该博客来源慕课网“数据结构探险之图篇”,慕课网使用C++语言实现,这里改用Java语言实现,这里采用邻接矩阵来保存图的基本关系,该篇博客实现了图的基本操作,广度优先遍历方法(递归和非递归方式),深度优先遍历,最小生成树算法(普里姆算法,卡鲁斯尔算法),算法在代码中已有详细说明
Node.java类为节点类,存储节点的基本信息
Edge.java类为边类,在生成最小生成树时使用
CMap.java类是实现图的基本操作的类,里面封装了操作图的函数
GraphTest.java类是测试类,生成图及深度和广度遍历图
MinimumSpanningTreeTest.java测试克鲁斯卡尔算法生成最小生成树
MinTreeTest2.java测试普里姆算法生成最小生成树
这是该工程的源码下载地址:https://download.youkuaiyun.com/download/yuanhengzhw/10410176
Node.java类
package graph;
public class Node {
char m_cData;
boolean m_bIsVisited;
public Node(char data)
{
m_cData=data;
m_bIsVisited=false;
}
public Node()
{
m_cData=0;
}
}Edge.java类
package graph;
public class Edge {
public int m_iNodeIndexA;
public int m_iNodeIndexB;
public int m_iWeightValue;
public boolean m_bSelected;
public Edge(int m_iNodeIndexA, int m_iNodeIndexB, int m_iWeightValue,
boolean m_bSelected) {
this.m_iNodeIndexA = m_iNodeIndexA;
this.m_iNodeIndexB = m_iNodeIndexB;
this.m_iWeightValue = m_iWeightValue;
this.m_bSelected = m_bSelected;
}
}CMap.java类
package graph;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Vector;
public class CMap {
private int m_iCapacity;//图中最多可容纳的顶点数
private int m_iNodeCount;//已经添加的顶点数
private Node m_NodeArray[];//用来存放顶点的数组
private int m_Matrix[];//用来存放邻接矩阵
private Edge m_Edge[];//存放最小生成树的边
public CMap(int capacity)
{
m_iCapacity=capacity;
m_iNodeCount=0;
m_NodeArray=new Node[capacity];
m_Matrix=new int[capacity*capacity];
m_Edge=new Edge[capacity-1];
}
public boolean addNode(Node node)
{
if(node==null)
return false;
m_NodeArray[m_iNodeCount]=node;
m_iNodeCount++;
return true;
}
public void resetNode()
{
for(int i=0;i<m_iNodeCount;i++)
m_NodeArray[i].m_bIsVisited=false;
}
/**
* 向有向图中加入值
* @param row
* @param col
* @param val
*/
public boolean setValueToMatrixForDirectedGraph(int row,int col,int val)
{
if(row<0||row>m_iCapacity)
{
return false;
}
if(col<0||col>m_iCapacity)
{
return false;
}
m_Matrix[row*m_iCapacity+col]=val;
return true;
}
/**
* 向无向图中加入值
* @param row
* @param col
* @param val
* @return
*/
public boolean setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(int row,int col,int val)
{
if(row<0||row>m_iCapacity)
{
return false;
}
if(col<0||col>m_iCapacity)
{
return false;
}
m_Matrix[row*m_iCapacity+col]=val;
m_Matrix[col*m_iCapacity+row]=val;
return true;
}
/**
* 获取邻接矩阵中某个位置的值
* @param row
* @param col
* @return
*/
public int getValueFromMatrix(int row,int col)
{
if(row<0||row>m_iCapacity)
{
return 0;
}
if(col<0||col>m_iCapacity)
{
return 0;
}
return m_Matrix[row*m_iCapacity+col];
}
/**
* 打印邻接矩阵
*/
public void printMatrix()
{
