
一、API:
InputStreamReader: 解码

OutputStreamWriter: 编码

将控制台输入的字符转换成大写,遇到over就结束程序。
public class TransStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//字节流
InputStream in=System.in;
//将字节流转换成字符流桥梁。 转换流
InputStreamReader isr =new InputStreamReader(in);
//字符流
BufferedReader bufr=new BufferedReader(isr);
String readLin=null;
while ((readLin=bufr.readLine())!=null){
if ("over".equals(readLin)){
break;
}
System.out.println(readLin.toUpperCase());
}
}
}
二、示意图:

三、编码演示
1、读取键盘录入的数据,并打印在控制台上
/**
* @author James
* @create 2020-01-04 15:36
*
*
* 读取键盘录入的数据,并打印在控制台上
*
* 键盘本身就是一个标准的输入设置。
* 对于Java而言,对于这种输入设备都有对应的对象。
*
*/
public class ReadKey {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//readKey();
/* System.out.println((int)'\r');//13
System.out.println((int)'\n');//10*/
readKey2();
}
private static void readKey2() throws IOException {
/**
*
* 获取用户录入的数据
* 并将数据转换成大写显示在控制台上
* 如果用户输入的是over,结束键盘录入
*
* 思路:
* 1、键盘录入只会读取一个字符,若要判断over,则需将录入的字符拼接成字符串。
* 2、需要一个容器。StringBuilder。
* 3、在用户回车之前,将录入的数据变成字符串判断即可。
*/
//一直接受用户录入
//1、创建容器
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
//2、获取键盘读取流
InputStream in= System.in;
//3、定义变量记录读取到的字节。并循环获取
int ch=0;
while ((ch=in.read())!=-1) {
//在存储之前需要判断是否为换行标记,换行不存
if (ch == '\r') {
continue;
}
if (ch == '\n') {
String temp = sb.toString();
if ("over".equals(temp)) {
break;
}
//转换为大写输出
System.out.println(temp.toUpperCase());
sb.delete(0,sb.length());
} else {
//4、将读取到的字节存储到容器中
sb.append((char) ch);
// System.out.println(ch);
}
}
}
private static void readKey() throws IOException {
InputStream in = System.in;
//阻塞式方法。当没有数据录入时,会一直等待
int ch = in.read();
System.out.println(ch);
}
}
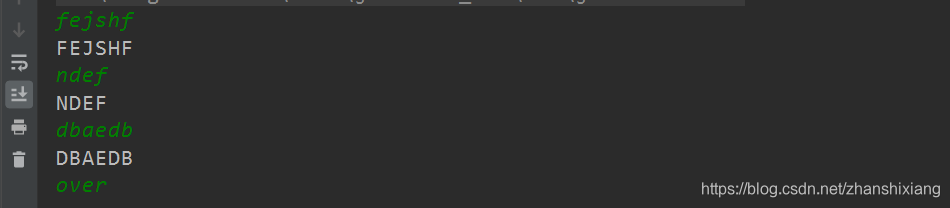
2、使用转换流
public class TransStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//字节流
InputStream in=System.in;
//将字节流转换成字符流桥梁。 转换流
InputStreamReader isr =new InputStreamReader(in);
//字符流
BufferedReader bufr=new BufferedReader(isr);
String readLin=null;
while ((readLin=bufr.readLine())!=null){
if ("over".equals(readLin)){
break;
}
System.out.println(readLin.toUpperCase());
}
}
}

3、装换流中的指定编码方式演示
public class TransStreamDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//使用文本字符流写入中文
writerText_1();
//使用转换流的方式写入中文
writerText_2();
//以Utf-8的编码写入中文
writerText_3();
//使用默认的编码格式读取UTF-8编码的文件
readText_1();
//使用指定的utf-8编码格式,读取默认的编码格式所编码的文件
readText_2();
}
/**
* 使用默认的编码格式读取UTF-8编码的文件
*/
private static void readText_1() throws IOException {
FileReader fr=new FileReader("utf8—1.txt");
char[] buf = new char[1024];
int len=fr.read(buf);
String str=new String(buf,0,len);
System.out.println(str);
fr.close();
/**
* 娴g姴銈
*/
}
/**
* 使用指定的utf-8编码格式,读取默认的编码格式所编码的文件
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void readText_2() throws IOException {
InputStreamReader isr =new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("gbk_3.txt"),"utf-8");
char[] buf = new char[1024];
int len=isr.read(buf);
String str=new String(buf,0,len);
System.out.println(str);//你好
isr.close();
}
/**
*
* 以Utf-8的编码写入中文
* 同样 “你好” 二字 gbk是四个字节, utf-8是六个字节
*
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void writerText_3() throws IOException {
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("utf8—1.txt"),"UTF-8");
osw.write("你好");
osw.close();
}
//使用转换流的方式写入中文
private static void writerText_2() throws IOException {
//默认编码方式
//OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("gbk_2.txt"));
//以GBK为编码
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("gbk_3.txt"),"GBK");
/**
* OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("gbk_2.txt"));
* FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("gbk_1.txt");
* 这两句代码的功能是等同的。
* FileWriter:其实就是转换流指定了本机默认码表的体现。而且这个转换流的子类对象,可以方便操作文本文件。
* 简单说:操作文件的字节流+本机默认的编码表。
* 这是按照默认码表来操作文件的便捷类。
*
* 如果操作文本文件需要明确具体的编码。FileWriter就不行了。必须用转换流。
*
*/
osw.write("你好");
osw.close();
}
private static void writerText_1() throws IOException {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("gbk_1.txt");
fw.write("你好");
fw.close();
}
}






















 761
761

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










