线程的定义和概念
线程,有时被称为轻量进程,是程序执行流的最小单元。线程是进程中的一个实体,是被系统独立调度和分派的基本单位,线程自己不拥有系统资源,只拥有一点儿在运行中必不可少的资源,但它可与同属一个进程的其它线程共享进程所拥有的全部资源。一个线程可以创建和撤消另一个线程,同一进程中的多个线程之间可以并发执行。由于线程之间的相互制约,致使线程在运行中呈现出间断性。线程也有就绪、阻塞和运行三种基本状态。就绪状态是指线程具备运行的所有条件,逻辑上可以运行,在等待处理机;运行状态是指线程占有处理机正在运行;阻塞状态是指线程在等待一个事件(如某个信号量),逻辑上不可执行。每一个程序都至少有一个线程,若程序只有一个线程,那就是程序本身。
python线程的模块
_thread
threading
import _thread
import threading
import time
def job():
print("这是一个需要执行的任务")
# 激活的线程个数
print("当前线程的个数:", threading.active_count())
# 打印当前线程的详细信息
print("当前线程信息:", threading.current_thread())
time.sleep(100)
if __name__ == "__main__":
job()
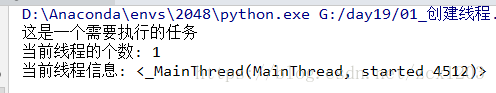
_thread模块中创建多线程
import _thread
import threading
import time
def job(name):
print("这是一个需要执行的任务")
# # 激活的线程个数
# print("当前线程的个数:", threading.active_count())
# # 打印当前线程的详细信息
# print("当前线程信息:", threading.current_thread())
print(name, time.ctime())
time.sleep(2)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建多个线程, 但是没有开始执行任务;
_thread.start_new_thread(job,('thread1', ))
_thread.start_new_thread(job,('thread2', ))
while True:
pass
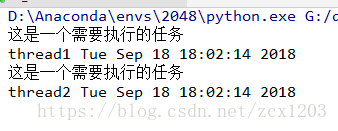
threading创建多线程
import threading
import time
def job(name):
print("这是一个需要执行的任务: %s" %(name))
# 激活的线程个数
print("当前线程的个数:", threading.active_count())
# 打印当前线程的详细信息
print("当前线程信息:", threading.current_thread())
# time.sleep(100)
print(name, time.ctime())
if __name__ == "__main__":
job('job0')
# 创建多个线程
t1 = threading.Thread(target=job, name='job1', args=("job1-name",))
t1.start()
t2 = threading.Thread(target=job, name='job2', args=("job2-name",))
t2.start()
print('hello')
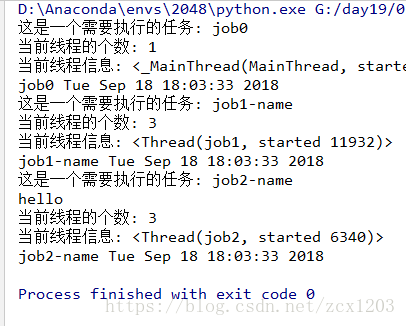
多线程的join方法
- join() :等待所有的子线程执行结束之后, 继续执行主线程的内容;
import threading
import time
def music(name):
for i in range(2):
print("正在听音乐%s" %(name))
time.sleep(1)
def code(name):
for i in range(2):
print("正在编写代码%s" %(name))
time.sleep(2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time = time.time()
# music("中国梦")
# code("爬虫")
t1 = threading.Thread(target=music, args=("中国梦",))
t2 = threading.Thread(target=code, args=("爬虫", ))
t1.start()
t2.start()
# 等待所有的子线程执行结束之后, 继续执行主线程的内容;
t1.join()
t2.join()
print("花费时间: %s" %(time.time()-start_time))
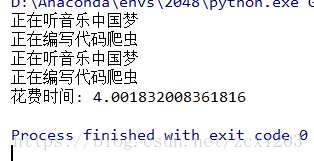
set_daemon方法实现
- set_daemon:当主线程执行结束, 让没有执行的线程强制结束
import threading
import time
# 任务1:
def music(name):
for i in range(2):
print("正在听音乐%s" %(name))
time.sleep(1)
# 任务2:
def code(name):
for i in range(2):
print("正在编写代码%s" %(name))
time.sleep(2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time = time.time()
# music("中国梦")
# code("爬虫")
t1 = threading.Thread(target=music, args=("中国梦",))
t2 = threading.Thread(target=code, args=("爬虫", ))
# 将t1线程生命为守护线程, 如果设置为True, 子线程启动, 当主线程执行结束, 子线程也结束
# 设置setDaemon必须在启动线程之前进行设置;
t1.setDaemon(True)
t2.setDaemon(True)
t1.start()
t2.start()
# 等待所有的子线程执行结束之后, 继续执行主线程的内容;
# t1.join()
# t2.join()
print("花费时间: %s" %(time.time()-start_time))

