Linux V4l2子系统分析2(基于Linux6.6)---结构体介绍
一、v4l2调用过程
在 Linux 系统中,/dev/videoX 设备节点代表一个视频设备,通常用于视频捕捉(例如网络摄像头)或视频回放(例如电视卡)。当用户空间的应用程序访问 /dev/videoX 时,内核会通过 V4L2(Video for Linux 2)子系统管理硬件设备和数据流,完成视频数据的捕获、输出、控制等功能。
下面是用户空间程序通过 /dev/videoX 设备节点进行操作时,内核处理过程的详细介绍。
1.1、用户空间请求过程
假设用户空间应用程序执行了一些常见的操作,如打开设备、设置参数、捕获图像等。以下是主要操作的过程:
1.打开设备
int fd = open("/dev/video0", O_RDWR);
- 用户空间应用程序通过
open()系统调用打开/dev/video0设备文件。 - 内核通过 字符设备驱动 查找设备节点
/dev/video0对应的设备驱动程序,找到与video_device结构相关的函数,完成设备的初始化和打开过程。
2.内核如何处理设备打开
当用户调用 open("/dev/videoX") 时,内核会调用以下过程:
-
字符设备驱动注册:视频设备驱动会在内核启动时通过
register_chrdev()或v4l2_device_register()等函数注册到 V4L2 子系统,并与/dev/videoX设备节点进行关联。 -
文件操作结构(file_operations):当应用程序打开设备时,内核会通过
struct file_operations中的open()函数来处理打开设备的请求。对于 V4L2 设备,内核通常会调用v4l2_open()或驱动程序自定义的打开函数。 -
视频设备实例化:设备的初始化和资源分配会在
open()函数中进行,驱动程序会通过 V4L2 API 初始化相关设备资源(如设备上下文、缓冲区队列等)。 -
返回文件描述符:如果设备打开成功,内核返回一个文件描述符(
fd),用户可以通过该描述符进一步进行操作。
3.设置视频格式
struct v4l2_format fmt;
fmt.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
fmt.fmt.pix.width = 640;
fmt.fmt.pix.height = 480;
fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat = V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV;
fmt.fmt.pix.field = V4L2_FIELD_NONE;
ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_S_FMT, &fmt);
- 用户通过
ioctl()调用设置设备的格式,例如分辨率、像素格式等。 - 内核通过 VIDIOC_S_FMT 控制命令来设置设备的格式,这个命令会被传递到驱动程序中。
4.内核如何处理 VIDIOC_S_FMT 命令
当内核接收到 VIDIOC_S_FMT IOCTL 请求时,驱动程序会执行以下步骤:
-
IOCTL 调用:
ioctl()系统调用会根据命令类型查找对应的设备操作函数,例如video_ioctl2()。 -
格式设置:驱动程序会根据用户空间传入的
v4l2_format结构,设置设备的捕获或回放格式,通常会设置图像的宽度、高度、像素格式等。 -
验证格式:驱动程序会检查设备是否支持所请求的格式,如果不支持,返回错误。
-
更新设备参数:驱动程序会更新设备的状态和参数,准备好以新的格式进行捕获或回放。
5.捕获图像数据
ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_STREAMON, &buf_type);
ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &buf);
ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_DQBUF, &buf);
- 用户调用
VIDIOC_STREAMON启动视频流,告诉驱动开始传输视频数据。 - 然后,用户通过
VIDIOC_QBUF向设备队列中提交缓冲区,并通过VIDIOC_DQBUF获取捕获的数据。
6.内核如何处理视频数据流
-
缓冲区队列管理:内核通过缓冲区队列管理(通常是内存映射缓冲区或用户指针缓冲区)来处理数据的传输。缓冲区被分配并提交到设备,以便视频数据可以捕获到这些缓冲区中。
-
VIDIOC_STREAMON:当内核接收到
VIDIOC_STREAMON命令时,会通知设备开始捕获数据或播放数据。设备开始将数据流传输到缓冲区队列中。 -
缓冲区排队与出队:应用程序通过
VIDIOC_QBUF向设备提交缓冲区,等待设备将捕获的数据写入缓冲区。完成捕获后,设备通过VIDIOC_DQBUF命令将数据从缓冲区中取出。 -
数据传输:视频捕获设备将帧数据(例如图像或视频流)从硬件中传输到用户空间的缓冲区。
7.关闭设备
close(fd);
- 用户关闭设备后,内核会调用相应的
release()函数来释放设备资源,终止缓冲区队列等操作。
1.2、内核调用过程
当用户空间应用程序操作 /dev/videoX 时,内核调用过程如下:
-
设备文件操作:
- 用户空间通过文件系统的接口(如
open()、read()、ioctl()等)与内核交互,访问/dev/videoX。 - 内核通过字符设备驱动的
file_operations表查找相关的驱动函数。
- 用户空间通过文件系统的接口(如
-
驱动程序处理请求:
- 内核将请求传递给设备的驱动程序,驱动程序通过实现的 V4L2 函数处理设备请求。例如,
v4l2_open()处理设备的打开,v4l2_ioctl()处理 IOCTL 命令等。
- 内核将请求传递给设备的驱动程序,驱动程序通过实现的 V4L2 函数处理设备请求。例如,
-
设备控制:
- 驱动程序根据请求设置硬件设备参数,如图像格式、分辨率等。
-
数据传输:
- 驱动程序通过缓冲区队列和 V4L2 API 与硬件进行数据交换,将视频帧传输到用户空间,或者从用户空间传输到设备。
-
事件通知:
- 内核通过事件机制(如
select()、poll()等)向应用程序报告设备状态变化,支持异步操作。
