SystemServer 进程
简介
SystemServer 进程,是zygote 进程启动的过程中,孵化出来的第一个进程。它作为系统进程的同时,是App 进程和 Zygote进程交互的桥梁。
- App进程通过IPC机制 和 systemServer进程建立联系。
- systemServer进程,通过socket连接。通知zygote 进程,fork出App进程。
- zygote 进程 和systemServer 进程 同生死,共同支撑着android系统。
启动流程
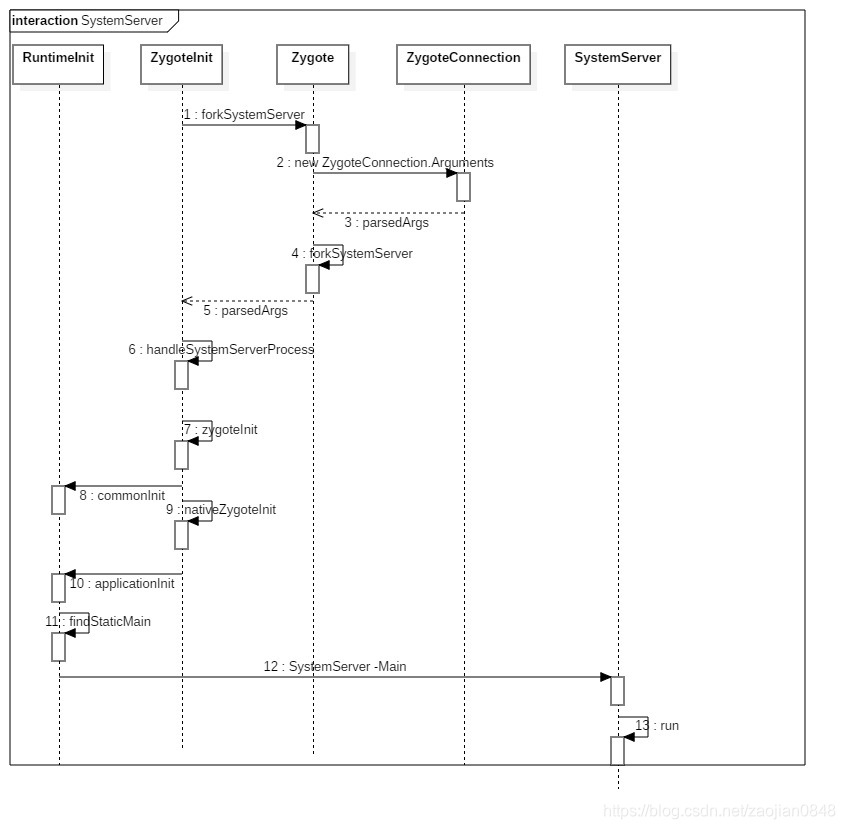
上一节,已经分析了systemServer 进程的出生。接下来梳理一下,它自己的身世。
//ZygoteInit.class
private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName,
ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
l/***********************省略若干******************/
//若干命令
//名称 “nice-name=system_serve”
//systemServer 全限定名 “com.android.server.SystemServer”
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
String args[] = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1023,1024,1032,1065,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--nice-name=system_server",
"--runtime-args",
"--target-sdk-version=" + VMRuntime.SDK_VERSION_CUR_DEVELOPMENT,
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try {
//1.ZygoteConnection 是对 LocalSocket 的封装
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
boolean profileSystemServer = SystemProperties.getBoolean(
"dalvik.vm.profilesystemserver", false);
if (profileSystemServer) {
parsedArgs.runtimeFlags |= Zygote.PROFILE_SYSTEM_SERVER;
}
//2.通过zygote fork出 systemServer 进程,并返回 进程id(Pid)
/* Request to fork the system server process */
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.runtimeFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
//如果pid >0 ->进程成功 fork出来
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) {
//如果设备有第二个zygote 进程
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
// 3.等待第二个socket孵化
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
//关闭systemserver中的 LocalServerSocket(写时复制,导致 systemServer 进程,共享了 zygote 进程的 LocalServerSocket)
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
//4.接下来处理ZygoteConnection 中Arguments
return handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
return null;
}
1. ZygoteConnection.Arguments
//ZygoteConnection/Arguments
Arguments(String args[]) throws IllegalArgumentException {
parseArgs(args);
}
//将{
// "--setuid=1000",
// "--setgid=1000",
// //setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,102//1,1023,1024,1032,1065,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010",
// "--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
// "--nice-name=system_server",
// "--runtime-args",
// "--target-sdk-version=" + VMRuntime.SDK_VERSION_CUR_DEVELOPMENT,
// "com.android.server.SystemServer",
// } 参数赋给了 静态变量 Arguments
private void parseArgs(String args[])
throws IllegalArgumentException {
***
}
2. Zygote.forkSystemServer( )
//Zygote.java
public static int forkSystemServer(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags,
int[][] rlimits, long permittedCapabilities, long effectiveCapabilities) {
VM_HOOKS.preFork();
// Resets nice priority for zygote process.
