基本概念
二叉树:每个节点最多有两颗子树,即左子树和右子树,次序不可以颠倒(即先有左才能有右)
满二叉树:除最后一层无任何子节点外,每一层上的所有节点都有两个子节点二叉树。即如果一个二叉树的层数为k,且节点总数是2^k-1,则它就是满二叉树。
平衡二叉树:它是一颗空树或者它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不能超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一颗平衡二叉树。平衡二叉树的常用实现方法有红黑树(非严格平衡的二叉查找树)、AVL(平衡二叉搜索树)、替罪羊树、Treap、伸展树等。
二叉树高度:顾名思义就是二叉树的层数
广度优先遍历:即是层次遍历,从上往下对每一层依次访问,在每一层中,从左往右(也可以从右往左)访问结点,访问完一层就进入下一层,直到没有结点可以访问为止。
深度优先遍历:对每一个可能的分支路径深入到不能再深入为止,而且每个结点只能访问一次。要特别注意的是,二叉树的深度优先遍历比较特殊,可以细分为前(先)序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历。前中后序遍历主要针对的是根节点访问的具体时机,具体说明如下:
1)前(先)序遍历:对任一子树,先访问根,然后遍历其左子树,最后遍历其右子树,即 中->左->右
2)中序遍历:对任一子树,先遍历其左子树,然后访问根,最后遍历其右子树,即 左->中->右
3)后序遍历:对任一子树,先遍历其左子树,然后遍历其右子树,最后访问根,即 左->右->中
二叉树的深度优先遍历的非递归的通用做法是采用栈(先进后出),而广度优先遍历的非递归的通用做法是采用队列(先进先出)
二叉树操作
二叉树对象
/**
* 二叉树
**/
public class BinaryTree<T extends Comparable<T>> {
//根节点
private Node root;
class Node {
//节点数据
private T data;
//父节点
private Node parent;
//左子节点
private Node leftChild;
//右子节点
private Node rightChild;
// 构造方法
public Node(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public Node root() {
return root;
}
}二叉树创建、删除
/**
* 增加节点
*
* @param data
* @return
*/
public boolean add(T data) {
boolean flag = false;
if (!exist(data)) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (root == null) {
root = newNode;
} else {
// 找到父节点
Node parent = findParent(data);
if (parent != null) {
if (parent.data.compareTo(data) > 0) {
parent.leftChild = newNode;
} else {
parent.rightChild = newNode;
}
//新建节点的parent指向父节点
newNode.parent = parent;
}
}
flag = true;
}
return flag;
}
/**
* 删除节点
*
* @param data
* @return
*/
public boolean remove(T data) {
boolean flag = false;
Node node = getNode(data);
if (node != null) {
if (node == root) {
// 删除的是根节点
if (node.leftChild == null && node.rightChild == null) {
root = null;
} else if (node.leftChild != null && node.rightChild == null) {
node.leftChild.parent = null;
root = node.leftChild;
} else if (node.leftChild == null && node.rightChild != null) {
node.rightChild.parent = null;
root = node.rightChild;
} else {
//找到要删节点的左节点
Node leftChild = split(data);
root = leftChild;
