目录
一、system_server进程介绍
Android system_server进程由zygote进程fork创建,是framework层的核心进程,主要由ASM、PMS等系统服务组成,给app提供Binder调用、与native & hal进程通信。
二、system_server进程启动流程
system_server进程启动入口:
// frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String[] argv) {
...
if (startSystemServer) {
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, zygoteSocketName, zygoteServer);
}
...
}
private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName,
ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
...
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.mUid, parsedArgs.mGid,
parsedArgs.mGids,
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.mPermittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.mEffectiveCapabilities);
...
}
// frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/Zygote.java
static int forkSystemServer(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags,
int[][] rlimits, long permittedCapabilities, long effectiveCapabilities) {
ZygoteHooks.preFork();
int pid = nativeForkSystemServer(
uid, gid, gids, runtimeFlags, rlimits,
permittedCapabilities, effectiveCapabilities);
// Set the Java Language thread priority to the default value for new apps.
Thread.currentThread().setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
ZygoteHooks.postForkCommon();
return pid;
}
// frameworks/base/core/jni/com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp
static jint com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkSystemServer(
JNIEnv* env, jclass, uid_t uid, gid_t gid, jintArray gids,
jint runtime_flags, jobjectArray rlimits, jlong permitted_capabilities,
jlong effective_capabilities) {
...
// fork出system_server子进程
pid_t pid = zygote::ForkCommon(env, true, fds_to_close, fds_to_ignore, true);
// 通过JNI调用SystemServer类的main方法
if (pid == 0) {
SpecializeCommon(env, uid, gid, gids, runtime_flags, rlimits, permitted_capabilities,
effective_capabilities, MOUNT_EXTERNAL_DEFAULT, nullptr, nullptr, true,
false, nullptr, nullptr, /* is_top_app= */ false,
/* pkg_data_info_list */ nullptr,
/* allowlisted_data_info_list */ nullptr, false, false);
} else if (pid > 0) {
...
}
return pid;
}通过JNI调用SystemServer类的main方法:
// frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
public static void main(String[] args) {
...
new SystemServer().run();
}
private void run() {
...
// Start services.
startBootstrapServices(t);
startCoreServices(t);
startOtherServices(t);
startApexServices(t);
updateWatchdogTimeout(t);
...
}2.1 startBootstrapServices
启动系统最重要的服务,执行startService和startBootPhase方法,如下:
// frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
private void startBootstrapServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
// 启动watchdog线程
final Watchdog watchdog = Watchdog.getInstance();
watchdog.start();
...
// 启动AMS
ActivityTaskManagerService atm = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
ActivityTaskManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
mActivityManagerService = ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.startService(
mSystemServiceManager, atm);
mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager);
mActivityManagerService.setInstaller(installer);
mWindowManagerGlobalLock = atm.getGlobalLock();
// 启动PMS
mPowerManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerManagerService.class);
// 启动ThermalManagerService
mSystemServiceManager.startService(ThermalManagerService.class);
...
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(t, SystemService.PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
}startService:通过反射的方式调用服务的onStart方法,
// frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/SystemServiceManager.java
public <T extends SystemService> T startService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
final String name = serviceClass.getName();
// Create the service.
if (!SystemService.class.isAssignableFrom(serviceClass)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create " + name
+ ": service must extend " + SystemService.class.getName());
}
final T service;
try {
Constructor<T> constructor = serviceClass.getConstructor(Context.class);
service = constructor.newInstance(mContext);
}
...
startService(service);
return service;
}
public void startService(@NonNull final SystemService service) {
// Check if already started
String className = service.getClass().getName();
if (mServiceClassnames.contains(className)) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Not starting an already started service " + className);
return;
}
mServiceClassnames.add(className);
// Register it.
mServices.add(service);
// Start it.
long time = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
try {
service.onStart();
}
}PMS服务执行onStart和startBootPhase方法:
public void onStart() {
publishBinderService(Context.POWER_SERVICE, mBinderService, /* allowIsolated= */ false,
DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_DEFAULT | DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL);
publishLocalService(PowerManagerInternal.class, mLocalService);
Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this);
Watchdog.getInstance().addThread(mHandler);
}
@Override
public void onBootPhase(int phase) {
if (phase == PHASE_SYSTEM_SERVICES_READY) {
systemReady();
} else if (phase == PHASE_THIRD_PARTY_APPS_CAN_START) {
incrementBootCount();
} else if (phase == PHASE_BOOT_COMPLETED) {
synchronized (mLock) {
...
}
...
