写在前面:当潮水退去,但愿我有底裤!
- 栈:仅在表尾进行插入和删除的线性表.
- java实现循序栈
package stack;
/**
* User: ZhangQi
* Date: 2019/3/13
* Time: 11:21
* Desc: 栈抽象数据类型
*/
public interface StackTest {
/**
* 初始化栈
* @param n
*/
void createStack(int n);
/**
* 判断栈是否为空
* @return
*/
boolean isEmpty();
/**
* 压栈
* @param n
* @return
*/
boolean push(int n);
/**
* 弹栈
* @return
*/
int pop();
/**
* 获取栈顶元素
* @return
*/
int peek();
}
package stack;
/**
* User: ZhangQi
* Date: 2019/3/13
* Time: 11:24
* Desc: 抽象栈实现类
*/
public class StackTestImpl implements StackTest {
private int[] data;
private int n;
private int top;
@Override
public void createStack(int n) {
this.data = new int[n];
this.n = n-1;
this.top = -1;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
if(this.top == -1) return true;
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean push(int num) {
if(this.top == this.n ) return false;
this.data[++top] = num;
return true;
}
@Override
public int pop() {
if(isEmpty()) throw new StackException();
return this.data[top--];
}
@Override
public int peek() {
if(isEmpty()) throw new StackException();
return this.data[top];
}
}
package stack;
/**
* User: ZhangQi
* Date: 2019/3/13
* Time: 11:42
* Desc: 自定义空栈异常
*/
public class StackException extends RuntimeException {
public StackException() {
super("栈已经为空了,大人!");
}
}
package stack;
/**
* User: ZhangQi
* Date: 2019/3/13
* Time: 11:18
* Desc: 循序栈测试类
*/
public class ArrStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StackTestImpl stack = new StackTestImpl();
stack.createStack(10);
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty());
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty());
System.out.println(stack.peek());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.peek());
}
}
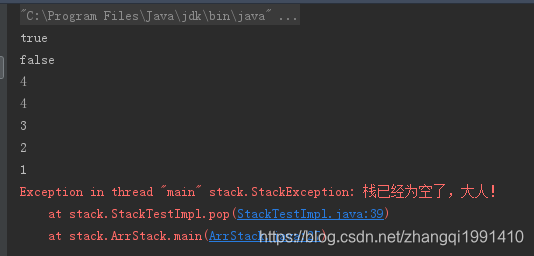
循序栈测试结果:
3. 用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作。 队列中的元素为int类型。
package stack;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* User: ZhangQi
* Date: 2019/3/14
* Time: 11:33
* Desc: 用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作。 队列中的元素为int类型
*/
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
/** 重点是:stack2每次pop的时候,如果为空则必须将stack1中所有的元素push进来 */
public int pop() {
if (stack1.empty() && stack2.empty())
throw new RuntimeException("queue is empty");
if (stack2.empty()) {
while (!stack1.empty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}
- 输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否可能为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如序列1,2,3,4,5是某栈的压入顺序,序列4,5,3,2,1是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但4,3,5,1,2就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。(注意:这两个序列的长度是相等的)
package stack;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* User: ZhangQi
* Date: 2019/3/14
* Time: 11:33
* Desc: 输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否可能为该栈的弹出顺序。
* 假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如序列1,2,3,4,5是某栈的压入顺序,序列4,5,3,2,1是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,
* 但4,3,5,1,2就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。(注意:这两个序列的长度是相等的)
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*借用一个辅助的栈,遍历压栈顺序,先讲第一个放入栈中,这里是1,
* 然后判断栈顶元素是不是出栈顺序的第一个元素,这里是4,很显然1≠4,
* 所以我们继续压栈,直到相等以后开始出栈,出栈一个元素,则将出栈顺序向后移动一位,直到不相等,
* 这样循环等压栈顺序遍历完成,如果辅助栈还不为空,说明弹出序列不是该栈的弹出顺序
* @param pushA
* @param popA
* @return
*/
public boolean IsPopOrder(int[] pushA, int[] popA) {
if (pushA == null || popA == null) return false;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < pushA.length; i++) {
stack.push(pushA[i]);
while (!stack.empty() && stack.peek() == popA[index]) {
stack.pop();
index++;
}
}
return stack.size() == 0;
}
}
- 定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈中所含最小元素的min函数(时间复杂度应为O(1))
package stack;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* User: ZhangQi
* Date: 2019/3/14
* Time: 11:33
* Desc: 定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈中所含最小元素的min函数(时间复杂度应为O(1))
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*思路:用一个栈data保存数据,用另外一个栈min保存依次入栈最小的数
* 比如,data中依次入栈,5, 4, 3, 8, 10, 11, 12, 1
* 则min依次入栈,5, 4, 3,no,no, no, no, 1
*/
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
if (stack2.empty()) {
stack2.push(node);
} else if (node <= stack2.peek()) {
stack2.push(node);
}
}
public void pop() {
int num = stack1.pop();
if (num == stack2.peek()) stack2.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack1.peek();
}
public int min() {
return stack2.peek();
}
}
- 请编写一个程序,按升序对栈进行排序(即最大元素位于栈顶),要求最多只能使用一个额外的栈存放临时数据,但不得将元素复制到别的数据结构中。给定一个int[] numbers(C++中为vector<int>),其中第一个元素为栈顶,请返回排序后的栈。请注意这是一个栈,意味着排序过程中你只能访问到最后一个元素。
测试样例:
[1,2,3,4,5]
返回:[5,4,3,2,1]
package stack;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* User: ZhangQi
* Date: 2019/3/14
* Time: 11:33
* Desc: 请编写一个程序,按升序对栈进行排序(即最大元素位于栈顶),要求最多只能使用一个额外的栈存放临时数据,但不得将元素复制到别的数据结构中
*/
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> twoStacksSort(int[] numbers) {
if (numbers == null) return null;
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
stack1.push(numbers[i]);
}
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<>();
while (!stack1.empty()) {
int tmp = stack1.pop();
if (stack2.empty()) {
stack2.push(tmp);
} else {
while (!stack2.empty() && stack2.peek() > tmp) {
stack1.push(stack2.pop());
}
stack2.push(tmp);
}
}
ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
while (!stack2.empty()) {
arr.add(stack2.pop());
}
return arr;
}
}





 本文详细介绍了Java中栈的实现方式,包括自定义循序栈的接口与实现类,以及如何利用两个栈实现队列。此外,还探讨了栈在解决实际问题中的应用,如判断弹出序列的有效性、实现O(1)时间复杂度的最小元素查找、以及栈的排序算法。
本文详细介绍了Java中栈的实现方式,包括自定义循序栈的接口与实现类,以及如何利用两个栈实现队列。此外,还探讨了栈在解决实际问题中的应用,如判断弹出序列的有效性、实现O(1)时间复杂度的最小元素查找、以及栈的排序算法。
















 192
192

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








