Linux MMC子系统4(基于Linux6.6)---MMC host模块介绍
一、概述
1.1、MMC Host模块概述
Linux 中的 MMC Host模块实现了与不同类型的 MMC 存储设备(如 SD 卡、eMMC 卡等)的通信接口。该模块与硬件相关的控制逻辑(如卡插拔、数据传输等)结合在一起,为操作系统提供一致的 API,以便高层应用与存储设备交互。
主要职责:
- 初始化和管理 MMC 主机控制器。
- 提供 数据读写 功能,确保数据能够在主机和 MMC 卡之间正确传输。
- 卡插拔管理,检测和处理卡的插入与拔出。
- 电源管理,对 MMC 卡提供必要的电源控制。
1.2、MMC Host模块的工作原理
MMC Host模块通过硬件接口与 MMC 存储设备进行通信。在 Linux 内核中,MMC host 控制器通常由一个设备驱动来表示,该驱动可以是与硬件相关的特定驱动(例如,SD/MMC 控制器的驱动)。
核心流程:
-
主机控制器初始化:
- 驱动程序在加载时初始化 MMC 主机控制器。通常,它会通过设备树(Device Tree)或 ACPI 等机制来识别硬件。
- 主机控制器驱动会注册到内核中的 MMC 子系统,以便系统能够发现和管理与该控制器连接的 MMC 卡。
-
卡的插入和拔出检测:
- MMC 卡的插入和拔出是通过硬件中断或轮询机制来检测的。主机控制器驱动会响应这些事件。
- 当检测到卡插入时,主机控制器会初始化卡并将其加入到内核的 MMC 子系统中。
- 当卡被拔出时,内核会释放相关资源并通知上层。
-
数据传输:
- 一旦卡被识别并准备好,MMC Host 驱动会提供接口,允许用户空间或内核中的块设备层进行读写操作。
- 数据传输是通过 DMA(Direct Memory Access)或中断驱动的方式进行的。MMC Host 驱动会负责管理传输过程。
-
卡的管理:
- MMC Host模块还会管理与卡的配置和状态相关的信息,例如卡的容量、类型、读取和写入的时序。
-
电源管理:
- MMC Host模块还负责管理电源的切换与控制,确保电源状态在不同的工作模式(例如,休眠模式和工作模式)之间切换。
1.3、MMC Host 控制器的类型
Linux 支持多种不同类型的 MMC 主机控制器。这些控制器根据硬件平台的不同,可能会有不同的实现方式。
- SDHCI(Secure Digital Host Controller Interface):SDHCI 是一种标准接口,广泛应用于支持 SD 卡的控制器。
- eMMC 控制器:eMMC 是一种嵌入式多媒体卡,具有类似于 SD 卡的工作原理,但其设计主要用于内嵌存储。
- UHS-I/II 控制器:这些是支持高速传输的控制器,通常支持更高的数据传输速率,适用于 UHS 卡。
- MMC 本地控制器:某些嵌入式系统使用定制的本地控制器,它们可能不完全符合 SDHCI 标准,但仍然能够支持 MMC 卡。
二、相关的数据结构及关联
该模块最重要的数据结构为mmc_host,用于描述一个mmc controller,而围绕着mmc controller又定义了相应的数据结构,用于描述mmc controller的各种行为(包括针对该mmc controller的访问方法抽象而来的数据结构mmc_host_ops、该mmc controller相关的参数抽象而来的数据结构体mmc_ios、针对mmc card相关的电源管理及在位检测方法抽象而来的数据结构mmc_bus_ops)等。
这些结构体之间的关联如下图所示,这些数据结构以mmc_host为核心,围绕着mmc_host定义了相应的数据结构与方法。它们之间的关联简要说明如下:
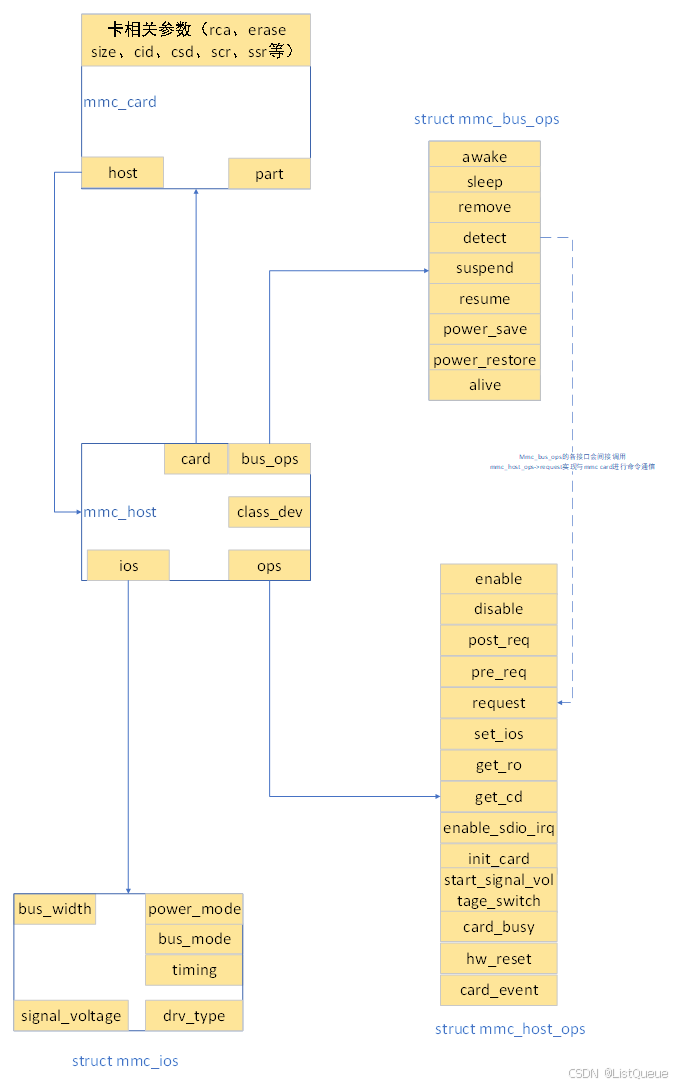
- mmc_host、mmc_card之间的绑定关系,当通过中断/poll机制检测到mmc_card后,即完成它们之间的绑定工作(通常mmc_rescan完成mmc_card的在位检测等等);
- mmc_host的总线相关的参数均定义于mmc_ios中,通过该类型的变量,即可完成mmccontroller的总线配置等;
- mmc_host借助mmc_bus_ops中的成员,即可完成针对mmc_card的sleep/awake,即完成mmc card的休眠与唤醒,也支持mmc card的remove,实现mmc card的注销等等功能;
- 针对mmc_controller而访问方法,抽象了mmc_bus_ops结构体,该结构体的成员实现mmc_controller的访问方法(主要是request接口),这类似于i2c模块的transfer以及spi模块的spi_sync/spi_async方法,均是controller访问device的方法。
2.1、mmc_host数据结构
如下mmc_host的定义,该结构体的内容较多,此处忽略了些,主要的定义内容如下:
- 定义device类型的变量,主要用来使用设备模型相关的接口,以及在sysfs/下完成对应设备目录及属性文件的创建以及用于与用户层通信相关的event、纳入mmc host class中等等,此处的变量用于借助设备模型与系统中注册的设备、class完成关联等;
- 定义mmc_host_ops类型的变量,用于定义本mmc_host的操作接口(包括与mmc card通信的接口request、卡检测相关的接口等);
- 定义块设备相关的参数,包括段大小、块大小等等;
- 定义mmc_host的能力集相关的参数,包括4bit数据模式、mmc high speed mode、sd high speed mode、spi mode、8bit data、noneremovable mode(emmc mode)、cd与wp引脚的active high/low等等;
- 定义mmc_ios类型的变量,主要用于记录该mmc host的总线时钟频率、位宽、模式、电压等信息;
- 定义mmc_card类型的变量,主要用于mmc_host与mmc_card的绑定;
- 定义mmc_slot类型的变量,主要用于实现卡的在位检测等(目前该成员基本上不使用,只需cd引脚或者poll模式即可进行mmc card的在位检测等),这也是卡的在位检测的一种手段,不过目前大多数mmc_host驱动基本上不使用该变量;
- Mmc card检测相关的延迟工作队列(主要用于mmc_rescan机制使用,在mmc_alloc_host中即设置该工作队列的callback为mmc_rescan,该机制支持poll、中断两种方式,针对中断方式,则在各mmc_host的cd引脚对应的中断处理函数中调用mmc_detect_change接口即调度该工作队列的callback;针对poll机制,则只需设置mmc_host的caps变量,置位MMC_CAP_NEEDS_POLL即可)
include/linux/mmc/host.h
struct mmc_host {
struct device *parent;
struct device class_dev;
struct mmc_devfeq_clk_scaling clk_scaling;
int index;
const struct mmc_host_ops *ops;
const struct mmc_cmdq_host_ops *cmdq_ops;
struct mmc_pwrseq *pwrseq;
unsigned int f_min;
unsigned int f_max;
unsigned int f_init;
u32 ocr_avail;
u32 ocr_avail_sdio; /* SDIO-specific OCR */
u32 ocr_avail_sd; /* SD-specific OCR */
u32 ocr_avail_mmc; /* MMC-specific OCR */
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP
struct notifier_block pm_notify;
#endif
u32 max_current_330;
u32 max_current_300;
u32 max_current_180;
u32 caps; /* Host capabilities */
u32 caps2; /* More host capabilities */
u32 cached_caps2;
mmc_pm_flag_t pm_caps; /* supported pm features */
#ifdef CONFIG_MMC_CLKGATE
int clk_requests; /* internal reference counter */
unsigned int clk_delay; /* number of MCI clk hold cycles */