}| 服务名称 | 作用 | |
| 1 | ArtModuleServiceInitializer | 初始化 ART 模块服务管理器 |
| 2 | Watchdog | 系统守护线程,监听系统服务是否发生死锁 |
| 3 | platformCompat | 平台兼容性服务,为其他服务提供兼容性支持 |
| 4 | FileIntegrityService | 文件完整性服务,响应应用和系统的完整性请求 |
| 5 | Installer | 安装器服务,等待 Installd 启动完成 |
| 6 | DeviceIdentifiersPolicyService | 设备标识符策略服务,注册在启动应用程序管理器之前 |
| 7 | UriGrantsManagerService | URI 授权管理服务 |
| 8 | PowerStatsService | 电源统计数据跟踪服务 |
| 9 | MemtrackProxyService | 内存跟踪代理服务,早于 ActivityManagerService 启动 |
| 10 | AccessCheckingService | 访问检查服务,提供新的权限和应用操作实现 |
| 11 | ActivityManagerService | 系统核心服务,管理活动和任务 |
| 12 | DataLoaderManagerService | 数据加载器管理服务 |
| 13 | IncrementalService | 增量安装服务 |
| 14 | PowerManagerService | 电源管理服务 |
| 15 | ThermalManagerService | 热管理服务 |
| 16 | HintManagerService | 提示管理服务 |
| 17 | RecoverySystemService | 设备进入Recovery模式时提供各种功能和操作 |
| 18 | LightsService | LED 和显示背光管理服务 |
| 19 | DisplayOffloadService | 显示卸载服务 |
| 20 | SidekickService | SidekickService服务通常与其他应用程序一起工作,为用户提供额外的功能和支持 |
| 21 | DisplayManagerService | 显示管理器服务 |
| 22 | DomainVerificationService | selinux权限验证服务 |
| 23 | PackageManagerService | 包管理器服务,管理应用程序包和应用程序 |
| 24 | DexUseManagerLocal | 本地 Dex 使用管理器 |
| 25 | OtaDexOptService | A/B OTA dexopt 管理服务 |
| 26 | UserManagerService | 用户管理服务 |
| 27 | OverlayManagerService | 用于管理和处理窗口覆盖(Overlay)相关的操作 |
| 28 | ResourcesManagerService | 资源管理器服务 |
| 29 | SensorPrivacyService | 传感器隐私管理服务 |
| 30 | SensorService | 传感器服务 |
2.2 startCoreServices
启动系统核心服务,如下:
private void startCoreServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
...
mSystemServiceManager.startService(SystemConfigService.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BatteryService.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(UsageStatsService.class);
mActivityManagerService.setUsageStatsManager(
LocalServices.getService(UsageStatsManagerInternal.class));
mWebViewUpdateService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(WebViewUpdateService.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(CachedDeviceStateService.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BinderCallsStatsService.LifeCycle.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(LooperStatsService.Lifecycle.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(ROLLBACK_MANAGER_SERVICE_CLASS);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(NativeTombstoneManagerService.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BugreportManagerService.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(GpuService.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(RemoteProvisioningService.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(CpuMonitorService.class);
}| 服务名称 | 作用 | |
| 1 | SystemConfigService | 用于管理和提供系统级别的配置信息。SystemConfigService服务为应用程序和系统组件提供了一种访问系统配置信息的方式 |
| 2 | BatteryService | 用于管理和提供电池相关的信息和功能。BatteryService服务为应用程序和系统组件提供了一种访问电池状态和控制电池使用的方式 |
| 3 | WebViewUpdateService | 用于管理和提供WebView组件的更新信息。WebView是Android系统中的一个内置组件,用于在应用程序中显示和处理网页内容 |
| 4 | CachedDeviceStateService | 用于缓存和提供设备状态信息。这个服务会在设备启动时创建,并在整个系统运行过程中提供设备状态信息 |
| 5 | BinderCallsStatsService | 为系统提供了一种收集和分析Binder通信性能数据的服务 |
| 6 | LooperStatsService | 为系统提供了一种收集和分析Looper线程性能数据的服务 |
| 7 | RollbackManagerService | 为系统提供了一种管理和实现系统回滚功能的方式,以便在出现问题时快速恢复系统状态 |
| 8 | NativeTombstoneManagerService | 为系统提供了一种管理和收集Native堆栈Tombstone信息,以便在进程发生native crash时快速定位问题 |
| 9 | BugreportManagerService | 为系统提供了一种管理和实现Bugreport信息,以便在需要时快速收集系统和程序状态信息 |
| 10 | GpuService | 为系统提供了一种访问GPU信息和控制GPU使用的服务 |
| 11 | RemoteProvisioningService | 为系统提供了一种管理和实现远程设备配置功能,以便在需要时远程配置设备 |
| 12 | CpuMonitorService | 用于管理和提供CPU相关的信息和功能 |
2.3 startOtherServices
启动系统其它的服务,如下:
private void startOtherServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
...
