目录
2017
1. 回文数+素数
输入n;输出1-n中既是素数,又是回文数的数,以及总数(数目)是多少?(100<=n<=1000)
思路:
1. 采用贪心算法,遍历1-n,设置素数和回文数的或条件,满足则输出,并且count++;
2. 素数的检测算法,回文数的检测算法,见C语言经典机试题
输入输出截图: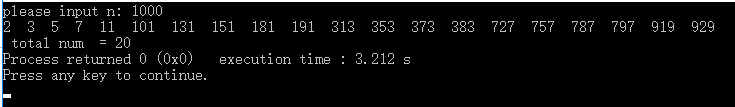
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int IsPrime(int n);
int IsHuiwen(int n);
int main()
{
int n, i, count = 0, flag=0;
// IsPrime();
printf("please input n: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
flag = IsPrime(i) && IsHuiwen(i);
if(flag)
{
printf("%d ", i);
count++;
}
}
printf("\n total num = %d", count);
return 0;
}
int IsPrime(int n)
{
int i, flag=1;
if(n==1) flag=0;
for(i=2; i*i<=n; i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
{
flag = 0;
break;
}
}
return flag;
}
int IsHuiwen(int n)
{
int a[4]={0};
int len=0, p1=0, p2=0, i=0; //数组实际长度,头尾指针
int num=n, flag=1; // 剩下的大小, flag
// 提取n的各个位数
while(num>0)
{
a[i] = num%10;
num = num/10;
i++;
}
len = i;
p2 = len-1;
// 对各个位数比较是否对称
for(; p1<p2; p1++,p2--)
{
if(a[p1] != a[p2])
{
flag = 0;
break;
}
}
return flag;
}
2. 字符串
解密——加密的算法是26个英文字母,向后移三位为密文(a加密为d...最后x->a;y->b;z->c)有大小写。输入密文,计算明文
思路:
1. 注意解密左移时不能直接-3,对(abc)这样的字幕应该是+23,d及其以后可以直接-3;
2. 计算距离时要添加绝对值, if((abs(ip[i]-'a')<3) || (abs(ip[i]-'A')<3)),如D-a是负数,满足<3的条件,但D应该是-3而不是+23;所以绝对值很重要;
3. 注意对于op[], 要在最后的位置上添加'\0'
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
char ip[30], op[30];
int i;
printf("please input encrypt data: ");
scanf("%s", ip);
for(i=0; i<strlen(ip); i++)
{
// 直接-3会溢出的字符
if((abs(ip[i]-'a')<3) || (abs(ip[i]-'A')<3))
{
op[i] = ip[i] + 23;
}
else
{
op[i] = ip[i] - 3;
}
}
op[i] = '\0'; //结束标志位
printf("%s", op);
return 0;
}
2016
1. 桶排序+提取数字的各个位数
(30分)从键盘输入一个整型数据(int型),编写程序判断该整数共有几位,并输出包含各个数字的个数。例如,从键盘输入整数16644,该整数共有5位,其中有1个1,2个6,2个4。
注:(1)此题不能使用指针、结构体、共用体、文件、goto、枚举类型进行编程。
(2)用标准C语言编程,所有变量必须在第一条可执行语句前定义。
(3)输入输出格式要和以下给定格式完全一致。
程序运行结果示例1:
Please enter the number:
12226↙
12226: 5 bits
1: 1
2: 3
6: 1
程序运行结果示例2:
Please enter the number:
-12243↙
-12243: 5 bits
1: 1
2: 2
3: 1
4: 1
说明:
输入提示信息: "Please enter the number:\n"
输出格式:"%d: %d\n"
答案:
思路:1. 把input取绝对值num;定义一个桶数组A[10], 用来记录每一位出现的次数;
2.对num进行循环,每次%10得到尾数,然后用桶数组对其进行标记。num每次迭代会/10,直到num为0
3. 对桶数组A进行输出
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int abs(int num)
{
if(num >= 0)
return num;
else
return -num;
}
int main()
{
// int x = -12264;
// printf("%d", abs(x));
// exit(0);
int A[10] = {0};
int input, num ,geWei, i=0, j=0;
printf("Please enter the number:\n");
scanf("%d", &input);
num = abs(input);
while(num != 0)
{
geWei = num%10;
A[geWei]++;
num = num /10;
i++; // input的位数
}
printf("%d: %d bits\n", input, i); //位数输出
// 输出桶
for(j=0; j<10; j++)
{
if(A[j]!=0)
{
printf("%d: %d\n", j, A[j]);
