目录
前言
在看大佬的博客的时候被大佬的能力深深折服,想尝试着和大佬一样手写一个Spring框架,记录手写框架过程。每写一个步骤我都会将我不懂的地方进行解释。
根据Spring框架我们需要创建出一个Spring容器,一个SpringConfig配置类来代替xml文件。以及一些必要的注解。
创建自定义注解
观察Spring框架中的注解,对元注解@Target与@Retention进行解释
@Target该注解说明了自定义的Annotation修饰的对象范围:Annotation可被用于 packages、types(类、接口、枚举、Annotation类型)、类型成员(方法、构造方法、成员变量、枚举值)、方法参数和本地变量(如循环变量、catch参数)。
@Retention该注解作用是设置Annotation的保留时间。一共有三种策略。SOURCE(被编译器忽略)、CLASS(被保存在Class文件中,但在运行时不会被JVM保留,这是默认值)、RUNTIME(被保留在程序运行,可以通过反射获取到该注解)
了解过元注解后,接下来创建Spring框架中常见的注解如下
- @Component:会被Spring当作Bean进行扫描加载
- @Service:Component的派生注解,添加在Service的实现类上
- @Controller:Component的派生注解,添加在Controller类上
- @Repository:Component的派生注解,添加在Dao实现类上
- @Configuration:用来标记配置类,在启动时会被扫描
- @ComponentScan:指定需要扫描的包
但是暂时我们先不需要定义那么多衍生注解,只定义如下注解即可
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyComponent {
String value() default "";
}@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyConfiguration {
String value() default "";
}@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyComponentScan {
String[] value() default "";
}
创建配置类
创建出MySpringConfig配置类来代替xml文件,并添加扫描包注解。
@MyConfiguration
@MyComponentScan("com.zmt")
public class MySpringConfig {
}
创建Spirng容器
接下来创建出SpringApplicationContext容器,只添加必要的属性,实现包扫描即可
public class SpringApplicationContext {
//要传入的配置类
private Class<?> configClass;
//单例对象池,创建出的bean对线均存放在该Map集合中,方便自动装配时获取
private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> singletonObjects;
{
//容器被创建时进行初始化
singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
}
}接下来分析在Spring容器在启动时,会进行哪些操作。首先是根据配置类上的扫描注解去扫描指定包下的所有类,然后去将所有的bean对象加载到单例池中。那么我们定义一个init()方法去做这些事情
在扫描包路径时,去查看Spring是如何实现的
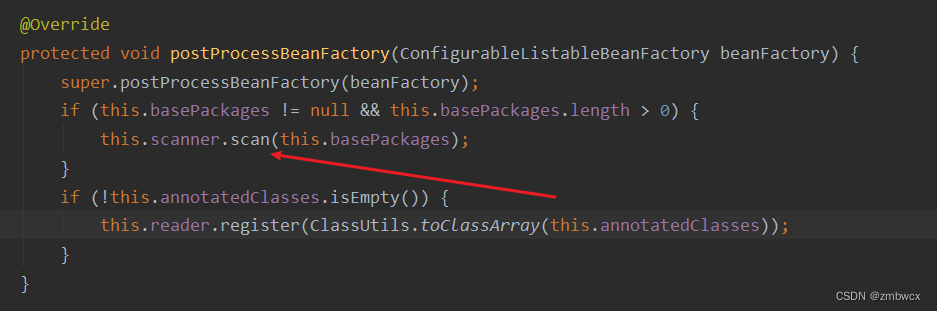
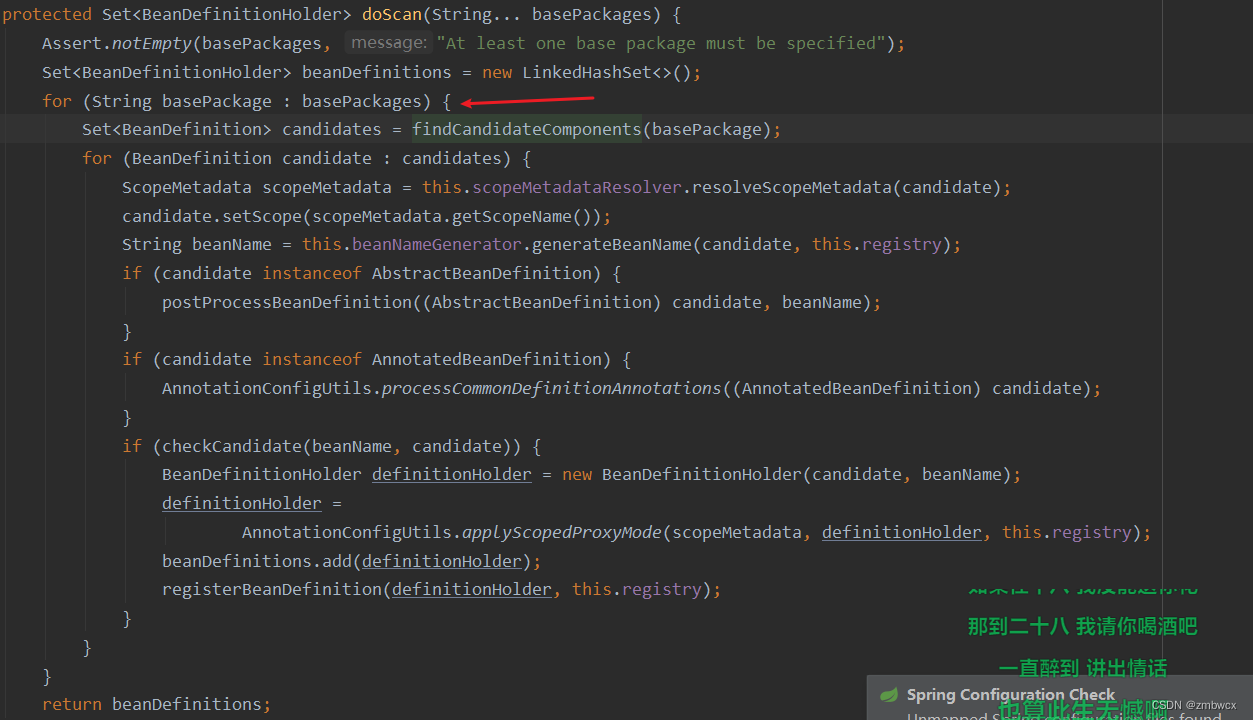
通过遍历注解中的包路径逐个扫描添加有注解的bean对象。那么我们模仿原生Spring的实现方式。
private void init() throws Exception {
//判断该类是否是配置类
MyConfiguration configuration = configClass.getAnnotation(MyConfiguration.class);
if (configuration == null) {
//说明不是配置类
throw new RuntimeException("该类不是配置类,目前只支持传入配置类");
}
//如果是配置类,那么获取需要扫描的类路径
MyComponentScan scan = configClass.getAnnotation(MyComponentScan.class);
if (scan == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("不存在扫描注解");
}
String[] paths = scan.value();
//遍历需要扫描的路径
for (String path : paths) {
path = URLDecoder.decode(path, "UTF-8");
//path这里还有作用,因此不建议将path接收replace的结果
// com/zmt