- 内核通过事件机制(如
-
设备释放:
- 用户调用
close()时,内核会通过release()函数释放设备资源,停止视频流,清理缓冲区等。
- 用户调用
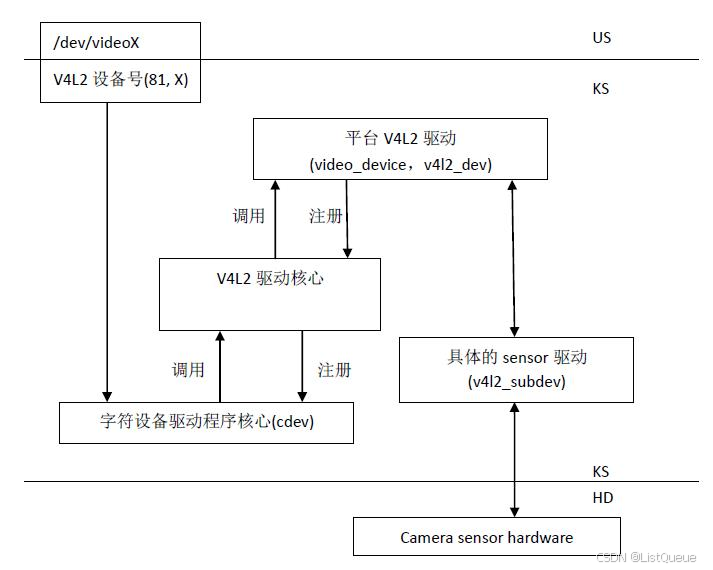
二、v4l2关联的文件
在 Linux 内核中,V4L2(Video for Linux 2)是用于视频捕捉、播放和控制的子系统,它提供了标准的 API 接口供用户空间程序与硬件设备交互。V4L2 在内核中的实现涉及多个关键文件,这些文件主要位于 drivers/media 目录下,涉及的模块主要与视频设备的注册、操作、缓冲区管理等相关。
以下是一些与 V4L2 关联的重要文件及其作用:
1. drivers/media/v4l2-core/v4l2-ioctl.c
- 作用:处理与 V4L2 设备的控制命令(ioctl 请求)相关的函数。
- 关键功能:包括处理视频设备的各种 IOCTL 操作,如设置格式(
VIDIOC_S_FMT)、获取帧缓冲(VIDIOC_QBUF)等。这个文件处理了用户空间发起的命令,并将其转交给对应的设备驱动。 - 常见函数:
v4l2_ioctl()v4l2_device_ioctl()
2. drivers/media/v4l2-core/v4l2-dev.c
- 作用:管理 V4L2 设备的注册和初始化。
- 关键功能:包括视频设备的注册、注销、以及设备控制结构的创建和销毁。它为设备提供了一个通用的接口,使得不同的驱动程序能够通过 V4L2 进行统一的设备管理。
- 常见函数:
v4l2_device_register()v4l2_device_unregister()v4l2_device_init()
3. drivers/media/v4l2-core/v4l2-fh.c
- 作用:处理文件句柄(file handle)相关的操作,管理与设备相关的打开和关闭操作。
- 关键功能:这个文件主要涉及与文件描述符和设备的关联管理。每个打开的视频设备都会分配一个文件句柄,用来跟踪设备的状态。
- 常见函数:
v4l2_fh_init()v4l2_fh_release()
4. drivers/media/v4l2-core/v4l2-buffer.c
- 作用:管理视频设备的缓冲区(buffer)相关操作。
- 关键功能:处理缓冲区的队列操作,分配、释放和操作缓冲区。对于视频捕获或输出,缓冲区管理至关重要,V4L2 使用缓冲区队列来实现帧的捕获和显示。
- 常见函数:
v4l2_buffer_alloc()v4l2_buffer_free()v4l2_buf_queue()v4l2_buf_dq()(入队与出队操作)
5. drivers/media/v4l2-core/v4l2-device.c
- 作用:处理与 V4L2 设备相关的具体实现,包括设备实例的创建、设备管理。
- 关键功能:这个文件定义了视频设备的抽象接口,设备注册时需要设置一些特性(如设备类型、操作方法等)。它帮助驱动程序管理与设备硬件的交互。
- 常见函数:
v4l2_device_init()v4l2_device_unregister()
6. drivers/media/v4l2-core/v4l2-compat-ioctl32.c
- 作用:处理 32 位和 64 位系统之间的兼容性问题,特别是在进行 IOCTL 操作时。
- 关键功能:当在 64 位系统中运行 32 位应用程序时,V4L2 提供了兼容性支持,确保数据结构能够正确地在不同位宽的系统之间传递。
- 常见函数:
v4l2_ioctl32()(用于处理32位用户空间请求)
7. drivers/media/v4l2-core/v4l2-async.c
- 作用:处理与 V4L2 设备异步事件相关的操作。
- 关键功能:V4L2 支持异步事件,如设备插拔、信号变化等。这个文件处理与异步事件的注册、回调等操作。
- 常见函数:
v4l2_async_notifier_register()v4l2_async_notifier_unregister()
8. include/linux/videodev2.h
- 作用:V4L2 的核心头文件,定义了 V4L2 API、数据结构、常量和控制命令。
- 关键功能:这是与 V4L2 操作相关的所有常量和数据结构的定义,包括格式、缓冲区、控制命令等。用户空间应用程序和内核驱动程序都依赖此文件定义的接口。
- 重要数据结构:
struct v4l2_format(描述视频格式)struct v4l2_buffer(描述视频缓冲区)struct v4l2_control(描述视频控制)
- 常见常量:
V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE(视频捕获缓冲区类型)V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV(视频像素格式)
9. drivers/media/v4l2-core/v4l2-ctrls.c
- 作用:管理 V4L2 控制接口,包括视频设备的各项参数控制。
- 关键功能:V4L2 支持通过控制接口来调整设备的各种参数(如亮度、对比度、色彩饱和度等)。
v4l2-ctrls.c负责管理和更新这些控制参数。 - 常见函数:
v4l2_ctrl_handler_init()v4l2_ctrl_new_std()v4l2_ctrl_g_ctrl()v4l2_ctrl_s_ctrl()
10. drivers/media/v4l2-core/v4l2-mem2mem.c
- 作用:处理 V4L2 内存到内存(mem-to-mem)操作,主要用于视频编码、解码等。
- 关键功能:这个文件提供了视频流的内存到内存的处理功能,例如视频压缩、解压缩等操作。
- 常见函数:
v4l2_m2m_queue_setup()v4l2_m2m_buffer_prepare()
三、v4l2重要的结构体
3.1、struct v4l2_device
每一个使用v4l2的设备都要创建一个struct v4l2_device,用来记录其他的media_device和子设备。该大结构体可以单独创建也可以嵌套进一个更大的结构体中。
include/media/v4l2-device.h
struct v4l2_device {
/* dev->driver_data points to this struct.