}
}
return 0;
}
2.字符串
(30分)用户密码设置模拟程序。编写函数让用户先输入(即设置)一串长度为8的密码,如果用户输入的密码长度不是8,则密码设置失败,函数返回0;如果密码长度是8,则让用户再输入一次密码进行确认,如果两次输入的密码相同,则密码设置成功,函数返回1,如果两次输入的密码不同,则设置失败,函数返回0。
编写主程序调用函数设置密码并根据密码设置是成功还是失败的不同情况输出不同的提示信息。函数原型如下:
int Setting(char password[]);
功能:设置密码
参数:passWord,存放密码数组,大小为20个字符;
返回值:设置成功返回1,设置失败返回0。
注:(1)此题不能使用指针、结构体、共用体、文件、goto、枚举类型进行编程。
(2)用标准C语言编程,所有变量必须在第一条可执行语句前定义。
(3)输入输出格式要和以下给定格式完全一致。
程序运行示例1:
Please input password with 8 characters:
12345678
Please input again:
12345678
Successfully set password:12345678
程序运行示例2:
Please input password with 8 characters:
1234567
Failure!
程序运行示例3:
Please input password with 8 characters:
12345678
Please input again:
1234567
Failure!
说明:
**输入提示信息:
"Please input password with 8 characters:\n"
"Please input again:\n"
**输入信息格式:"%s"
**输出信息及格式:
"Successfully set password:%s\n"
"Failure!\n"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int abs(int num)
{
if(num >= 0)
return num;
else
return -num;
}
int Setting(char password[]);
int main()
{
char psd1[20], psd2[20];
printf("Please input password with 8 characters:\n");
scanf("%s", psd1);
// 首次设置是8位
if(Setting(psd1))
{
printf("Please input again:\n");
scanf("%s", psd2);
if(strcmp(psd1, psd2) == 0) printf("Successfully set password:%s", psd1);
else printf("Failure!");
}
else printf("Failure!");
return 0;
}
int Setting(char password[])
{
if(strlen(password) == 8) return 1;
else return 0;
}
2015
1.谈心算法
(15 分)编程计算 n 以内(包括 n)含 6 的所有自然数(例如: 16, 26, 60, 606 等)的
倒数之和。其中 n 的值由键盘输入, 0<n<1000。
注:(1)不能使用指针、结构体、共用体、文件、 goto、枚举类型进行编程。
(2)用标准 C 语言编程,所有变量必须在第一条可执行语句前定义。
(3)输入输出格式要和以下给定格式完全一致。
运行示例:
Input n(0<n<1000)
600
0.85
输入提示信息: "Input n(0<n<1000)\n"
输入数据格式: "%d"
输出格式: "%.2f\n
答案:
思路:谈心算法,每次先判断num是否满足包含6的条件(用函数Include6),若满足则加到sum,然后对num--。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Include6(int num);
int main()
{
int n, num;
float sum=0;
printf("Input n(0<n<1000)\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
num = n;
while(num >= 6)
{
if(Include6(num)) {
sum += 1.0/num;
}
num--;
}
printf("%.2f\n", sum);
return 0;
}
// 是否包含6
int Include6(int num)
{
int bai, shi, ge, temp;
ge = num%10;
temp = num/10;
shi = temp%10;
bai = num/100;
if(ge==6 || shi==6 || bai==6) return 1;
else return 0;
}
2. 字符串gets()和strlen()
(15 分)用字符数组作函数参数,编程实现在字符串每个字符间插入一个空格的功能。
字符数组大小定义为 80 个字符。
要求:
(1)按如下函数原型进行编程:
void Insert(char s[]);
(2)在主函数中:
输入字符串,调用函数 Insert,将字符串插入空格; 然后打印插入空格后的字符串。
注:(1)不能使用指针、结构体、共用体、文件、 goto、枚举类型进行编程。
(2)用标准 C 语言编程,所有变量必须在第一条可执行语句前定义。
(3)输入输出格式要和以下给定格式完全一致。
运行示例:
Input a string:
abcdefg hijklmn
Insert result:
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n
输入提示信息为: "Input a string:\n"