leftChild.parent = null;
}
} else {
// 删除的是根节点
if (node.leftChild == null && node.rightChild == null) {
if (node.data.compareTo(node.parent.data) < 0) {
node.parent.leftChild = null;
} else {
node.parent.rightChild = null;
}
} else if (node.leftChild != null && node.rightChild == null) {
node.leftChild.parent = node.parent;
node.parent.rightChild = node.leftChild;
} else if (node.leftChild == null && node.rightChild != null) {
node.rightChild.parent = node.parent;
node.parent.rightChild = node.rightChild;
} else {
//找到要删节点的左节点
Node leftChild = split(data);
node.parent.leftChild = node.leftChild;
leftChild.parent = node.parent;
}
}
flag = true;
}
return flag;
}
/**
* 节点是否存在
*
* @param data
* @return
*/
public boolean exist(T data) {
boolean flag = false;
//从根节点开始遍历
Node temp = root;
while (temp != null) {
if (temp.data.compareTo(data) == 0) {
flag = true;
} else if (temp.data.compareTo(data) > 0) {
temp = temp.leftChild;
} else {
temp = temp.rightChild;
}
}
return flag;
}
/**
* 获取节点
*
* @param data
* @return
*/
public Node getNode(T data) {
//从根节点开始遍历
Node temp = root;
while (temp != null) {
if (temp.data.compareTo(data) == 0) {
return temp;
} else if (temp.data.compareTo(data) > 0) {
temp = temp.leftChild;
} else {
temp = temp.rightChild;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 查找节点的父节点
*
* @param data
* @return
*/
public Node findParent(T data) {
//从根节点开始遍历
Node temp = root;
Node prev = temp;
while (temp != null) {
//跳出循环时,temp 为 null,prev记录上一个节点,即为parent
prev = temp;
if (temp.data.compareTo(data) > 0) {
temp = temp.leftChild;
} else {
temp = temp.rightChild;
}
}
return prev;
}
/**
* 左右分隔节点
*
* @param data
* @return
*/
public Node split(T data) {
//找到节点
Node node = getNode(data);
//找到左节点的最大数节点
Node big = getBig(node.leftChild);
//将要分割节点的右节点的parent指向big
node.rightChild.parent = big;
//将big的右节点指向node的右节点
big.rightChild = node.rightChild;
return node.leftChild;
}
/**
* 获取最大节点
*
* @param node
* @return
*/
public Node getBig(Node node) {
Node temp = node;
while (temp != null) {
if (temp.rightChild != null) {
temp = temp.rightChild;
} else {
return temp;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 创建二叉树