String newPath = path.replace(".", "/");
//获取根路径,并去除最前面的/
String classPath = configClass.getResource("/").getPath().substring(1);
classPath = URLDecoder.decode(classPath,"UTF-8");
System.out.println("classPath:"+classPath);
//获取被扫描包的绝对路径
String absolutePath = configClass.getResource("/" + newPath).getPath();
absolutePath = URLDecoder.decode(absolutePath, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(absolutePath);
//遍历绝对路径的子包,寻找.class结尾的文件
File rootFile = new File(absolutePath);
if (rootFile.isFile()) {
throw new RuntimeException("不支持扫描具体类");
}
//说明指定路径是一个文件夹
//获取所有的类名称
List<String> listClass = dirFile(rootFile);
for (String absoluteClassPath : listClass) {
//完整类名,通过Class.forName()创建出该类
String fullClassName = absoluteClassPath.replace(classPath, "").replace("/",".");
//加载出该类
// Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(fullClassName);
ClassLoader classLoader = configClass.getClassLoader();
Class<?> aClass = classLoader.loadClass(fullClassName);
MyComponent myComponent = aClass.getAnnotation(MyComponent.class);
if (myComponent==null){
//该类不应该被加载
continue;
}
loadSingletonObjects(fullClassName, aClass, myComponent);
}
}
}首先是要对指定的配置类进行判断是否添加了@Configuration与@ComponentScan注解,其次我们要扫描指定包下的所有文件,为了实现遍历所有文件,我使用了递归的方法获取所有class文件的绝对路径。这两个方法的具体实现为
/**
* 遍历文件夹,获取所有类绝对路径集合
* @param rootFile
* @return
*/
private List<String> dirFile(File rootFile) {
List<String> fileList = new ArrayList<>();
if (rootFile.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = rootFile.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
fileList.addAll(dirFile(file));
}
} else {
//走到这说明已经不是文件夹了
String filePath = rootFile.getPath();
if (filePath.endsWith(".class")) {
//类的绝对路径
String classPath = filePath.replace("\\", "/").replace(".class","");
System.out.println(classPath);
fileList.add(classPath);
}
}
return fileList;
}获取了全部的class文件后,我们再去遍历全路径去判断哪些类上添加了bean注解,对需要被加载到单例池的对象,需要进一步处理,loadSingletonObjects方法如下
private void loadSingletonObjects(String fullClassName, Class<?> aClass, MyComponent myComponent) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//创建对象,加载到单例池中
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
//如果注解中没有没有给定值,那么采用类名首字母小写的方式
String beanName = myComponent.value();
if ("".equals(beanName)){
System.out.println(o+"没有指定bean名称");
}