Note: dev might be NULL if there is no parent device
as is the case with e.g. ISA devices. */
struct device *dev;
#if defined(CONFIG_MEDIA_CONTROLLER)
struct media_device *mdev;
#endif
/* used to keep track of the registered subdevs */
struct list_head subdevs;//这个很重要的,用来记录所有子设备的。
/* lock this struct; can be used by the driver as well if this
struct is embedded into a larger struct. */
spinlock_t lock;
/* unique device name, by default the driver name + bus ID */
char name[V4L2_DEVICE_NAME_SIZE];
/* notify callback called by some sub-devices. */
/* 子设备通知母设备时,就会回调这个接口*/
void (*notify)(struct v4l2_subdev *sd,
unsigned int notification, void *arg);
/* The control handler. May be NULL. */
/* 在注册子设备时,会将所有子设备的控制实例,链接到母设备中,便于user层
发送命令时,母设备能发送给对应的控制实例*/
struct v4l2_ctrl_handler *ctrl_handler;
/* Device's priority state */
struct v4l2_prio_state prio;
/* BKL replacement mutex. Temporary solution only. */
struct mutex ioctl_lock;
/* Keep track of the references to this struct. */
struct kref ref;
/* Release function that is called when the ref count goes to 0. */
void (*release)(struct v4l2_device *v4l2_dev);
};
该结构体存在的意义在于方便访问子设备,以及方便根据media_entry查找设备属性。其它的如果预先知道了设备名称,可以直接访问设备。V4L2 device是必须创建的。
- dev:dev一般存放设备的父亲设备,可以为空。
- mdev: media_device设备对象,一般用作设备的入口,用来查找设备类型。比如是source模块,还是sink模块。
- ctrl_handler:这是
struct v4l2_ctrl对象的聚集地,当使用struct v4l2_ctrl功能时,v4l2_device会记录所有子设备的ctrl对象,便于查找。
3.2、struct v4l2_ctrl_handler
该结构体专门用来记录一个或多个控制命令集合(例如设置gain,曝光时间等),目前发现三星平台是以ctrl_hanler的形式来表达sensor的控制方式。
include/media/v4l2-ctrls.h
struct v4l2_ctrl_handler {
struct mutex _lock;
struct mutex *lock;
struct list_head ctrls;
struct list_head ctrl_refs;
struct v4l2_ctrl_ref *cached;
struct v4l2_ctrl_ref **buckets;
v4l2_ctrl_notify_fnc notify;
void *notify_priv;
u16 nr_of_buckets;
int error;
bool request_is_queued;
struct list_head requests;
struct list_head requests_queued;
struct media_request_object req_obj;
};
它一般和struct v4l2_ctrl配合使用。可以理解成v4l2_ctrl_handler是v4l2_ctrl的仓库。查找v4l2_ctrl即可通过handler来查找。后面会举例子来解释这一层意思的。
3.3、struct v4l2_ctrl
include/media/v4l2-ctrls.h
struct v4l2_ctrl {
/* Administrative fields */
struct list_head node;
struct list_head ev_subs;
struct v4l2_ctrl_handler *handler;
struct v4l2_ctrl **cluster;
unsigned int ncontrols;
unsigned int done:1;
unsigned int is_new:1;
unsigned int has_changed:1;
unsigned int is_private:1;
unsigned int is_auto:1;
unsigned int is_int:1;
unsigned int is_string:1;
unsigned int is_ptr:1;
unsigned int is_array:1;
unsigned int is_dyn_array:1;
unsigned int has_volatiles:1;
unsigned int call_notify:1;
unsigned int manual_mode_value:8;
const struct v4l2_ctrl_ops *ops;
const struct v4l2_ctrl_type_ops *type_ops;
u32 id;
const char *name;
enum v4l2_ctrl_type type;
s64 minimum, maximum, default_value;
u32 elems;
u32 elem_size;
u32 new_elems;
u32 dims[V4L2_CTRL_MAX_DIMS];
u32 nr_of_dims;
union {
u64 step;
u64 menu_skip_mask;
};
union {
const char * const *qmenu;
const s64 *qmenu_int;
};
unsigned long flags;
void *priv;
void *p_array;
u32 p_array_alloc_elems;
s32 val;
struct {
s32 val;
} cur;
union v4l2_ctrl_ptr p_def;
union v4l2_ctrl_ptr p_new;
union v4l2_ctrl_ptr p_cur;
};
上面最重要的就是
- ev_subs:这个表示控件事件订阅列表,也就是说,所有订阅该 v4l2_ctrl的消息的对象,都会在该消息可用时收到一个事件。该事件会自动queue到对应订阅者对象的
subscribed列表中。 - handler:该控制对象所属的
struct v4l2_ctrl_handler的控制仓库对象。 - ops:操作ctrl的方法,具体各个方法的含义,下方备注都很清楚。
3.4、struct v4l2_ctrl_ops
include/media/v4l2-ctrls.h
/** struct v4l2_ctrl_ops - The control operations that the driver has to provide.
* @g_volatile_ctrl: Get a new value for this control. Generally only relevant
* for volatile (and usually read-only) controls such as a control
* that returns the current signal strength which changes
* continuously.
* If not set, then the currently cached value will be returned.
* @try_ctrl: Test whether the control's value is valid. Only relevant when
* the usual min/max/step checks are not sufficient.
* @s_ctrl: Actually set the new control value. s_ctrl is compulsory. The
* ctrl->handler->lock is held when these ops are called, so no
* one else can access controls owned by that handler.
*/
struct v4l2_ctrl_ops {
int (*g_volatile_ctrl)(struct v4l2_ctrl *ctrl);
int (*try_ctrl)(struct v4l2_ctrl *ctrl);
int (*s_ctrl)(struct v4l2_ctrl *ctrl);
};
3.5、struct v4l2_fh
此结构用于描述消息队列,设备的消息都会链接在此对象中,我们也可以在struct video_device结构体中看到有struct v4l2_fh的数据域。
include/media/v4l2-fh.h
struct v4l2_fh {
struct list_head list;
struct video_device *vdev;
struct v4l2_ctrl_handler *ctrl_handler;
enum v4l2_priority prio;
/* Events */
wait_queue_head_t wait;
struct mutex subscribe_lock;
struct list_head subscribed;
struct list_head available;
unsigned int navailable;
u32 sequence;
struct v4l2_m2m_ctx *m2m_ctx;
};
- list:链表入口,因为一个设备可能有好几条消息队列。(一般情况下打开一次设备会创建一个消息队列,不过一般请看下只会打开一次)
- vdev:拥有此消息队列的video设备
- ctrl_handler:这其中也牵扯很多其它结构体,只需要了解这与控制元素相关就可以了。
- prio:消息队列优先级。
- wait:等待队列,由于可能有几个线程同时访问消息队列,所有等待消息队列可用的线程都会记录在这个等待列表中。
- subscribed:这个是订阅消息链表。只有订阅的消息才能够queue到消息队列中,反之是无法queue到队列中的。
- available:消息队列,可用的消息都以链表的形式保存在这里。
- navailable:消息队列中可用消息的数量。
- sequence:序列号,此数据域会一直自加下去,直到内核对象消亡。
注意:struct v4l2_fh结构体一般保存在struct file的private_data数据域。一般打开video设备文件时,会在标准的open接口中调用v4l2_fh_open接口。如下的代码中可以发现在open时会为struct v4l2_fh分配内存。
drivers/media/v4l2-core/v4l2-fh.c
int v4l2_fh_open(struct file *filp)
{
struct video_device *vdev = video_devdata(filp);
struct v4l2_fh *fh = kzalloc(sizeof(*fh), GFP_KERNEL);
filp->private_data = fh;
if (fh == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
v4l2_fh_init(fh, vdev);
v4l2_fh_add(fh);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(v4l2_fh_open);
3.6、struct video_device
video_device一般用来描述一个出帧的设备,所以从kernel中的dev目录下,发现有几个videoX设备,即可认为有几个Camera.