for(int i=0;i<m_iCapacity;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<m_iCapacity;j++)
{
System.out.print(m_Matrix[i*m_iCapacity+j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
* 深度优先遍历
* @param nodeindex
*/
public void depthFirstTraverse(int nodeindex)
{
int value=0;
System.out.print(m_NodeArray[nodeindex].m_cData+" ");
m_NodeArray[nodeindex].m_bIsVisited=true;
for(int i=0;i<m_iCapacity;i++)
{
value=getValueFromMatrix(nodeindex, i);
if(value!=0)
{
if(m_NodeArray[i].m_bIsVisited)
{
continue;
}else{
depthFirstTraverse(i);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 广度优先遍历方法1
* @param nodeindex
*/
public void breadthFirstTraverse(int nodeindex)
{
System.out.print(m_NodeArray[nodeindex].m_cData+" ");
m_NodeArray[nodeindex].m_bIsVisited=true;
List<Integer> curList=new ArrayList<>();
curList.add(nodeindex);
breadthFirstTraverseImpl(curList);
}
private void breadthFirstTraverseImpl(List<Integer> preList) {
int value=0;
List<Integer> curList=new ArrayList<>();
for(int j=0;j<preList.size();j++)
{
for(int i=0;i<m_iCapacity;i++)
{
value=getValueFromMatrix(preList.get(j), i);
if(value!=0)
{
if(m_NodeArray[i].m_bIsVisited)
{
continue;
}else{
System.out.print(m_NodeArray[i].m_cData+" ");
m_NodeArray[i].m_bIsVisited=true;
curList.add(i);
}
}
}
}
if(curList.size()==0)
{
return;
}else{
breadthFirstTraverseImpl(curList);
}
}
/**
* 采用队列原理广度优先遍历图
* @param nodeindex
*/
public void breadthFirstTraverseByQueue(int nodeindex)
{
List<Integer> queue=new ArrayList<>();
queue.add(nodeindex);
int value=0;
while(queue.size()>0)
{
//输出出栈节点信息
Node node=m_NodeArray[queue.get(0)];
if(!node.m_bIsVisited)
{
System.out.print(node.m_cData+" ");
node.m_bIsVisited=true;
}
//出栈
nodeindex=queue.get(0);
queue.remove(0);
//寻找node节点下一层且没有被访问的节点
for(int j=0;j<m_iCapacity;j++)
{
if(m_NodeArray[j].m_bIsVisited)
{
//节点被访问,不加入队列
continue;
}
value=getValueFromMatrix(nodeindex, j);
if(value!=0)
{
queue.add(j);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 普里姆生成树
* @param nodeIndex
*/
public void primTree(int nodeIndex)
{
int value=0;
int edgeCount=0;
List<Integer> nodeList=new ArrayList<>();
nodeList.add(nodeIndex);
m_NodeArray[nodeIndex].m_bIsVisited=true;
List<Edge> nodeEdge=new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println(m_NodeArray[nodeIndex].m_cData+" ");
//结束条件,边数为m_iCapacity-1结束
while(edgeCount<m_iCapacity-1)
{
int temp=nodeList.get(nodeList.size()-1);
for(int i=0;i<m_iCapacity;i++)
{
value=getValueFromMatrix(temp, i);
if(value!=0)
{
if(m_NodeArray[i].m_bIsVisited)
{
continue;
}else{
Edge edge=new Edge(temp, i, value, false);
