-
基本特点
-
语法底子
- 基本特点
- Java 代码 任何情况下都区分大小写
- 强类型语言
- 语法底子
- 字符集A <-----> Unicode <-----> 字符集B. Java中正常显示的代码采用的是Unicode字符集
- 四种整型都是有符号的,byte,short,int ,long字节分别为1,2,4,8 。float 占有4个字节,double 占有8个。
- 单引号表示一个字符的字面常量值,双引号括起来一个字符串。
- 数值之间自动类型转换,但不保证不损失精确。强制转换类型丢多少是具体情况而定。
- 枚举类型,就是常量集合组成的一个变量类型。 All enums implicitly extend
java.lang.Enum. Because a class can only extend one parent (see Declaring Classes), the Java language does not support multiple inheritance of state , and therefore an enum cannot extend anything else. - 位运算包括 AND , OR , XOR ,NOT, <<,>>,和 >>>
- 字符串类型(String)不是Java 的内置数据类型,而是 Java.lang 标准库 提供的一个预定义类。支持截取,拼接,但是不可修改。比较字符串是否相等时,要明确的知道String和自己定义的类是没有什么本质区别的。所以 null 和 空串就很好理解了。字符串是 Unicode 码点 序列。Java编程语言不允许文字字符串跨越源文件中的行,因此必须在多行字符串的每行末尾使用+串联运算符。
String quote = "Now is the time for all good " + "men to come to the aid of their country."; - 码点是字符在UniCode 表中对应的的数值. 对于理解乱码很有用。
- 格式化输出 Java 核心1 P59
- 数组是一种数据结构,用来存储同一类型值的集合。数组允许长度为0,与null 不同【猜测是0的情况下,已经指定了句柄的指向地址,而null 显然句柄没有任何指向】。在编写一个结果为数组的方法时, 如果碰巧结果为空, 则这种语法形式就显得非常有用。 此时可以创建一个长度为 0 的数组。
- 深拷贝是两份存储,浅拷贝是指向同一份存储。
- 多维数组,是一维数组下的各空间又指向了一份一维数组。因此支持不规则的多维数组。
- 运算优先级为: 箭头指向变低

类定义:修饰符 类名 继承 实现 class body{ }
Field declarations are composed of three components, in order:
- Zero or more modifiers, such as
publicorprivate. - The field's type.
- The field's name
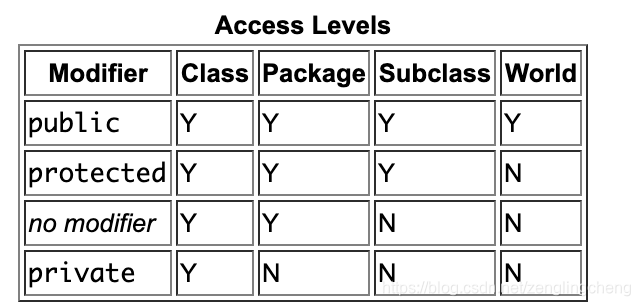
访问控制
the runtime system guarantees that static initialization blocks are called in the order that they appear in the source code.
Annotations, a form of metadata, provide data about a program that is not part of the program itself. Annotations have no direct effect on the operation of the code they annotate.
注释是元数据的一种形式,它提供有关程序的数据,该数据不属于程序本身。 注释对其注释的代码的操作没有直接影响
Annotations have a number of uses, among them:
Information for the compiler — Annotations can be used by the compiler to detect errors or suppress warnings.
Compile-time and deployment-time processing — Software tools can process annotation information to generate code, XML files, and so forth.
Runtime processing — Some annotations are available to be examined at runtime.
1.The at sign character (@) indicates to the compiler that what follows is an annotation.
If there is just one element named value, then the name can be omitted, as in:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
If the annotations have the same type, then this is called a repeating annotation:
@Author(name = "Jane Doe")
@Author(name = "John Smith")As of the Java SE 8 release, annotations can also be applied to the use of types. Here are some examples:
- Class instance creation expression:
new @Interned MyObject(); - Type cast:
myString = (@NonNull String) str; implementsclause:class UnmodifiableList<T> implements @Readonly List<@Readonly T> { ... }- Thrown exception declaration:
void monitorTemperature() throws @Critical TemperatureException { ... }
Java SE 8发行版不提供类型检查框架,但是允许您编写(或下载)类型检查框架,该框架被实现为与Java编译器结合使用的一个或多个可插拔模块。
There are a number of situations in software engineering when it is important for disparate groups of programmers to agree to a "contract" that spells out how their software interacts. Each group should be able to write their code without any knowledge of how the other group's code is written. Generally speaking, interfaces are such contracts.