*
* @param list
* @return
*/
public static BinaryTree createBinaryTree(List<Integer> list) {
BinaryTree<Integer> binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
for (Integer integer : list) {
binaryTree.add(integer);
}
return binaryTree;
}创建二叉树测试代码:
/**
* 二叉树测试
**/
public class BinaryTreeTest {
private BinaryTree createBinaryTree() {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(13, 65, 5, 97, 25, 37, 22, 4, 28, 32);
return BinaryTree.createBinaryTree(list);
}
@Test
public void createBinaryTreeTest() {
BinaryTree binaryTree = createBinaryTree();
}
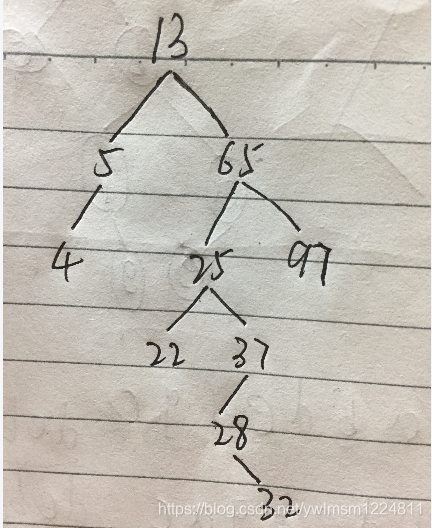
}生成的二叉树如下图所示:
递归和非递归查询二叉树高度(深度)
/**
* 递归获取二叉树深度
*
* @return
*/
public int recursiveGetTreeHight(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHight = recursiveGetTreeHight(root.leftChild);
int rightHight = recursiveGetTreeHight(root.rightChild);
return leftHight >= rightHight ? leftHight + 1 : rightHight + 1;
}
/**
* 非递归获取二叉树深度(广度遍历)
* <p>
* 思想:从根节点开始逐层遍历,每遍历完一层,层数+1
*
* @return
*/
public int normalGetTreeHight(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
// levelCount 每层节点总数,cursorIndex 当前层访问到的节点个数
int levelCount, cursorIndex;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 先将根节点放入链表list中
queue.offer(root);
// 二叉树高度
int hight = 0;
// 遍历的当前节点
Node currentNode;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
cursorIndex = 0;
levelCount = queue.size();
while (cursorIndex < levelCount) {
cursorIndex++;
currentNode = queue.poll();
if (currentNode.leftChild != null) {
queue.offer(currentNode.leftChild);
}
if (currentNode.rightChild != null) {
queue.offer(currentNode.rightChild);
}
}
// 遍历完一层,层数+1
hight++;
}
return hight;
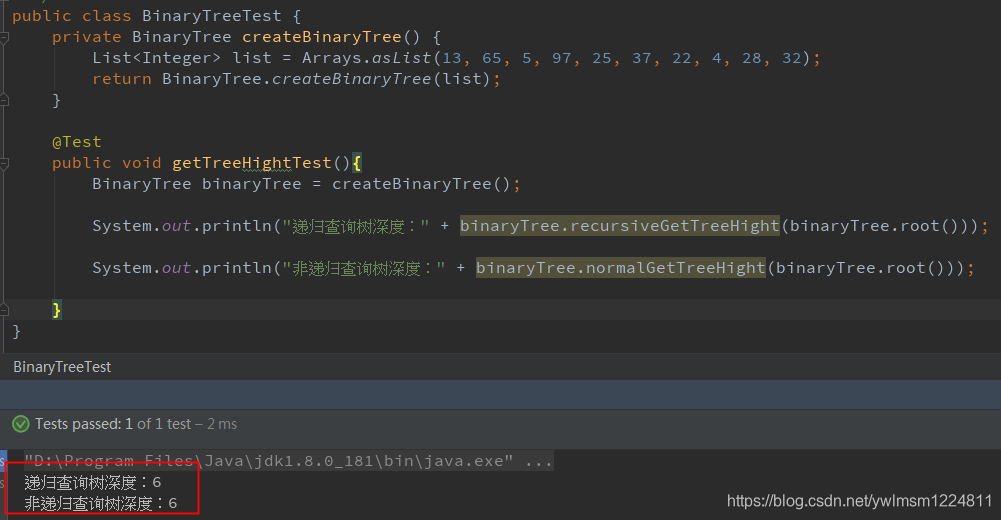
}查询二叉树高度(深度)测试代码:
/**
* 二叉树测试
**/
public class BinaryTreeTest {
private BinaryTree createBinaryTree() {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(13, 65, 5, 97, 25, 37, 22, 4, 28, 32);
return BinaryTree.createBinaryTree(list);
}
@Test
public void getTreeHightTest(){
BinaryTree binaryTree = createBinaryTree();
System.out.println("递归查询树深度:" + binaryTree.recursiveGetTreeHight(binaryTree.root()));