include/media/v4l2-dev.h
struct video_device {
#if defined(CONFIG_MEDIA_CONTROLLER)
struct media_entity entity;
struct media_intf_devnode *intf_devnode;
struct media_pipeline pipe;
#endif
const struct v4l2_file_operations *fops;
u32 device_caps;
/* sysfs */
struct device dev;
struct cdev *cdev;
struct v4l2_device *v4l2_dev;
struct device *dev_parent;
struct v4l2_ctrl_handler *ctrl_handler;
struct vb2_queue *queue;
struct v4l2_prio_state *prio;
/* device info */
char name[32];
enum vfl_devnode_type vfl_type;
enum vfl_devnode_direction vfl_dir;
int minor;
u16 num;
unsigned long flags;
int index;
/* V4L2 file handles */
spinlock_t fh_lock;
struct list_head fh_list;
int dev_debug;
v4l2_std_id tvnorms;
/* callbacks */
void (*release)(struct video_device *vdev);
const struct v4l2_ioctl_ops *ioctl_ops;
DECLARE_BITMAP(valid_ioctls, BASE_VIDIOC_PRIVATE);
struct mutex *lock;
};
- entity:video设备的入口属性,可用于查找video设备的名字和属性组。
- fops:此fops包含标准的open,ioctl,close等接口,该一系列接口会被包含在v4l2-dev.c中的标准字符设备的open,ioctl,close接口调用,后面会画一个简单的包含调用关系。
- cdev:为在v4l2-dev.c中创建的字符设备对象
- v4l2_dev:该video设备所依附的v4l2_device设备对象,不能为空。
- fh_lock:该video设备的消息队列锁,消息队列任何时候只能有一个线程在访问。
- fh_list:此video设备的消息队列,可以包含多个消息队列(每当打开一次video设备即会创建一个消息队列)
- ioctl_ops:v4l2核心调用的标准接口,包含stream_on,stream_off等。
3.7、struct v4l2_ioctl_ops
include/media/v4l2-ioctl.h
struct v4l2_ioctl_ops {
/* ioctl callbacks */
/* VIDIOC_QUERYCAP handler */
int (*vidioc_querycap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_capability *cap);
/* VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT handlers */
int (*vidioc_enum_fmt_vid_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f);
int (*vidioc_enum_fmt_vid_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f);
int (*vidioc_enum_fmt_vid_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f);
int (*vidioc_enum_fmt_sdr_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f);
int (*vidioc_enum_fmt_sdr_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f);
int (*vidioc_enum_fmt_meta_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f);
int (*vidioc_enum_fmt_meta_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_fmtdesc *f);
/* VIDIOC_G_FMT handlers */
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vid_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vid_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vid_out_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vbi_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vbi_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_sliced_vbi_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_sliced_vbi_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vid_cap_mplane)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_vid_out_mplane)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_sdr_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_sdr_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_meta_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_g_fmt_meta_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
/* VIDIOC_S_FMT handlers */
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vid_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vid_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vid_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vid_out_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vbi_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vbi_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_sliced_vbi_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_sliced_vbi_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vid_cap_mplane)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_vid_out_mplane)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_sdr_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_sdr_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_meta_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_s_fmt_meta_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
/* VIDIOC_TRY_FMT handlers */
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vid_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vid_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vid_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vid_out_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vbi_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vbi_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_sliced_vbi_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_sliced_vbi_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vid_cap_mplane)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_vid_out_mplane)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_sdr_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_sdr_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_meta_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
int (*vidioc_try_fmt_meta_out)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_format *f);
/* Buffer handlers */
int (*vidioc_reqbufs)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_requestbuffers *b);
int (*vidioc_querybuf)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_buffer *b);
int (*vidioc_qbuf)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_buffer *b);
int (*vidioc_expbuf)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_exportbuffer *e);
int (*vidioc_dqbuf)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_buffer *b);
int (*vidioc_create_bufs)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_create_buffers *b);
int (*vidioc_prepare_buf)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_buffer *b);
int (*vidioc_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh, unsigned int i);
int (*vidioc_g_fbuf)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_framebuffer *a);
int (*vidioc_s_fbuf)(struct file *file, void *fh,
const struct v4l2_framebuffer *a);
/* Stream on/off */
int (*vidioc_streamon)(struct file *file, void *fh,
enum v4l2_buf_type i);
int (*vidioc_streamoff)(struct file *file, void *fh,
enum v4l2_buf_type i);
/*
* Standard handling
*
* Note: ENUMSTD is handled by videodev.c
*/
int (*vidioc_g_std)(struct file *file, void *fh, v4l2_std_id *norm);
int (*vidioc_s_std)(struct file *file, void *fh, v4l2_std_id norm);
int (*vidioc_querystd)(struct file *file, void *fh, v4l2_std_id *a);
/* Input handling */
int (*vidioc_enum_input)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_input *inp);
int (*vidioc_g_input)(struct file *file, void *fh, unsigned int *i);
int (*vidioc_s_input)(struct file *file, void *fh, unsigned int i);
/* Output handling */
int (*vidioc_enum_output)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_output *a);
int (*vidioc_g_output)(struct file *file, void *fh, unsigned int *i);
int (*vidioc_s_output)(struct file *file, void *fh, unsigned int i);
/* Control handling */
int (*vidioc_queryctrl)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_queryctrl *a);
int (*vidioc_query_ext_ctrl)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_query_ext_ctrl *a);
int (*vidioc_g_ctrl)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_control *a);
int (*vidioc_s_ctrl)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_control *a);
int (*vidioc_g_ext_ctrls)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_ext_controls *a);
int (*vidioc_s_ext_ctrls)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_ext_controls *a);
int (*vidioc_try_ext_ctrls)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_ext_controls *a);
int (*vidioc_querymenu)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_querymenu *a);
/* Audio ioctls */
int (*vidioc_enumaudio)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_audio *a);
