Map 和 Set
一、搜索
1.1 概念及场景
Map和set是一种专门用来进行搜索的容器或者数据结构,其搜索的效率与其具体的实例化子类有关。 以前常见的搜索方式有:
- 直接遍历,时间复杂度为O(N),元素如果比较多效率会非常慢
- 二分查找,时间复杂度为O(log2) ,但搜索前必须要求序列是有序的
上述排序比较适合静态类型的查找,即一般不会对区间进行插入和删除操作了,而现实中的查找比如:
- 根据姓名查询考试成绩
- 通讯录,即根据姓名查询联系方式
- 不重复集合,即需要先搜索关键字是否已经在集合中
可能在查找时进行一些插入和删除的操作,即动态查找,那上述两种方式就不太适合了,本节介绍的Map和Set是一种适合动态查找的集合容器。
1.2 模型
一般把搜索的数据称为关键字(Key),和关键字对应的称为值(Value),将其称之为Key-value的键值对,所以模型会有两种:
- 纯 key 模型,比如:
- 有一个英文词典,快速查找一个单词是否在词典中
- 快速查找某个名字在不在通讯录中 - Key-Value 模型,比如:
- 统计文件中每个单词出现的次数,统计结果是每个单词都有与其对应的次数:<单词,单词出现的次数>
- 梁山好汉的江湖绰号:每个好汉都有自己的江湖绰号
而Map中存储的就是key-value的键值对,Set中只存储了Key。
二、Map 的使用
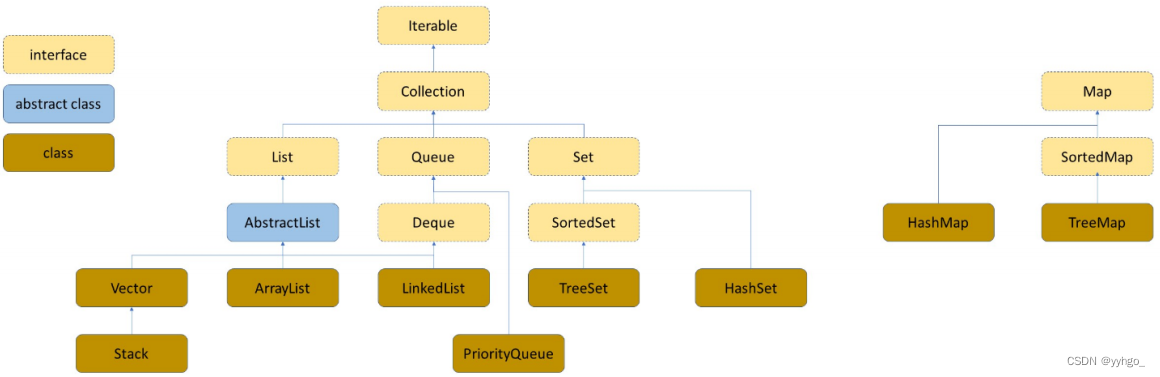
2.1 关于Map的说明
Map是一个接口类,该类没有继承自Collection,该类中存储的是<K,V>结构的键值对,并且K一定是唯一的,不能重复。
2.2 关于Map.Entry<K, V>的说明
Map.Entry<K, V> 是Map内部实现的用来存放<key, value>键值对映射关系的内部类,该内部类中主要提供了<key, value>的获取,value的设置以及Key的比较方式。
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| K getKey() | 返回 entry 中的 key |
| V getValue() | 返回 entry 中的 value |
| V setValue(V value) | 将键值对中的value替换为指定value |
注意:Map.Entry<K,V>并没有提供设置Key的方法
TreeMap集合类源码:

2.3 Map常用方法说明
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| V get(Object key) | 返回 key 对应的 value |
| V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) | 返回 key 对应的 value,key 不存在,返回默认值 |
| V put(K key, V value) | 插入 / 设置 key 对应的 value |
| V remove(Object key) | 删除 key 对应的映射关系 |
| Set keySet() | 返回所有 key 的不重复集合 |
| Collection values() | 返回所有 value 的可重复集合 |
| Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet() | 返回所有的 key-value 映射关系 |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | 判断是否包含 key |
| boolean containsValue(Object value) | 判断是否包含 value |
其中,Set<K> keySet(){}; 方法:

Map接口并没有像大部分接口一样实现了Iterable接口,这就导致Map的遍历很麻烦。而keySet方法就方便了我们去遍历Map:

注意:
- Map是一个接口,不能直接实例化对象,如果要实例化对象只能实例化其实现类TreeMap或者HashMap
- Map中存放键值对的Key是唯一的,value是可以重复的
- 在TreeMap中插入键值对时,key不能为空,否则就会抛NullPointerException异常,value可以为空。但是HashMap的key和value都可以为空。
- Map中的Key可以全部分离出来,存储到Set中来进行访问(因为Key不能重复)。
- Map中的value可以全部分离出来,存储在Collection的任何一个子集合中(value可能有重复)。
- Map中键值对的Key不能直接修改,value可以修改,如果要修改key,只能先将该key删除掉,然后再来进行重新插入。
- TreeMap中不能插入null的key,但是HashMap可以 ( 因为不需要比较大小 )。
- TreeMap和HashMap的区别
| Map底层结构 | TreeMap | HashMap |
|---|---|---|
| 底层结构 | 红黑树 | 哈希桶 |
| 插入/删除/查找时间复杂度 | O(log2N) | O(1) |
| 是否有序 | 关于Key有序 | 无序 |
| 线程安全 | 不安全 | 不安全 |
| 插入/删除/查找区别 | 需要进行元素比较 | 通过哈希函数计算哈希地址 |
| 比较与覆写 | key必须能够比较,否则会抛出ClassCastException异常 | 自定义类型需要覆写equals和hashCode方法 |
| 应用场景 | 需要Key有序场景下 | Key是否有序不关心,需要更高的时间性能 |
三、Set 的使用
3.1 关于Set的说明
Set与Map主要的不同有两点:Set是继承自Collection的接口类;Set中只存储了Key。
TreeMap和TreeSet当中存储元素的时候它们的Key一定要是可以比较的!!!(因为实现了SortedMap和SortedSet接口)
否则就会出现如下的异常:

3.2 Set常用方法说明
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 添加元素,但重复元素不会被添加成功 |
| void clear() | 清空集合 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判断 o 是否在集合中 |
| Iterator iterator() | 返回迭代器 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 删除集合中的 o |
| int size() | 返回set中元素的个数 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 检测set是否为空,空返回true,否则返回false |
| Object[] toArray() | 将set中的元素转换为数组返回 |
| boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) | 集合c中的元素是否在set中全部存在,是返回true,否则返回false |
| boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | 将集合c中的元素添加到set中,可以达到去重的效果 |
注意:
- Set是继承自Collection的一个接口类。
- Set中只存储了key,并且要求key一定要唯一。
- Set的底层是使用Map来实现的,其使用key与Object的一个默认对象作为键值对插入到Map中的。源码:(HashSet同)