String className = fullClassName.substring(fullClassName.lastIndexOf(".") + 1);
beanName = className.substring(0, 1).toLowerCase() + className.substring(1);
singletonObjects.put(beanName,o);
}提供最基本的getBean方法用于测试
public Object getBean(String beanName){
Object o = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (o==null){
throw new RuntimeException("不存在bean为:"+beanName);
}
return o;
}至此,Spring容器创建完成,接下来是SpringApplicaitonContext的完整代码
public class SpringApplication {
//配置类属性
private Class<?> configClass;
//单例池
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> singletonObjects;
//每创建一个容器都会有各自的单例池
{
singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
}
public SpringApplication(Class<?> configClass) throws Exception {
this.configClass = configClass;
this.init();
}
private void init() throws Exception {
//判断该类是否是配置类
MyConfiguration configuration = configClass.getAnnotation(MyConfiguration.class);
if (configuration == null) {
//说明不是配置类
throw new RuntimeException("该类不是配置类,目前只支持传入配置类");
}
//如果是配置类,那么获取需要扫描的类路径
MyComponentScan scan = configClass.getAnnotation(MyComponentScan.class);
if (scan == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("不存在扫描注解");
}
String[] paths = scan.value();
//遍历需要扫描的路径
for (String path : paths) {
path = URLDecoder.decode(path, "UTF-8");
//path这里还有作用,因此不建议将path接收replace的结果
// com/zmt
String newPath = path.replace(".", "/");
//获取根路径,并去除最前面的/
String classPath = configClass.getResource("/").getPath().substring(1);
classPath = URLDecoder.decode(classPath,"UTF-8");
System.out.println("classPath:"+classPath);
//获取被扫描包的绝对路径
String absolutePath = configClass.getResource("/" + newPath).getPath();
absolutePath = URLDecoder.decode(absolutePath, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(absolutePath);
//遍历绝对路径的子包,寻找.class结尾的文件
File rootFile = new File(absolutePath);
if (rootFile.isFile()) {
throw new RuntimeException("不支持扫描具体类");
}
//说明指定路径是一个文件夹
//获取所有的类名称
List<String> listClass = dirFile(rootFile);
for (String absoluteClassPath : listClass) {
//完整类名,通过Class.forName()创建出该类
String fullClassName = absoluteClassPath.replace(classPath, "").replace("/",".");
//加载出该类
// Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(fullClassName);
ClassLoader classLoader = configClass.getClassLoader();
Class<?> aClass = classLoader.loadClass(fullClassName);