输出字符串前提示: "Insert result:\n"
输出格式: "%s\n"
答案:
1.因为输入的字符串有空格, 所以不能用scanf,需要用gets()函数;
2. 字符串的结尾是'\0'。 因为预计不能用字符串处理函数,所以得手写
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N 100
void Insert(char s[]);
int main()
{
char s[100];
printf("Input a string:\n");
gets(s);
Insert(s);
return 0;
}
void Insert(char s[])
{
int i, j=0;
char s2[200];
for(i=0; s[i]!= '\0'; i++)
{
s2[j++] = s[i];
s2[j++] = ' ';
}
s2[j] = '\0';
printf("%s\n", s2);
}
3.(20 分)已知某大奖赛有 n 个选手参赛(n<=20), m 个评委(m<=5)为参赛选手评分(最
高 10 分,最低 0 分)。统分规则为:在每个选手的 m 个得分中,去掉一个最高分和一个最
低分后,取平均分做为该选手的最后得分。要求编程实现:
从键盘读入各个评委给各个选手的打分,函数原型如下
void ReadScore(float score[][M], int n, int m);
M 表示最大评委人数
接下来,统计参赛选手的得分,函数原型如下
void CountScore(float averagescore[], float score[][M], int n, int m);
最后输出各个选手的得分,函数原型如下
void PrintScore(float averagescore[], int n);
注:(1)不能使用指针、结构体、共用体、文件、 goto、枚举类型进行编程。
(2)用标准 C 语言编程,所有变量必须在第一条可执行语句前定义。
(3)输入输出格式要和以下给定格式完全一致。
运行示例如下:
Input the number of athletes
3
Input the number of judges
4
Input 4 judges' scores for 3 athletes
8.9 9.8 8.7 7.5
7.8 9.8 6.7 7.2
9.9 9.7 9.6 8.9
The final scores for each athlete
8.80
7.50
9.65
输入提示信息:
"Input the number of athletes\n"
"Input the number of judges\n"
"Input %d judges' scores for %d athletes\n"
输出提示信息:
"The final scores for each athlete\n"
输出格式:
"%.2f\n"
答案:
1. 向函数传递二维数组,数组的第二维度必须有常量,如score[ ][ M],需要先define M(M足够大);
2. 向函数传递二维数组时,可以省略数组长度,如void PrintScore(float averagescore[], int n);
3. 声明一位数组、二维数组,如score[][]时,可以直接averagescore[M], score[M][M],使其足够大。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define M 50
void ReadScore(float score[][M], int n, int m);
void CountScore(float averagescore[], float score[][M], int n, int m);
void PrintScore(float averagescore[], int n);
int main()
{
int m, n;
float score[M][M];
float averagescore[M];
printf("Input the number of athletes\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Input the number of judges\n");
scanf("%d", &m);
printf("Input %d judges' scores for %d athletes\n", m, n);
ReadScore(score, n, m);
CountScore(averagescore, score, n, m);
PrintScore(averagescore, n);
return 0;
}
void ReadScore(float score[][M], int n, int m)
{
int i, j;
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<m; j++)
{
scanf("%f", &score[i][j]);
}
}
}
void CountScore(float averagescore[], float score[][M], int n, int m)
{
int i, j;
float max, min, sum;
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
max = score[i][0];
min = score[i][0];
sum = score[i][0];
for(j=1; j<m; j++)
{
if(score[i][j] > max) max = score[i][j];
if(score[i][j] < min) min = score[i][j];
sum += score[i][j];
}
averagescore[i] = (sum - max - min)/(m-2);
