个参数值
// 获取ReflectionTestClass的无参构造函数
Type type = typeof(ReflectionTestClass);
ConstructorInfo constructor = type.GetConstructor(new Type[0]);
// 获取ReflectionTestClass的带一个参数的构造函数
ConstructorInfo constructor2 = type.GetConstructor(new Type[] { typeof(int) });
// 获取ReflectionTestClass的带两个参数的构造函数
ConstructorInfo constructor3 = type.GetConstructor(new Type[] { typeof(int), typeof(string) });
// 执行ReflectionTestClass的无参构造函数
ReflectionTestClass r = constructor.Invoke(null) as ReflectionTestClass;
// 执行ReflectionTestClass的带一个参数的构造函数
ReflectionTestClass r2 = constructor2.Invoke(new object[] { 1000 }) as ReflectionTestClass;
// 执行ReflectionTestClass的带两个参数的构造函数
ReflectionTestClass r3 = constructor3.Invoke(new object[] { 10000, "aaa" }) as ReflectionTestClass;
通过Type获取类中的公共成员变量
通过Type获取类中所有的公共成员变量(FieldInfo)[type.GetFields()]
Type type = typeof(ReflectionTestClass);
FieldInfo[] fieldList = type.GetFields();
通过Type获取指定名称的公共成员变量(FieldInfo)[type.GetField(变量名)]
Type type = typeof(ReflectionTestClass);
FieldInfo info = type.GetField("j");
通过Type获取类对象指定名称的公共成员变量并设置它的值
Type type = typeof(ReflectionTestClass);
FieldInfo info = type.GetField("j");
ReflectionTestClass cls = new ReflectionTestClass(1, "x");
// 获取属性值
string value = info.GetValue(cls) as string// value='x'
// 设置属性值
info.SetValue(cls, "w");// 设置为cls的j="w"
通过Type获取类的公共的成员方法
通过Type获取类的所有的公共成员方法(MethodInfo)[type.GetMethods()]
Type type = typeof(ReflectionTestClass);
MethodInfo[] methodList = type.GetMethods();
通过Type获取类的指定的公共成员方法(MethodInfo)[type.GetMethod(方法名, params)]
params需要对应方法的各个参数的类型
Type type = typeof(ReflectionTestClass);
// 获取不带参数的
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Speek", new Type[0]);
// 获取带一个参数的
MethodInfo method2 = type.GetMethod("Speek", new Type[] { typeof(string) });
通过Type获取类对象指定的公共成员方法并执行(MethodInfo][Invoke]
ReflectionTestClass cls = new ReflectionTestClass(1, "x");
Type type = typeof(ReflectionTestClass);
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Speek", new Type[0]);
MethodInfo method2 = type.GetMethod("Speek", new Type[] { typeof(string) });
// 执行不带参数的
method.Invoke(cls, null);
// 执行带一个参数的
method2.Invoke(cls, new object[] { "hello world" });
如果是静态方法,Invoke的第一个参数填null即可
其他
通过Type获取枚举(string) GetEnumNames GetEnumName
通过Type获取事件(EventInfo) GetEvents GetEvent
通过Type获取接口(Type) GetInterfaces GetInterface
通过Type获取属性(PropertyInfo) GetProperties GetProperty
Assembly
什么是Assembly
主要用来加载其他程序集,加载后,才能使用Type来获取其他程序集中的元信息。