nodeEdge.add(edge);
}
}
}
//从被选边集合中找出最小边
int edgeIndex=getMinEdge(nodeEdge);
nodeEdge.get(edgeIndex).m_bSelected=true;
//打印信息
System.out.println(nodeEdge.get(edgeIndex).m_iNodeIndexA+"----->"
+nodeEdge.get(edgeIndex).m_iNodeIndexB+","
+nodeEdge.get(edgeIndex).m_iWeightValue);
//加入一条权值最小边
m_Edge[edgeCount]=nodeEdge.get(edgeIndex);
edgeCount++;
int nextNodeIndex=nodeEdge.get(edgeIndex).m_iNodeIndexB;
nodeList.add(nextNodeIndex);
m_NodeArray[nextNodeIndex].m_bIsVisited=true;
System.out.println(m_NodeArray[nextNodeIndex].m_cData);
}
}
/**
* 寻找没有被选出的边
* @param nodeEdge
* @return
*/
private int getMinEdge(List<Edge> nodeEdge) {
int minWeight=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int edgeIndex=0;
for(int i=0;i<nodeEdge.size();i++)
{
//寻找没有被选出的边
if(!nodeEdge.get(i).m_bSelected)
{
//判断所选边两端点是否已经被访问,已经被访问则不加入入选边,否则会形成回路,得不到正确结果
if(m_NodeArray[nodeEdge.get(i).m_iNodeIndexA].m_bIsVisited&&m_NodeArray[nodeEdge.get(i).m_iNodeIndexB].m_bIsVisited)
{
continue;
}
if(minWeight>nodeEdge.get(i).m_iWeightValue)
{
minWeight=nodeEdge.get(i).m_iWeightValue;
edgeIndex=i;
}
}
}
if(minWeight==Integer.MAX_VALUE)
{
return -1;
}
return edgeIndex;
}
/**
* 克鲁斯卡尔算法生成树
*/
public void kruskalTree()
{
int value=0;
int edgeCount=0;
//定义存放节点集合的数组
//List<List<Integer>> nodeSets=new ArrayList<>();
//第一步:取出所用边
List<Edge> edgeList=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<m_iCapacity;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<m_iCapacity;j++)
{
value=getValueFromMatrix(i, j);
if(value!=0)
{
Edge edge=new Edge(i, j, value, false);
edgeList.add(edge);
}
}
}
//给选出的边排序
for(int i=0;i<edgeList.size()-1;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<edgeList.size();j++)
{
if(edgeList.get(i).m_iWeightValue>edgeList.get(j).m_iWeightValue)
{
//交换权重
int temp=edgeList.get(i).m_iWeightValue;
edgeList.get(i).m_iWeightValue=edgeList.get(j).m_iWeightValue;
edgeList.get(j).m_iWeightValue=temp;
//交换节点A
temp=edgeList.get(i).m_iNodeIndexA;
edgeList.get(i).m_iNodeIndexA=edgeList.get(j).m_iNodeIndexA;
edgeList.get(j).m_iNodeIndexA=temp;
//交换节点B
temp=edgeList.get(i).m_iNodeIndexB;
edgeList.get(i).m_iNodeIndexB=edgeList.get(j).m_iNodeIndexB;
edgeList.get(j).m_iNodeIndexB=temp;
}
}
}
//第二步:从所有边中取出组成最小生成树的边
//1.找到算法结束条件
int CalculationNum=0;
while(edgeCount<m_iCapacity-1&&CalculationNum<edgeList.size())
{
//2.从边集合中找到最小边
Edge edge=edgeList.get(CalculationNum);
CalculationNum++;
//判断是否形成回路,形成回来选取下一条边
if(CheckLoop(edgeCount,edge))
{
System.out.println("加入边"+edge.m_iNodeIndexA+","+edge.m_iNodeIndexB+"形成回路");
