Linux 音频子系统分析5(基于Linux6.6)---ALSA platform介绍
一、概述
在Platform部分,主要是平台相关的DMA操作和音频管理。流程是先将音频数据从内存通过DMA方式传输到CPU侧的dai接口,然后通过CPU的dai接口(通过I2S总线)将数据送达到Codec中,数据会在Codec侧进行解码操作,最终输出到耳机/音箱中。下图作为参考:
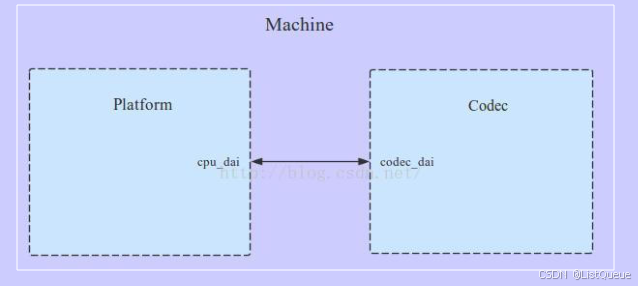
Platform驱动的主要作用是完成音频数据的管理,最终通过CPU的数字音频接口(DAI)把音频数据传送给Codec进行处理,最终由Codec输出驱动耳机或者是喇叭的音信信号。
在具体实现上,ASoC把Platform驱动分为两个部分:
-
snd_soc_dai_driver - 代表cpu侧的dai驱动,其中包括dai的配置(音频格式,clock,音量等)。
-
snd_soc_platform_driver - 代表平台使用的dma驱动,主要是数据的传输等。
其中,snd_soc_platform_driver负责管理音频数据,把音频数据通过dma或其他操作传送至cpu dai中,snd_soc_dai_driver则主要完成cpu一侧的dai的参数配置,同时也会通过一定的途径把必要的dma等参数与snd_soc_platform_driver进行交互。
1. Platform的概述
Platform 是 ASoC 中的一个核心概念,代表了与特定硬件平台或处理器(如 SoC,System on Chip)相关的音频硬件接口。它主要处理的是音频硬件与平台的连接、管理以及资源的配置。在 ASoC 的架构中,Platform 负责实现音频数据接口(DAI,Digital Audio Interface)与硬件的交互,它与 SoC 上的音频相关硬件模块进行紧密结合。
通常,Platform 涉及以下几个关键点:
- 音频硬件接口(DAI)管理:平台负责配置和控制与 SoC 上音频硬件(如音频处理器、音频 I/O 设备等)相关的接口。
- 资源分配和控制:平台负责分配和管理 SoC 中的音频硬件资源,比如时钟、复位、DMA(Direct Memory Access)等。它确保音频数据流正确传输并得到合理的资源支持。
- 系统与设备之间的桥梁:Platform 作为 Machine 和 Codec 之间的桥梁,管理从硬件平台到音频编解码器(Codec)的数据流。它负责确保平台上的音频数据正确地传递到音频编解码器,或从编解码器传输回平台。
2. Platform的结构
在 ASoC 中,platform 主要通过一个叫做 snd_soc_platform 的结构来进行描述。这个结构主要包含了与平台相关的设备信息和操作函数。
例如,snd_soc_platform 结构体中包含了如下字段:
- platform_ops:指向包含平台相关操作的结构体(如配置时钟、复位、DMA、音频传输等)。
- name:平台的名称。
- dev:指向平台设备的指针,用于获取与该平台相关的设备资源(如时钟、复位控制等)。
3. Platform与Machine和Codec的关系
在 ASoC 中,Platform 是 Machine 和 Codec 之间的桥梁,它充当了一个中介角色,协调两个组件之间的交互:
- Machine:代表的是整个音频系统的整体结构,它包括音频编解码器和平台的配置。
Machine通常会定义整个音频设备的架构,包括音频编解码器(Codec)和与平台相关的音频接口(DAI)链接。 - Platform:平台与具体的硬件接口密切相关,管理音频硬件资源,配置音频数据的传输和处理。平台需要保证时钟、复位等资源的配置,使得音频数据流可以顺畅地传递。
- Codec:音频编解码器负责实际的音频数据处理(例如模拟到数字转换、数字到模拟转换等),并提供与平台的音频接口连接。
通过 snd_soc_dai_link 结构,Platform、Machine 和 Codec 会协同工作,保证音频数据从平台到编解码器的正确传输,或者反向传输。
4. Platform的主要功能
-
时钟控制(Clock Control):在音频数据的传输过程中,时钟同步是至关重要的。Platform 负责时钟的配置与管理,确保所有音频数据流在适当的时钟同步下运行。
-
复位控制(Reset Control):平台负责音频硬件模块的复位,确保硬件在启动或恢复过程中处于正确的状态。
-
DMA 管理(DMA Management):许多音频平台会使用 DMA 来高效地传输音频数据。Platform 负责配置和管理 DMA 控制器,将音频数据从内存传输到音频编解码器,或反向传输数据。
-
设备树和硬件资源配置(Device Tree and Hardware Resource Configuration):在一些基于设备树的系统中,Platform 还负责从设备树中解析硬件配置信息,并根据这些配置来初始化音频硬件资源(如 GPIO、I2S 接口、时钟源等)。
二、Platform代码分析
2.1、platform注册
sound/soc/samsung/s3c24xx-i2s.c
- platform_driver
static struct platform_driver s3c24xx_iis_driver = {
.probe = s3c24xx_iis_dev_probe,
.driver = {
.name = "s3c24xx-iis",
},
};
arch/arm/mach-s3c/devs.c
- platform_device
#ifdef CONFIG_PLAT_S3C24XX
static struct resource s3c_iis_resource[] = {
[0] = DEFINE_RES_MEM(S3C24XX_PA_IIS, S3C24XX_SZ_IIS),
};
struct platform_device s3c_device_iis = {
.name = "s3c24xx-iis",
.id = -1,
.num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(s3c_iis_resource),
.resource = s3c_iis_resource,
.dev = {
.dma_mask = &samsung_device_dma_mask,