mSystemServiceManager.startService(DropBoxManagerService.class);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(ALARM_MANAGER_SERVICE_CLASS);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(CameraServiceProxy.class);
WindowManagerService.main(context, inputManager, !mFirstBoot,
pwm, mActivityManagerService.mActivityTaskManager);
// 这类系统服务可以做裁剪
if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_PRINTING)) {
t.traceBegin("StartPrintManager");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(PRINT_MANAGER_SERVICE_CLASS);
t.traceEnd();
}
}
if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_COMPANION_DEVICE_SETUP)) {
t.traceBegin("StartCompanionDeviceManager");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(COMPANION_DEVICE_MANAGER_SERVICE_CLASS);
t.traceEnd();
// VirtualDeviceManager depends on CDM to control the associations.
t.traceBegin("StartVirtualDeviceManager");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(VIRTUAL_DEVICE_MANAGER_SERVICE_CLASS);
t.traceEnd();
}
...
// 这里会启动launcher进程
mActivityManagerService.systemReady(() -> { ...}
...
// 启动systemui
startSystemUi(context, windowManagerF);
...
}| 服务名称 | 作用 | |
| 1 | KeyChainSystemService | 用于管理和提供密钥链(KeyChain)相关的信息和功能。密钥链是一种在Android系统中存储和管理敏感信息(如密码、密钥等)的机制,通常用于实现设备安全、数据加密等场景。 |
| 2 | DropBoxManagerService | app进程发生ANR、native crash时,收集相关debug信息 |
| 3 | ContentService | 为系统提供了一种管理和实现ContentProvider功能的方式,以便在需要时实现数据共享和访问 |
| 4 | AlarmManagerService | 定时任务 |
| 5 | InputManagerService | 管理和提供输入设备相关的信息和功能 |
| 6 | DeviceStateManagerService | 用于管理设备的状态信息 |
| 7 | WindowManagerService | 负责管理设备上的窗口和界面。它为应用程序提供了一个统一的接口,用于创建、显示、隐藏、移动、调整大小等操作窗口。 |
| 8 | BluetoothService | 理蓝牙设备的连接和通信。它提供了一系列API,允许应用程序通过蓝牙进行数据交换、文件传输、音频流传输等操作。 |
| 9 | StorageManagerService | 负责管理设备的存储空间。它为应用程序提供了一个统一的接口,用于访问设备的内部存储(如闪存)和外部存储(如SD卡)。 |
| 10 | OemLockService | 管理设备的OEM锁定状态 |
| 11 | DeviceIdleController | 管理设备的空闲状态。当设备处于空闲状态时,DeviceIdleController可以自动执行一些节能措施,如降低屏幕亮度、关闭无线网络等,以延长设备的电池寿命。 |
| 12 | DevicePolicyManagerService | 管理设备的策略和安全设置。 |
| 13 | StatusBarManagerService | 管理设备的状态栏。它提供了一系列API,允许应用程序在状态栏上显示通知、图标、进度条等信息。 |
| 14 | NetworkManagementService | 管理设备的网络连接。它提供了一系列API,允许应用程序获取设备的网络状态、连接类型、IP地址等信息,并可以控制设备的网络连接。 |
| 15 | NetworkStatsService | 统计设备的网络使用情况。它提供了一系列API,允许应用程序获取设备的网络流量统计信息,如总流量、各个应用程序的流量等。 |
| 16 | NetworkPolicyManagerService | 管理设备的网络策略。它提供了一系列API,允许设备管理员对设备的网络连接进行策略管理,如限制应用程序的网络访问、设置网络优先级等。 |
| 17 | SystemUpdateManagerService | 管理设备的系统更新。它提供了一系列API,允许对设备的系统更新进行管理,如检查系统更新、下载系统更新、安装系统更新等。 |
| 18 | NotificationManagerService | 管理设备的通知。它提供了一系列API,允许应用程序在通知栏上显示通知,如消息通知、提醒通知等。 |
| 19 | DeviceStorageMonitorService | 监控设备的存储空间。它提供了一系列API,允许应用程序获取设备的存储空间信息,如总容量、已用容量、可用容量等。 |
| 20 | AudioService | 管理设备的音频。允许应用程序控制设备的音频输出,如播放音乐、播放铃声等。 |
| 21 | BroadcastRadioService | 管理设备的广播电台。允许应用程序接收广播电台的节目,如新闻、音乐等。 |
| 22 | AdbService | 管理设备的ADB连接。允许开发人员通过ADB连接设备,进行调试和测试。 |
| 23 | UsbService | 管理设备的USB连接。允许应用程序通过USB连接设备,进行数据传输和通信 |
| 24 | GestureLauncher | 用于识别和响应用户的手势操作。允许应用程序检测和响应用户的手势操作,如滑动、捏合、旋转等。 |
| 25 | SensorNotificationService | 管理设备的传感器通知。允许应用程序获取设备的传感器信息,如加速度计、陀螺仪等 |
| 26 | DiskStatsService | 管理设备的磁盘状态。允许应用程序获取设备的磁盘状态信息,如分区大小、使用情况等。 |
| 27 | RuntimeService | 管理设备的运行时环境。允许应用程序获取设备的运行时信息,如内存使用情况、CPU使用情况等。 |
| 28 | GraphicsStatsService | 管理设备的图形性能 |
| 29 | FaceSensorService | 管理设备的面部识别功能 |
| 30 | HealthService | 用于管理设备的健康状态。允许应用程序获取设备的健康状态信息,如电池电量、温度等。 |