bool clk_gated; /* clock gated */
struct workqueue_struct *clk_gate_wq; /* clock gate work queue */
struct delayed_work clk_gate_work; /* delayed clock gate */
unsigned int clk_old; /* old clock value cache */
spinlock_t clk_lock; /* lock for clk fields */
struct mutex clk_gate_mutex; /* mutex for clock gating */
struct device_attribute clkgate_delay_attr;
unsigned long clkgate_delay;
#endif
/* host specific block data */
unsigned int max_seg_size; /* see blk_queue_max_segment_size */
unsigned short max_segs; /* see blk_queue_max_segments */
unsigned short unused;
unsigned int max_req_size; /* maximum number of bytes in one req */
unsigned int max_blk_size; /* maximum size of one mmc block */
unsigned int max_blk_count; /* maximum number of blocks in one req */
unsigned int max_busy_timeout; /* max busy timeout in ms */
/* private data */
spinlock_t lock; /* lock for claim and bus ops */
struct mmc_ios ios; /* current io bus settings */
struct mmc_ios cached_ios;
/* group bitfields together to minimize padding */
unsigned int use_spi_crc:1;
unsigned int claimed:1; /* host exclusively claimed */
unsigned int bus_dead:1; /* bus has been released */
#ifdef CONFIG_MMC_DEBUG
unsigned int removed:1; /* host is being removed */
#endif
unsigned int can_retune:1; /* re-tuning can be used */
unsigned int doing_retune:1; /* re-tuning in progress */
unsigned int retune_now:1; /* do re-tuning at next req */
unsigned int retune_paused:1; /* re-tuning is temporarily disabled */
int rescan_disable; /* disable card detection */
int rescan_entered; /* used with nonremovable devices */
int need_retune; /* re-tuning is needed */
int hold_retune; /* hold off re-tuning */
unsigned int retune_period; /* re-tuning period in secs */
struct timer_list retune_timer; /* for periodic re-tuning */
bool trigger_card_event; /* card_event necessary */
struct mmc_card *card; /* device attached to this host */
wait_queue_head_t wq;
struct task_struct *claimer; /* task that has host claimed */
struct task_struct *suspend_task;
int claim_cnt; /* "claim" nesting count */
struct delayed_work detect;
int detect_change; /* card detect flag */
struct mmc_slot slot;
const struct mmc_bus_ops *bus_ops; /* current bus driver */
unsigned int bus_refs; /* reference counter */
unsigned int bus_resume_flags;
#define MMC_BUSRESUME_MANUAL_RESUME (1 << 0)
#define MMC_BUSRESUME_NEEDS_RESUME (1 << 1)
bool ignore_bus_resume_flags;
unsigned int sdio_irqs;
struct task_struct *sdio_irq_thread;
bool sdio_irq_pending;
atomic_t sdio_irq_thread_abort;
mmc_pm_flag_t pm_flags; /* requested pm features */
struct led_trigger *led; /* activity led */
#ifdef CONFIG_REGULATOR
bool regulator_enabled; /* regulator state */
#endif
struct mmc_supply supply;
struct dentry *debugfs_root;
bool err_occurred;
u32 err_stats[MMC_ERR_MAX];
ktime_t last_failed_rq_time;
ktime_t last_completed_rq_time;
struct mmc_async_req *areq; /* active async req */
struct mmc_context_info context_info; /* async synchronization info */
/* Ongoing data transfer that allows commands during transfer */
struct mmc_request *ongoing_mrq;
#ifdef CONFIG_FAIL_MMC_REQUEST
struct fault_attr fail_mmc_request;
#endif
unsigned int actual_clock; /* Actual HC clock rate */
unsigned int slotno; /* used for sdio acpi binding */
int dsr_req; /* DSR value is valid */
u32 dsr; /* optional driver stage (DSR) value */
#ifdef CONFIG_MMC_EMBEDDED_SDIO
struct {
struct sdio_cis *cis;
struct sdio_cccr *cccr;
struct sdio_embedded_func *funcs;
int num_funcs;
} embedded_sdio_data;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_BLOCK
int latency_hist_enabled;
struct io_latency_state io_lat_read;
struct io_latency_state io_lat_write;
#endif
bool sdr104_wa;
/*
* Set to 1 to just stop the SDCLK to the card without
* actually disabling the clock from it's source.