resetNicePriority();
//通过native 方法
int pid = nativeForkSystemServer(
uid, gid, gids, runtimeFlags, rlimits, permittedCapabilities, effectiveCapabilities);
// Enable tracing as soon as we enter the system_server.
if (pid == 0) {
Trace.setTracingEnabled(true, runtimeFlags);
}
VM_HOOKS.postForkCommon();
return pid;
}
3. waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName)
//ZygoteInit.java
private static void waitForSecondaryZygote(String socketName) {
//socketName 的重新命名
String otherZygoteName = Process.ZYGOTE_SOCKET.equals(socketName) ?
Process.SECONDARY_ZYGOTE_SOCKET : Process.ZYGOTE_SOCKET;
ZygoteProcess.waitForConnectionToZygote(otherZygoteName);
}
//ZygoteProcess
public static void waitForConnectionToZygote(String socketName) {
final LocalSocketAddress address =
new LocalSocketAddress(socketName, LocalSocketAddress.Namespace.RESERVED);
waitForConnectionToZygote(address);
}
//ZygoteProcess
public static void waitForConnectionToZygote(LocalSocketAddress address) {
//每一秒连接1次,尝试20次
for (int n = 20; n >= 0; n--) {
try {
//ZygoteState 封装了LocalSocket 连接 服务端(zygote) 的操作
final ZygoteState zs = ZygoteState.connect(address);
zs.close();
return;
} catch (IOException ioe) {
...
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
}
}
Slog.wtf(LOG_TAG, "Failed to connect to Zygote through socket " + address.getName());
}
4. handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs)
private static Runnable handleSystemServerProcess(ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs) {
// set umask to 0077 so new files and directories will default to owner-only permissions.
Os.umask(S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO);
if (parsedArgs.niceName != null) {
//设置了systemServer的进程名称
Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName);
}
//加载“Systemserver” 的类路径
final String systemServerClasspath = Os.getenv("SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH");
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
//该类,在加载到dalvik 虚拟机中,会进行 dexOpt 优化
performSystemServerDexOpt(systemServerClasspath);
// Capturing profiles is only supported for debug or eng builds since selinux normally
// prevents it.
boolean profileSystemServer = SystemProperties.getBoolean(
"dalvik.vm.profilesystemserver", false);
if (profileSystemServer && (Build.IS_USERDEBUG || Build.IS_ENG)) {
try {
//为system server准备概要文件并不需要特殊的配置文件selinux权限。从安装程序的角度来看,系统服务器是一个常规包可以捕获概要信息。
prepareSystemServerProfile(systemServerClasspath);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Failed to set up system server profile", e);
}
}
}
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
String[] args = parsedArgs.remainingArgs;
// If we have a non-null system server class path, we'll have to duplicate the
// existing arguments and append the classpath to it. ART will handle the classpath
// correctly when we exec a new process.