在软件工程中有很多情况,对于不同的程序员群体来说,同意一份阐明其软件交互方式的“合同”很重要。每个小组都应该能够编写其代码,而无需了解另一小组的代码是如何编写的。一般来说,接口就是这样的契约。
接口的如何实现升级
public interface DoIt {
void doSomething(int i, double x);
int doSomethingElse(String s);
}这样做死的很惨
public interface DoIt {
void doSomething(int i, double x);
int doSomethingElse(String s);
boolean didItWork(int i, double x, String s);
}要给其他人选择的权利。
public interface DoItPlus extends DoIt {
boolean didItWork(int i, double x, String s);
}
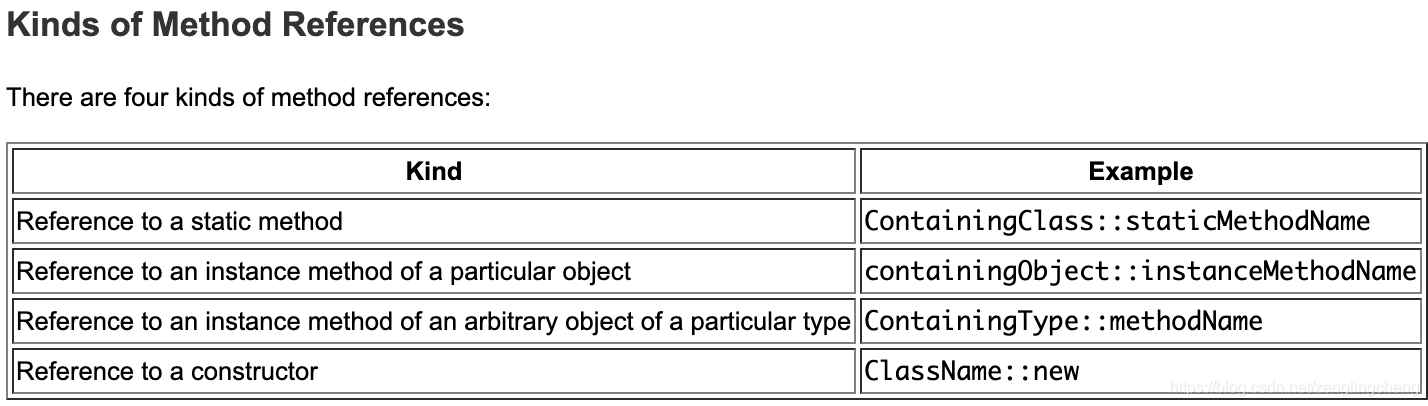
Lambda表达式使您能够执行此操作,将功能视为方法参数,或将代码视为数据。
Collections are used to store, retrieve, manipulate, and communicate aggregate data
集合用于存储,检索,操作和传达汇总数据
包装类的使用。装箱和拆箱操作是编译的功能。
There are three reasons that you might use a Number object rather than a primitive:
- As an argument of a method that expects an object (often used when manipulating collections of numbers).
- To use constants defined by the class, such as
MIN_VALUEandMAX_VALUE, that provide the upper and lower bounds of the data type. - To use class methods for converting values to and from other primitive types, for converting to and from strings, and for converting between number systems (decimal, octal, hexadecimal, binary).