*/
bool card_clock_off;
struct extcon_dev *extcon;
struct notifier_block card_detect_nb;
#ifdef CONFIG_MMC_PERF_PROFILING
struct {
unsigned long rbytes_drv; /* Rd bytes MMC Host */
unsigned long wbytes_drv; /* Wr bytes MMC Host */
ktime_t rtime_drv; /* Rd time MMC Host */
ktime_t wtime_drv; /* Wr time MMC Host */
ktime_t start;
} perf;
bool perf_enable;
#endif
struct mmc_trace_buffer trace_buf;
enum dev_state dev_status;
bool wakeup_on_idle;
struct mmc_cmdq_context_info cmdq_ctx;
int num_cq_slots;
int dcmd_cq_slot;
bool cmdq_thist_enabled;
/*
* several cmdq supporting host controllers are extensions
* of legacy controllers. This variable can be used to store
* a reference to the cmdq extension of the existing host
* controller.
*/
void *cmdq_private;
struct mmc_request *err_mrq;
bool inlinecrypt_support; /* Inline encryption support */
atomic_t rpmb_req_pending;
struct mutex rpmb_req_mutex;
unsigned long private[0] ____cacheline_aligned;
};
2.2、Mmc card
该结构体变量的定义如下,主要内容如下:
- host完成mmc_card与mmc_host的绑定;
- dev完成将该mmc_card与系统中的设备、总线、驱动的关联(即完成与系统设备驱动总线的关联与绑定操作);
- 卡类型与卡状态记录
- 卡相关的寄存器信息记录(主要从mmc card中读取),包括cid、csd、scr、ssr等内容
- Mmc card的分区信息,主要完成块设备的创建(由mmc driver实现)
- 若为sdio设备,则有cccr、cis等(关于sdio的部分,请参考sdio协议相关的文档)
include/linux/mmc/card.h
/*
* MMC device
*/
struct mmc_card {
struct mmc_host *host; /* the host this device belongs to */
struct device dev; /* the device */
u32 ocr; /* the current OCR setting */
unsigned int rca; /* relative card address of device */
unsigned int type; /* card type */
#define MMC_TYPE_MMC 0 /* MMC card */
#define MMC_TYPE_SD 1 /* SD card */
#define MMC_TYPE_SDIO 2 /* SDIO card */
#define MMC_TYPE_SD_COMBO 3 /* SD combo (IO+mem) card */
unsigned int state; /* (our) card state */
unsigned int quirks; /* card quirks */
unsigned int quirk_max_rate; /* max rate set by quirks */
#define MMC_QUIRK_LENIENT_FN0 (1<<0) /* allow SDIO FN0 writes outside of the VS CCCR range */
#define MMC_QUIRK_BLKSZ_FOR_BYTE_MODE (1<<1) /* use func->cur_blksize */
/* for byte mode */
#define MMC_QUIRK_NONSTD_SDIO (1<<2) /* non-standard SDIO card attached */
/* (missing CIA registers) */
#define MMC_QUIRK_NONSTD_FUNC_IF (1<<4) /* SDIO card has nonstd function interfaces */
#define MMC_QUIRK_DISABLE_CD (1<<5) /* disconnect CD/DAT[3] resistor */
#define MMC_QUIRK_INAND_CMD38 (1<<6) /* iNAND devices have broken CMD38 */
#define MMC_QUIRK_BLK_NO_CMD23 (1<<7) /* Avoid CMD23 for regular multiblock */
#define MMC_QUIRK_BROKEN_BYTE_MODE_512 (1<<8) /* Avoid sending 512 bytes in */
/* byte mode */
#define MMC_QUIRK_LONG_READ_TIME (1<<9) /* Data read time > CSD says */
#define MMC_QUIRK_SEC_ERASE_TRIM_BROKEN (1<<10) /* Skip secure for erase/trim */
#define MMC_QUIRK_BROKEN_IRQ_POLLING (1<<11) /* Polling SDIO_CCCR_INTx could create a fake interrupt */
#define MMC_QUIRK_TRIM_BROKEN (1<<12) /* Skip trim */
#define MMC_QUIRK_BROKEN_HPI (1<<13) /* Disable broken HPI support */
#define MMC_QUIRK_BROKEN_SD_DISCARD (1<<14) /* Disable broken SD discard support */
#define MMC_QUIRK_BROKEN_SD_CACHE (1<<15) /* Disable broken SD cache support */
#define MMC_QUIRK_BROKEN_CACHE_FLUSH (1<<16) /* Don't flush cache until the write has occurred */
bool written_flag; /* Indicates eMMC has been written since power on */
bool reenable_cmdq; /* Re-enable Command Queue */
unsigned int erase_size; /* erase size in sectors */
unsigned int erase_shift; /* if erase unit is power 2 */
unsigned int pref_erase; /* in sectors */
unsigned int eg_boundary; /* don't cross erase-group boundaries */
unsigned int erase_arg; /* erase / trim / discard */
u8 erased_byte; /* value of erased bytes */
u32 raw_cid[4]; /* raw card CID */
u32 raw_csd[4]; /* raw card CSD */
u32 raw_scr[2]; /* raw card SCR */
u32 raw_ssr[16]; /* raw card SSR */
struct mmc_cid cid; /* card identification */
struct mmc_csd csd; /* card specific */
struct mmc_ext_csd ext_csd; /* mmc v4 extended card specific */
struct sd_scr scr; /* extra SD information */
struct sd_ssr ssr; /* yet more SD information */
struct sd_switch_caps sw_caps; /* switch (CMD6) caps */
struct sd_ext_reg ext_power; /* SD extension reg for PM */
struct sd_ext_reg ext_perf; /* SD extension reg for PERF */
unsigned int sdio_funcs; /* number of SDIO functions */
atomic_t sdio_funcs_probed; /* number of probed SDIO funcs */
struct sdio_cccr cccr; /* common card info */
