一、ELMO
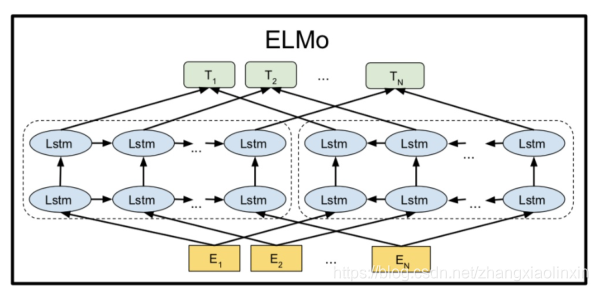
ELMO的基本思想是利用双向的LSTM结构,对于某个语言模型的目标,在大量文本上进行预训练,从LSTM layer中得到contextual embedding,其中较低层的LSTM代表了比较简单的语法信息,而上层的LSTM捕捉的是依赖于上下文的语义信息。ELMO的全称就是Embeddings from Language Models。对于下游的任务,再将这些不同层的向量线性组合,再做监督学习。
ELMo算法过程为:
- 先在大语料上以language model为目标训练出bidirectional LSTM模型;
- 然后利用LSTM产生词语的表征;
ELMo模型包含多layer的bidirectional LSTM,可以这么理解:
高层的LSTM的状态可以捕捉词语意义中和语境相关的那方面的特征(比如可以用来做语义的消歧),而低层的LSTM可以找到语法方面的特征(比如可以做词性标注)。
详细来说,对于N个标记(t1,t2,.....,tN)(t_1,t_2,.....,t_N)(t1,t2,.....,tN) ,forward language model学习的是根据(t1,t2,.....,tk−1)(t_1,t_2,.....,t_k-1)(t1,t2,.....,tk−1) 的信息推测的概率:
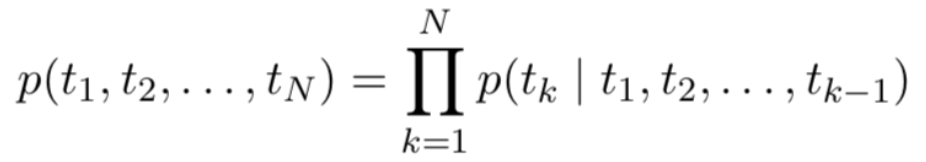
而 backward language model学习的是依据(tk+1,.....,tN)(t_k+1,.....,t_N)(tk+1,.....,tN) 的信息推测tkt_ktk 的概率:
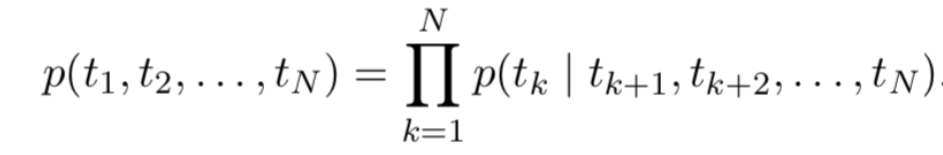
而bidirectional LSTM就是将两者结合起来,其目标是最大化
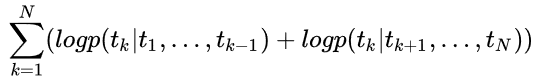

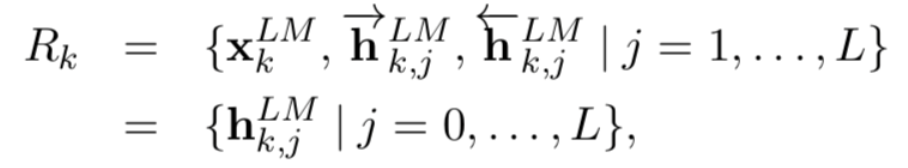

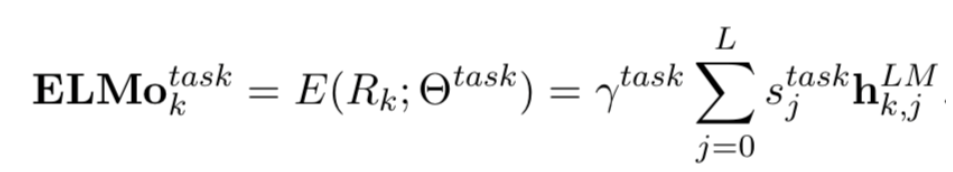
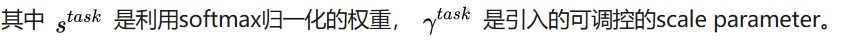
采用了ELMO预训练产生的contextual embedding之后,在各项下游的NLP任务中,准确率都有显著提高。
二、GPT
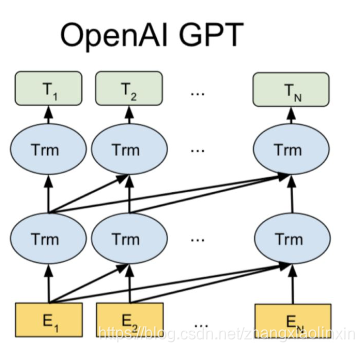
GPT全称是Generative Pre-Training, 和之后的BERT模型一样,它的基本结构也是Transformer。
GPT的核心思想是利用Transformer模型对大量文本进行无监督学习,其目标函数就是语言模型最大化语句序列出现的概率,不过这里的语言模型仅仅是forward单向的,而不是双向的。得到这些embedding后,再对下游的task进行supervised fine-tuning。
GPT的训练分为两个阶段:1)无监督预训练语言模型;2)各个任务的微调。
模型结构图:
三、BERT
BERT原理与GPT有相似之处,不过它利用了双向的信息,因而其全称是Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers。
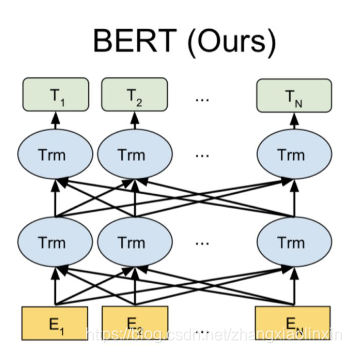
BERT做无监督的pre-training时有两个目标:
一个是将输入的文本中 k%的单词遮住,然后预测被遮住的是什么单词。
另一个是预测一个句子是否会紧挨着另一个句子出现。
预训练时在大量文本上对这两个目标进行优化,然后再对特定任务进行fine-tuning。BERT由于采用了Transformer结构能够更好的捕捉全局信息,并且利用了上下文的双向信息,所以其效果要优于之前的方法,它大大提高了各项NLP任务的性能。







 本文介绍了三种深度学习在自然语言处理领域的模型:ELMo、GPT和BERT。ELMo通过双向LSTM预训练得到上下文敏感的词嵌入;GPT采用Transformer结构进行无监督预训练;BERT则引入了双向Transformer,通过遮盖预测和下一句预测任务进行预训练,显著提升了NLP任务的性能。
本文介绍了三种深度学习在自然语言处理领域的模型:ELMo、GPT和BERT。ELMo通过双向LSTM预训练得到上下文敏感的词嵌入;GPT采用Transformer结构进行无监督预训练;BERT则引入了双向Transformer,通过遮盖预测和下一句预测任务进行预训练,显著提升了NLP任务的性能。
















 638
638

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








