- 深度学习是以数据推动的学科,深层神经网络一般都需要大量的训练数据才能获得比较理想的结果。在数据量有限的情况下,可以通过数据增强(Data Augmentation)来, 提高模型鲁棒性,避免过拟合。
- 数据增强的方法有很多种,比如旋转、水平翻转、垂直翻转、随机裁剪、色彩扰动、加入噪声、随机缩放等等。本文只讨论和实现两种最常用和最基本的方法:随机裁剪和水平翻转。
一、随机裁剪
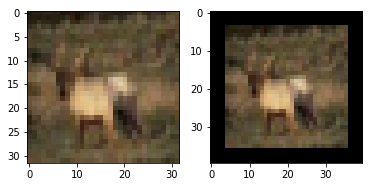
以cifar-10数据集为例,这个数据集的图像大小为32x32x3,按照大多数论文中的随机裁剪方法,将图像每边填充4个像素,添加的像素值为0,也就是说填充后的图像大小为40x40x3,然后随机裁剪为32x32x3的图像。
填充⬇
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
#读入图像的部分省略,图片变量img
#利用cv2.copyMakeBorder函数将原图片填充
img_padding = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, 4, 4, 4, 4, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=0)
plt.subplot(121)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.subplot(122)
plt.imshow(img_padding)输出⬇
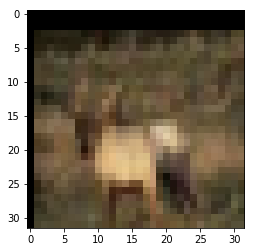
裁剪⬇
import numpy as np
#我们要将图片裁剪为32*32,所以初始化两个随机变量,np.random.randint函数为左闭右开,也就是说取值范围是0到8,不包含8
h = np.random.randint(0,8)
w = np.random.randint(0,8)
img_crop = img_padding[h:h+32,w:w+32,:]
plt.imshow(img_crop)输出⬇
二、水平翻转
水平翻转我们用到是np.fliplr函数,直接上代码
#随机生成0-1之间的小数
random_flip = np.random.random()
#因为是随机翻转,所以翻转和不反转概率应该各占50%
if random_flip > 0.5:
img_flip = np.fliplr(img_crop)
plt.imshow(img_flip)输出⬇

三、完整代码
def data_augment(x):
'''
输入x为minibatch,大小比如(64,32,32,3)
'''
for i in range(x.shape[0]):
temp = cv2.copyMakeBorder(x[i,:,:,:], 4, 4, 4, 4, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=0)
h = np.random.randint(0,8)
w = np.random.randint(0,8)
temp = temp[h:h+32,w:w+32,:]
random_flip = np.random.random()
if random_flip > 0.5:
temp = np.fliplr(temp)
x[i,:,:,:] = temp
return x
























 1209
1209

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