.coherent_dma_mask = DMA_BIT_MASK(32),
}
};
#endif /* CONFIG_PLAT_S3C24XX */
匹配上之后,调用 s3c24xx_iis_dev_probe函数。
sound/soc/samsung/s3c24xx-i2s.c
static int s3c24xx_iis_dev_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int ret = 0;
struct resource *res;
res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0);
if (!res) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Can't get IO resource.\n");
return -ENOENT;
}
s3c24xx_i2s.regs = devm_ioremap_resource(&pdev->dev, res);
if (IS_ERR(s3c24xx_i2s.regs))
return PTR_ERR(s3c24xx_i2s.regs);
s3c24xx_i2s_pcm_stereo_out.dma_addr = res->start + S3C2410_IISFIFO;
s3c24xx_i2s_pcm_stereo_in.dma_addr = res->start + S3C2410_IISFIFO;
ret = devm_snd_soc_register_component(&pdev->dev,
&s3c24xx_i2s_component, &s3c24xx_i2s_dai, 1);
if (ret) {
pr_err("failed to register the dai\n");
return ret;
}
ret = samsung_asoc_dma_platform_register(&pdev->dev);
if (ret)
pr_err("failed to register the dma: %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
该函数主要完成:
- i2s控制器的地址映射,dma的地址映射;
- 通过samsung_asoc_dma_platform_register注册dma相关;
- 通过devm_snd_soc_register_component注册一个component组件。传入的参数分别是snd_soc_component_driver和snd_soc_dai_driver。
2.2、snd_soc_dai driver驱动注册
首先通过devm_snd_soc_register_component注册一个component组件。传入的参数分别是snd_soc_component_driver和snd_soc_dai_driver,这个跟codec的dai的结构类似。
sound/soc/samsung/s3c24xx-i2s.c
static const struct snd_soc_dai_ops s3c24xx_i2s_dai_ops = {
.trigger = s3c24xx_i2s_trigger,
.hw_params = s3c24xx_i2s_hw_params,
.set_fmt = s3c24xx_i2s_set_fmt,
.set_clkdiv = s3c24xx_i2s_set_clkdiv,
.set_sysclk = s3c24xx_i2s_set_sysclk,
};
static struct snd_soc_dai_driver s3c24xx_i2s_dai = {
.probe = s3c24xx_i2s_probe,
.suspend = s3c24xx_i2s_suspend,
.resume = s3c24xx_i2s_resume,
.playback = {
.channels_min = 2,
.channels_max = 2,
.rates = S3C24XX_I2S_RATES,
.formats = SNDRV_PCM_FMTBIT_S8 | SNDRV_PCM_FMTBIT_S16_LE,},
.capture = {
.channels_min = 2,
.channels_max = 2,
.rates = S3C24XX_I2S_RATES,
.formats = SNDRV_PCM_FMTBIT_S8 | SNDRV_PCM_FMTBIT_S16_LE,},
.ops = &s3c24xx_i2s_dai_ops,
};
static const struct snd_soc_component_driver s3c24xx_i2s_component = {
.name = "s3c24xx-i2s",
};
snd_soc_dai_driver 该结构需要自己根据不同的soc芯片进行定义,其主要有以下几个:
- probe、remove 回调函数,分别在声卡加载和卸载时被调用;
- suspend、resume 电源管理回调函数;
- ops 指向snd_soc_dai_ops结构,用于配置和控制该dai;
- playback snd_soc_pcm_stream结构,用于指出该dai支持的声道数,码率,数据格式等能力;
- capture snd_soc_pcm_stream结构,用于指出该dai支持的声道数,码率,数据格式等能力;
- 对于devm_snd_soc_register_component这个接口,其最终调用snd_soc_register_component这个接口。
sound/soc/soc-core.c
int snd_soc_register_component(struct device *dev,
const struct snd_soc_component_driver *component_driver,
struct snd_soc_dai_driver *dai_drv,
int num_dai)
{
struct snd_soc_component *component;
int ret;
