传送门

 题目大意:
题目大意:
有n个数字,可以添加m个数字,使得n+m个数字两两之间差值的绝对值都存在在当前的数组中。
思路:
首先,如果数组中有负数。例如:-5,3对于这两个数字来说,|3-(-5)| = 8,会不断衍生更大的数字,无法满足条件。
其次,通过枚举情况,我们发现所有数字之间满足是非零最小数的所有整数倍。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define debug(a) cout << #a << ": " << a << endl;
#define LL long long
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
bool si = true,s0 = false;
int x,ans,ma = 0;
cin >> x;
ans = x;
ma = max(ma,x);
if(x < 0) si = false;
else if(x == 0) s0 = true;
for(int i = 1;i < n;++i) {
cin >> x;
if(x < 0) si = false;
else if(x == 0) s0 = true;
ans = __gcd(x,ans);
ma = max(ma,x);
}
int cnt = 0;
if(s0) cnt++;
cnt += (ma / ans);
if(cnt <= 300 && si) {
cout << "YES" << endl << cnt << endl;
int m = ans;
if(s0) cout << 0 << ' ';
while(ma != ans) {
cout << ans << ' ';
ans += m;
}
cout << ma << endl;
}
else {
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
IO;
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
总结:
数字的性质,需要有一定的打表和数字感觉。
传送门

 题目大意:
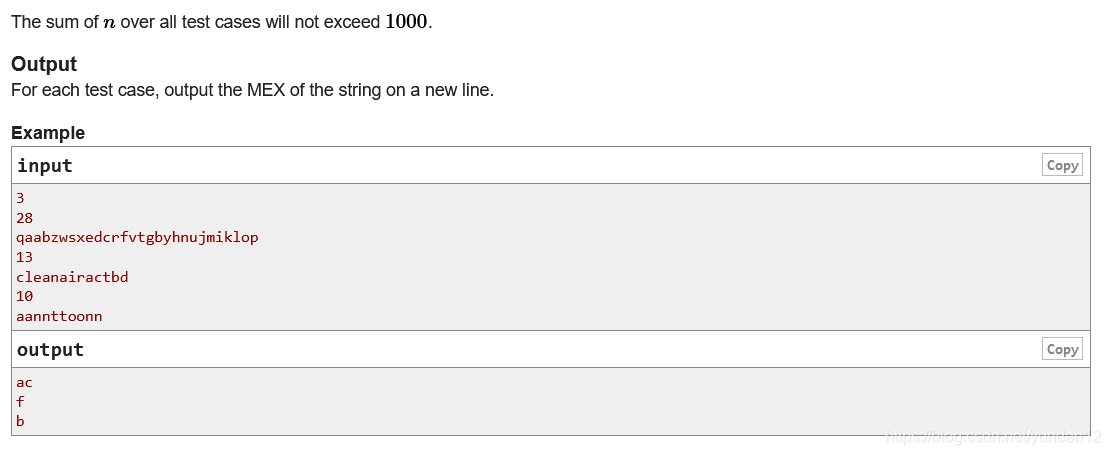
题目大意:
求未出现的最小的字典序的字符串
思路:
由于数据量范围较小,可以将每一个出现的字符串记录下来,从最小序枚举未出现的字符串
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define debug(a) cout << #a << ": " << a << endl;
#define LL long long
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
int a[30];
int b[30][30];
int c[30][30][30];
void solve()
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
memset(b,0,sizeof(b));
memset(c,0,sizeof(c));
int n;
cin >> n;
string s;
cin >> s;
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i) {
a[s[i]-'a'] = 1;
if(i < n-1) b[s[i]-'a'][s[i+1]-'a'] = 1;
if(i < n-2) c[s[i]-'a'][s[i+1]-'a'][s[i+2]-'a'] = 1;
}
//cout << 1 << endl;
for(int i = 0;i < 26;++i) {
if(a[i] == 0) {
cout << char(i+'a') << endl;
return ;
}
}
for(int i = 0;i < 26;++i) {
for(int j = 0;j < 26;++j) {
if(b[i][j] == 0) {
cout << char(i+'a') << char(j+'a') << endl;
return ;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0;i < 26;++i) {
for(int j = 0;j < 26;++j) {
for(int k = 0;k <26;++k) {
if(c[i][j][k] == 0) {
cout << char(i+'a') << char(j+'a') << char(k+'a') << endl;
return ;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
总结:
数据量较小时,枚举的做法正确率高,但是代码量大
传送门

