一、使用环境
1、VMwar虚拟机安装Ubuntu_kinetic_16.04
2、GPS为千寻位置D300
二、使用流程:
1、按照厂家需求安装配置好GPS设备
2、GPS设备连接电脑
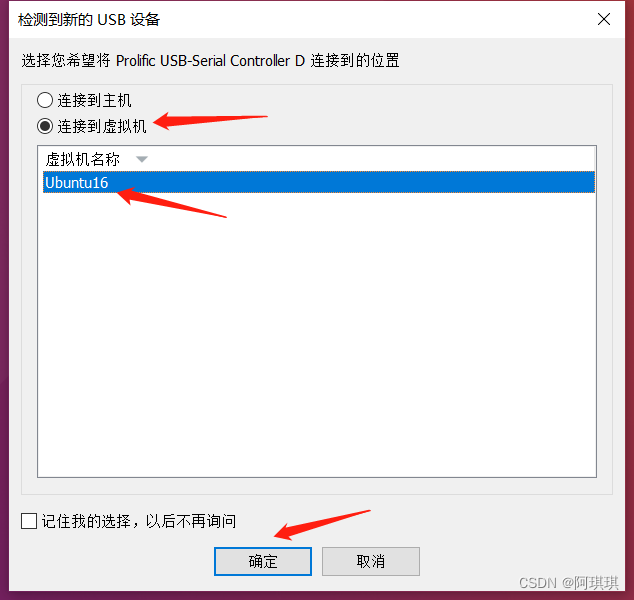
3、设备连接查询:
ls /dev/tty*
查看设备是否正确接入,最简单的方法就是插入前后进行对比(就可以知道设备):

4、使用串口助手读取数据:
sudo apt install cutecom
sudo cutecom
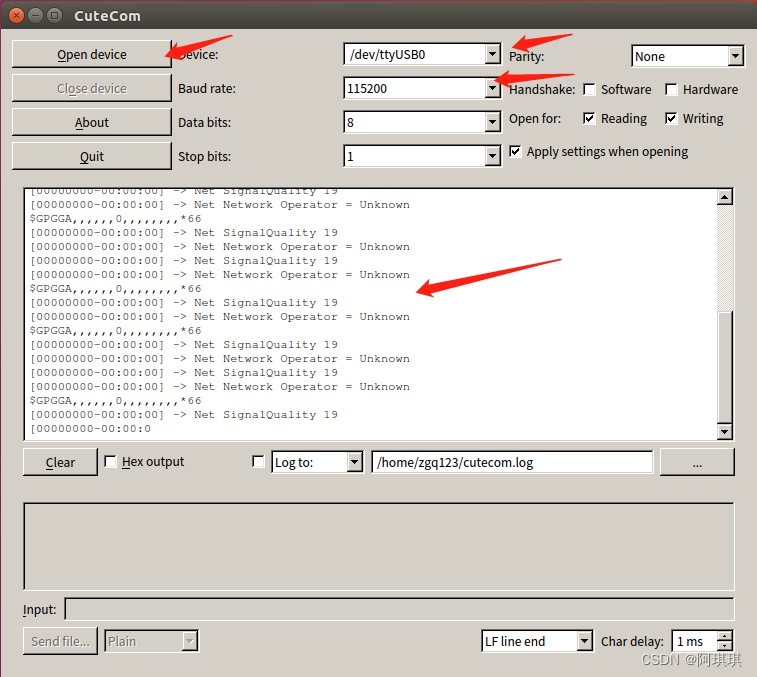
分别为打开串口、设备串口设备、波特率、数据展示界面(我的是在室内,所以没有数据,以及SIM卡也有警告信号不好)
3、使用ROS功能包mea_navsat_driver用于解析NMEA数据
参考链接:ros wiki: http://wiki.ros.org/nmea_navsat_driver
github源码:https://github.com/ros-drivers/nmea_navsat_driver
(1)安装mea_navsat_driver
(2)打开新的终端:
roscore
(3)安装的mea_navsat_driver需要手动配置launch文件(包含设备ID和波特率):
roscd nmea_navsat_driver/launch