加载Assembly
- 加载同一文件夹下的其他程序集
Assembly.Load(“程序集名称”) - 加载不同文件夹下的其他程序集
Assembly.LoadFrom(“程序集完全路径”)
或
Assembly.LoadFile(“程序集完全路径”)
通过Assembly获取所有Type
Assembly对象.GetTypes()
通过Assembly获取指定Type
Assembly对象.GetType(“包含命名空间的类型名”)
Activator
Activator的作用
用于将Type对象快捷实例化为对象
通过Activator创建类对象
无参构造 Activator.CreateInstance(Type)
Type type = typeof(ReflectionTestClass);
ReflectionTestClass cls = Activator.CreateInstance(type) as ReflectionTestClass;
有参构造 Activator.CreateInstance(Type, 可变长度参数)
Type type = typeof(ReflectionTestClass);
ReflectionTestClass cls = Activator.CreateInstance(type, 10, "hello") as ReflectionTestClass;
总结
通过Assembly可获取Type,Activator可创建Type类型的实例对象,Type可获取类型的所有公共成员并执行实例对象的公共方法
特性
什么是特性
特性是一种允许我们向程序的程序集添加元数据的语言结构,它用于保存程序结构信息的某种特殊类型的类。
特性提供功能强大的方法以将声明信息与C#代码(类型、方法、属性、变量)相关联。特性与程序实体关联后,即可在运行时使用反射查询特性信息。
特性的目的是告诉编译器把程序的某组元数据嵌入程序集中,它可以放置在几乎所有的声明中
通俗地说,特性的本质是一个类,我们可以利用特性类为元数据添加额外的信息。
比如为一个类、成员变量、成员方法、属性添加更多的额外信息。
之后可以通过反射来获取这些额外的信息。
自定义特性
所有的特性类都继承自Attribute类,类名以Attribute结尾,类中的内容根据具体需求来写。例如,下面写一个简单的描述自定义类信息的特性:
class DefineInfoAttribute : Attribute
{
private string info;
public DefineInfoAttribute(string info = "")
{
this.info = info;
}
public string GetInfo()
{
return info;
}
}
特性的使用
基本语法
[特性名(构造函数参数列表)],写在类、方法、变量、属性的上一行,参数的左边,表示他们具有该特性。特性名省略Attrbute字样。
本质上就是在调用特性类的构造函数。
使用定义个特性来修饰自定义类
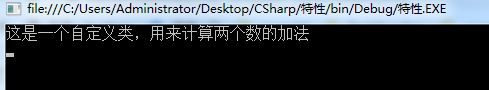
[DefineInfo("这是一个自定义类,用来计算两个数的加法")]
class CustomClass
{
[DefineInfo("两个数相加的结果")]
public float result;
[DefineInfo("计算两个数相加的方法")]
public void Sum([DefineInfo("第一个数")]float a, [DefineInfo("第二个数")]float b)
{
result = a + b;
}
}
判断一个类是否被某个特性修饰 Type.IsDefined
CustomClass cls = new CustomClass();
Type clsType = cls.GetType();
// 第二个参数表示是否检查其父类
if (clsType.IsDefined(typeof(DefineInfoAttribute), false))
{
Console.WriteLine("类CustomClass被DefineInfoAttribute特性修饰");
}
获取一个类的所有特性 Type.GetCustomAttributes
CustomClass cls = new CustomClass();
Type clsType = cls.GetType();
if (clsType.IsDefined(typeof(DefineInfoAttribute), false))
{
Console.WriteLine("类CustomClass被DefineInfoAttribute特性修饰");
}
// 参数表示是否检查其父类
object[] allAttribute = clsType.GetCustomAttributes(true);
foreach (var item in allAttribute)
{
if (item is DefineInfoAttribute)
{
Console.WriteLine((item as DefineInfoAttribute).GetInfo());
}
}
同样的,除了类,属性、方法、变量也都可以获取到修饰他们的特性类,同样的调用其GetCustomAttributes方法即可获得。
限制自定义特性的使用范围 AttributeUsage
使用AttributeUsage特性来修饰特性,可以限制自定义特性的使用范围。Attributeusage也是一个特性。