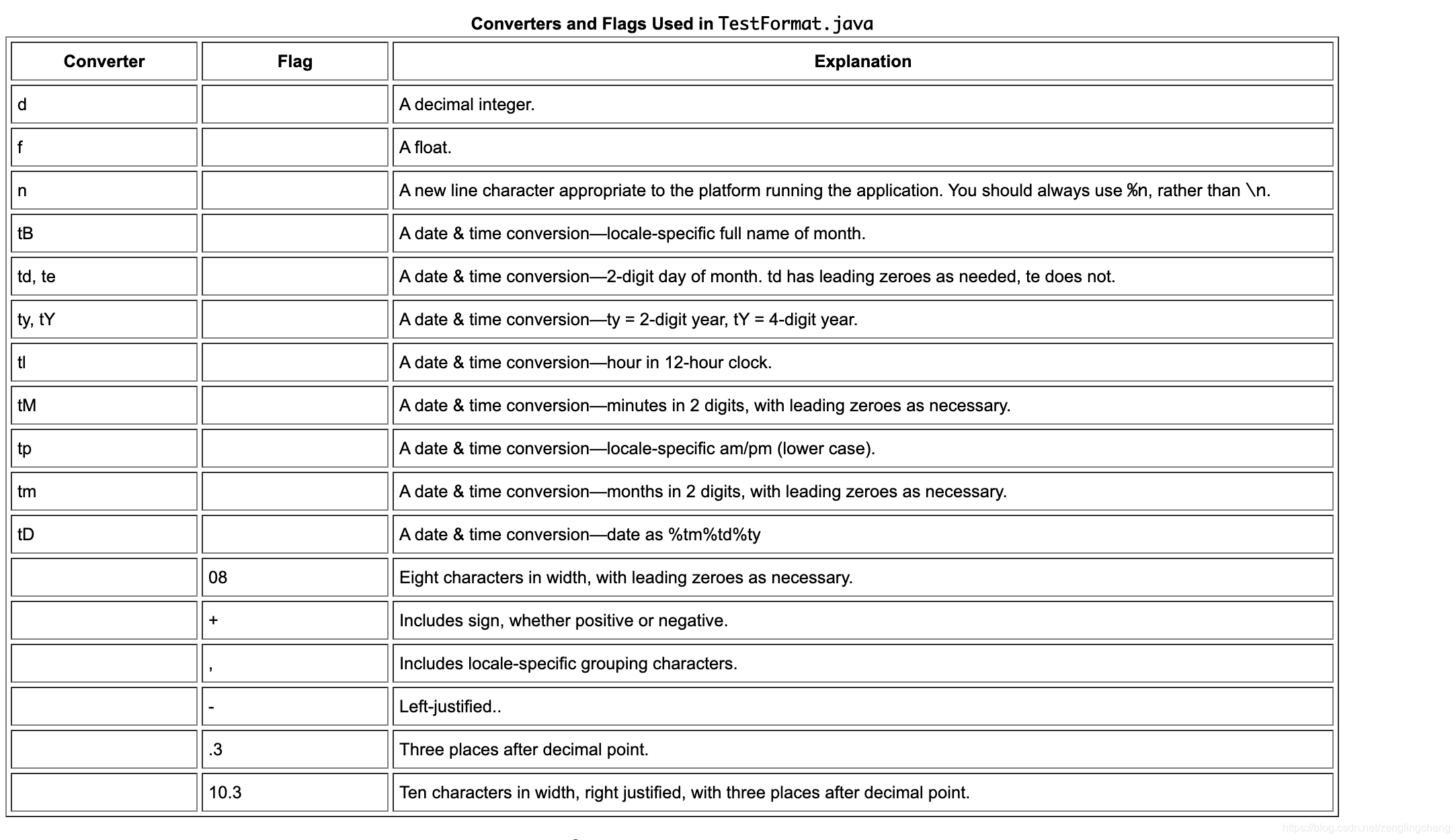
格式化数据展示的操作
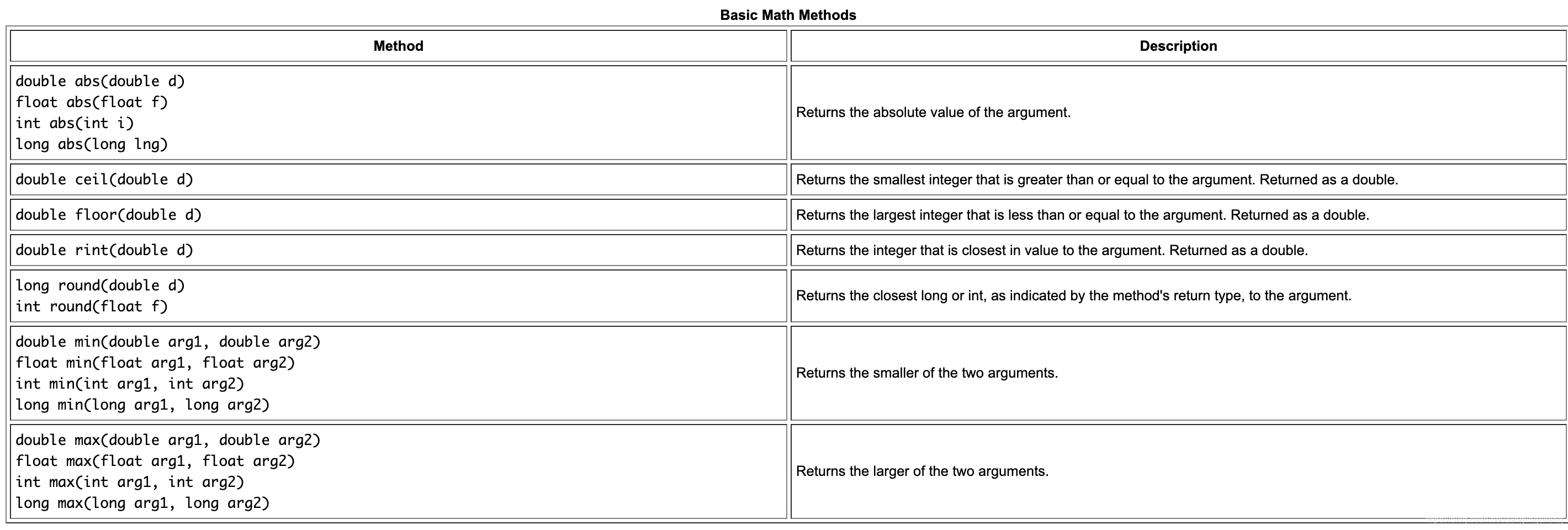
简而言之,泛型在定义类,接口和方法时使类型(类和接口)成为参数。 与方法声明中使用的更熟悉的形式参数非常相似,类型参数为您提供了一种使用不同输入重复使用相同代码的方法。 区别在于形式参数的输入是值,而类型参数的输入是类型。
定义一个泛型类
class name<T1, T2, ..., Tn> { /* ... */ }
调用或实例化泛型类型
Box<Integer> integerBox;
定义泛型方法 public static <K, V> boolean compare(Pair<K, V> p1, Pair<K, V> p2) {
return p1.getKey().equals(p2.getKey()) &&
p1.getValue().equals(p2.getValue());
}定义泛型的约束条件
public <U extends Number> void inspect(U u){
System.out.println("T: " + t.getClass().getName());
System.out.println("U: " + u.getClass().getName());
}The preceding example illustrates the use of a type parameter with a single bound, but a type parameter can have multiple bounds:
<T extends B1 & B2 & B3>
A type variable with multiple bounds is a subtype of all the types listed in the bound. If one of the bounds is a class, it must be specified first. For example:
Class A { /* ... */ }
interface B { /* ... */ }
interface C { /* ... */ }
class D <T extends A & B & C> { /* ... */ }
If bound A is not specified first, you get a compile-time error:
class D <T extends B & A & C> { /* ... */ } // compile-time error
定义有界泛型类方法
public interface Comparable<T> {
public int compareTo(T o);
}
The resulting code will be:
public static <T extends Comparable<T>> int countGreaterThan(T[] anArray, T elem) {
int count = 0;
for (T e : anArray)
if (e.compareTo(elem) > 0)
++count;
return count;
}
Box<Integer> is not a subtype of Box<Number> even though Integer is a subtype of Number.
编译器为泛型提供了类型推断的能力。