component = devm_kzalloc(dev, sizeof(*component), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!component)
return -ENOMEM;
ret = snd_soc_component_initialize(component, component_driver, dev);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
return snd_soc_add_component(component, dai_drv, num_dai);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(snd_soc_register_component);此函数和snd_soc_register_codec的大体流程一致,都是初始化snd_soc_component的实例,然后注册dai,最终将注册的dai放入到component->dai_list中,然后将分配的component放入到component_list链表中。ops字段指向一个snd_soc_dai_ops结构,该结构实际上是一组回调函数的集合,dai的配置和控制几乎都是通过这些回调函数来实现的。
sound/soc/samsung/s3c24xx-i2s.c
static const struct snd_soc_dai_ops s3c24xx_i2s_dai_ops = {
.trigger = s3c24xx_i2s_trigger,
.hw_params = s3c24xx_i2s_hw_params,
.set_fmt = s3c24xx_i2s_set_fmt,
.set_clkdiv = s3c24xx_i2s_set_clkdiv,
.set_sysclk = s3c24xx_i2s_set_sysclk,
}
- trigger:数据传送的开始,暂停,恢复和停止时,该函数会被调用。
- hw_params:驱动的hw_params阶段,该函数会被调用。通常,该函数会通过snd_soc_dai_get_dma_data函数获得对应的dai的dma参数,获得的参数一般都会保存在snd_pcm_runtime结构的private_data字段。然后通过snd_pcm_set_runtime_buffer函数设置snd_pcm_runtime结构中的dma buffer的地址和大小等参数。要注意的是,该回调可能会被多次调用,具体实现时要小心处理多次申请资源的问题。
- set_fmt:设置dai的格式
- set_clkdiv: 设置分频系数
- set_sysclk: 设置dai的主时钟
2.3、dma注册
对于DMA,首先要配置一些DMA的参数,对于该接口中,在dai的probe函数中有一个初始化dma的接口:
sound/soc/samsung/s3c24xx-i2s.c
static struct snd_dmaengine_dai_dma_data s3c24xx_i2s_pcm_stereo_out = {
.chan_name = "tx",
.addr_width = 2,
};
static struct snd_dmaengine_dai_dma_data s3c24xx_i2s_pcm_stereo_in = {
.chan_name = "rx",
.addr_width = 2,
};
snd_soc_dai_init_dma_data(dai, &s3c24xx_i2s_pcm_stereo_out,
&s3c24xx_i2s_pcm_stereo_in);
通过该接口会将dma的channel,name,size分别配置到dai的playback和capture中;注册dma的实现,该接口中有samsung_dmaengine_pcm_config结构,是传输pcm数据平台的DMA的相关配置。比如DMA传输之前要做方向,位数,源地址,目的地址的配置。这些都是个具体平台相关的。
sound/soc/soc-generic-dmaengine-pcm.c
/**
* snd_dmaengine_pcm_register - Register a dmaengine based PCM device
* @dev: The parent device for the PCM device
* @config: Platform specific PCM configuration
* @flags: Platform specific quirks
*/
int snd_dmaengine_pcm_register(struct device *dev,
const struct snd_dmaengine_pcm_config *config, unsigned int flags)
{
const struct snd_soc_component_driver *driver;
struct dmaengine_pcm *pcm;
int ret;
pcm = kzalloc(sizeof(*pcm), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!pcm)
return -ENOMEM;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_FS
pcm->component.debugfs_prefix = "dma";
#endif
if (!config)
config = &snd_dmaengine_pcm_default_config;
pcm->config = config;
pcm->flags = flags;
ret = dmaengine_pcm_request_chan_of(pcm, dev, config);
if (ret)
goto err_free_dma;
if (config->process)
driver = &dmaengine_pcm_component_process;
else
driver = &dmaengine_pcm_component;
ret = snd_soc_component_initialize(&pcm->component, driver, dev);
if (ret)
goto err_free_dma;