}
}
void PrintScore(float averagescore[], int n)
{
int i;
printf("The final scores for each athlete\n");
for(i=0; i<n; i++) printf("%.2f\n", averagescore[i]);
}
2014
1.杨辉三角
(15分)在屏幕上显示如下的杨辉三角形:
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
1 5 10 10 5 1
1 6 15 20 15 6 1
1 7 21 35 35 21 7 1
… … … … … … … … … …
请按照如下给定的函数原型编程计算并输出n(n<=15)行杨辉三角形。
其中, n值由用户在主函数中通过键盘输入。
void YHTriangle(int a[][15], int n);/*用于计算杨辉三角形*/
void PrintYHTriangle(int a[][15], int n);/*用于打印杨辉三角形*/
**输入提示信息要求: "Input n(n<=15):\n"
**输入格式: "%d"
**输出格式: "%5d"
注:
严格按C标准编程。 各函数中的变量声明写在所有可执行语句之前。
不能使用指针、 结构体、 共用体、 文件、 goto、 枚举类型进行编程。
答案:
杨辉三角+二维数组
输出答案:
2. double型变量,%e形式输出
(15分)国王的许诺。 相传国际象棋是古印度舍罕王的宰相达依尔发明的。 舍罕王十分喜欢象棋, 决定让宰相自己选择何种赏赐。 这位聪明的宰相指着8× 8共64格的象棋盘说, 在第1个格子中放1粒,第2个格子中放2粒,第3个格子中放4粒,以后每一格都比前一格增加1倍,依此放完棋盘上的64个格子。请分别采用两种累加方法(直接计算累加的通项,利用前项计算后项)计算共需要多少粒麦子,这些麦子合多少立方米(已知1立方米麦子约1.42e8粒)。
**输入格式: 无
**输出格式:
"sum = %e\n"
"volum = %e\n
注:
严格按C标准编程。 各函数中的变量声明写在所有可执行语句之前。
不能使用指针、 结构体、 共用体、 文件、 goto、 枚举类型进行编程。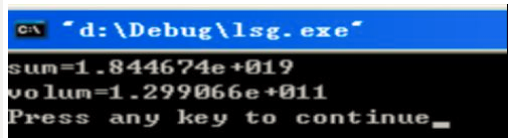
答案:
注意:此处的每一格的粒子数num和总数sum都要用double型的变量,否则会溢出。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
int i;
double num=1, volume, sum=0, temp=1.42e8;
for(i=0; i<64; i++)
{
sum += num;
num *= 2;
}
volume = sum / temp;
printf("sum = %e\n", sum);
printf("volum = %e\n", volume);
return 0;
}
3.字符串处理
(20分)输入一行字符(最长不超过80字符), 用函数编程统计其中有多少个单词。 假设单词之间以空格分开。
函数原型: int CountWords(char str[]);
**输入提示信息: "Input a string:\n"
**输出提示信息: "Numbers of words = %d\n"
例如:
Input a string:
I am a student
Numbers of words = 4
注:
严格按C标准编程。 各函数中的变量声明写在所有可执行语句之前。
不能使用指针、 结构体、 共用体、 文件、 goto、 枚举类型进行编程、
答案:
1. 字符串的输入:gets()函数
2. 字符串的结尾:'\0'
3. 考虑边界,什么单词都不输入时
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
# define N 50
int main()
{
char s[50];
int i, count = 0;
printf("Input a string:\n");
gets(s);
for(i=0; s[i]!='\0'; i++)
{
if(s[i] == ' ') count++;
}
if(strlen(s)!=0) count++; // 统计的是空格数量,单词比空格多1
printf("Numbers of words = %d\n", count);
return 0;
}
2013
1.递推关系
(15分)猴子吃桃问题。猴子第一天摘下若干个桃子,当即吃了一半,还不过瘾,又多吃了一
个。第二天早上又将剩下的桃子吃掉一半,又多吃了一个。以后每天早上都吃了前一天剩下的一半零
一个。到第10天早上再想吃时,见只剩一个桃子。求第一天共摘了多少桃子。
要求:
(1)输出格式要求:"%d\n"
(2)不允许使用递归、链表、指针、结构体、goto、共用体、文件、枚举类型。
(3)纯C语言编程,所有变量必须在第一条可执行语句前定义。
****注:要求(2)-(3)也适用于所有编程题。
答案:
列出地推关系即可,前一天剩余的桃子数是(当日桃子数总额+1) * 2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SIZE 51
int main()
{
int rest = 1, day=10, ans;
for(; day!=1 ; day--)
{
rest = (rest+1) * 2;
}
ans = rest / 2 + 1;
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
2.排序
(15分)用一个整型数组feedback保存不超过20个调查的反馈意见。
其中每个反馈意见是1-10范围中的一个整数。
用函数编程计算这些反馈意见的中位数。
中位数指的是将数据排序后,数值大小排列在数组中间的数。如果原始数据的个数是偶数,那么中位
数等于中间那两个元素的算术平均值。