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Struct, AllowMultiple = true, Inherited = true)]
参数一:AttributeTargets【AttributeTargets】 特性能够用在什么地方
参数二:AllowMultiple【bool】 一个目标是否可以使用多个该特性修饰
参数三:Inherited 【bool】特性是否能被派生类重写或者成员继承
// 该特性只能修饰类或者结构体,一个目标可以使用该特性进行多次修饰,且可以继承
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Struct, AllowMultiple = true, Inherited = true)]
class DefineInfoAttribute : Attribute
{
private string info;
public DefineInfoAttribute(string info = "")
{
this.info = info;
}
public string GetInfo()
{
return info;
}
}
系统自带特性
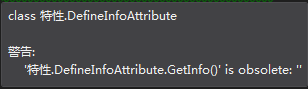
过时特性 Obsolete
用于提示用户,使用的方法或者成员已经过时,建议使用新方法。
// 第一个参数用于显示调用该过时方法时提示的内容,第二个参数为false是,调用该过时方法时仅仅是警告,如果为true,调用该过时方法时会报错
[Obsolete("调用该过时方法时提示的内容", false)]
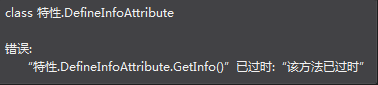
调用者信息特性 CallerFilePath、CallerLineNumber、CallerMemberName
提示函数被哪个文件[CallerFilePath]、哪一行的代码[[CallerLineNumber]]、哪个函数[[CallerMemberName]]调用
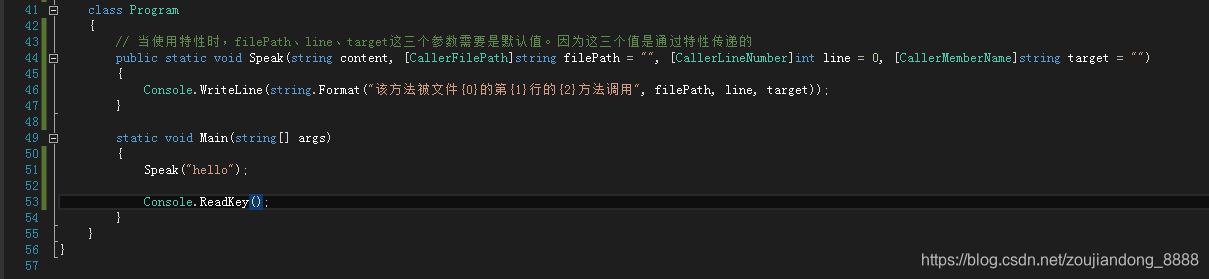
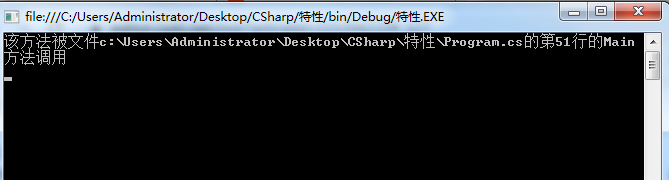
// 当使用特性时,filePath、line、target这三个参数填默认值即可。因为这三个值通过特性可以传递
public void Speak(string content, [CallerFilePath]string filePath = "", [CallerLineNumber]int line = 0, [CallerMemberName]string target = "")
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("该方法被文件{0}的第{1}行的{2}方法调用", filePath, line, target));
}
当在外部调用该方法时
条件编译特性 Conditional
它会和预处理器指令#define配合使用,主要可以用在一些调试代码上,有时想执行,有时不想执行的情况。
[Conditional("UNITY_EDITOR")]
public static void Func()
{
Console.WriteLine("function Func");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Func();
Console.ReadKey();
}
当没有定义UNITY_EDITOR宏,就算是执行了Func方法也不会打印function Func
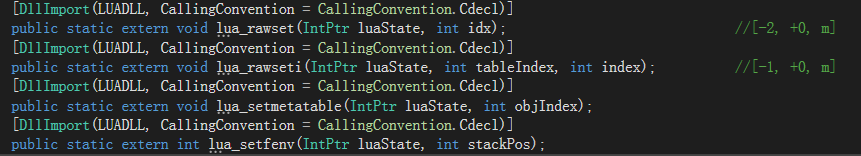
外部Dll包函数特性 DllImport
用来标记非.Net的函数,表明该函数在一个外部的Dll中定义。
一般用来调用C或者C++ Dll包写好的方法
需要使用static extern来修饰该方法。
// 把Test.dll中的Add方法引入到C#代码中,以达到可以在C#中调用非C#语言包中的方法。
[DllImport("Test.dll")]
public static extern int Add(int a, int b);
例如,在ToLua框架中,C#调用C包装中的方法:
迭代器
迭代器是什么
迭代器iterator有时又被称为光标cursor;是程序设计的软件设计模式,迭代器模式提供一个方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中的各个元素,而又不暴露其内部标识。
从表现效果上看,是可以在容器对象(例如链表或者数组)上遍历访问接口,设计人员无需关心容器对象的内存分布的实现细节。
可以用foreach遍历的类,都是实现了迭代器的。
标准迭代器的实现方法
关键接口:IEnumerable、IEnumerator
命名空间:using System.Collections;
可以用过同时实现IEnumerable和IEnumerator这两个接口来实现标准迭代器。
class CustomList : IEnumerable, IEnumerator
{
private int[] list;
private int index = -1;
public CustomList(params int[] initlist)
{
list = initlist;
}
#region IEnumerable 如果写了这个方法,但是不继承IEnumerable,也是可以的