MyComponent myComponent = aClass.getAnnotation(MyComponent.class);
if (myComponent==null){
//该类不应该被加载
continue;
}
loadSingletonObjects(fullClassName, aClass, myComponent);
}
}
}
private void loadSingletonObjects(String fullClassName, Class<?> aClass, MyComponent myComponent) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//创建对象,加载到单例池中
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
//如果注解中没有没有给定值,那么采用类名首字母小写的方式
String beanName = myComponent.value();
if ("".equals(beanName)){
System.out.println(o+"没有指定bean名称");
}
String className = fullClassName.substring(fullClassName.lastIndexOf(".") + 1);
beanName = className.substring(0, 1).toLowerCase() + className.substring(1);
singletonObjects.put(beanName,o);
}
/**
* 遍历文件夹,获取所有类绝对路径集合
* @param rootFile
* @return
*/
private List<String> dirFile(File rootFile) {
List<String> fileList = new ArrayList<>();
if (rootFile.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = rootFile.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
fileList.addAll(dirFile(file));
}
} else {
//走到这说明已经不是文件夹了
String filePath = rootFile.getPath();
if (filePath.endsWith(".class")) {
//类的绝对路径
String classPath = filePath.replace("\\", "/").replace(".class","");
System.out.println(classPath);
fileList.add(classPath);
}
}
return fileList;
}
public Object getBean(String beanName){
Object o = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (o==null){
throw new RuntimeException("不存在bean为:"+beanName);
}
return o;
}
}
测试
接下来进行测试看能否成功将添加了注解的类加载到单例池中
public class SpringStart {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(SpringConfig.class);
UserController userController = (UserController) springApplication.getBean("userController");
System.out.println(userController);
}
}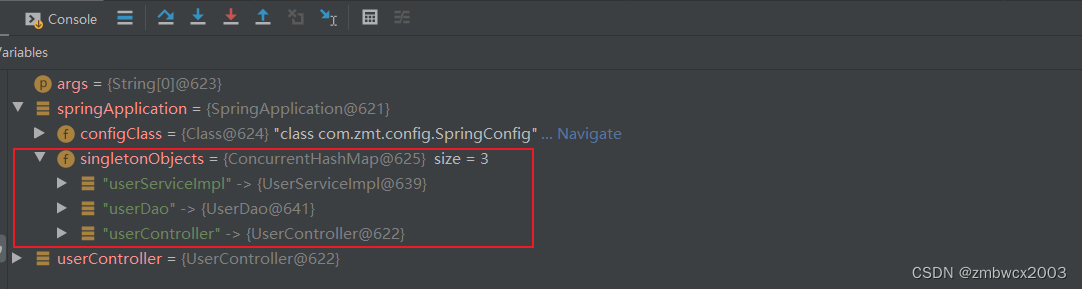
亲测可以进行多个包扫描也可以自定义bean名称。 那么我们的第一个功能就实现结束了,接下来我们需要完善我们的Spring,接下来是实现封装BeanDefinitionMap。
问题
这里最大的问题就是对文件如何进行处理,以及类名的如何获取,以及格式处理,需要注意的是,路径中存在中文的一定要对其进行编码格式转换,对于类路径获取存在疑惑的,可以去观看我的另一篇博客getResource()方法的使用以及路径问题-优快云博客




 本文介绍了如何从零开始手写Spring框架,包括创建自定义注解(@Target和@Retention),配置类(MyConfiguration和MyComponentScan)以及Spring容器的实现,重点在于注解的使用和类扫描机制。
本文介绍了如何从零开始手写Spring框架,包括创建自定义注解(@Target和@Retention),配置类(MyConfiguration和MyComponentScan)以及Spring容器的实现,重点在于注解的使用和类扫描机制。

















 973
973

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