int (*vidioc_g_audio)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_audio *a);
int (*vidioc_s_audio)(struct file *file, void *fh,
const struct v4l2_audio *a);
/* Audio out ioctls */
int (*vidioc_enumaudout)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_audioout *a);
int (*vidioc_g_audout)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_audioout *a);
int (*vidioc_s_audout)(struct file *file, void *fh,
const struct v4l2_audioout *a);
int (*vidioc_g_modulator)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_modulator *a);
int (*vidioc_s_modulator)(struct file *file, void *fh,
const struct v4l2_modulator *a);
/* Crop ioctls */
int (*vidioc_g_pixelaspect)(struct file *file, void *fh,
int buf_type, struct v4l2_fract *aspect);
int (*vidioc_g_selection)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_selection *s);
int (*vidioc_s_selection)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_selection *s);
/* Compression ioctls */
int (*vidioc_g_jpegcomp)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_jpegcompression *a);
int (*vidioc_s_jpegcomp)(struct file *file, void *fh,
const struct v4l2_jpegcompression *a);
int (*vidioc_g_enc_index)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_enc_idx *a);
int (*vidioc_encoder_cmd)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_encoder_cmd *a);
int (*vidioc_try_encoder_cmd)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_encoder_cmd *a);
int (*vidioc_decoder_cmd)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_decoder_cmd *a);
int (*vidioc_try_decoder_cmd)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_decoder_cmd *a);
/* Stream type-dependent parameter ioctls */
int (*vidioc_g_parm)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_streamparm *a);
int (*vidioc_s_parm)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_streamparm *a);
/* Tuner ioctls */
int (*vidioc_g_tuner)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_tuner *a);
int (*vidioc_s_tuner)(struct file *file, void *fh,
const struct v4l2_tuner *a);
int (*vidioc_g_frequency)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_frequency *a);
int (*vidioc_s_frequency)(struct file *file, void *fh,
const struct v4l2_frequency *a);
int (*vidioc_enum_freq_bands)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_frequency_band *band);
/* Sliced VBI cap */
int (*vidioc_g_sliced_vbi_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_sliced_vbi_cap *a);
/* Log status ioctl */
int (*vidioc_log_status)(struct file *file, void *fh);
int (*vidioc_s_hw_freq_seek)(struct file *file, void *fh,
const struct v4l2_hw_freq_seek *a);
/* Debugging ioctls */
#ifdef CONFIG_VIDEO_ADV_DEBUG
int (*vidioc_g_register)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_dbg_register *reg);
int (*vidioc_s_register)(struct file *file, void *fh,
const struct v4l2_dbg_register *reg);
int (*vidioc_g_chip_info)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_dbg_chip_info *chip);
#endif
int (*vidioc_enum_framesizes)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_frmsizeenum *fsize);
int (*vidioc_enum_frameintervals)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_frmivalenum *fival);
/* DV Timings IOCTLs */
int (*vidioc_s_dv_timings)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_dv_timings *timings);
int (*vidioc_g_dv_timings)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_dv_timings *timings);
int (*vidioc_query_dv_timings)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_dv_timings *timings);
int (*vidioc_enum_dv_timings)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_enum_dv_timings *timings);
int (*vidioc_dv_timings_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_dv_timings_cap *cap);
int (*vidioc_g_edid)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_edid *edid);
int (*vidioc_s_edid)(struct file *file, void *fh,
struct v4l2_edid *edid);
int (*vidioc_subscribe_event)(struct v4l2_fh *fh,
const struct v4l2_event_subscription *sub);
int (*vidioc_unsubscribe_event)(struct v4l2_fh *fh,
const struct v4l2_event_subscription *sub);
/* For other private ioctls */
long (*vidioc_default)(struct file *file, void *fh,
bool valid_prio, unsigned int cmd, void *arg);
};
此结构体中包含了很多方法,鉴于篇幅太长,这里就列举几个简单常用的示意一下。详细代码还是看源码吧。
- vidioc_querycap:这个用于获取设备能力的接口,一般在操作设备之前,应用软件需要先获取到设备的能力,才能下发与之匹配的命令。要不然有些命令,很难服从。
- vidioc_g_priority:见名知意,获取权限相关的。(标准的set,get)
3.8、struct v4l2_subdev
include/media/v4l2-subdev.h
struct v4l2_subdev {
#if defined(CONFIG_MEDIA_CONTROLLER)
struct media_entity entity;
#endif
struct list_head list;
struct module *owner;
bool owner_v4l2_dev;
u32 flags;
struct v4l2_device *v4l2_dev;
const struct v4l2_subdev_ops *ops;
const struct v4l2_subdev_internal_ops *internal_ops;
struct v4l2_ctrl_handler *ctrl_handler;
char name[V4L2_SUBDEV_NAME_SIZE];
u32 grp_id;
void *dev_priv;
void *host_priv;
struct video_device *devnode;
struct device *dev;
struct fwnode_handle *fwnode;
struct list_head async_list;
struct list_head async_subdev_endpoint_list;
struct v4l2_async_notifier *subdev_notifier;
struct list_head asc_list;
struct v4l2_subdev_platform_data *pdata;
struct mutex *state_lock;
/*
* The fields below are private, and should only be accessed via
* appropriate functions.
*/
struct led_classdev *privacy_led;
/*
* TODO: active_state should most likely be changed from a pointer to an
* embedded field. For the time being it's kept as a pointer to more
* easily catch uses of active_state in the cases where the driver
* doesn't support it.
*/
struct v4l2_subdev_state *active_state;
u64 enabled_streams;
};
- v4l2_dev:该子设备所依附的v4l2_device(注意v4l2_device存在的作用就是便于访问和记录子设备)
- internal_ops:子设备的注册/注销以及打开/关闭接口,这个会被v4l2-subdev.c中标准的open/close接口调用。所以是内部的。
- ctrl_handler:该子设备的消息队列管理对象。
- devnode:子设备的设备对象,其实subdev也是一个video_device,只是由v4l2核心把设备节点名字更改了罢了。
3.9、struct v4l2_subdev_ops
include/media/v4l2-subdev.h
- 接口结构体介绍
struct v4l2_subdev_ops {
const struct v4l2_subdev_core_ops *core;
const struct v4l2_subdev_tuner_ops *tuner;
const struct v4l2_subdev_audio_ops *audio;
const struct v4l2_subdev_video_ops *video;
const struct v4l2_subdev_vbi_ops *vbi;
const struct v4l2_subdev_ir_ops *ir;
const struct v4l2_subdev_sensor_ops *sensor;
const struct v4l2_subdev_pad_ops *pad;
};
上面包含所以子设备的操作接口,可以看到有video,audio,ir,sensor等媒体设备。这里其实常用的只是core域所包含的方法。
static const struct v4l2_subdev_internal_ops msm_eeprom_internal_ops = {
.open = msm_eeprom_open,
.close = msm_eeprom_close,
};
//上面包含标准的接口,会被v4l2-subdev.c中的open/close调用
static struct v4l2_subdev_core_ops msm_eeprom_subdev_core_ops = {
.ioctl = msm_eeprom_subdev_ioctl,
};
//如上面实现了当前eeprom专属的ioctl,用户可以在此接口添加自己的ioctl命令
static struct v4l2_subdev_ops msm_eeprom_subdev_ops = {
.core = &msm_eeprom_subdev_core_ops,
};
//上面
上面以高通的eeprom子设备为例子,介绍了子设备的接口实现。最后的msm_eeprom_subdev_ops 会被注册到v4l2_subdev的ops域。
v4l2-dev.c
|(1.open/clsoe/ioctl)
|
|----->v4l2-subdev.c
|(2.sub-dev,open,close,ioctl)
|
|-------->msm_eeprom.c
|-------->3.(open,close,ioctl)
调用流程如上所示
1.v4l2-dev.c中实现了标准的open,close,ioctl,这些是真正被字符设备使用的。
2.v4l2-subdev.c中的open,close,ioctl被v4l2-dev中对应的接口调用
3.此为用户自己定义的,同样被上一级调用
drivers/media/v4l2-core/v4l2-subdev.c
- ioctl扩展
static long subdev_do_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, void *arg,
struct v4l2_subdev_state *state)
{
struct video_device *vdev = video_devdata(file);
struct v4l2_subdev *sd = vdev_to_v4l2_subdev(vdev);
struct v4l2_fh *vfh = file->private_data;
struct v4l2_subdev_fh *subdev_fh = to_v4l2_subdev_fh(vfh);
bool ro_subdev = test_bit(V4L2_FL_SUBDEV_RO_DEVNODE, &vdev->flags);
bool streams_subdev = sd->flags & V4L2_SUBDEV_FL_STREAMS;
bool client_supports_streams = subdev_fh->client_caps &
V4L2_SUBDEV_CLIENT_CAP_STREAMS;
int rval;
/*
* If the streams API is not enabled, remove V4L2_SUBDEV_CAP_STREAMS.
