mybatis核心组件之MapperMethod
注释: 跟踪
mapper执行接口方法到数据库执行
sql语句的源码过程
// mybatis-spring
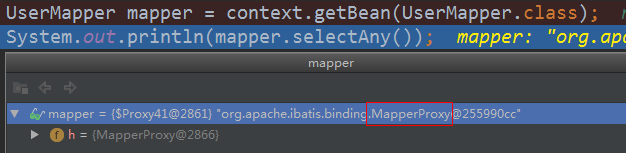
UserMapper mapper = context.getBean(UserMapper.class);
System.out.println(mapper.selectAny());
可以看到mapper是MapperProxy产生的代理类,那么MapperProxy中可定有invok方法对目标方法进行了增强处理
MapperProxy
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 如果方法是Object类的方法,则直接反射执行
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable var5) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(var5);
}
} else {
// 获取MapperMethod
MapperMethod mapperMethod = this.cachedMapperMethod(method);
// 执行sql语句
return mapperMethod.execute(this.sqlSession, args);
}
}
- 先判断执行的方法是不是Object类的方法,比如
tostring,hashcode等方法,是的话则直接反射执行这些方法 - 如果不是,从缓存中获取MapperMethod,如果为空则创建并加入缓存,然后执行
sql语句
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
// 根据方法从缓存中获取
MapperMethod mapperMethod = (MapperMethod)this.methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
// 不存在则创建一个
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(this.mapperInterface, method, this.sqlSession.getConfiguration());
// 放入缓存
this.methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
MapperMethod
构造函数
private final MapperMethod.SqlCommand command;
private final MapperMethod.MethodSignature method;
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new MapperMethod.SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MapperMethod.MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
SqlCommand一个内部类 封装了SQL标签的类型 insert update delete select
MethodSignature一个内部类 封装了方法的参数信息 返回类型信息等
execute执行
判断sql的执行类型,执行相应的方法
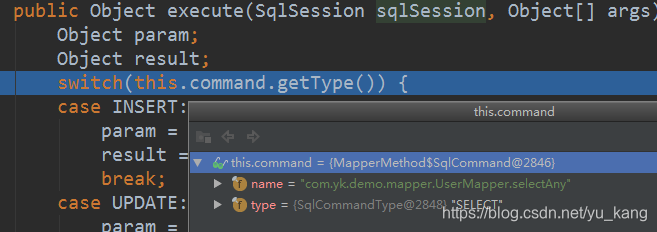
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object param;
Object result;
switch(this.command.getType()) {
case INSERT:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case UPDATE:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case DELETE:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case SELECT:
if (this.method.returnsVoid() && this.method.hasResultHandler()) { // 返回类型为void
this.executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (this.method.returnsMany()) { // 返回类型为集合或数组
result = this.executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (this.method.returnsMap()) {// 由@MapKey控制返回
result = this.executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (this.method.returnsCursor()) {// 返回类型为Cursor<T>,采用游标
result = this.executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
// 其他类型
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(this.command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + this.command.getName());
}
if (result == null && this.method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !this.method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + this.command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + this.method.getReturnType() + ").");
} else {
return result;
}
}
抽出这一段代码跟踪一下源码
// 其他类型
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(this.command.getName(), param);
convertArgsToSqlCommandParam解析入参
ParamNameResolver.getNamedParams
public Object convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(Object[] args) {