多线程应用_批量管理主机
# 基于ssh用于连接远程服务器做操作:远程执行命令, 上传文件, 下载文件
import threading
import paramiko
from paramiko.ssh_exception import NoValidConnectionsError, AuthenticationException
def connect(cmd, hostname, port=22, user='root'):
# ssh root@172.25.254.250
# 创建一个ssh对象;
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
# 返回一个私钥对象
private_key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file('id_rsa')
# 2. 解决问题:如果之前没有;连接过的ip, 会出现
# Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
# 自动选择yes
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
try:
# 3. 连接服务器
client.connect(hostname=hostname,
port=port,
username=user,
pkey=private_key
)
# 4. 执行操作
stdin, stdout, stderr = client.exec_command(cmd)
except NoValidConnectionsError as e:
print("%s连接失败" %(hostname))
except AuthenticationException as e:
print("%s密码错误" %(hostname))
else:
# 5. 获取命令的执行结果;
result = stdout.read().decode('utf-8')
print("%s运行结果:" %(hostname), result)
finally:
# 6. 关闭连接
client.close()
# for count in range(254):
# host = '172.25.254.%s' %(count+1)
# print(host.center(50, '*'))
# connect('uname', host)
# 用来存储创建的所有线程对象;
threads = []
for count in range(254):
host = '172.25.254.%s' %(count+1)
# print(host.center(50, '*'))
t = threading.Thread(target=connect, args=('uname', host))
threads.append(t)
t.start()
# join方法, 等待所有的子线程执行结束;
_ = [thread.join() for thread in threads]
print("任务执行结束........")
多线程应用_获取IP地理位置
import json
import threading
from urllib.request import urlopen
import time
def job(ip):
"""获取指定ip对应的地理位置"""
url = "http://ip.taobao.com/service/getIpInfo.php?ip=%s" % (ip)
# 根据url获取网页的内容, 并且解码为utf-8格式, 识别中文;
text = urlopen(url).read().decode('utf-8')
# 将获取的字符串类型转换为字典, 方便处理
d = json.loads(text)['data']
country = d['country']
city = d['city']
print("%s:" %(ip), country, city)
def has_many_thread():
start_time = time.time()
threads = []
ips = ['172.25.254.250', '8.8.8.8',
'172.25.254.250', '8.8.8.8',
'172.25.254.250', '8.8.8.8' ]
for ip in ips:
# 实例化线程对象
t = threading.Thread(target=job, args=(ip, ))
threads.append(t)
# 启动线程执行任务
t.start()
# join方法
[thread.join() for thread in threads]
print("Success, 使用多线程运行时间为:%s" %(time.time()-start_time))
def has_no_thread():
start_time = time.time()
ips = ['172.25.254.250', '8.8.8.8',
'172.25.254.250', '8.8.8.8',
'172.25.254.250', '8.8.8.8']
for ip in ips:
job(ip)
print("Success, 未使用多线程运行时间为:%s" % (time.time() - start_time))
if __name__ == '__main__':
has_many_thread()
has_no_thread()








 本文介绍了线程的定义和概念,线程是程序执行流的最小单元,有就绪、阻塞和运行三种状态。还阐述了Python中创建多线程的模块,如_thread和threading,以及多线程的join和set_daemon方法,最后列举了多线程在批量管理主机和获取IP地理位置方面的应用。
本文介绍了线程的定义和概念,线程是程序执行流的最小单元,有就绪、阻塞和运行三种状态。还阐述了Python中创建多线程的模块,如_thread和threading,以及多线程的join和set_daemon方法,最后列举了多线程在批量管理主机和获取IP地理位置方面的应用。
















 5054
5054

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