System.out.println("非递归查询树深度:" + binaryTree.normalGetTreeHight(binaryTree.root()));
}
}运行结果:
二叉树的前中后序遍历
/**
* 前序遍历(即深度遍历)(中->左->右)
*
* @param node
*/
public void preOrder(Node node) {
if (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + ",");
preOrder(node.leftChild);
preOrder(node.rightChild);
}
}
/**
* 中序遍历(即深度遍历)(左->中->右)
*
* @param node
*/
public void middleOrder(Node node) {
if (node != null) {
middleOrder(node.leftChild);
System.out.print(node.data + ",");
middleOrder(node.rightChild);
}
}
/**
* 后序遍历(即深度遍历)(左->右->中)
*
* @param node
*/
public void afterOrder(Node node) {
if (node != null) {
afterOrder(node.leftChild);
afterOrder(node.rightChild);
System.out.print(node.data + ",");
}
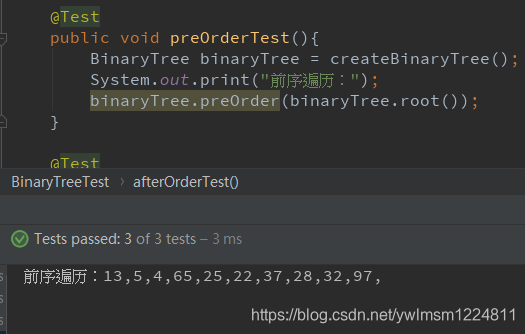
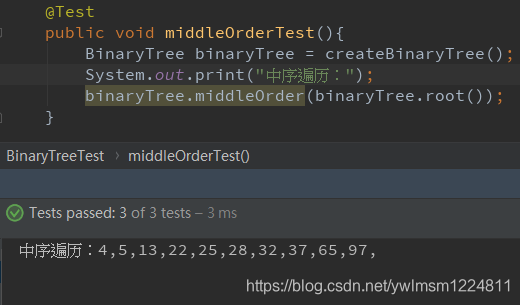
}二叉树的前中后序遍历测试代码:
/**
* 二叉树测试
**/
public class BinaryTreeTest {
private BinaryTree createBinaryTree() {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(13, 65, 5, 97, 25, 37, 22, 4, 28, 32);
return BinaryTree.createBinaryTree(list);
}
@Test
public void preOrderTest(){
BinaryTree binaryTree = createBinaryTree();
System.out.print("前序遍历:");
binaryTree.preOrder(binaryTree.root());
}
@Test
public void middleOrderTest(){
BinaryTree binaryTree = createBinaryTree();
System.out.print("中序遍历:");
binaryTree.middleOrder(binaryTree.root());
}
@Test
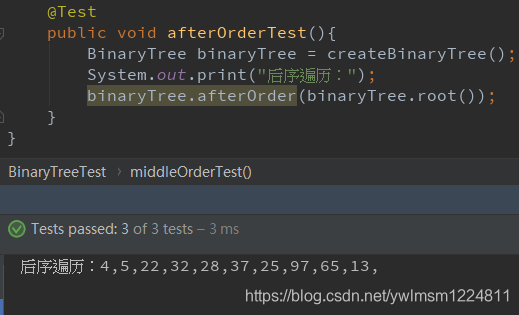
public void afterOrderTest(){
BinaryTree binaryTree = createBinaryTree();
System.out.print("后序遍历:");
binaryTree.afterOrder(binaryTree.root());
}
}运行结果:
前序遍历:13,5,4,65,25,22,37,28,32,97,
中序遍历:4,5,13,22,25,28,32,37,65,97,
后序遍历:4,5,22,32,28,37,25,97,65,13,
如下图所示:
递归和非递归深度优先遍历
/**
* 非递归深度优先遍历,采用栈实现(先进后出)
* <p>
* 思想:沿着某一个分支一直遍历到底,利用此特点可以使用栈,先将右节点入栈、然后再左节点入栈,这样子出栈就是先左节点然后右节点
*
* @param root
*/
public void depthFirstSearch(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
Node currentNode;
while (!stack.empty()) {
currentNode = stack.pop();
System.out.print(currentNode.data + ",");
if (currentNode.rightChild != null) {
stack.push(currentNode.rightChild);
}
if (currentNode.leftChild != null) {
stack.push(currentNode.leftChild);