sudo vim nmea_serial_driver.launch
(4)修改USB口和波特率
<launch>
<!-- A simple launch file for the nmea_serial_driver node. -->
<arg name="port" default="/dev/ttyACM0" />
<arg name="baud" default="9600" />
<arg name="frame_id" default="gps" />
<arg name="use_GNSS_time" default="False" />
<arg name="time_ref_source" default="gps" />
<arg name="useRMC" default="False" />
<node name="nmea_serial_driver_node" pkg="nmea_navsat_driver" type="nmea_serial_driver" output="screen">
<param name="port" value="$(arg port)"/>
<param name="baud" value="$(arg baud)" />
<param name="frame_id" value="$(arg frame_id)" />
<param name="use_GNSS_time" value="$(arg use_GNSS_time)" />
<param name="time_ref_source" value="$(arg time_ref_source)" />
<param name="useRMC" value="$(arg useRMC)" />
</node>
</launch>
(5)给USB设备权限(重要,不然读取不到):
sudo chmod 777 /dev/ttyUSB0(自己设备的ID,不要复制我的)
(6)运行nmea_serial_driver 节点:
roslaunch nmea_navsat_driver nmea_serial_driver.launch
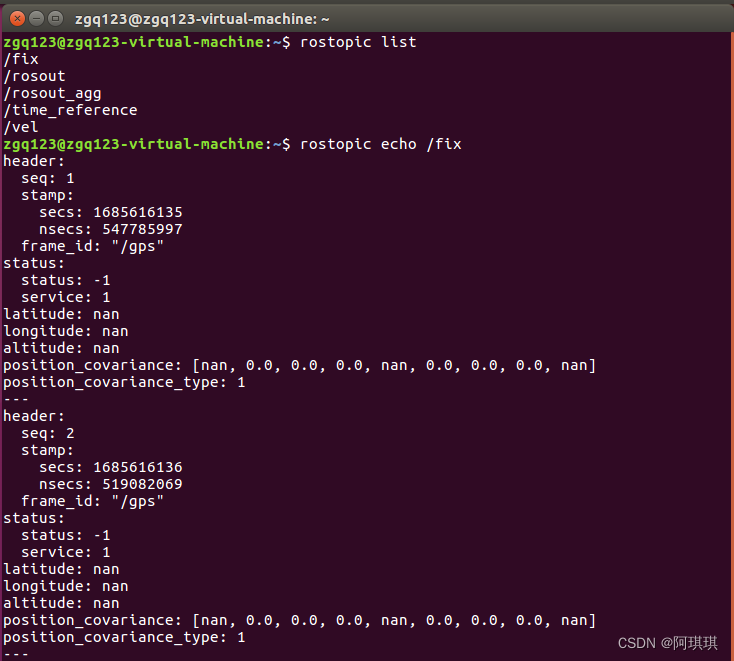
(7)查看话题输出(别看我的全是0,因为我在室内给大家分享的文章):
rostopic echo /fix
三、大家有问题可以私聊我,我可能只有休息时间回复哦!




 本文详细介绍了如何在Ubuntu16.04虚拟机中,通过VMware安装并配置GPS设备千寻D300,使用ROS的nmea_navsat_driver解析NMEA数据。步骤包括安装设备,通过串口助手检查连接,修改launch文件设置波特率和设备ID,赋予USB设备权限,最后启动ROS节点并查看话题输出。
本文详细介绍了如何在Ubuntu16.04虚拟机中,通过VMware安装并配置GPS设备千寻D300,使用ROS的nmea_navsat_driver解析NMEA数据。步骤包括安装设备,通过串口助手检查连接,修改launch文件设置波特率和设备ID,赋予USB设备权限,最后启动ROS节点并查看话题输出。


