要求:
(1) 首先从键盘输入反馈意见个数,输入提示信息为
"Input total number of feedbacks\n"
(2) 然后任意从键盘输入n个(假设输入的反馈意见个数为n)值在1-10范围中的整数,输入提
示信息为
"Input feedbacks\n"
只提示一次。
(3) 编写函数Median,计算n个数的中位数,函数原型为:
int Median(int answer[], int n);
(4) 在主函数调用函数Median,并输出中位数。
输出格式要求:"Median value=%d\n"
(5) 如果使用排序算法,请使用选择排序算法按从大到小的顺序排序,其函数原型为;
void DataSort(int a[], int n);
(6) 程序运行示例如下
Input total number of feedbacks
9
Input feedbacks
9 8 7 1 2 6 7 8 5
Median value=7
答案:
冒泡排序,然后再求中位数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 排序
void DataSort(int a[], int n);
int Median(int answer[], int n);
int main()
{
int a[15], n, i, mid;
printf("Input total number of feedbacks\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Input feedbacks\n");
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
DataSort(a, n);
printf("after bubblesort\n");
// for(i=0; i<n; i++) printf("%d ", a[i]);
mid = Median(a, n);
printf("Median value=%d\n", mid);
return 0;
}
void DataSort(int a[], int n)
{
int i, j, temp;
for(i=n-1; i>=1; i--)
{
for(j=0; j<=i-1; j++)
{
if(a[j] < a[j+1])
{
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j+1];
a[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int Median(int answer[], int n)
{
int mid;
if(n%2 == 1) mid = answer[n/2];
else mid = (answer[n/2 - 1] + answer[n/2]) / 2;
return mid;
}
3. 字符串排序
(20分)请用二维字符数组方法编程实现按奥运会参赛国国名在字典中的顺序对其入场次序进行
排序后打印输出。假设参赛国个数为10个,每个国名最大长度20个字符。
要求:
(1) 从键盘输入10个国名
(2) 要求读入的国名可以包含有空格
(3) 使用交换排序算法实现国名按字典序排序,函数原型为
void SortString(char str[][MAX_LEN], int n);
(4) 输出提示信息为"Sorted results\n"
输出数据格式要求: 一行输出一个字符串。
(5) 程序运行示例如下
South Korea
Finland
United States
England
Australia
Brazil
Egypt
China
Mexico
Spain
Sorted results
Australia
Brazil
China
Egypt
England
Finland
Mexico
South Korea
Spain
United States
答案:
需要用到字符串比较函数strcmp,strcpy。注意,字符串的赋值和比较需要用到函数,而不可以直接使用==或=;
排序方法:冒泡排序。调试过程中冒泡排序出了点问题
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_LEN 20
void SortString(char str[][MAX_LEN], int n);
int strCompare(char a[], char b[]);
int main()
{
char str[10][MAX_LEN];
int i;
for(i=0; i<10; i++)
{
gets(str[i]);
printf("i=%d\n", i);
}
SortString(str, 10);
printf("Sorted results\n");
for(i=0; i<10; i++) printf("%s\n", str[i]);
return 0;
}
void SortString(char str[][MAX_LEN], int n)
{
int i, j;
char temp[MAX_LEN];
for(i=n-1; i>=1; i--)
{
for(j=0; j<=i-1; j++)
{
if(strcmp(str[j], str[j+1]) > 0)
{
strcpy(temp, str[j]);
strcpy(str[j], str[j+1]);
strcpy(str[j+1], temp);
}
}
}
}
2012 强制类型转换
1.百万富翁问题:一个百万富翁遇到一个陌生人,陌生人找他谈了一个换钱的计
划。该计划如下:我每天给你 10 万元,你第一天给我 1 分钱,第二天 2 分钱,
第三天 4 分钱。。。
这样交换 30 天后,百万富翁交出了多少钱?陌生人交出了多少钱?(注意
一个是万元,一个是分)
输出格式要求: %ld 输出,单位是元
答案:
注意:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