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
// 在这里重置index到初始位置
Reset();
return this;
}
#endregion
#region IEnumerator
public object Current
{
get
{
return list[index];
}
}
// 循环是否继续
public bool MoveNext()
{
return ++index < list.Length;
}
// 重置光标位置 一般在GetEnumerator方法中调用
public void Reset()
{
index = -1;
}
#endregion
}
CustomList list = new CustomList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9);
// foreach的本质:
// 先通过GetEnumerator方法获取in后面这个对象的IEnumerator(获取一次)
// 每次foreach,执行得到这个IEnumerator对象中的MoveNext方法
// 只要MoveNext方法返回值为true,表示还有元素可以访问,就会去得到Current,然后赋值给item
foreach(int item in list)
{
Console.WriteLine(item.ToString());
}
用yield return语法糖实现迭代器
yield return是C#提供给我们的语法糖,所谓语法糖也称糖衣语法,主要作用是将复杂逻辑简单化,可以增加程序的可读性,从而减少程序代码出错的机会。
关键接口IEnumerable
命名空间:using System.Collections;
让想要通过foreach遍历自定义类实现接口中的方法GetEnumerator即可。
class CustomList1 : IEnumerable
{
private int[] list;
public CustomList1(params int[] initlist)
{
list = initlist;
}
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
foreach(int item in list)
{
// yield关键字配合迭代器使用,可以理解为暂时返回,保留当前的状态,外部的每次foreach执行一次yield return
yield return item;
}
}
}
CustomList1 list1 = new CustomList1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9);
// 每次foreach的in操作执行一次yield return,从而能将当前的光标对应的值赋值给item
foreach(int item in list1)
{
Console.WriteLine(item.ToString());
}
用yield return语法糖为泛型类实现迭代器
class CustomList2<T> : IEnumerable
{
private T[] list;
public CustomList2(params T[] initlist)
{
list = initlist;
}
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
foreach(T item in list)
{
yield return item;
}
}
}
CustomList2<int> list2 = new CustomList2<int>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9);
foreach(int item in list2)
{
Console.WriteLine(item.ToString());
}
特殊语法
var隐式类型
var是一种特殊的变量类型,它可以用来表示任意类型的变量。
注意:
- var不能作为类成员,只能用于临时变量申明,也就是一般写在函数语句块中
- var必须初始化
- 使用var申明的变量类型在初始化后,其类型就确定了,后面不能被更改
设置对象初始值
申明对象时,可以通过直接写大括号的形式初始化对象部分或者全部公共变量和属性
class Person
{
private int id;
public Person()
{
}
public Person(int id)
{
this.id = id;
}
public string Name;
public int Age
{
get;
set;
}
}
// 初始化所有的公共成员
Person person = new Person(1) { Name = "小明", Age = 20 };
// 初始化部分的公共成员
Person person1 = new Person(2) { Name = "小红" };
// 如果通过不带参数的构造函数实例化对象,对象类型后可以不用加括号 Person person2 = new Person() { Name = "小李", Age = 22 };
Person person2 = new Person { Name = "小李", Age = 22 };
设置集合初始值
申明集合时,也可以通过大括号直接初始化
int[] ary = new int[]{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