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
String[] amendedArgs = new String[args.length + 2];
amendedArgs[0] = "-cp";
amendedArgs[1] = systemServerClasspath;
System.arraycopy(args, 0, amendedArgs, 2, args.length);
args = amendedArgs;
}
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
parsedArgs.niceName, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(), null, args);
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected return from WrapperInit.execApplication");
} else {
//设置systemServer 类的ClassLoader
ClassLoader cl = null;
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
cl = createPathClassLoader(systemServerClasspath, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion);
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
}
/*
* Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
*/
return ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs, cl);
}
/* should never reach here */
}
//ZygoteInit.class
public static final Runnable zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (RuntimeInit.DEBUG) {
Slog.d(RuntimeInit.TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ZygoteInit");
//1.重定向输出流
RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams();
//2.
RuntimeInit.commonInit();
//3
ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();
//4
return RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
}
1. RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams()
//RuntimeInit.class
/**
* Redirect System.out and System.err to the Android log.
*/
//关闭Java输出流,打开android的输出流
public static void redirectLogStreams() {
System.out.close();
System.setOut(new AndroidPrintStream(Log.INFO, "System.out"));
System.err.close();
System.setErr(new AndroidPrintStream(Log.WARN, "System.err"));
}
2. RuntimeInit.commonInit()
//RuntimeInit.java
protected static final void commonInit() {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Entered RuntimeInit!");
/*
* set handlers; these apply to all threads in the VM. Apps can replace
* the default handler, but not the pre handler.
*/
LoggingHandler loggingHandler = new LoggingHandler();
//进程出错堆栈的捕获方式
Thread.setUncaughtExceptionPreHandler(loggingHandler);
// 发生JE问题,弹窗提醒用户
Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(new KillApplicationHandler(loggingHandler));
/*
* Install a TimezoneGetter subclass for ZoneInfo.db
*/
TimezoneGetter.setInstance(new TimezoneGetter() {
@Override
public String getId() {
return SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.timezone");
}
});
TimeZone.setDefault(null);
/*
* Sets handler for java.util.logging to use Android log facilities.
* The odd "new instance-and-then-throw-away" is a mirror of how
* the "java.util.logging.config.class" system property works. We
* can't use the system property here since the logger has almost
* certainly already been initialized.
*/
LogManager.getLogManager().reset();
new AndroidConfig();
/*
* Sets the default HTTP User-Agent used by HttpURLConnection.
*/
String userAgent = getDefaultUserAgent();
System.setProperty("http.agent", userAgent);
/*
* Wire socket tagging to traffic stats.
*/
NetworkManagementSocketTagger.install();
/*
* If we're running in an emulator launched with "-trace", put the
* VM into emulator trace profiling mode so that the user can hit
* F9/F10 at any time to capture traces. This has performance
* consequences, so it's not something you want to do always.
*/
String trace = SystemProperties.get("ro.kernel.android.tracing");
if (trace.equals("1")) {
Slog.i(TAG, "NOTE: emulator trace profiling enabled");
Debug.enableEmulatorTraceOutput();
}
initialized = true;
}
JE (Java layer exception) 一般是在应用层和框架层发生的异常,通常是由Java代码,XML代码引起的。比如各种RuntimeException, ANR(Application Not Responding)、SWT(Software Watchdog Timeout)等
//RuntimeInit.java
private static class LoggingHandler implements Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler {
public volatile boolean mTriggered = false;
//没有catch中的错误信息
@Override
public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) {
mTriggered = true;
// Don't re-enter if KillApplicationHandler has already run
if (mCrashing) return;
// mApplicationObject is null for non-zygote java programs (e.g. "am")
// There are also apps running with the system UID. We don't want the
// first clause in either of these two cases, only for system_server.
if (mApplicationObject == null && (Process.SYSTEM_UID == Process.myUid())) { //系统错误
Clog_e(TAG, "*** FATAL EXCEPTION IN SYSTEM PROCESS: " + t.getName(), e);
} else {
//
StringBuilder message = new StringBuilder();
// The "FATAL EXCEPTION" string is still used on Android even though
// apps can set a custom UncaughtExceptionHandler that renders uncaught
// exceptions non-fatal.
message.append("FATAL EXCEPTION: ").append(t.getName()).append("\n");
final String processName = ActivityThread.currentProcessName();
if (processName != null) {
message.append("Process: ").append(processName).append(", ");
}
message.append("PID: ").append(Process.myPid());
Clog_e(TAG, message.toString(), e);
}
}
}
/**
* Handle application death from an uncaught exception. The framework
* catches these for the main threads, so this should only matter for
* threads created by applications. Before this method runs, the given
* instance of {@link LoggingHandler} should already have logged details
* (and if not it is run first).