ret = snd_soc_add_component(&pcm->component, NULL, 0);
if (ret)
goto err_free_dma;
return 0;
err_free_dma:
dmaengine_pcm_release_chan(pcm);
kfree(pcm);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(snd_dmaengine_pcm_register);- 此处分配一个dmaengine_pcm结构,然后根据传入的config和flag设置pcm。
- 获取dma的传输通道,根据传输的是否是半双工,设置pcm的通道。
- 调用snd_soc_add_component函数注册platformd到ASOC core。
sound/soc/soc-core.c
snd_soc_add_component函数:
int snd_soc_add_component(struct snd_soc_component *component,
struct snd_soc_dai_driver *dai_drv,
int num_dai)
{
int ret;
int i;
mutex_lock(&client_mutex);
if (component->driver->endianness) {
for (i = 0; i < num_dai; i++) {
convert_endianness_formats(&dai_drv[i].playback);
convert_endianness_formats(&dai_drv[i].capture);
}
}
ret = snd_soc_register_dais(component, dai_drv, num_dai);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(component->dev, "ASoC: Failed to register DAIs: %d\n",
ret);
goto err_cleanup;
}
if (!component->driver->write && !component->driver->read) {
if (!component->regmap)
component->regmap = dev_get_regmap(component->dev,
NULL);
if (component->regmap)
snd_soc_component_setup_regmap(component);
}
/* see for_each_component */
list_add(&component->list, &component_list);
err_cleanup:
if (ret < 0)
snd_soc_del_component_unlocked(component);
mutex_unlock(&client_mutex);
if (ret == 0)
snd_soc_try_rebind_card();
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(snd_soc_add_component);
三、举例应用
1. Platform应用举例:树莓派(Raspberry Pi)音频平台
背景
树莓派是一个流行的嵌入式平台,广泛用于各种开发和音频应用。树莓派的音频平台通常包括 I2S(Inter-IC Sound)接口、音频编解码器(Codec)和音频处理功能。Linux 内核中的 ALSA ASoC 框架被用来处理音频的流和硬件资源配置。
Platform驱动的实现
在树莓派的音频驱动中,Platform 部分主要负责与硬件平台相关的资源管理,比如配置时钟、复位控制、DMA 管理等。具体来说,树莓派会使用 bcm2835-i2s 驱动来支持 I2S 总线,而音频设备和音频编解码器的操作则由 bcm2835 平台驱动控制。
以下是一个简化的例子,展示了树莓派如何使用 Platform 处理音频硬件资源:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <sound/soc.h>
static int bcm2835_i2s_platform_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
pr_info("bcm2835 I2S platform probe\n");
/* 在这里初始化硬件资源,例如时钟、复位、DMA等 */
return 0;
}
static int bcm2835_i2s_platform_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
pr_info("bcm2835 I2S platform remove\n");
/* 在这里释放硬件资源 */
return 0;
}
static struct platform_driver bcm2835_i2s_platform_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "bcm2835-i2s",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
.probe = bcm2835_i2s_platform_probe,
.remove = bcm2835_i2s_platform_remove,
};
module_platform_driver(bcm2835_i2s_platform_driver);
MODULE_AUTHOR("Raspberry Pi");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Raspberry Pi I2S platform driver");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
在这个例子中:
bcm2835_i2s_platform_probe:这是树莓派 I2S 平台驱动的probe函数,在其中初始化与 I2S 总线相关的硬件资源,例如时钟、DMA 控制器等。bcm2835_i2s_platform_remove:这是对应的remove函数,用于在卸载时清理硬件资源。