}
}
}
/**
* 递归深度优先遍历,采用栈实现(先进后出)
* <p>
* 思想:沿着某一个分支一直遍历到底,利用此特点可以使用栈,先将右节点入栈、然后再左节点入栈,这样子出栈就是先左节点然后右节点
*
* @param root
*/
public void recursionDepthFirstSearch(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
System.out.print(root.data + ",");
recursionDepthFirstSearch(root.leftChild);
recursionDepthFirstSearch(root.rightChild);
}深度优先遍历测试代码:
/**
* 二叉树测试
**/
public class BinaryTreeTest {
private BinaryTree createBinaryTree() {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(13, 65, 5, 97, 25, 37, 22, 4, 28, 32);
return BinaryTree.createBinaryTree(list);
}
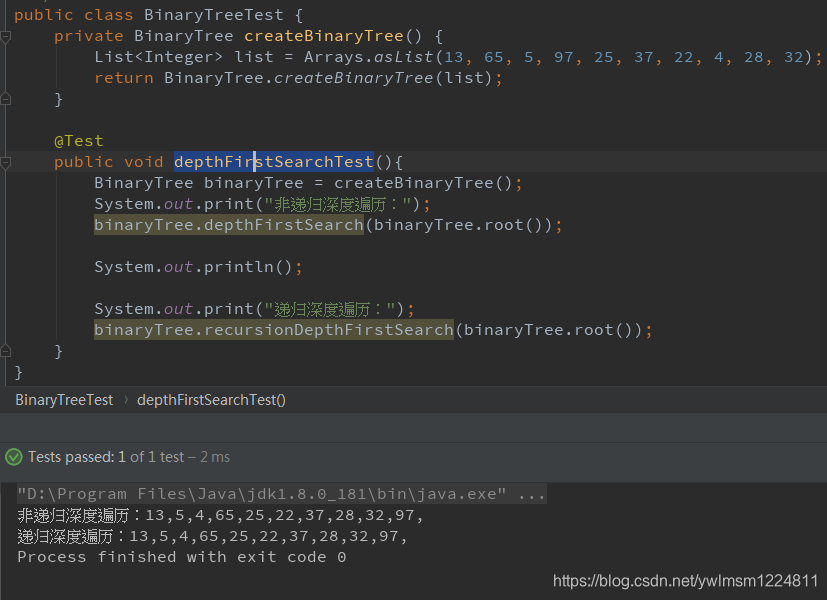
@Test
public void depthFirstSearchTest(){
BinaryTree binaryTree = createBinaryTree();
System.out.print("非递归深度遍历:");
binaryTree.depthFirstSearch(binaryTree.root());
System.out.println();
System.out.print("递归深度遍历:");
binaryTree.recursionDepthFirstSearch(binaryTree.root());
}
}运行结果:
广度优先遍历
/**
* 广度优先遍历,采用队列实现(先进先出)
* <p>
* 思想:从左到右一层层的遍历,先往队列中插入左节点,再插右节点,这样出队就是先左后右了
*
* @param root
*/
public void breadthFirstSearch(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
Node currentNode;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
currentNode = queue.poll();
System.out.print(currentNode.data + ",");
if (currentNode.leftChild != null) {
queue.offer(currentNode.leftChild);
}
if (currentNode.rightChild != null) {
queue.offer(currentNode.rightChild);
}
}
}广度优先遍历测试代码:
/**
* 二叉树测试
**/
public class BinaryTreeTest {
private BinaryTree createBinaryTree() {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(13, 65, 5, 97, 25, 37, 22, 4, 28, 32);
return BinaryTree.createBinaryTree(list);
}
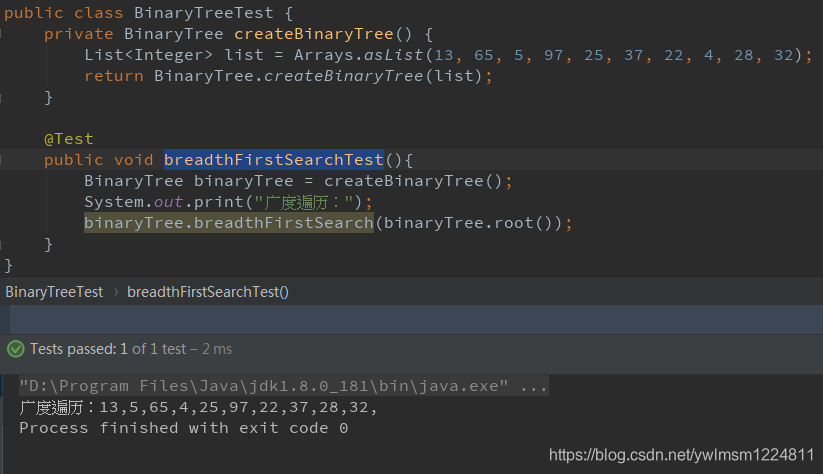
@Test
public void breadthFirstSearchTest(){
BinaryTree binaryTree = createBinaryTree();
System.out.print("广度遍历:");
binaryTree.breadthFirstSearch(binaryTree.root());
}
}运行结果:








 本文深入讲解二叉树的基本概念,包括二叉树的定义、满二叉树、平衡二叉树,以及二叉树的创建、删除、遍历等操作。同时,详细介绍了二叉树的深度优先和广度优先遍历算法,提供了递归和非递归的实现方法。
本文深入讲解二叉树的基本概念,包括二叉树的定义、满二叉树、平衡二叉树,以及二叉树的创建、删除、遍历等操作。同时,详细介绍了二叉树的深度优先和广度优先遍历算法,提供了递归和非递归的实现方法。
















 741
741

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