| 31 | SdkSandboxManagerService | 管理设备的SDK沙盒环境。允许应用程序获取设备的SDK沙盒信息,如应用程序的权限、资源等。 |
| 32 | PermissionPolicyService | 管理设备的权限策略 |
| 33 | LockSettingsService | 管理设备的锁定设置,如屏幕锁定方式、密码等。 |
| 34 | LauncherAppsService | 管理设备的启动器应用程序。允许应用程序获取设备的启动器应用程序信息,如启动器应用程序的名称、图标等。 |
| 35 | AppServiceManager | 管理设备的应用程序服务 |
| 36 | GameManagerService | 用于管理游戏的运行和状态 |
| 37 | LocationManagerService | 用于管理设备的位置信息,允许应用程序获取设备的位置信息,如经纬度、海拔等 |
| 38 | FingerprintSensor | 管理设备的指纹识别功能 |
| 39 | IoTSystemService | 理设备的物联网功能 |
| 40 | SafetyCenterService | 理设备的安全功能。允许应用程序获取设备的安全信息,如病毒扫描、防火墙等 |
| 其它系统服务: KeyAttestationApplicationIdProviderService、BinaryTransparencyService、SchedulingPolicyService、TelecomLoaderService、TelephonyRegistry、EntropyMixer、AccountManagerService、InstallSystemProviders、 RoleManagerService、VibratorManagerService、DynamicSystemService、ConsumerIrService、ResourceEconomy、 CameraServiceProxy、VrManagerService、IpConnectivityMetrics、NetworkWatchlistService、PinnerService、 ProfcollectForwardingService、SignedConfigService、AppIntegrityService、LogcatManagerService、 InputMethodManagerService、AccessibilityManagerService、UiModeManagerService、LocaleManagerService、 GrammaticalInflectionService、AppHibernationService、LockSettingsService、PersistentDataBlockService、 MusicRecognitionManagerService、SpeechRecognitionManagerService、AppPredictionService、 ContentSuggestionsService、SearchUiService、SmartspaceService、FontManagerService、TextServicesManager、 TextClassificationManagerService、NetworkScoreService、RttService、WifiAwareService、WifiP2PService、 LowpanService、PacProxyService、ConnectivityService、MiCarNetService、VpnManagerService、VcnManagementService、UpdateLockService、TimeDetectorService、CountryDetectorService、 TimeZoneDetectorService、AltitudeService、LocationTimeZoneManagerService、GnssTimeUpdateService、 SearchManagerService、WallpaperManagerService、WallpaperEffectsGenerationService、SoundTriggerMiddlewareService、DockObserver、ThermalObserver、WiredAccessoryManagerService、 MidiManagerService、SerialService、HardwarePropertiesManagerService、TwilightService、ColorDisplayService、 SoundTriggerService、TrustManagerService、BackupManager、AppWidgetService、VoiceRecognitionManager、 ContextHubSystemService、NetworkTimeUpdateService、EmergencyAffordanceService、DreamManagerService、 CoverageService、PrintManager、AttestationVerificationService、CompanionDeviceManager、VirtualDeviceManager、RestrictionManager、MediaSessionService、HdmiControlService、TvInteractiveAppManager、TvInputManager、TunerResourceManager、MediaResourceMonitor、 TvRemoteService、MediaRouterService、IrisSensor、FingerprintSensor、BiometricService、 AuthService、DynamicCodeLoggingService、PruneInstantAppsJobService、ShortcutService、 CrossProfileAppsService、PeopleService、MediaMetricsManager、BackgroundInstallControlService、 MediaProjectionManager、WearPowerService、WearConnectivityService、WearDisplayService、 WearTimeService、WearGlobalActionsService、SliceManagerService、 StatsCompanion、StatsPullAtomService、BootstrapAtomService、IncidentCompanionService、 AdServicesManagerService、OnDevicePersonalizationSystemService、MmsService、AutoFillService、 CredentialManagerService、TranslationManagerService、SelectionToolbarManagerService、ClipboardService、 TracingServiceProxy、DeviceSpecificServices、MediaCommunicationService、 AppCompatOverridesService、HealthConnectManagerService等 | ||
2.4 startApexServices
启动系统apex服务,如下:
private void startApexServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