struct sdio_cis cis; /* common tuple info */
struct sdio_func *sdio_func[SDIO_MAX_FUNCS]; /* SDIO functions (devices) */
struct sdio_func *sdio_single_irq; /* SDIO function when only one IRQ active */
u8 major_rev; /* major revision number */
u8 minor_rev; /* minor revision number */
unsigned num_info; /* number of info strings */
const char **info; /* info strings */
struct sdio_func_tuple *tuples; /* unknown common tuples */
unsigned int sd_bus_speed; /* Bus Speed Mode set for the card */
unsigned int mmc_avail_type; /* supported device type by both host and card */
unsigned int drive_strength; /* for UHS-I, HS200 or HS400 */
struct dentry *debugfs_root;
struct mmc_part part[MMC_NUM_PHY_PARTITION]; /* physical partitions */
unsigned int nr_parts;
struct workqueue_struct *complete_wq; /* Private workqueue */
};
mmc_ios
该结构体主要定义mmc总线相关的参数,主要包括时钟频率、电源、总线模式、电源状态、总线带宽、支持的信号电压值等等这些参数的设置可通过mmc_host_ops->set_ios实现。
include/linux/mmc/host.h
struct mmc_ios {
unsigned int clock; /* clock rate */
unsigned short vdd;
unsigned int power_delay_ms; /* waiting for stable power */
/* vdd stores the bit number of the selected voltage range from below. */
unsigned char bus_mode; /* command output mode */
#define MMC_BUSMODE_OPENDRAIN 1
#define MMC_BUSMODE_PUSHPULL 2
unsigned char chip_select; /* SPI chip select */
#define MMC_CS_DONTCARE 0
#define MMC_CS_HIGH 1
#define MMC_CS_LOW 2
unsigned char power_mode; /* power supply mode */
#define MMC_POWER_OFF 0
#define MMC_POWER_UP 1
#define MMC_POWER_ON 2
#define MMC_POWER_UNDEFINED 3
unsigned char bus_width; /* data bus width */
#define MMC_BUS_WIDTH_1 0
#define MMC_BUS_WIDTH_4 2
#define MMC_BUS_WIDTH_8 3
unsigned char timing; /* timing specification used */
#define MMC_TIMING_LEGACY 0
#define MMC_TIMING_MMC_HS 1
#define MMC_TIMING_SD_HS 2
#define MMC_TIMING_UHS_SDR12 3
#define MMC_TIMING_UHS_SDR25 4
#define MMC_TIMING_UHS_SDR50 5
#define MMC_TIMING_UHS_SDR104 6
#define MMC_TIMING_UHS_DDR50 7
#define MMC_TIMING_MMC_DDR52 8
#define MMC_TIMING_MMC_HS200 9
#define MMC_TIMING_MMC_HS400 10
#define MMC_TIMING_SD_EXP 11
#define MMC_TIMING_SD_EXP_1_2V 12
unsigned char signal_voltage; /* signalling voltage (1.8V or 3.3V) */
#define MMC_SIGNAL_VOLTAGE_330 0
#define MMC_SIGNAL_VOLTAGE_180 1
#define MMC_SIGNAL_VOLTAGE_120 2
unsigned char drv_type; /* driver type (A, B, C, D) */
#define MMC_SET_DRIVER_TYPE_B 0
#define MMC_SET_DRIVER_TYPE_A 1
#define MMC_SET_DRIVER_TYPE_C 2
#define MMC_SET_DRIVER_TYPE_D 3
bool enhanced_strobe; /* hs400es selection */
};
2.3、mmc_host_ops
该数据结构定义了mmc_host的操作方法,主要包括如下:
- 若mmc_host支持enable、disable,则需要实现这两个接口(可参考mmc_controller的用户手册);
- pre_req、request、post_req主要定义了mmc controller访问mmc card的方法,mmc controller驱动至少应完成request接口的定义
- set_ios接口主要用于设置mmc_controller总线相关的参数,mmc_host需要完成该接口的定义;
- get_ro用于获取mmc card 的读写权限,若mmc controller提供检测mmc card读写权限的功能,则需要提供该接口
- get_cd为卡是否在位的检测接口(该接口非必须),可查看mmc controller的用户手册,确定是否支持;
- init_card接口为mmc card初始化接口,这个主要是对mmc card/mmc controller一些特定的初始化参数,若没有需要特殊对待项,该接口不需要事先;
- 剩下几个接口,大多数驱动也没有实现,这几个接口可参考具体的mmc协议,大多数的mmc host驱动基本上不需要实现。
include/linux/mmc/host.h
struct mmc_host_ops {
/*
* It is optional for the host to implement pre_req and post_req in
* order to support double buffering of requests (prepare one
* request while another request is active).
* pre_req() must always be followed by a post_req().
* To undo a call made to pre_req(), call post_req() with
* a nonzero err condition.
*/
void (*post_req)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_request *req,
int err);
void (*pre_req)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_request *req);
void (*request)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_request *req);
/* Submit one request to host in atomic context. */
int (*request_atomic)(struct mmc_host *host,
struct mmc_request *req);
/*
* Avoid calling the next three functions too often or in a "fast
* path", since underlaying controller might implement them in an
* expensive and/or slow way. Also note that these functions might
* sleep, so don't call them in the atomic contexts!
*/
/*
* Notes to the set_ios callback:
* ios->clock might be 0. For some controllers, setting 0Hz
* as any other frequency works. However, some controllers
* explicitly need to disable the clock. Otherwise e.g. voltage
* switching might fail because the SDCLK is not really quiet.
