字节流与字符流的操作的本质区别只有一个:字节流是原生的操作,而字符流是经过处理后的操作。 在进行网络数据传输、磁盘数据保存所保存的支持数据类型只有:字节,所以磁盘中的数据必须先读取到内存后才可以操作,内存可以可以帮助我们把字节变成字符。字符更加适合操作中文。
字节流:InputStream 、OutputStream
字符流:Reader、Writer;
不管使用的是字节流还是字符流,其基本的操作流程几乎是固定的,以文件操作为例
1、要根据文件路径创建File类对象
2、根据字节流或字符流的子类实例化父类对象;
3、进行我们数据的读取或写入操作;
4、关闭流(close() 必须关闭)
对于IO操作属于资源处理,所有的资源处理操作的最后必须要进行关闭,如果你在项目里面没有执行关闭,那么这种关闭就再也执行不了,除非关闭整个项目。(网络资源,数据库资源都必须关闭)
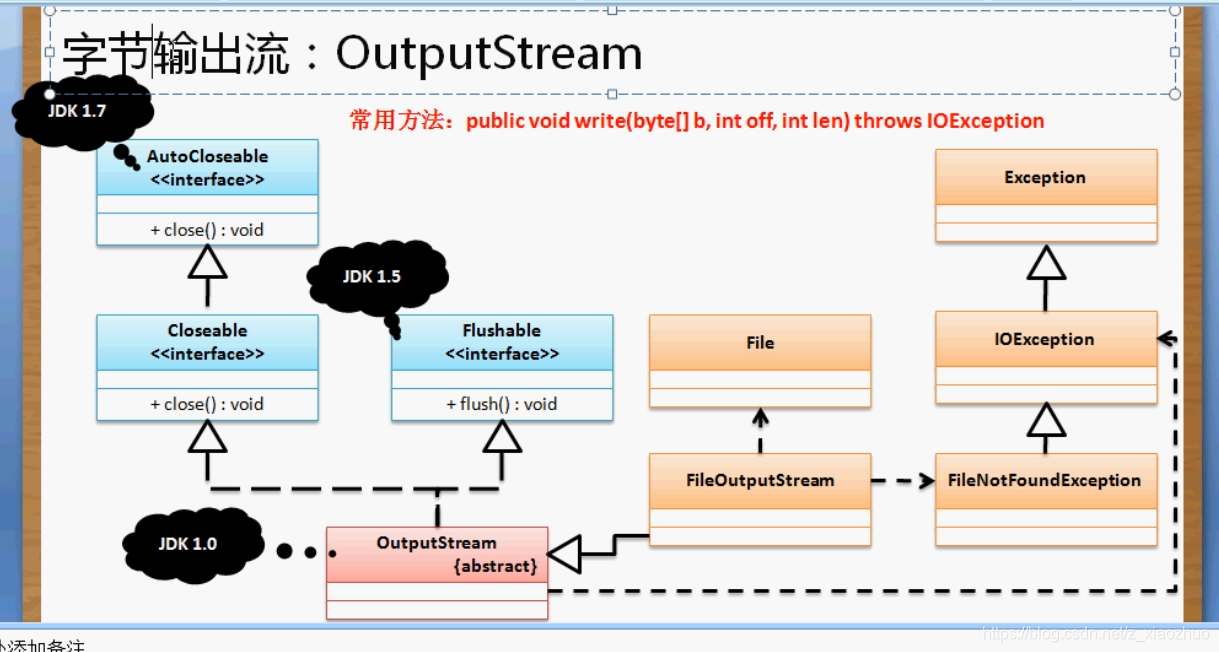
字节输出流:OutputStream
OutputStream类实现啦Closeable、Flushable两个接口
Closeable:public void close() throws IOException;
Flushable:public void flush() throws IOException; //flush 清空
在OutputStream类里面实际上还定义有其他方法:
public void write(byte[] b) throws IOException
OutputStream是一个抽象类,需要子类实例化父类对象,方法都被父类已经定义好了,我们只关注子类的构造方法
//根据索引部分输出
public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file=new File("f:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"); //1、通过File类定义文件路径
if(!file.getParentFile().exists()){ //必须保证父目录存在
file.getParentFile().mkdirs(); //如果不存在创建目录
}
//2、OutputStream是一个抽象类,所以需要子类实例化,意味着只能进行文件处理
OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream(file);
//3、进行文件输出处理操作
String msg="www.Google.com\r\n"; //要输出的文件内容 /r/n换行操作
//将内容变成字节数组
out.write(msg.getBytes());
//部分输出,输出前三个
out.write(msg.getBytes(), 0, 3);
//4、关闭流close()
out.close();
}
}
InputStream:
//读取数据到字节数组里,返回数据读取个数
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException
---返回值:如果数组长度大于数据长度,则返回读取数据长度
如果数据长度大于数组长度,则返回数组长度
如果没有数据啦,还继续读取数据,则返回-1
//读取部分数据到字节数组中
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException
---返回值:
每次只读取传递数组的部内容,如果读取满啦则返回数组长度,如果没有读取满,就是读取数据的个数,如果读取最后没有数据返回-1;
//读取单个字节
public abstract int read () throws IOException
---返回值:
每次读取一个字节内容,读取没有数据,返回-1;
public class TestINnputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file=new File("f:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"); //通过File类定义文件路径