continue;
}
//如果没有形成回路,则将该边信息加入到边信息中
m_Edge[edgeCount]=edge;
edgeCount++;
//输出该边的信息
System.out.println(m_NodeArray[edge.m_iNodeIndexA].m_cData+"--->"+
m_NodeArray[edge.m_iNodeIndexB].m_cData+","+
edge.m_iNodeIndexA+"--->"+
edge.m_iNodeIndexB+","+
edge.m_iWeightValue);
}
}
/*
* 判断是否形成回路
* true代表形成回路
* false代表没有形成回路
*/
public boolean CheckLoop(int edgeCount,Edge edge)
{
List<Integer> loops=new ArrayList<>();
loops.add(edge.m_iNodeIndexA);
loops.add(edge.m_iNodeIndexB);
for(int i=0;i<edgeCount;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<edgeCount;j++)
{
Edge temp=m_Edge[j];
if(temp.m_iNodeIndexA==loops.get(loops.size()-1))
{
loops.add(temp.m_iNodeIndexB);
}else if(temp.m_iNodeIndexB==loops.get(loops.size()-1)){
loops.add(temp.m_iNodeIndexA);
}
if(loops.get(0)==loops.get(loops.size()-1))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}GraphTest.java类
package graph;
public class GraphTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 图的存储 与 图的遍历
*
* A
* / \
* B D
* / \ / \
* C F G - H
* \ /
* E
*/
CMap cmap=new CMap(8);
Node nodeA=new Node('A');//0
Node nodeB=new Node('B');//1
Node nodeC=new Node('C');//2
Node nodeD=new Node('D');//3
Node nodeE=new Node('E');//4
Node nodeF=new Node('F');//5
Node nodeG=new Node('G');//6
Node nodeH=new Node('H');//7
cmap.addNode(nodeA);
cmap.addNode(nodeB);
cmap.addNode(nodeC);
cmap.addNode(nodeD);
cmap.addNode(nodeE);
cmap.addNode(nodeF);
cmap.addNode(nodeG);
cmap.addNode(nodeH);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(0, 1, 1);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(0, 3, 1);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(1, 2, 1);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(1, 5, 1);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(3, 6, 1);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(3, 7, 1);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(2, 4, 1);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(5, 4, 1);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(6, 7, 1);
cmap.printMatrix();
//深度优先遍历
System.out.println("深度优先遍历");
cmap.depthFirstTraverse(0);
//广度优先遍历方法
cmap.resetNode();
System.out.println("\n广度优先遍历方法");
cmap.breadthFirstTraverse(0);
//采用队列原理广度优先遍历图
cmap.resetNode();
System.out.println("\n采用队列原理广度优先遍历图");
cmap.breadthFirstTraverseByQueue(0);
}
}MinimumSpanningTreeTest.java类
package graph;
public class MinimumSpanningTreeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
A
/ | \
B---F---E
\ / \ /
C----D
A B C D E F
0 1 2 3 4 5
A-B 6 A-E 5 A-F 1
B-C 3 B-F 2
C-F 8 C-D 7
D-F 4 D-E 2