double term = 0.01, sum1 = 1, sum2;
int i;
for(i=2; i<=30; i++)
{
term *= 2;
sum1 += term;
}
sum2 = 100000 * 30;
printf("sum1 = %ld\n", (long)sum1);
printf("sum2 = %ld\n", (long)sum2);
return 0;
}
2.矩阵乘法(重点)
计算两个矩阵的乘积,第一个是 2*3,第二个是 3*2
答案:
注意,理清三层循环的逻辑
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a[2][3] = {{1,2,3},{4,5,6}};
int b[3][2] = {{1,2}, {3,4}, {5,6} };
int c[2][2];
int i, j, k, term, sum;
for(i=0; i<2; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<2; j++)
{
sum = 0;
for(k=0; k<3; k++)
{
term= a[i][k]*b[k][j];
sum += term;
}
c[i][j] = sum;
}
}
//output
for(i=0; i<2; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<2; j++)
{
printf("%d ", c[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
输出: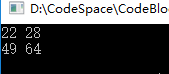
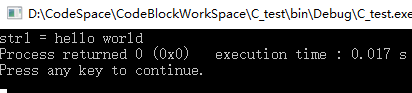
3.手写字符串拼接MyStract
不用 strcat 函数,自己编写一个字符串链接函数 MyStrcat(char dstStr[],charsrcStr[]),注意要单独编成函数,提交的时候提交全部的程序,包括 main。
答案
双指针拼接
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void MyStrcat(char dstStr[], char charsrcStr[]);
int main()
{
char str1[] = "hello ", str2[] = "world";
MyStrcat(str1, str2);
printf("str1 = %s", str1);
return 0;
}
void MyStrcat(char dstStr[],char charsrcStr[])
{
int p1, p2;
for(p1=0; dstStr[p1]!='\0'; p1++)
{ }
// ´Ëʱp1Ö¸Ïò'\0'
for(p2=0; charsrcStr[p2]!='\0'; p2++)
{
dstStr[p1+p2] = charsrcStr[p2];
}
dstStr[p1+p2] = '\0';
}
2011
1. 字符串逆置
答案:
注意:求数组长度时只能在主函数区,当数组A作为参数被传递到函数时,此时它表示指针,这是sizeof(A)/sizeof(int)=1永远存在。所以需要传递字符串长度
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void inverse(int A[], int len);
int main()
{
int A[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7, 8};
int B[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
int i, len;
len = sizeof(A)/sizeof(int);
inverse(A, len);
for(i=0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(int); i++) printf("%d ", A[i]);
return 0;
}
void inverse(int A[], int len)
{
int p1, p2, temp;
for(p1=0, p2=len-1; p1 < p2; p1++, p2--)
{
temp = A[p1];
A[p1] = A[p2];
A[p2] = temp;
}
}
2. 最大公约数
![]()
答案:
欧几里得法,也成辗转相除法。对a和b连续进行求余运算,知道余数为0。此时非0的除数即是最大公约数。
通过该性质: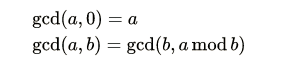
例子如下:123456 和 7890 的最大公因数是 6,
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int gcd(int a, int b);
int main()
{
int a, b, max, min, num;
while(scanf("%d %d", &a, &b)!=EOF)
{
if(a>=b)
{
max = a; min = b;
}
else
{
max = b; min = a;
}
num = gcd(max, min);
printf("gcd = %d\n", num);
}
return 0;
}
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if(b==0) return a;
gcd(b, a%b);
}























 4007
4007

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