if(file.exists()){ //判断文件是否存在,存在才可以读取
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
InputStream in=new FileInputStream(file);
byte []b=new byte[1024]; //每次最多可以读取1024个字节
int len=in.read(b); //此时数据读取到数组之中
System.out.println("数据【"+new String(b,0,len)+"】");
}
}
}
字符输出流:
Writer抽象类,子类实例化父类对象
public class TestWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file=new File("f:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"); //1、通过File类定义文件路径
if(!file.getParentFile().exists()){ //必须保证父目录存在
file.getParentFile().mkdirs(); //如果不存在创建目录
}
String str="世界和平";
Writer writer=new FileWriter(file,true);
writer.write(str); //直接输入字符串
writer.close();
}
}
字符输入流
Reader抽象类。
在Reader类里面不会定义有一个方法可以直接读取数据为字符串。
public class TestReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file=new File("f:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"); //1、通过File类定义文件路径
if(file.exists()){ //判断文件是否存在
Reader reader=new FileReader(file);
char []data=new char[1024];
int len=reader.read(data);
System.out.println("读出数据【"+new String(data,0,len) +"】");
reader.close(); //关闭流
}
}
}
字节流与字符流的区别:
在我们实际开发中,我们优先考虑字节流,只有在处理中文的时候才使用到字符流,因为字符流会使用到内存缓冲
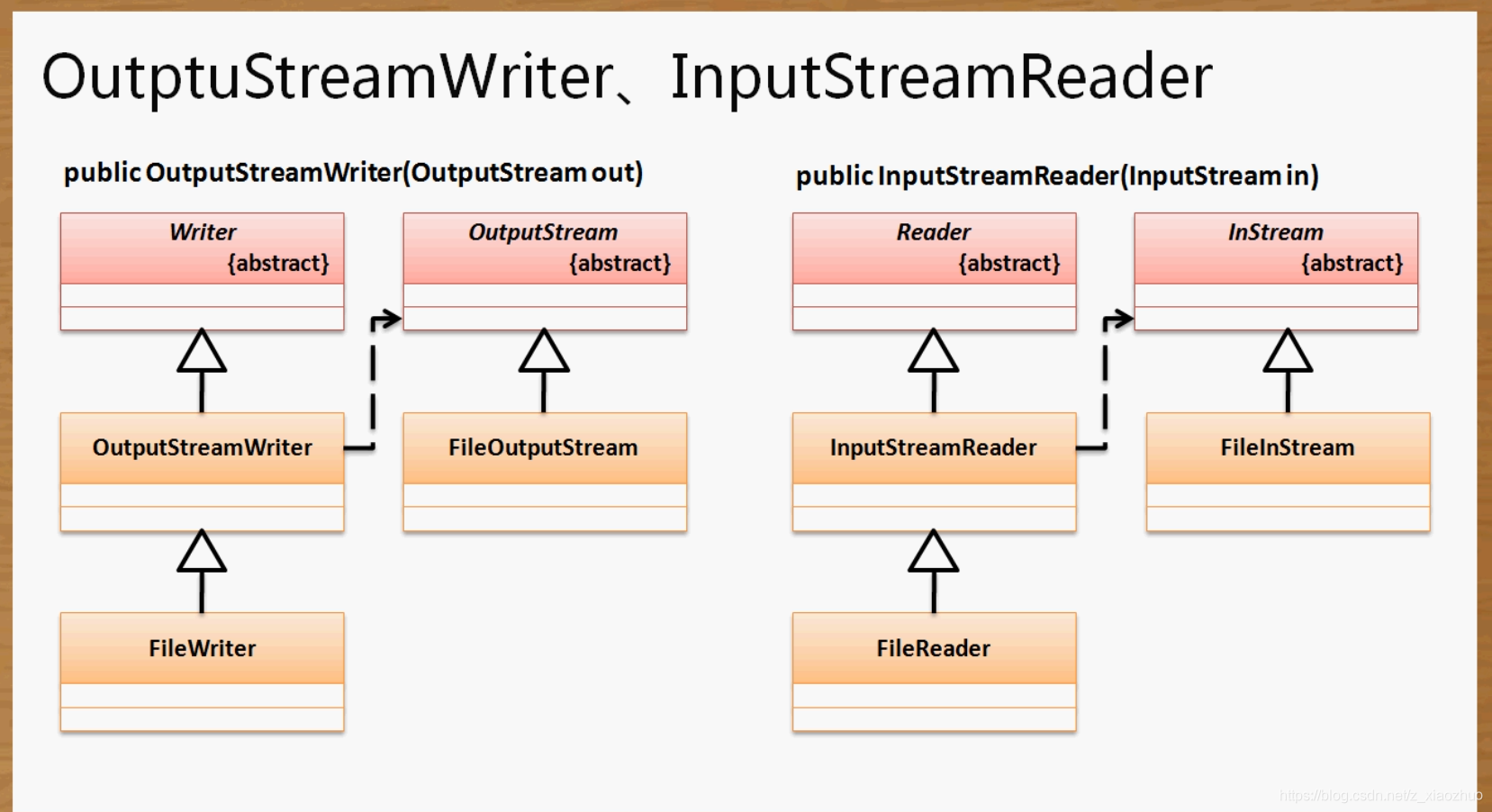
转换流:
OutputStreamWriter:将字节输出流变成字符输出流;
InputStreamReader: 将字节输入流转变成字符输入流
public class TestOutputStreamWrider {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file=new File("f:"+File.separator+"hello.txt"); //1、通过File类定义文件路径
if(!file.getParentFile().exists()){ //必须保证父目录存在
file.getParentFile().mkdirs(); //如果不存在创建目录
}
OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream(file);
OutputStreamWriter outwriter=new OutputStreamWriter(out);
outwriter.write("转角爱哈哈个");
outwriter.close();
}
}
OutputStream类的继承结构
转换流的继承结构























 483
483

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