* Remove this when the API is no longer experimental.
*/
if (!v4l2_subdev_enable_streams_api)
streams_subdev = false;
switch (cmd) {
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_QUERYCAP: {
struct v4l2_subdev_capability *cap = arg;
memset(cap->reserved, 0, sizeof(cap->reserved));
cap->version = LINUX_VERSION_CODE;
cap->capabilities =
(ro_subdev ? V4L2_SUBDEV_CAP_RO_SUBDEV : 0) |
(streams_subdev ? V4L2_SUBDEV_CAP_STREAMS : 0);
return 0;
}
case VIDIOC_QUERYCTRL:
/*
* TODO: this really should be folded into v4l2_queryctrl (this
* currently returns -EINVAL for NULL control handlers).
* However, v4l2_queryctrl() is still called directly by
* drivers as well and until that has been addressed I believe
* it is safer to do the check here. The same is true for the
* other control ioctls below.
*/
if (!vfh->ctrl_handler)
return -ENOTTY;
return v4l2_queryctrl(vfh->ctrl_handler, arg);
case VIDIOC_QUERY_EXT_CTRL:
if (!vfh->ctrl_handler)
return -ENOTTY;
return v4l2_query_ext_ctrl(vfh->ctrl_handler, arg);
case VIDIOC_QUERYMENU:
if (!vfh->ctrl_handler)
return -ENOTTY;
return v4l2_querymenu(vfh->ctrl_handler, arg);
case VIDIOC_G_CTRL:
if (!vfh->ctrl_handler)
return -ENOTTY;
return v4l2_g_ctrl(vfh->ctrl_handler, arg);
case VIDIOC_S_CTRL:
if (!vfh->ctrl_handler)
return -ENOTTY;
return v4l2_s_ctrl(vfh, vfh->ctrl_handler, arg);
case VIDIOC_G_EXT_CTRLS:
if (!vfh->ctrl_handler)
return -ENOTTY;
return v4l2_g_ext_ctrls(vfh->ctrl_handler,
vdev, sd->v4l2_dev->mdev, arg);
case VIDIOC_S_EXT_CTRLS:
if (!vfh->ctrl_handler)
return -ENOTTY;
return v4l2_s_ext_ctrls(vfh, vfh->ctrl_handler,
vdev, sd->v4l2_dev->mdev, arg);
case VIDIOC_TRY_EXT_CTRLS:
if (!vfh->ctrl_handler)
return -ENOTTY;
return v4l2_try_ext_ctrls(vfh->ctrl_handler,
vdev, sd->v4l2_dev->mdev, arg);
case VIDIOC_DQEVENT:
if (!(sd->flags & V4L2_SUBDEV_FL_HAS_EVENTS))
return -ENOIOCTLCMD;
return v4l2_event_dequeue(vfh, arg, file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK);
case VIDIOC_SUBSCRIBE_EVENT:
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, core, subscribe_event, vfh, arg);
case VIDIOC_UNSUBSCRIBE_EVENT:
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, core, unsubscribe_event, vfh, arg);
#ifdef CONFIG_VIDEO_ADV_DEBUG
case VIDIOC_DBG_G_REGISTER:
{
struct v4l2_dbg_register *p = arg;
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, core, g_register, p);
}
case VIDIOC_DBG_S_REGISTER:
{
struct v4l2_dbg_register *p = arg;
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, core, s_register, p);
}
case VIDIOC_DBG_G_CHIP_INFO:
{
struct v4l2_dbg_chip_info *p = arg;
if (p->match.type != V4L2_CHIP_MATCH_SUBDEV || p->match.addr)
return -EINVAL;
if (sd->ops->core && sd->ops->core->s_register)
p->flags |= V4L2_CHIP_FL_WRITABLE;
if (sd->ops->core && sd->ops->core->g_register)
p->flags |= V4L2_CHIP_FL_READABLE;
strscpy(p->name, sd->name, sizeof(p->name));
return 0;
}
#endif
case VIDIOC_LOG_STATUS: {
int ret;
pr_info("%s: ================= START STATUS =================\n",
sd->name);
ret = v4l2_subdev_call(sd, core, log_status);
pr_info("%s: ================== END STATUS ==================\n",
sd->name);
return ret;
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_G_FMT: {
struct v4l2_subdev_format *format = arg;
if (!client_supports_streams)
format->stream = 0;
memset(format->reserved, 0, sizeof(format->reserved));
memset(format->format.reserved, 0, sizeof(format->format.reserved));
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, pad, get_fmt, state, format);
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_S_FMT: {
struct v4l2_subdev_format *format = arg;
if (format->which != V4L2_SUBDEV_FORMAT_TRY && ro_subdev)
return -EPERM;
if (!client_supports_streams)
format->stream = 0;
memset(format->reserved, 0, sizeof(format->reserved));
memset(format->format.reserved, 0, sizeof(format->format.reserved));
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, pad, set_fmt, state, format);
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_G_CROP: {
struct v4l2_subdev_crop *crop = arg;
struct v4l2_subdev_selection sel;
if (!client_supports_streams)
crop->stream = 0;
memset(crop->reserved, 0, sizeof(crop->reserved));
memset(&sel, 0, sizeof(sel));
sel.which = crop->which;
sel.pad = crop->pad;
sel.target = V4L2_SEL_TGT_CROP;
rval = v4l2_subdev_call(
sd, pad, get_selection, state, &sel);
crop->rect = sel.r;
return rval;
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_S_CROP: {
struct v4l2_subdev_crop *crop = arg;
struct v4l2_subdev_selection sel;
if (crop->which != V4L2_SUBDEV_FORMAT_TRY && ro_subdev)
return -EPERM;
if (!client_supports_streams)
crop->stream = 0;
memset(crop->reserved, 0, sizeof(crop->reserved));
memset(&sel, 0, sizeof(sel));
sel.which = crop->which;
sel.pad = crop->pad;
sel.target = V4L2_SEL_TGT_CROP;
sel.r = crop->rect;
rval = v4l2_subdev_call(
sd, pad, set_selection, state, &sel);
crop->rect = sel.r;
return rval;
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_ENUM_MBUS_CODE: {
struct v4l2_subdev_mbus_code_enum *code = arg;
if (!client_supports_streams)
code->stream = 0;
memset(code->reserved, 0, sizeof(code->reserved));
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, pad, enum_mbus_code, state,
code);
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_ENUM_FRAME_SIZE: {
struct v4l2_subdev_frame_size_enum *fse = arg;
if (!client_supports_streams)
fse->stream = 0;
memset(fse->reserved, 0, sizeof(fse->reserved));
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, pad, enum_frame_size, state,
fse);
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_G_FRAME_INTERVAL: {