return this.paramNameResolver.getNamedParams(args);
}
解析@Param注解
names是SortedMap,在构造函数中赋值的,判断入参有没有@Param注解。
key是入参的顺序,从0开始;value是@Param中的值
如果没有@Param注解,则value值为arg0、arg1…
将入参名与值匹配
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {
int paramCount = this.names.size();
if (args != null && paramCount != 0) {
// 只有一个入参时,返回入参值
if (!this.hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {
return args[((Integer)this.names.firstKey()).intValue()];
} else {
// 多个入参时,返回一个Map
Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap();
int i = 0;
for(Iterator i$ = this.names.entrySet().iterator(); i$.hasNext(); ++i) {
Entry<Integer, String> entry = (Entry)i$.next();
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[((Integer)entry.getKey()).intValue()]);
String genericParamName = "param" + String.valueOf(i + 1);
if (!this.names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {
param.put(genericParamName, args[((Integer)entry.getKey()).intValue()]);
}
}
return param;
}
} else {
return null;
}
}
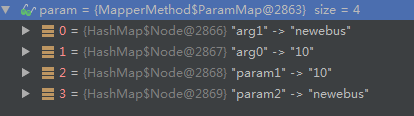
示例1: 多个入参,没有加@Param注解
@Select("SELECT count(0) from es_inter_invokfaillog where rownum = #{num} and invok_type=#{type}")
public Integer selectAny(int num,String type);
这样执行sql会报错,找不到num,可以改为#{arg1}或#{param1}
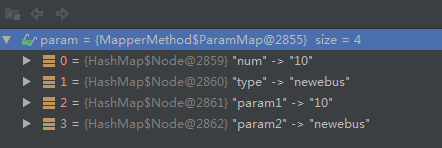
示例2:多个入参,加@Param注解
@Select("SELECT count(0) from es_inter_invokfaillog where rownum = #{num} and invok_type=#{type}")
public Integer selectAny(@Param("num")int num,@Param("type")String type);
示例3:多个入参,部分加@Param注解,部分不加
@Select("SELECT count(0) from es_inter_invokfaillog where rownum = #{num} and invok_type=#{arg1}")
public Integer selectAny(@Param("num")int num,String type);
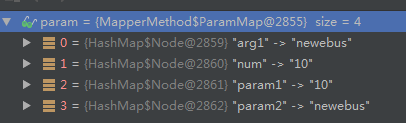
提示:只有一个入参时不存在这些问题,因为一个入参直接返回的是它的值,是一个String不是Map
执行SqlSessionTemplate中的方法
这里的sqlSession就是SqlSessionTemplate,mybatis与spring的整合之SqlSessionTemplate
result = sqlSession.selectOne(this.command.getName(), param);
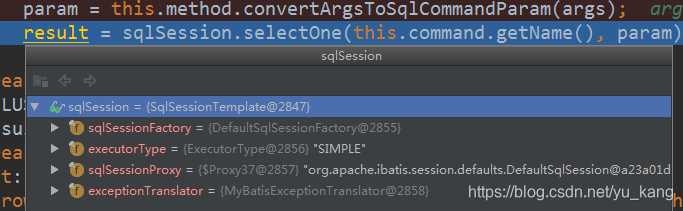
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.sqlSessionProxy.selectOne(statement, parameter);
}
sqlSessionProxy是动态代理生成的,每一次执行方法时都会重新去 new 一个DefaultSqlSession,可以看下invoke方法部分代码
// 获取session,这里有个事物的判断
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory, SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType, SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
Object unwrapped;
try {
// 真正执行sql语句的地方
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!SqlSessionUtils.isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
unwrapped = result;
}





 本文详细探讨了Mybatis核心组件MapperMethod的工作原理,包括MapperProxy如何处理目标方法的增强,MapperMethod的构造及执行过程。重点讲解了MapperMethod的构造函数,如SqlCommand和MethodSignature的作用,以及execute方法中的convertArgsToSqlCommandParam解析入参的逻辑,涉及@Param注解的处理。同时,文章还提及了SqlSessionTemplate在执行过程中的角色。
本文详细探讨了Mybatis核心组件MapperMethod的工作原理,包括MapperProxy如何处理目标方法的增强,MapperMethod的构造及执行过程。重点讲解了MapperMethod的构造函数,如SqlCommand和MethodSignature的作用,以及execute方法中的convertArgsToSqlCommandParam解析入参的逻辑,涉及@Param注解的处理。同时,文章还提及了SqlSessionTemplate在执行过程中的角色。
















 283
283

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