E-F 9
*/
CMap cmap=new CMap(6);
Node nodeA=new Node('A');//0
Node nodeB=new Node('B');//1
Node nodeC=new Node('C');//2
Node nodeD=new Node('D');//3
Node nodeE=new Node('E');//4
Node nodeF=new Node('F');//5
cmap.addNode(nodeA);
cmap.addNode(nodeB);
cmap.addNode(nodeC);
cmap.addNode(nodeD);
cmap.addNode(nodeE);
cmap.addNode(nodeF);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(0, 1, 6);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(0, 4, 5);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(0, 5, 1);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(1, 2, 3);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(1, 5, 2);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(2, 5, 8);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(2, 3, 7);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(3, 5, 4);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(3, 4, 2);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(4, 5, 9);
//普里姆算法
cmap.primTree(0);
//克鲁斯卡尔算法
//cmap.kruskalTree();
}
}MinTreeTest2.java类
附加卡鲁斯卡尔算法的过程或原理,该类的数据与下图中的数据一致
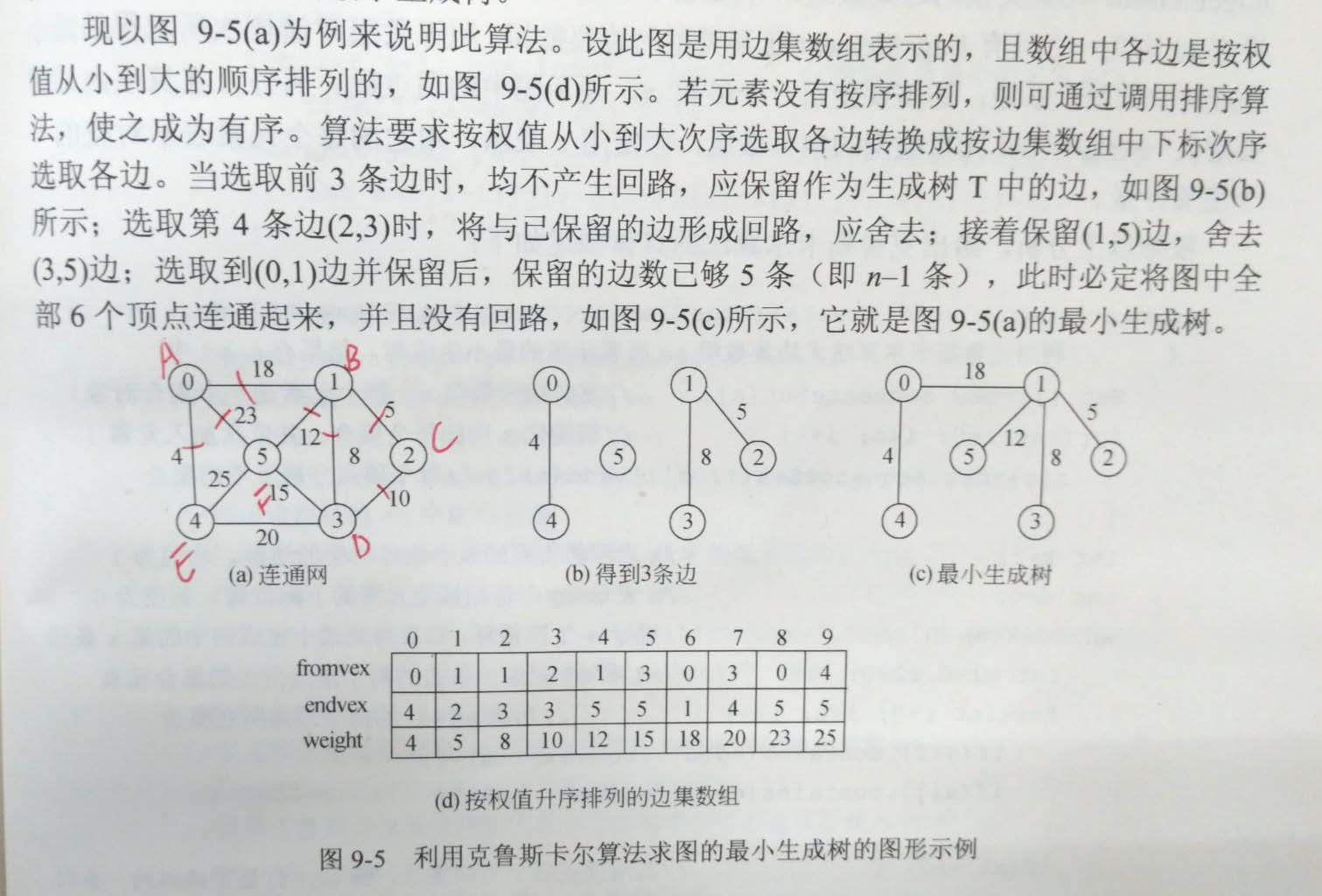
package graph;
public class MinTreeTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* A-----B
* |\ /| \
* | F | C
* | / \ | /
* E-----D
*/
CMap cmap=new CMap(6);
Node nodeA=new Node('A');//0
Node nodeB=new Node('B');//1
Node nodeC=new Node('C');//2
Node nodeD=new Node('D');//3
Node nodeE=new Node('E');//4
Node nodeF=new Node('F');//5
cmap.addNode(nodeA);
cmap.addNode(nodeB);
cmap.addNode(nodeC);
cmap.addNode(nodeD);
cmap.addNode(nodeE);
cmap.addNode(nodeF);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(0, 1, 18);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(0, 4, 4);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(0, 5, 23);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(1, 5, 12);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(1, 3, 8);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(1, 2, 5);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(2, 3, 10);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(3, 5, 15);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(3, 4, 20);
cmap.setValueToMatrixForUndirectedGraph(4, 5, 25);
//cmap.primTree(0);
//克鲁斯卡尔算法
cmap.kruskalTree();
}
}










 本文详细介绍图数据结构的Java实现,包括邻接矩阵存储、基本操作、深度优先与广度优先遍历算法,以及最小生成树算法(普里姆算法与克鲁斯卡尔算法)。通过具体代码实例展示了如何构建和遍历图,以及如何生成最小生成树。
本文详细介绍图数据结构的Java实现,包括邻接矩阵存储、基本操作、深度优先与广度优先遍历算法,以及最小生成树算法(普里姆算法与克鲁斯卡尔算法)。通过具体代码实例展示了如何构建和遍历图,以及如何生成最小生成树。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








