一、数据校验
1、前端数据校验
表单校验 ,绑定校验规则:rules="dataRule"
<el-form ref="dataForm" :model="dataForm" :rules="dataRule" label-width="140px"
@keyup.enter.native="dataFormSubmit()">
定义自定义校验器
var checkAge = (rule, value, callback) => {
if (!value) {
return callback(new Error('年龄不能为空'));
}
setTimeout(() => {
if (!Number.isInteger(value)) {
callback(new Error('请输入数字值'));
} else {
if (value < 18) {
callback(new Error('必须年满18岁'));
} else {
callback();
}
}
}, 1000);
};
var validatePass = (rule, value, callback) => {
if (value === '') {
callback(new Error('请输入密码'));
} else {
if (this.ruleForm.checkPass !== '') {
this.$refs.ruleForm.validateField('checkPass');
}
callback();
}
};
var validatePass2 = (rule, value, callback) => {
if (value === '') {
callback(new Error('请再次输入密码'));
} else if (value !== this.ruleForm.pass) {
callback(new Error('两次输入密码不一致!'));
} else {
callback();
}
};
添加对象数据,激活校验器
rules: {
pass: [
{ validator: validatePass, trigger: 'blur' }
],
checkPass: [
{ validator: validatePass2, trigger: 'blur' }
],
age: [
{ validator: checkAge, trigger: 'blur' }
]
}
};
2、后端数据校验
(1)代码示例:
校验参数注解:
@Documented
@Constraint(validatedBy = {ListValueValidator.class})
@Target({METHOD, FIELD, ANNOTATION_TYPE, CONSTRUCTOR, PARAMETER, TYPE_USE})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface ListValue {
String message() default "{com.yuan.gulimall.common.utils.validator.ListValue.message}";
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
int[] values() default {};
}
参数校验器:
public class ListValueValidator implements ConstraintValidator<ListValue, Integer> {
private Set<Integer> valueSet = new HashSet<>();
@Override
public void initialize(ListValue constraintAnnotation) {
ConstraintValidator.super.initialize(constraintAnnotation);
int[] vals = constraintAnnotation.values();
for (int val : vals) {
valueSet.add(val);
}
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(Integer value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
return valueSet.contains(value);
}
}
(2)后端常见的校验注解,在javax.validation.constraints包下
来自豆包的解释:
-
AssertFalse:被注解的元素必须为false。常用于布尔类型字段的验证。 -
AssertTrue:被注解的元素必须为true,同样用于布尔类型字段验证。 -
DecimalMax:被注解的元素值必须小于等于指定的最大值,适用于数字类型,如BigDecimal、BigInteger、byte、short、int、long等。 -
DecimalMin:被注解的元素值必须大于等于指定的最小值,适用类型同DecimalMax。 -
Digits:验证被注解的数字是否在指定的整数位数和小数位数范围内,适用于数字类型。 -
Email:验证被注解的字符串是否是一个有效的电子邮件地址。 -
Future:被注解的元素必须是一个将来的日期,常用于java.util.Date、java.time.LocalDate等日期类型。 -
FutureOrPresent:被注解的元素必须是一个将来或当前的日期。 -
Max:被注解的元素值必须小于等于指定的最大值,适用于数值类型。 -
Min:被注解的元素值必须大于等于指定的最小值,适用于数值类型。 -
Negative:被注解的元素必须是一个负数,适用于数值类型。 -
NegativeOrZero:被注解的元素必须是负数或零,适用于数值类型。 -
NotBlank:验证被注解的字符串不为null,且去除两端空白字符后长度大于 0,常用于字符串类型。 -
NotEmpty:验证被注解的元素不为null且不为空,适用于集合、数组、Map 等类型,也适用于字符串。 -
NotNull:被注解的元素不能为null。 -
Null:被注解的元素必须为null。 -
Past:被注解的元素必须是一个过去的日期,适用于日期类型。 -
PastOrPresent:被注解的元素必须是一个过去或当前的日期。 -
Pattern:被注解的字符串必须匹配指定的正则表达式。 -
Positive:被注解的元素必须是一个正数,适用于数值类型。 -
PositiveOrZero:被注解的元素必须是正数或零,适用于数值类型。 -