- Set最大的功能就是对集合中的元素进行去重。
- 实现Set接口的常用类有TreeSet和HashSet,还有一个LinkedHashSet,其是在HashSet的基础上维护了一个双向链表来记录元素的插入次序。
- Set中的Key不能修改,如果要修改,先将原来的删除掉,然后再重新插入。
- TreeSet中不能插入null的key,但是HashSet可以 ( 因为不需要比较大小 )。
- TreeSet和HashSet的区别:
| Set底层结构 | TreeSet | HashSet |
|---|---|---|
| 底层结构 | 红黑树 | 哈希桶 |
| 插入/删除/查找时间复杂度 | O(log2N) | O(1) |
| 是否有序 | 关于Key有序 | 不一定有序 |
| 线程安全 | 不安全 | 不安全 |
| 插入/删除/查找区别 | 按照红黑树的特性来进行插入和删除 | 1. 先计算key哈希地址 2. 然后进行插入和删除 |
| 比较与覆写 | key必须能够比较,否则会抛出ClassCastException异常 | 自定义类型需要覆写equals和hashCode方法 |
| 应用场景 | 需要Key有序场景下 | Key是否有序不关心,需要更高的时间性能 |
四、HashMap解析与实现
当key与value都为整形时,代码实现:
public class HashBuck {
static class Node{
public int key;
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int key, int val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
public Node[] array;
public int usedSize;
public HashBuck(){
array = new Node[8];
}
public void put(int key,int val){
int index = key % array.length;
// 遍历Index下标的链表,如果有相同的key那么替换
Node cur = array[index];
while(cur != null){
if(cur.key == key){
cur.val = val;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
// 进行头插法(JDK1.7及以前采用的是头插法;JDK1.8开始采用尾插法)
Node node = new Node(key, val);
node.next = array[index];
array[index] = node;
usedSize++;
// 判断负载因子有没有超过默认负载因子
if(loadFactor() >= 0.75f){
// 扩容
// array = Arrays.copyOf(array,2*array.length); 不对!数据对应的哈希地址改变了!!!
resize();
}
}
private void resize(){
Node[] newArray = new Node[2*array.length];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
Node cur = array[i];
while(cur != null){
Node curNext = cur.next;
int newIndex = cur.key % newArray.length;
// 拿着cur节点,进行插入到新的位置
cur.next = newArray[newIndex];
newArray[newIndex] = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
}
array = newArray;
}
private float loadFactor() {
return usedSize * 1.0f / array.length;
}
public int get(int key){
int index = key % array.length;
Node cur = array[index];
while(cur != null){
if(cur.key == key){
return cur.val;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return -1;
}
}
若key是引用类型,我们可以通过hashCode方法得到一个整形进而代入哈希函数:
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = hash % array.length;
我们认为:两个相同的key经过hashCode方法得到的整数应该是相等的,但是经过验证我们发现并不是,所以我们在定义一个类时一定要重写hashCode方法!!!
若是Person类,通过id字符串来进行生成、比较:
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Person person = (Person) o;
return Objects.equals(id, person.id);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id);
为什么equals和hashCode方法一般都是放在一起重写的呢?
通过hashCode方法与哈希函数我们得到了哈希地址,然后我们避免不了在哈希桶里进行比较key是否相等,这时就需要重写equals方法!

因为hashCode只是确定了哪个桶!
已重写了Person类中的hashCode方法和equals方法,下列代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person1 = new Person("123456");
Person person2 = new Person("123456");
System.out.println(person1.hashCode());
System.out.println(person2.hashCode());
HashBuck<Person,Integer> hashBuck = new HashBuck<>();
hashBuck.put(person1,10);
System.out.println(hashBuck.get(person2));
}
因为person1和person2的id是相同的,认为person1与person2等同,所以get取出的是10。
我们定义一个Person类,然后来用泛型实现HashMap,代码实现:
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* Description:
* User: 95439
* Date: 2022-11-08
* Time: 15:59
*/
public class Person {
public String id;
public Person(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Person person = (Person) o;
return Objects.equals(id, person.id);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id);
}
}
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* Description:
* User: 95439
* Date: 2022-11-08
* Time: 9:23
*/
public class HashBuck<K,V> {
static class Node<K,V>{
K key;
V val;
Node next;
public Node(K key, V val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
Node<K,V>[] array = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[10];
public int usedSize;
public void put(K key,V val){
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = hash % array.length;
Node<K,V> cur = array[index];
while(cur != null){
if(cur.key.equals(val)){
cur.val = val;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
Node<K,V> node = new Node<>(key,val);
node.next = array[index];
array[index] = node;
usedSize++;
if(loadFactor() >= 0.75f){
// 扩容
// array = Arrays.copyOf(array,2*array.length); 不对!数据对应的哈希地址改变了!!!
resize();
}
}
private void resize(){
Node<K,V>[] newArray = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[2*array.length];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
Node<K,V> cur = array[i];
while(cur != null){
Node<K,V> curNext = cur.next;
int hash = cur.key.hashCode();
int newIndex = hash % newArray.length;
// 拿着cur节点,进行插入到新的位置
cur.next = newArray[newIndex];
newArray[newIndex] = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
}
array = newArray;
}
private float loadFactor() {
return usedSize * 1.0f / array.length;
}
public V get(K key){
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = hash % array.length;
Node<K,V> cur = array[index];
while(cur != null){
if(cur.key.equals(key)){
return cur.val;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
}
五、HashMap源码细节
源码中的hash方法:

由源码中不带参数(参数是哈希表容量和负载因子)的构造方法得知:

传了哈希表容量的构造方法:


链表存储变为红黑树存储:
![]()



综上,所以是在链表长度大于 8 并且数组长度大于 64 时才变为红黑树存储。
红黑树存储要求Key必须可以比较:



综上,就算没有实现comparable或者comparator也会通过hashcode进行比较。(Key并没有变为有序,而是按照hashcode的大小去比较的)
六、典型OJ题
例一: 只出现一次的数字
OJ链接
代码实现:
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
HashSet<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++){
if(hashSet.contains(nums[i])){
hashSet.remove(nums[i]);
}else{
hashSet.add(nums[i]);
}
}
for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++){
if(hashSet.contains(nums[i])){
return nums[i];
}
}
return -1;
}
}
例二: 复制带随机指针的链表
OJ链接
思路:
第一次遍历用Map存储新旧节点间的对应关系,然后再经过一次遍历修改next、random,即可得到新链表:

代码实现:
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
HashMap<Node,Node> map = new HashMap<>();
// 1.遍历原来的链表,存储对应关系
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null){
Node node = new Node(cur.val);
map.put(cur,node);
cur = cur.next;
}
// 2.第二次遍历链表,修改next、random
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
}
例三: 宝石与石头
OJ链接
代码实现:
class Solution {
public int numJewelsInStones(String jewels, String stones) {
HashSet<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < jewels.length();i++){
set.add(jewels.charAt(i));
}
for(int i = 0;i < stones.length();i++){
if(set.contains(stones.charAt(i))){
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}
例四: 坏键盘打字
OJ链接
细节: 想用for-each循环时需要先转化为数组:

代码实现:
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
// str1:需要输入的;str2:实际输出的
private static void func(String str1,String str2){
HashSet<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
for(char ch : str2.toUpperCase().toCharArray()){
set.add(ch);
}
HashSet<Character> brokenSet = new HashSet<>();
for(char ch : str1.toUpperCase().toCharArray()){
if(!set.contains(ch) && !brokenSet.contains(ch)){
brokenSet.add(ch);
System.out.print(ch);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
while(scan.hasNextLine()){
String str1 = scan.nextLine();
String str2 = scan.nextLine();
func(str1,str2);
}
}
}
例五: 前K个高频单词
OJ链接
思路:(注意返回的答案应该按单词出现频率由高到低排序;如果不同的单词有相同出现频率,按字典顺序排序)

细节:
源码中:

代码实现:
public class Solution {
public List<String> topKFrequent(String[] words, int k) {
// 1.遍历words数组,统计每个字符串出现的次数
HashMap<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (String word : words) {
if(map.get(word) == null){
map.put(word,1);
}else{
map.put(word,map.get(word)+1);
}
}
// 2.建立大小为K的小根堆,每个元素就是一个Entry(建堆是通过比较value,value相同时比较key)
PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> minHeap =
new PriorityQueue<>(k, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>() {
@Override
public int compare(Map.Entry<String, Integer> o1, Map.Entry<String, Integer> o2) {
return o1.getValue().equals(o2.getValue()) ? o2.getKey().compareTo(o1.getKey()) : o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue());
}
});
for (Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry: map.entrySet()) {
if(minHeap.size() < k){
minHeap.offer(entry);
}else{
Map.Entry<String,Integer> top = minHeap.peek();
// 出堆
if(entry.getValue().compareTo(top.getValue()) > 0){
minHeap.poll();
minHeap.offer(entry);
}else if(entry.getValue().equals(top.getValue())){ // 频率相同,字典序小的进来
if(entry.getKey().compareTo(top.getKey()) < 0){
minHeap.poll();
minHeap.offer(entry);
}
}
}
}
// 3.放入List
List<String> ret = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ret.add(minHeap.poll().getKey());
}
Collections.reverse(ret); // 使用Collections工具类中的反转方法
return ret;
}
}








 本文深入讲解Map和Set这两种数据结构的原理与应用,包括搜索效率、键值对模型、常用方法、底层实现以及典型编程题解答。
本文深入讲解Map和Set这两种数据结构的原理与应用,包括搜索效率、键值对模型、常用方法、底层实现以及典型编程题解答。

















 1700
1700

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