 题目大意:
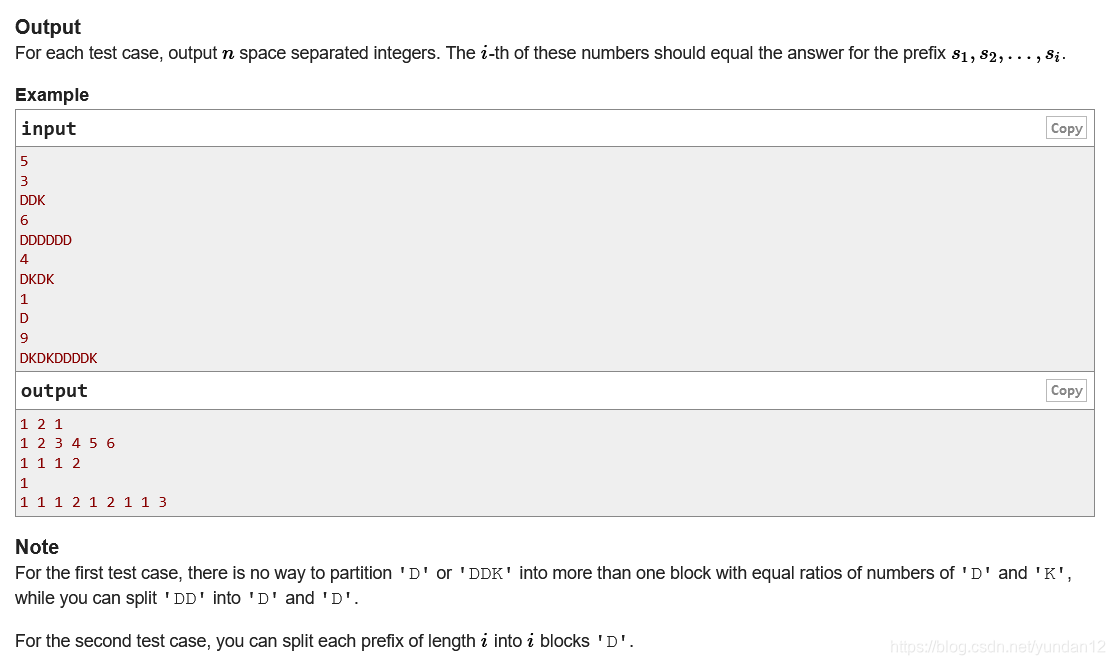
题目大意:
将字符串可以分割为最多多少个比例相同的子串,分割后所有子串必须比例相同。
思路:
每次将当前比例的个数加1,例如:如果之前有1:2的比例,对于2:4的样例就可以拆成两个1:2的样例。依次类推,除以最大公因数的比例所求出的个数就是最大个数。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
map<pair<int,int>,int> cnt;
void solve()
{
cnt.clear();
int n;
cin >> n;
string s;
cin >> s;
int l = 0,r = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i) {
if(s[i] == 'D') l++;
else r++;
int t = __gcd(l,r);
cnt[{l/t,r/t}]++;
cout << cnt[{l/t,r/t}] << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
总结:
数字比例的性质,记作拆分性。
传送门