任何一个 有 A 类型身份的。横向扩展【继承关系的一个上界,至少继承过A的】
To write the method that works on lists of Number and the subtypes of Number, such as Integer, Double, and Float, you would specify List<? extends Number>. The term List<Number> is more restrictive than List<? extends Number> because the former matches a list of type Number only, whereas the latter matches a list of type Number or any of its subclasses.
要编写适用于Number列表和Number的子类型(例如Integer,Double和Float)的方法,您可以指定List <? 扩展Number>。 术语List <Number>比List <? 扩展Number>,因为前者仅匹配Number类型的列表,而后者匹配Number类型或其任何子类的列表。
The unbounded wildcard type is specified using the wildcard character (?), for example, List<?>. This is called a list of unknown type. There are two scenarios where an unbounded wildcard is a useful approach:
If you are writing a method that can be implemented using functionality provided in the Object class.
When the code is using methods in the generic class that don't depend on the type parameter. For example, List.size or List.clear. In fact, Class<?> is so often used because most of the methods in Class<T> do not depend on T.
继承关系的最子孙的是A【这里指integer】
To write the method that works on lists of Integer and the supertypes of Integer, such as Integer, Number, and Object, you would specify List<? super Integer>.
The term List<Integer> is more restrictive than List<? super Integer> because the former matches a list of type Integer only, whereas the latter matches a list of any type that is a supertype of Integer.





















 191
191

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