// 括号可以省略 List<int> list = new List<int>{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
List<int> list = new List<int>(){ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
// 括号可以省略 Dictionary<int, string> dict = new Dictionary<int, string> { { 1, "1" }, { 2, "2" } };
Dictionary<int, string> dict = new Dictionary<int, string>() { { 1, "1" }, { 2, "2" } };
// 括号可以省略
Dictionary<int, Person> dict1 = new Dictionary<int, Person>() { { 1, new Person { Name = "小红", Age = 20 } }, { 2, new Person { Name = "小明", Age = 22 } } };
匿名类型
var可以申明为自定义的匿名类型
var v = new { age = 10 };
Console.WriteLine(v.age);
可空类型
值类型是不能赋值为空的
// 错误
int a = null;
申命值类型的时候在后面加上?,可以赋值为空
// 不会报错
int? a = null;
判断可空值类型是否为空
int? a = null;
if(a.HasValue)
{
// 或者Console.WriteLine(a.Value);
Consoloe.WriteLine(a);
}
安全获取可空值类型
int? a = null;
// 如果为空返回int的默认值
Console.WriteLine(a.GetValueOrDefault());
// 如果为空返回指定的值 这里并不会将50赋值给a,a的值还是为空
Console.WriteLine(a.GetValueOrDefault(50));
安全执行空的引用类型的方法
object o = null;
// 加了?之后,如果o为空,则不会执行其ToString()方法
Console.WriteLine(o?.ToString());
Action action = null;
if(action != null)
{
action();
}
// 等效于上面的写法
action?.Invoke();
空合并操作符
空合并操作符:??
左边值 ?? 右边值
如果左边值为空,则返回右边值,否则返回左边值
可以适用于可空值类型以及引用类型
// 可空值类型
int? a = null;
// 如果a为空,返回100,否则返回a
int b = a ?? 100;
// 引用类型
string str = null;
Console.WriteLine(str ?? "Hello World");
内插字符串
关键字:$
用$来构造字符串,让字符串中可以拼接变量
int age = 20;
string name = "小明";
Console.WriteLine($"{name}的年龄为{age}");
单句逻辑简略写法
if、while或者for等循环语句
如果后面只有一句代码时,可以省略{}
if(true)
Console.WriteLine("Hello");
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++)
Console.WriteLine("Hi");
while(true)
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
属性和方法
如果属性里面只有一句代码,可以省略{},使用=>代替,其中get满足缩略写法的时候不需要写return
如果方法中只有一句代码,可以省略{},使用=>代替。如果有返回值,不需要写return
Class Person
{
public Person()
{
}
private string name;
public string Name
{
// 注意:这里不能写return,否则会报错
get => name;
set => name = value;
}
// 不需要写return,否则会报错。
public string ToString() => $"名字叫{name}";
}










 本文详细介绍了C#中的ArrayList、Stack、Queue和Hashtable等高级数据类型,以及它们的增删查改操作。接着,讨论了泛型的概念、分类、作用,以及如何使用泛型类和泛型方法。此外,还涵盖了泛型约束、装箱拆箱、委托、事件、匿名函数、Lambda表达式和闭包等概念。最后,探讨了多线程、预处理器指令、反射和特性在C#编程中的应用。
本文详细介绍了C#中的ArrayList、Stack、Queue和Hashtable等高级数据类型,以及它们的增删查改操作。接着,讨论了泛型的概念、分类、作用,以及如何使用泛型类和泛型方法。此外,还涵盖了泛型约束、装箱拆箱、委托、事件、匿名函数、Lambda表达式和闭包等概念。最后,探讨了多线程、预处理器指令、反射和特性在C#编程中的应用。
















 828
828

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