该平台驱动负责配置树莓派上的音频硬件接口,并确保正确地初始化硬件资源(如时钟、复位和 DMA)。
2. Platform应用举例:NXP i.MX SoC 音频平台
背景
NXP 的 i.MX 系列处理器广泛应用于嵌入式音频应用,这些 SoC 通常带有丰富的音频硬件接口,如 I2S、PCM、SPDIF 等。i.MX SoC 使用 ASoC 框架来支持音频硬件平台的管理,Platform 在其中负责处理硬件资源的初始化和配置。
Platform驱动的实现
在 i.MX 平台中,Platform 驱动通常与音频硬件接口(如 I2S)相关联,负责初始化和管理与音频传输相关的硬件资源。下面是一个简化的 i.MX Platform 驱动示例,展示如何管理音频硬件资源。
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <sound/soc.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
static int imx_audio_platform_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
pr_info("i.MX audio platform probe\n");
/* 在这里配置音频硬件资源,如时钟、复位等 */
return 0;
}
static int imx_audio_platform_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
pr_info("i.MX audio platform remove\n");
/* 清理资源 */
return 0;
}
static struct platform_driver imx_audio_platform_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "imx-audio-platform",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
.probe = imx_audio_platform_probe,
.remove = imx_audio_platform_remove,
};
module_platform_driver(imx_audio_platform_driver);
MODULE_AUTHOR("NXP");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("i.MX audio platform driver");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
在这个例子中:
imx_audio_platform_probe:用于初始化与音频硬件相关的资源,通常涉及配置时钟、复位控制、DMA 资源等。imx_audio_platform_remove:清理硬件资源。
该驱动通过 platform_driver 启动和管理音频硬件资源,确保 i.MX 平台的音频硬件正常工作。
3. Platform应用举例:Allwinner SoC 音频平台
背景
Allwinner SoC(例如 A10、A20 等)广泛应用于低成本的嵌入式系统,这些系统通常会集成 I2S 总线、音频编解码器和其他音频接口。ASoC 框架帮助在这些 SoC 中进行音频硬件的资源管理。
Platform驱动的实现
在 Allwinner SoC 平台中,Platform 驱动与音频硬件接口(如 I2S、PCM)相结合,负责硬件资源的管理。以下是一个 Allwinner SoC 上音频平台驱动的示例。
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <sound/soc.h>
static int allwinner_audio_platform_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
pr_info("Allwinner audio platform probe\n");
/* 配置硬件资源,如时钟、复位、DMA等 */
return 0;
}
static int allwinner_audio_platform_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
pr_info("Allwinner audio platform remove\n");
/* 释放硬件资源 */
return 0;
}
static struct platform_driver allwinner_audio_platform_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "allwinner-audio-platform",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
.probe = allwinner_audio_platform_probe,
.remove = allwinner_audio_platform_remove,
};
module_platform_driver(allwinner_audio_platform_driver);
MODULE_AUTHOR("Allwinner");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Allwinner audio platform driver");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
代码说明:
allwinner_audio_platform_probe:在此函数中初始化 Allwinner SoC 上与音频相关的硬件资源(如时钟和复位控制)。allwinner_audio_platform_remove:释放与音频平台相关的硬件资源。





















 2476
2476

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