 题目大意:
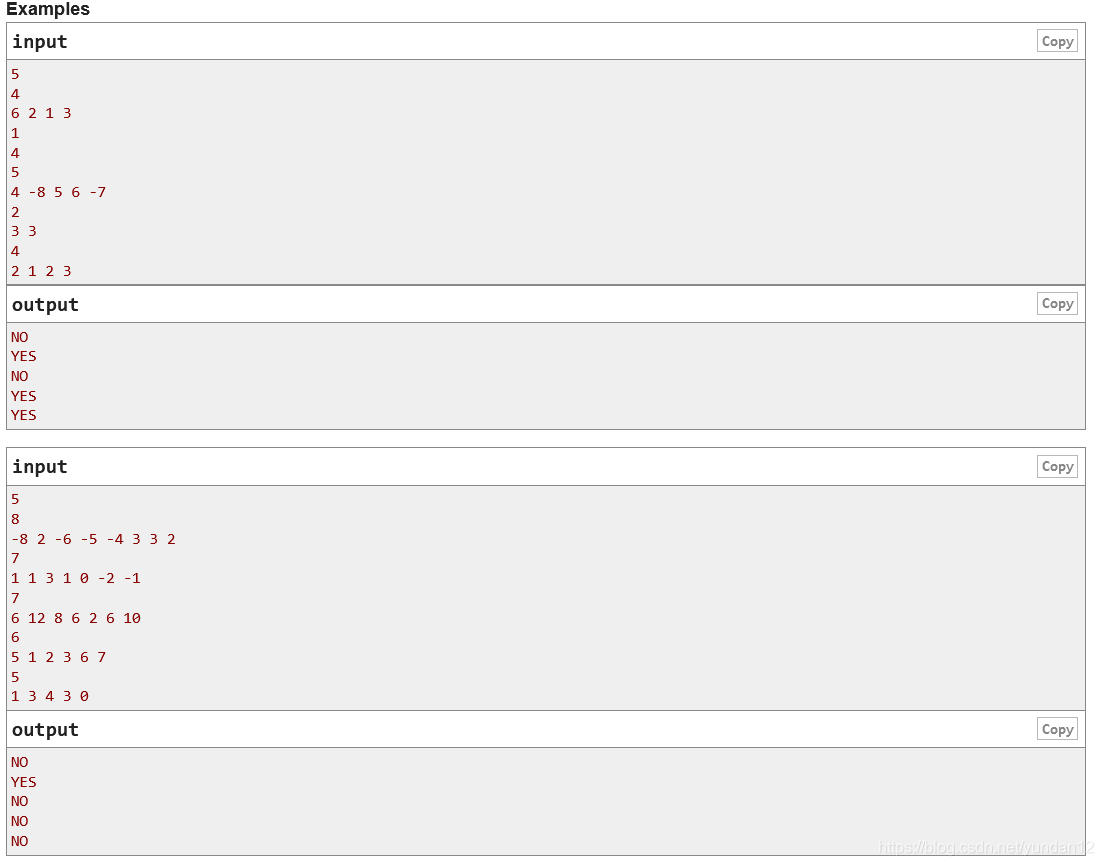
题目大意:
给定一个b序列,是否存在一个a序列满足a1,a2,…,a2i-1满足a1到a2i-1的中位数为bi
思路:
假定a序列刚开始为空,a1 = b1,那么对于下一个bj来讲,bj在a序列中一定要紧邻bj-1,中位数性质。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define debug(a) cout << #a << ": " << a << endl;
#define LL long long
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
const int maxn = 2e5+10;
int a[maxn];
set<int> s;
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0;i < n;++i) {
cin >> a[i];
}
s.clear();
s.insert(a[0]);
bool si = true;
for(int i = 1;i < n;++i) {
int pre = a[i-1];
if(pre != a[i]) {
if(pre < a[i]) {
auto it = s.upper_bound(pre);
if((it != s.end()) && (*it < a[i])) {
si = false;
break;
}
}
else {
auto it = s.lower_bound(pre);
if((it != s.begin()) && (*(--it) > a[i])) {
si = false;
break;
}
}
}
s.insert(a[i]);
}
if(si) cout << "YES" << endl;
else cout << "NO" << endl;
}
int main()
{
IO;
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
总结:
中位数的性质,具有强烈的数学渲染感。







 本文探讨了如何在给定数字序列中添加元素以确保任意差值存在数组内,涉及非负数和最小倍数原理;同时解析了寻找未出现字典序字符串的方法,以及处理字符串比例拆分和保持中位数规律的挑战。这些算法展示了数学在信息技术中的应用。
本文探讨了如何在给定数字序列中添加元素以确保任意差值存在数组内,涉及非负数和最小倍数原理;同时解析了寻找未出现字典序字符串的方法,以及处理字符串比例拆分和保持中位数规律的挑战。这些算法展示了数学在信息技术中的应用。
















 205
205

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