*/
void (*set_ios)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_ios *ios);
/*
* Return values for the get_ro callback should be:
* 0 for a read/write card
* 1 for a read-only card
* -ENOSYS when not supported (equal to NULL callback)
* or a negative errno value when something bad happened
*/
int (*get_ro)(struct mmc_host *host);
/*
* Return values for the get_cd callback should be:
* 0 for a absent card
* 1 for a present card
* -ENOSYS when not supported (equal to NULL callback)
* or a negative errno value when something bad happened
*/
int (*get_cd)(struct mmc_host *host);
void (*enable_sdio_irq)(struct mmc_host *host, int enable);
/* Mandatory callback when using MMC_CAP2_SDIO_IRQ_NOTHREAD. */
void (*ack_sdio_irq)(struct mmc_host *host);
/* optional callback for HC quirks */
void (*init_card)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_card *card);
int (*start_signal_voltage_switch)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_ios *ios);
/* Check if the card is pulling dat[0] low */
int (*card_busy)(struct mmc_host *host);
/* The tuning command opcode value is different for SD and eMMC cards */
int (*execute_tuning)(struct mmc_host *host, u32 opcode);
/* Prepare HS400 target operating frequency depending host driver */
int (*prepare_hs400_tuning)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_ios *ios);
/* Execute HS400 tuning depending host driver */
int (*execute_hs400_tuning)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_card *card);
/* Optional callback to prepare for SD high-speed tuning */
int (*prepare_sd_hs_tuning)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_card *card);
/* Optional callback to execute SD high-speed tuning */
int (*execute_sd_hs_tuning)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_card *card);
/* Prepare switch to DDR during the HS400 init sequence */
int (*hs400_prepare_ddr)(struct mmc_host *host);
/* Prepare for switching from HS400 to HS200 */
void (*hs400_downgrade)(struct mmc_host *host);
/* Complete selection of HS400 */
void (*hs400_complete)(struct mmc_host *host);
/* Prepare enhanced strobe depending host driver */
void (*hs400_enhanced_strobe)(struct mmc_host *host,
struct mmc_ios *ios);
int (*select_drive_strength)(struct mmc_card *card,
unsigned int max_dtr, int host_drv,
int card_drv, int *drv_type);
/* Reset the eMMC card via RST_n */
void (*card_hw_reset)(struct mmc_host *host);
void (*card_event)(struct mmc_host *host);
/*
* Optional callback to support controllers with HW issues for multiple
* I/O. Returns the number of supported blocks for the request.
*/
int (*multi_io_quirk)(struct mmc_card *card,
unsigned int direction, int blk_size);
/* Initialize an SD express card, mandatory for MMC_CAP2_SD_EXP. */
int (*init_sd_express)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_ios *ios);
#ifdef CONFIG_SCM_CM
void (*auto_clk_gate)(struct mmc_host *host, int auto_gate);
void (*pre_select_hs400)(struct mmc_host *host);
void (*post_select_hs400)(struct mmc_host *host);
void (*pre_hs400_to_hs200)(struct mmc_host *host);
void (*dump_host_register)(struct mmc_host *host);
void (*encrypt_config)(struct mmc_host *host, unsigned int enc_flag);
#endif
};
2.4、mmc_bus_ops
该接口主要是针对mmc card的sleep/awake的操作,因mmc card也需要进行sleep/awake等接口,这些接口类似于设备驱动的电源管理(suspend/resume)相关的接口。该结构体中的成员,不需要进行实现,mmc子系统已经完成,mmc子系统根据mmc各协议版本针对sleep/awake的支持情况,实现对应的操作:
- 若为mmc 4.3及以上的协议,则支持sleep/awake接口;
- remove接口实现mmc card的移除操作,主要是解除mmc card与mmc host的绑定,并将mmc card从mmc 总线上移除;
- detect/alive主要是卡在位检测以及卡是否移除检测;
- 针对suspend/resume接口,针对mmc 不同版本的协议,其功能有所不同:
- 若card支持poweroff notify机制,则进入poweroff状态;
- 若card支持sleep状态,则进入sleep状态,针对mmc rev>=1.3的情况;
- card不支持以上两种状态,则向card发送deselect命令。
- 针对power_restore接口,即为mmc_power_restore接口,该接口目前即调用mmc_init_card,根据mmc 协议,完成mmc card的初始化操作。
drivers/mmc/core/core.h
struct mmc_bus_ops {
void (*remove)(struct mmc_host *);
void (*detect)(struct mmc_host *);
int (*pre_suspend)(struct mmc_host *);
int (*suspend)(struct mmc_host *);
int (*resume)(struct mmc_host *);
int (*runtime_suspend)(struct mmc_host *);
int (*runtime_resume)(struct mmc_host *);
int (*alive)(struct mmc_host *);
int (*shutdown)(struct mmc_host *);
int (*hw_reset)(struct mmc_host *);
int (*sw_reset)(struct mmc_host *);
bool (*cache_enabled)(struct mmc_host *);
int (*flush_cache)(struct mmc_host *);
};
以上即是mmc host相关的数据结构及其关联。上面没有介绍mmc_request、mmc_command等结构体,这些结构体主要是用于传输mmc相关的命令和数据,这些结构体主要用于完成数据传输的,此处不再详述。
三、Mmc host相关的接口
从两个方面进行介绍mmc host相关的接口:mmc host的添加、mmc host的移除。已经介绍了mmc_host数据结构及其关联,因此针对mmc host的添加而言,需要对mmc host相关的参数进行初始化,主要包括块设备相关参数的配置、cd/wp相关的接口定义、mmc_host_ops中相应函数的实现(包括request、set_ios、get_ro、get_cd)等,然后调用mmc_add_host将该host对应的device注册至系统的device_kset中,并与mmc_host_class关联。
3.1、Mmc host的添加
针对mmc host的添加,主要涉及mmc_alloc_host、mmc_add_host这两个接口。
3.1.1、mmc_alloc_host接口分析
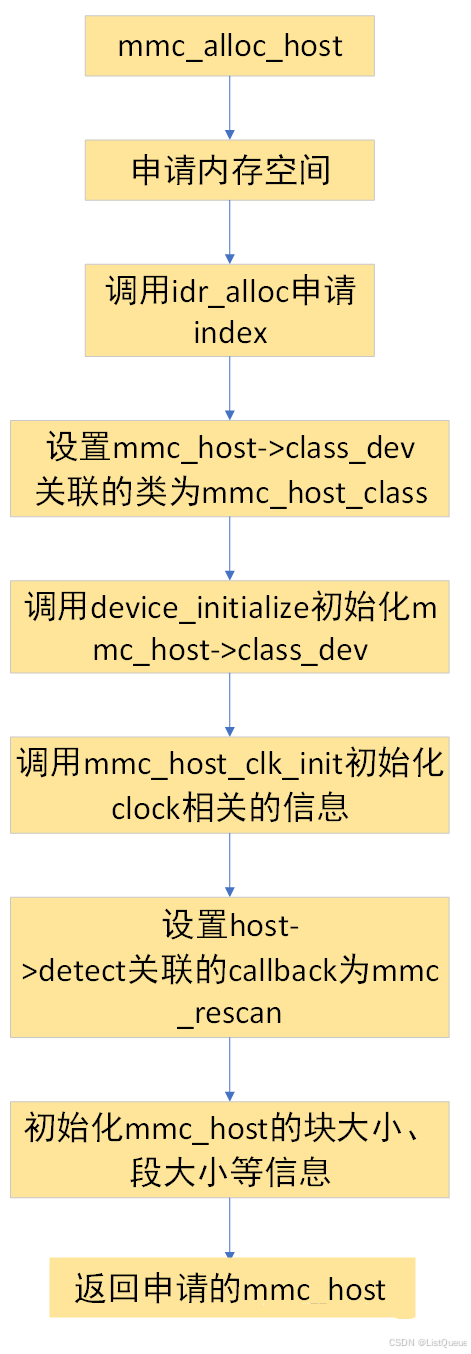
该接口主要用于申请一个mmc_host类型的内存空间,并对申请的mmc_host进行初始化,主要内容如下:
- 此mmc_host类型变量的内存是动态申请的,该mmc_host内存的释放与否由引用计数mmc_host->class_dev.kobject.kref决定,当引用计数为0时,则调用kobject->kobj_type->release进行释放,该接口最终调用mmc_host_class->dev_release接口,实现mmc_host的释放
- 调用device_initialize进行mmc_host->class_dev的初始化,主要设置该class_dev所依附的device_kset及kobj_type等(该接口是设备驱动模型中的接口,想详细了解的朋友,请参考之前写的文章),通过设置该class_dev属于mmc_host_class。
- 初始化host->detect队列,并设置该队列对应的处理接口为mmc_rescan,用于mmc/sd卡的检测,具体应用如下:
- 若该mmc_host支持卡的在位检测(一般通过cd引脚检测,并配置成中断模式),则在中断处理函数中可调用mmc_detect_change,唤醒该延迟工作队列,即调用mmc_rescan实现卡的rescan;
- 若mmc_host不支持卡的在位检测功能(即不存在cd引脚检测),则将mmc_host设置为poll模式,在poll模式下,当在执行mmc_add_host时执行一次mmc_rescan时,在mmc_rescan的结尾根据该poll模式,设置延迟调度该队列的时间为1s,则该延迟工作队列以1s为周期进行卡的rescan。
drivers/mmc/core/host.c
/**
* mmc_alloc_host - initialise the per-host structure.
* @extra: sizeof private data structure
* @dev: pointer to host device model structure
*
* Initialise the per-host structure.
*/
struct mmc_host *mmc_alloc_host(int extra, struct device *dev)
{
int index;
struct mmc_host *host;
int alias_id, min_idx, max_idx;
host = kzalloc(sizeof(struct mmc_host) + extra, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!host)
return NULL;
/* scanning will be enabled when we're ready */
host->rescan_disable = 1;
alias_id = of_alias_get_id(dev->of_node, "mmc");
if (alias_id >= 0) {
index = alias_id;
} else {
min_idx = mmc_first_nonreserved_index();
max_idx = 0;
index = ida_simple_get(&mmc_host_ida, min_idx, max_idx, GFP_KERNEL);
if (index < 0) {
kfree(host);
return NULL;
}
}
host->index = index;
dev_set_name(&host->class_dev, "mmc%d", host->index);
host->ws = wakeup_source_register(NULL, dev_name(&host->class_dev));
host->parent = dev;
host->class_dev.parent = dev;
host->class_dev.class = &mmc_host_class;
device_initialize(&host->class_dev);
device_enable_async_suspend(&host->class_dev);
if (mmc_gpio_alloc(host)) {
put_device(&host->class_dev);
return NULL;
}
spin_lock_init(&host->lock);
init_waitqueue_head(&host->wq);
INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&host->detect, mmc_rescan);
INIT_WORK(&host->sdio_irq_work, sdio_irq_work);
timer_setup(&host->retune_timer, mmc_retune_timer, 0);
/*
* By default, hosts do not support SGIO or large requests.
* They have to set these according to their abilities.