Size:验证被注解的对象(如字符串、集合、数组等)的大小(长度、元素个数等)在指定的范围内。
(3)自定义参数校验器
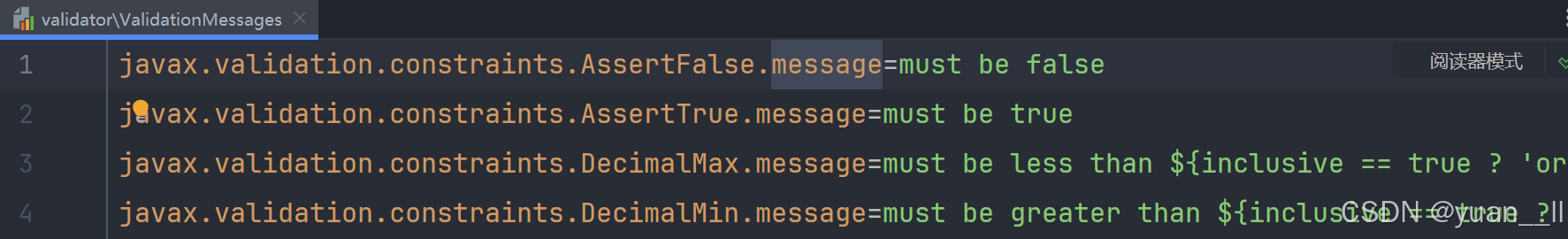
1、创建参数校验注解,参照对象NotNull参考前三个注解,加上前三个属性。其中message这个属性参照的是以下图片(双shirt搜索文件)然后在resource目录下创建一个ValidationMessages.properties的文件,在键为注解类名+message,值为显示显示信息
@Target({ METHOD, FIELD, ANNOTATION_TYPE, CONSTRUCTOR, PARAMETER, TYPE_USE })
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Repeatable(List.class)
@Documented
@Constraint(validatedBy = { })//用到的参数校验器
public @interface NotNull {
String message() default "{javax.validation.constraints.NotNull.message}";
Class<?>[] groups() default { };
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default { };
/**
* Defines several {@link NotNull} annotations on the same element.
*
* @see javax.validation.constraints.NotNull
*/
@Target({ METHOD, FIELD, ANNOTATION_TYPE, CONSTRUCTOR, PARAMETER, TYPE_USE })
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Documented
@interface List {
NotNull[] value();
}
}
2、创建参数校验器
从参照注解类的@Constraint(validatedBy = { })注解点进去,然后点进去ConstraintValidator类
@Documented
@Target({ ANNOTATION_TYPE })
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Constraint {
/**
* {@link ConstraintValidator} classes implementing the constraint. The given classes
* must reference distinct target types for a given {@link ValidationTarget}. If two
* {@code ConstraintValidator}s refer to the same type, an exception will occur.
* <p>
* At most one {@code ConstraintValidator} targeting the array of parameters of
* methods or constructors (aka cross-parameter) is accepted. If two or more
* are present, an exception will occur.
*
* @return array of {@code ConstraintValidator} classes implementing the constraint
*/
Class<? extends ConstraintValidator<?, ?>>[] validatedBy();
}
发现这是一个接口,那就编写一个类实现这个接口。initialize(A constraintAnnotation)方法中,传入的参数为用到这个参数校验器的校验注解。校验逻辑写在boolean isValid(T value, ConstraintValidatorContext context)方法上
public interface ConstraintValidator<A extends Annotation, T> {
/**
* Initializes the validator in preparation for
* {@link #isValid(Object, ConstraintValidatorContext)} calls.
* The constraint annotation for a given constraint declaration
* is passed.
* <p>
* This method is guaranteed to be called before any use of this instance for
* validation.
* <p>
* The default implementation is a no-op.
*
* @param constraintAnnotation annotation instance for a given constraint declaration
*/
default void initialize(A constraintAnnotation) {
}
/**
* Implements the validation logic.
* The state of {@code value} must not be altered.
* <p>
* This method can be accessed concurrently, thread-safety must be ensured
* by the implementation.
*
* @param value object to validate
* @param context context in which the constraint is evaluated
*
* @return {@code false} if {@code value} does not pass the constraint
*/
boolean isValid(T value, ConstraintValidatorContext context);
}




















 1826
1826

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