struct v4l2_subdev_frame_interval *fi = arg;
if (!client_supports_streams)
fi->stream = 0;
memset(fi->reserved, 0, sizeof(fi->reserved));
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, video, g_frame_interval, arg);
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_S_FRAME_INTERVAL: {
struct v4l2_subdev_frame_interval *fi = arg;
if (ro_subdev)
return -EPERM;
if (!client_supports_streams)
fi->stream = 0;
memset(fi->reserved, 0, sizeof(fi->reserved));
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, video, s_frame_interval, arg);
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_ENUM_FRAME_INTERVAL: {
struct v4l2_subdev_frame_interval_enum *fie = arg;
if (!client_supports_streams)
fie->stream = 0;
memset(fie->reserved, 0, sizeof(fie->reserved));
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, pad, enum_frame_interval, state,
fie);
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_G_SELECTION: {
struct v4l2_subdev_selection *sel = arg;
if (!client_supports_streams)
sel->stream = 0;
memset(sel->reserved, 0, sizeof(sel->reserved));
return v4l2_subdev_call(
sd, pad, get_selection, state, sel);
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_S_SELECTION: {
struct v4l2_subdev_selection *sel = arg;
if (sel->which != V4L2_SUBDEV_FORMAT_TRY && ro_subdev)
return -EPERM;
if (!client_supports_streams)
sel->stream = 0;
memset(sel->reserved, 0, sizeof(sel->reserved));
return v4l2_subdev_call(
sd, pad, set_selection, state, sel);
}
case VIDIOC_G_EDID: {
struct v4l2_subdev_edid *edid = arg;
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, pad, get_edid, edid);
}
case VIDIOC_S_EDID: {
struct v4l2_subdev_edid *edid = arg;
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, pad, set_edid, edid);
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_DV_TIMINGS_CAP: {
struct v4l2_dv_timings_cap *cap = arg;
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, pad, dv_timings_cap, cap);
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_ENUM_DV_TIMINGS: {
struct v4l2_enum_dv_timings *dvt = arg;
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, pad, enum_dv_timings, dvt);
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_QUERY_DV_TIMINGS:
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, video, query_dv_timings, arg);
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_G_DV_TIMINGS:
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, video, g_dv_timings, arg);
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_S_DV_TIMINGS:
if (ro_subdev)
return -EPERM;
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, video, s_dv_timings, arg);
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_G_STD:
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, video, g_std, arg);
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_S_STD: {
v4l2_std_id *std = arg;
if (ro_subdev)
return -EPERM;
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, video, s_std, *std);
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_ENUMSTD: {
struct v4l2_standard *p = arg;
v4l2_std_id id;
if (v4l2_subdev_call(sd, video, g_tvnorms, &id))
return -EINVAL;
return v4l_video_std_enumstd(p, id);
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_QUERYSTD:
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, video, querystd, arg);
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_G_ROUTING: {
struct v4l2_subdev_routing *routing = arg;
struct v4l2_subdev_krouting *krouting;
if (!v4l2_subdev_enable_streams_api)
return -ENOIOCTLCMD;
if (!(sd->flags & V4L2_SUBDEV_FL_STREAMS))
return -ENOIOCTLCMD;
memset(routing->reserved, 0, sizeof(routing->reserved));
krouting = &state->routing;
if (routing->num_routes < krouting->num_routes) {
routing->num_routes = krouting->num_routes;
return -ENOSPC;
}
memcpy((struct v4l2_subdev_route *)(uintptr_t)routing->routes,
krouting->routes,
krouting->num_routes * sizeof(*krouting->routes));
routing->num_routes = krouting->num_routes;
return 0;
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_S_ROUTING: {
struct v4l2_subdev_routing *routing = arg;
struct v4l2_subdev_route *routes =
(struct v4l2_subdev_route *)(uintptr_t)routing->routes;
struct v4l2_subdev_krouting krouting = {};
unsigned int i;
if (!v4l2_subdev_enable_streams_api)
return -ENOIOCTLCMD;
if (!(sd->flags & V4L2_SUBDEV_FL_STREAMS))
return -ENOIOCTLCMD;
if (routing->which != V4L2_SUBDEV_FORMAT_TRY && ro_subdev)
return -EPERM;
memset(routing->reserved, 0, sizeof(routing->reserved));
for (i = 0; i < routing->num_routes; ++i) {
const struct v4l2_subdev_route *route = &routes[i];
const struct media_pad *pads = sd->entity.pads;
if (route->sink_stream > V4L2_SUBDEV_MAX_STREAM_ID ||
route->source_stream > V4L2_SUBDEV_MAX_STREAM_ID)
return -EINVAL;
if (route->sink_pad >= sd->entity.num_pads)
return -EINVAL;
if (!(pads[route->sink_pad].flags &
MEDIA_PAD_FL_SINK))
return -EINVAL;
if (route->source_pad >= sd->entity.num_pads)
return -EINVAL;
if (!(pads[route->source_pad].flags &
MEDIA_PAD_FL_SOURCE))
return -EINVAL;
}
krouting.num_routes = routing->num_routes;
krouting.routes = routes;
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, pad, set_routing, state,
routing->which, &krouting);
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_G_CLIENT_CAP: {
struct v4l2_subdev_client_capability *client_cap = arg;
client_cap->capabilities = subdev_fh->client_caps;
return 0;
}
case VIDIOC_SUBDEV_S_CLIENT_CAP: {
struct v4l2_subdev_client_capability *client_cap = arg;
/*
* Clear V4L2_SUBDEV_CLIENT_CAP_STREAMS if streams API is not
* enabled. Remove this when streams API is no longer
* experimental.