*/
host->max_segs = 1;
host->max_seg_size = PAGE_SIZE;
host->max_req_size = PAGE_SIZE;
host->max_blk_size = 512;
host->max_blk_count = PAGE_SIZE / 512;
host->fixed_drv_type = -EINVAL;
host->ios.power_delay_ms = 10;
host->ios.power_mode = MMC_POWER_UNDEFINED;
return host;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(mmc_alloc_host);
针对mmc_alloc_host接口,比较重要的即为上述3中的host->detect队列的初始化,通过对该队列的设置,则可以接入mmc子系统的mmc rescan流程,实现mmc card的rescan功能。
3.1.2、mmc_add_host接口
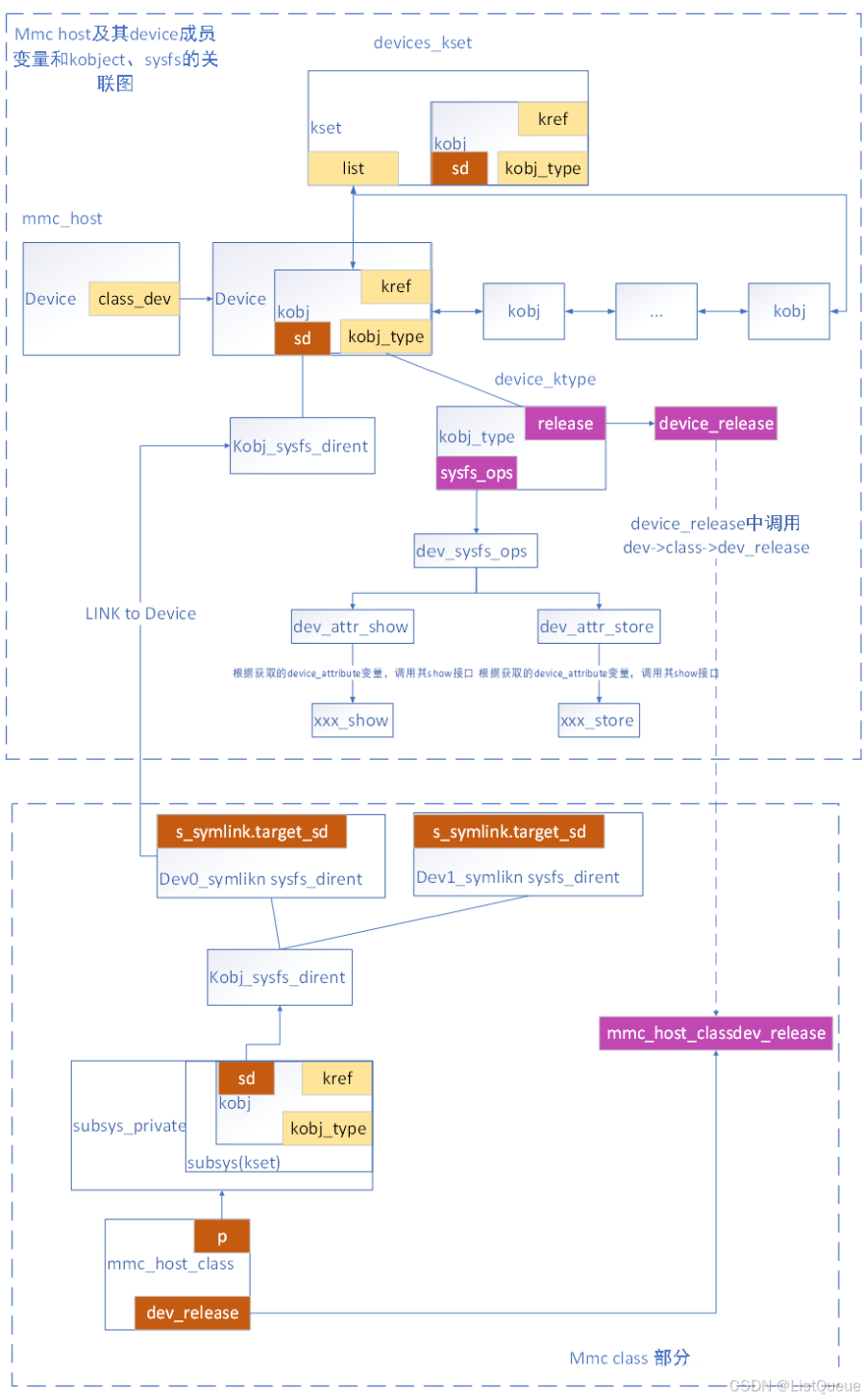
该接口主要完成将mmc_host对应的class_dev注册至系统的device_kset中,并完成与mmc_host_class的关联操作。该接口主要完成如下两个功能:
- 调用device_add接口,完成mmc_host与系统device_kset、mmc_host_class的关联,经过此步骤后则在sysfs目录下完成该mmc_host对应kobject的目录创建以及相关的属性文件的创建,并完成与mmc_host_class的关联;
- 调用mmc_start_host接口,从而调用mmc_detect_change接口,唤醒mmc_host->detect队列,从而执行mmc_rescan接口,执行一次mmc rescan操作。
drivers/mmc/core/host.c
/**
* mmc_add_host - initialise host hardware
* @host: mmc host
*
* Register the host with the driver model. The host must be
* prepared to start servicing requests before this function
* completes.
*/
int mmc_add_host(struct mmc_host *host)
{
int err;
err = mmc_validate_host_caps(host);
if (err)
return err;
err = device_add(&host->class_dev);
if (err)
return err;
led_trigger_register_simple(dev_name(&host->class_dev), &host->led);
mmc_add_host_debugfs(host);
mmc_start_host(host);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(mmc_add_host);

经过以上两个接口后,mmc_host即完成了与mmc_host_class、device_kset的关联,即完成了mmc_host与设备驱动模型间的关联,数据结构之间的关联如下。
3.2、Mmc host移除
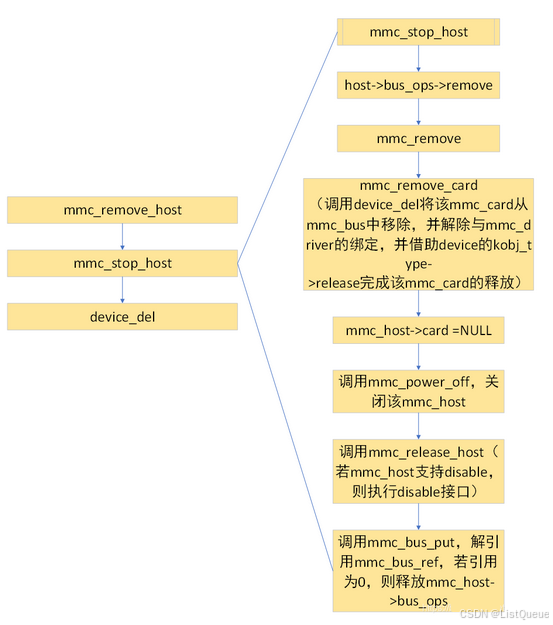
Mmc host移除的接口为mmc_remove_host,该接口实现的功能,可分为如下几种:
- 调用mmc_stop_host接口,完成如下几个功能:
- 调用mmc_host->bus_ops->remove,即mmc_remove接口(此处针对mmc/sd,针对sdio,则不是该接口),实现mmc_card对应的device类型成员的注销,解除与mmc_bus、mmc_driver的绑定(同时也会去除mmc block device的注销);
- 调用mmc_power_off、mmc_release_host,关闭mmc controller;
- 调用mmc_bus_put,主要用于解除mmc_host与mmc_host_ops的绑定;
- 调用device_del,注销该mmc_host对应的class_dev,同时借助device模型的device_release接口,最终调用mmc_host_classdev_release接口,释放mmc_host对应的动态内存,完成mmc_host的释放操作。
drivers/mmc/core/core.c
void mmc_stop_host(struct mmc_host *host)
{
__mmc_stop_host(host);
/* clear pm flags now and let card drivers set them as needed */
host->pm_flags = 0;
if (host->bus_ops) {
/* Calling bus_ops->remove() with a claimed host can deadlock */
host->bus_ops->remove(host);
mmc_claim_host(host);
mmc_detach_bus(host);
mmc_power_off(host);
mmc_release_host(host);
return;
}
mmc_claim_host(host);
mmc_power_off(host);
mmc_release_host(host);
}
以上便是mmc_host的添加与移除的接口。
四、完成一个mmc host驱动需要哪些步骤
4.1、mmc_host_ops相关的接口实现
实现mmc_host_ops中各函数指针,针对mmc_host_ops,如下几个接口需要重点关注:
- 必须要实现的函数为request(该接口为mmc controller的通信方法);
- set_ios(该接口用于设置mmc controller的总线相关的参数:总线位宽、总线模式等等,可参考mmc_ios数据结构),
- get_ro接口主要用于判断一个mmc_card是否是只读的(该接口不是必须的);
- get_cd接口主要用于卡的在位检测的,可根据硬件设计决定是否需要实现该接口;
- enable/disable为使能/去使能mmc controller接口,这个与具体的mmc controller有关;
4.2、platform driver的实现
针对一个 mmc host driver,在目前的内核中(不管是否使用设备树),一般创建一个platform driver驱动,该驱动与mmc host对应的platform device关联,而在platform driver的probe接口中,进行mmc host的创建与添加操作。
4.3、platform driver的probe接口中实现mmc host的添加
- 调用mmc_alloc_host接口,申请一个mmc_host类型的变量,并进行初始化;