*/
private static class KillApplicationHandler implements Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler {
private final LoggingHandler mLoggingHandler;
/**
* Create a new KillApplicationHandler that follows the given LoggingHandler.
* If {@link #uncaughtException(Thread, Throwable) uncaughtException} is called
* on the created instance without {@code loggingHandler} having been triggered,
* {@link LoggingHandler#uncaughtException(Thread, Throwable)
* loggingHandler.uncaughtException} will be called first.
*
* @param loggingHandler the {@link LoggingHandler} expected to have run before
* this instance's {@link #uncaughtException(Thread, Throwable) uncaughtException}
* is being called.
*/
public KillApplicationHandler(LoggingHandler loggingHandler) {
this.mLoggingHandler = Objects.requireNonNull(loggingHandler);
}
@Override
public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) {
try {
ensureLogging(t, e);
// Don't re-enter -- avoid infinite loops if crash-reporting crashes.
if (mCrashing) return;
mCrashing = true;
// Try to end profiling. If a profiler is running at this point, and we kill the
// process (below), the in-memory buffer will be lost. So try to stop, which will
// flush the buffer. (This makes method trace profiling useful to debug crashes.)
if (ActivityThread.currentActivityThread() != null) {
ActivityThread.currentActivityThread().stopProfiling();
}
// Bring up crash dialog, wait for it to be dismissed
ActivityManager.getService().handleApplicationCrash(
mApplicationObject, new ApplicationErrorReport.ParcelableCrashInfo(e));
} catch (Throwable t2) {
if (t2 instanceof DeadObjectException) {
// System process is dead; ignore
} else {
try {
Clog_e(TAG, "Error reporting crash", t2);
} catch (Throwable t3) {
// Even Clog_e() fails! Oh well.
}
}
} finally {
// Try everything to make sure this process goes away.
//杀死进程
Process.killProcess(Process.myPid());
System.exit(10);
}
}
3.ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit()
nativeZygoteInit() 是一个navtive 方法 。有兴趣可以看下 更底层源码
4.RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader)
//RuntimeInit.java
protected static Runnable applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) {
// If the application calls System.exit(), terminate the process
// immediately without running any shutdown hooks. It is not possible to
// shutdown an Android application gracefully. Among other things, the
// Android runtime shutdown hooks close the Binder driver, which can cause
// leftover running threads to crash before the process actually exits.
nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup(true);
// We want to be fairly aggressive about heap utilization, to avoid
// holding on to a lot of memory that isn't needed.
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.75f);
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion);
final Arguments args = new Arguments(argv);
// The end of of the RuntimeInit event (see #zygoteInit).
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
// Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
return findStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
}
//RuntimeInit.java
/**
* Invokes a static "main(argv[]) method on class "className".
* Converts various failing exceptions into RuntimeExceptions, with
* the assumption that they will then cause the VM instance to exit.
*
* @param className Fully-qualified class name
* @param argv Argument vector for main()
* @param classLoader the classLoader to load {@className} with
*/
//通过反射 ,走到了systemServer 的main () 方法里面
protected static Runnable findStaticMain(String className, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) {
Class<?> cl;
try {
cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
ex);
}
Method m;
try {
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing static main on " + className, ex);
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
}
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Main method is not public and static on " + className);
}
/*这个抛出会被ZygoteInit.main()捕获,它会做出响应
* 通过调用异常的run()方法。这样的安排
*清除设置中需要的所有堆栈帧
*加快进程。
* */
return new MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}
本章主要梳理了,systemServer 从fork开始 到 进入自己main 函数的流程。
























 308
308

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