*/
if (!v4l2_subdev_enable_streams_api)
client_cap->capabilities &= ~V4L2_SUBDEV_CLIENT_CAP_STREAMS;
/* Filter out unsupported capabilities */
client_cap->capabilities &= V4L2_SUBDEV_CLIENT_CAP_STREAMS;
subdev_fh->client_caps = client_cap->capabilities;
return 0;
}
default:
return v4l2_subdev_call(sd, core, ioctl, cmd, arg);
}
return 0;
}
上面是v4l2-subdev中实现的ioctl,其它命令都是标准的,用户需要实现对应的功能才能调用,要不然可能会出异常。default即可以调用用户自己定义的命令,可以看到对应的就是core方法中的ioctl方法,这也就是上面高通定义的。
3.10、小结
经过上面的总结,可以大概知道设备从属关系如下所示:
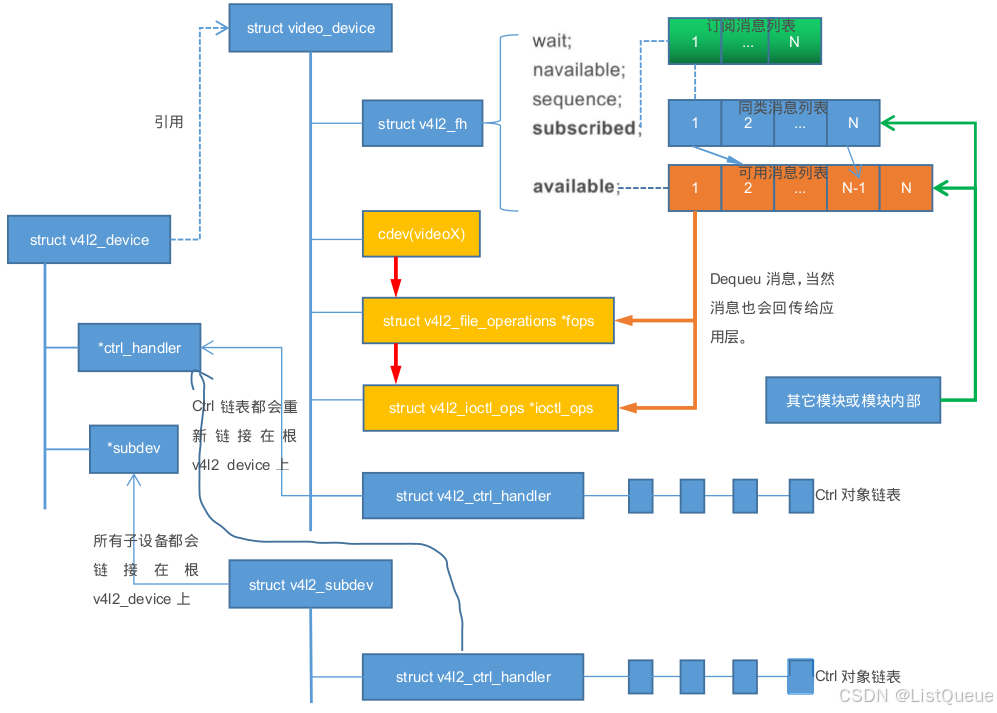
- v4l2_device记录所有子设备和支持的control命令,便于用户查找设备(只是记录)。其实用户查找设备,一般通过下面即将介绍的
struct media_entity entity结构来记录。所有子设备的media_entiry对象都会挂接到v4l2_device对应的media设备上。 - video和sub_device的等级属于同一级别,只是在注册设备时取了不同名字而已。
四、meida_device介绍
- media_device.c:该为media设备的通用操作公共接口
- media_devnode.c:此为media设备对应的字符设备驱动标准接口,注册的media设备都是使用一套接口的。注意做一下客制化。
media_devnode.c
|
|------------>media_device.c(公用)
4.1、media_device重要的结构体介绍
就目前个人了解到,media设备存在的意义,便于发现媒体设备内部的拓扑结构。就目前v4l2框架使用media设备,只是为了发现v4l2子设备的拓扑结构。所以也不会记录太深入。
include/media/media-device.h
struct media_device {
/* dev->driver_data points to this struct. */
struct device *dev;
struct media_devnode *devnode;
char model[32];
char driver_name[32];
char serial[40];
char bus_info[32];
u32 hw_revision;
u64 topology_version;
u32 id;
struct ida entity_internal_idx;
int entity_internal_idx_max;
struct list_head entities;
struct list_head interfaces;
struct list_head pads;
struct list_head links;
/* notify callback list invoked when a new entity is registered */
struct list_head entity_notify;
/* Serializes graph operations. */
struct mutex graph_mutex;
struct media_graph pm_count_walk;
void *source_priv;
int (*enable_source)(struct media_entity *entity,
struct media_pipeline *pipe);
void (*disable_source)(struct media_entity *entity);
const struct media_device_ops *ops;
struct mutex req_queue_mutex;
atomic_t request_id;
};
部分域介绍
- dev:对应的父设备对象,一般是v4l2-device对象。
- devnode:当前media设备对象,其实还是字符设备。
- model:设备模型,可以根据这个来查找设备
- entities:设备入口双向链表,所有设备都会挂接到这里。
之前一直没看结构体的注释,老是认为dev指针域就是指media设备的设备对象。看到注释才发现是父设备。真正的media设备是struct media_devnode devnode, 但是这个结构体中有很多猫腻。具体请看下面结构体。每一个media设备都是字符设备,他们也有自己的属性文件(这一注册过程会记录在下一篇笔记中)。
ret = device_create_file(&mdev->devnode.dev, &dev_attr_model);
属性文件的路径是:/sys/bus/media/devices/media0(高通平台为例)
msm:/sys/bus/media/devices # ls -l
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 1970-01-06 01:01 media0 -> …/…/…/devices/soc/1b00000.qcom,msm-cam/media0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 1970-01-06 01:01 media1 -> …/…/…/devices/soc/1b0c000.qcom,cci/1b0c000.qcom,cci:qcom,camera@0/media1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 1970-01-06 01:01 media2 -> …/…/…/devices/soc/1b0c000.qcom,cci/1b0c000.qcom,cci:qcom,camera@2/media2
4.2、media_devnode
include/media/media-devnode.h
struct media_devnode {
struct media_device *media_dev;
/* device ops */
const struct media_file_operations *fops;
/* sysfs */
struct device dev; /* media device */
struct cdev cdev; /* character device */
struct device *parent; /* device parent */
/* device info */
int minor;
unsigned long flags; /* Use bitops to access flags */
/* callbacks */
void (*release)(struct media_devnode *devnode);
};
此结构对应一个字符设备
- 1dev:这里明确指出是meida设备。
- 2 cdev:也明确指出是字符设备。
- 3 parent:明确指出是父亲节点,这个就是上面media_device设备的父亲节点。可以把media_device中的dev指针域当作所有子节点的的父节点。
4.3、struct media_file_operations
include/media/media-devnode.h
struct media_file_operations {
struct module *owner;
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
__poll_t (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
long (*ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
int (*open) (struct file *);
int (*release) (struct file *);
};
上面的接口定义在media_device.c中,但会被media_devnode.c中的标准接口调用。





















 674
674

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