- 对mmc_host进行设置,包括设置mmc_host的caps(如emmc,则设置MMC_CAP_NONREMOVABLE)、若不支持卡在位检测引脚,则设置mmc_host的caps的MMC_CAP_NEEDS_POLL位等;
- 设置mmc_host的ops为上述一中定义的变量;
- 调用mmc_add_host,将该mmc_host注册至系统,并完成一次mmc rescan操作。
针对mmc host驱动而言,大致即为以上步骤,当然了针对mmc controller的复杂程度以及mmc controller通信相关的dma等操作,mmc host驱动的编写可能不是那么简单,但知道上述流程后,并参考其他厂家的host驱动,相对而言不会太复杂。
4.4实现步骤详解
1. 添加头文件与定义数据结构
包括 MMC 子系统相关的头文件,并定义驱动所需的控制器数据结构。
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/mmc/host.h>
#include <linux/mmc/card.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/io.h> // 用于内存映射IO
2. 定义硬件控制器的初始化函数
初始化硬件控制器的寄存器和硬件资源。您需要实现对硬件的配置和初始化,包括时钟、复位、DMA、IRQ等。
static int my_mmc_host_init(struct mmc_host *host)
{
// 硬件初始化代码
// 比如配置硬件寄存器、时钟设置、DMA配置等
return 0;
}
3. 定义请求处理函数
MMCHost 驱动必须实现对 mmc_request 请求的处理。每次 MMC 卡需要读写数据时,都会通过 mmc_request 结构体传递请求。在此函数中,需要处理读取或写入数据的操作。
static int my_mmc_request(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_request *mrq)
{
struct mmc_command *cmd = mrq->cmd;
struct mmc_data *data = mrq->data;
// 根据命令类型处理不同的请求
if (cmd) {
// 处理命令
}
if (data) {
// 处理数据传输
if (data->flags & MMC_DATA_READ) {
// 读取数据
} else if (data->flags & MMC_DATA_WRITE) {
// 写入数据
}
}
return 0;
}
4. 实现 mmc_ops 操作接口
需要定义一个 mmc_ops 结构体,包含必要的操作函数,例如卡初始化、请求处理、启动命令等。
static const struct mmc_ops my_mmc_ops = {
.init = my_mmc_host_init, // 初始化函数
.request = my_mmc_request, // 处理请求函数
// 其他必要的操作
};
5. 配置 MMC 主机控制器
创建并配置 mmc_host 结构体,并设置必要的硬件操作接口。使用 mmc_add_host() 函数注册主机控制器。
static int my_mmc_host_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct mmc_host *host;
int ret;
// 分配并初始化 mmc_host 结构体
host = mmc_alloc_host(0, &pdev->dev);
if (!host) {
return -ENOMEM;
}
// 设置操作接口
host->ops = &my_mmc_ops;
// 初始化硬件
ret = my_mmc_host_init(host);
if (ret) {
mmc_free_host(host);
return ret;
}
// 注册主机控制器
ret = mmc_add_host(host);
if (ret) {
mmc_free_host(host);
return ret;
}
return 0;
}
6. 检测卡的插拔事件
对于插拔事件,可以通过硬件中断或轮询来检测。当检测到卡插入或拔出时,需要执行相应的操作。
static void my_mmc_card_inserted(struct mmc_host *host)
{
// 处理卡插入事件,初始化卡,配置参数等
}
static void my_mmc_card_removed(struct mmc_host *host)
{
// 处理卡拔出事件,释放资源,停止DMA等
}
7. 电源管理
管理电源切换非常重要,尤其在嵌入式系统中。需要实现电源开启、关闭及时钟控制等操作。
static int my_mmc_host_suspend(struct device *dev)
{
// 关闭时钟或进入低功耗模式
return 0;
}
static int my_mmc_host_resume(struct device *dev)
{
// 恢复时钟或退出低功耗模式
return 0;
}
8. 清理工作
在驱动卸载时,需要清理分配的资源,注销 MMC 主机控制器,释放内存。
static int my_mmc_host_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct mmc_host *host = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
mmc_remove_host(host);
mmc_free_host(host);
return 0;
}
9. 注册平台设备和驱动
最后,在设备树或者通过 platform_device 和 platform_driver 来注册设备和驱动。
static struct platform_driver my_mmc_driver = {
.probe = my_mmc_host_probe,
.remove = my_mmc_host_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "my_mmc_host_driver",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
};
module_platform_driver(my_mmc_driver);
10.测试与调试
开发完驱动后,您需要进行测试:
- 使用 dmesg 和 /var/log/messages 等日志工具来调试和检查驱动的输出。
- 在实际硬件上插入和拔出 MMC 卡,观察驱动是否能正确响应。
- 运行
mmc工具和其他测试用例来验证读写功能。





















 6831
6831

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