List<ApexSystemServiceInfo> services = ApexManager.getInstance().getApexSystemServices();
for (ApexSystemServiceInfo info : services) {
String name = info.getName();
String jarPath = info.getJarPath();
t.traceBegin("starting " + name);
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(jarPath)) {
mSystemServiceManager.startService(name);
} else {
mSystemServiceManager.startServiceFromJar(name, jarPath);
}
t.traceEnd();
}
}三、如何使用系统服务
3.1 app进程调用系统服务
以PMS服务为例,app进程通过获取PMS服务代理---PowerManager对象,调用PowerManager中的接口:
// 获取PowerManager实例
PowerManager powerManager = (PowerManager) getSystemService(Context.POWER_SERVICE);
// 调用PowerManager类中的接口
PowerManager.WakeLock wakeLock = powerManager.newWakeLock(PowerManager.PARTIAL_WAKE_LOCK, "MyWakeLockTag");
3.2 native进程调用系统服务
通过binder对parcel数据通信:
#include <binder/IServiceManager.h>
#include <binder/Parcel.h>
sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager();
sp<IBinder> binder = sm->getService(String16("power"));
if (!binder) {
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
Parcel data, result;
data.writeInterfaceToken(String16("android.os.IPowerManager"));
char d[] = {0x00};
data.write(d, sizeof(d));
// 6表示对应的方法ID
binder->transact(6, data, &result);或者直接调用binder接口:
#include <binder/IActivityManager.h>
#include <binder/IBinder.h>
#include <binder/IServiceManager.h>
int openContentProviderFile(const String16& uri)
{
int fd = -1;
sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager();
sp<IBinder> binder = sm->getService(String16("activity"));
sp<IActivityManager> am = interface_cast<IActivityManager>(binder);
if (am != NULL) {
fd = am->openContentUri(uri);
}
return fd;
}3.3 system_server进程中两个服务之间的调用
system_server进程中的服务间调用属于进程内部通信。如PMS服务启动时会将内部的mLocalService对象注册到本地service管理中,对外提供一个PowerManagerInternal类及接口,给其它服务调用,如下:
// 其它服务中通过获取PowerManagerInternal对象,调用接口
private PackageManagerInternal mPackageManagerInternal;
mLocalPowerManager = getLocalService(PowerManagerInternal.class);
mLocalPowerManager.getLowPowerState(
ServiceType.QUICK_DOZE).batterySaverEnabled);
// frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/PowerManagerInternal.java
// 抽象方法,在具体实现类中实现
public abstract PowerSaveState getLowPowerState(int serviceType);
// frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/power/PowerManagerService.java
public final class PowerManagerService extends SystemService
implements Watchdog.Monitor {
...
@Override
public void onStart() {
// 注册到servicemanager中,用于进程间通信
publishBinderService(Context.POWER_SERVICE, mBinderService, /* allowIsolated= */ false,
DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_DEFAULT | DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL);
// 加入到本地service中,用于进程内部调用
publishLocalService(PowerManagerInternal.class, mLocalService);
...
}
// 内部类继承PowerManagerInternal,并实现父类抽象方法
final class LocalService extends PowerManagerInternal {
...
@Override
public PowerSaveState getLowPowerState(@ServiceType int serviceType) {
return mBatterySaverPolicy.getBatterySaverPolicy(serviceType);
}
...
}
...
}四、如何添加一个系统服务
添加步骤:
1)准备系统服务代码DemoSystemService.java和Android.bp文件
// 继承SystemService,实现Watchdog.Monitor接口
public final class DemoManagerService extends SystemService
implements Watchdog.Monitor {
// 服务名称为 "demo"
String SERVICE_NAME = "demo";
...
// 重写onStart和onBootPhase方法
@Override
public void onStart() {
// 发布服务
publishBinderService(SERVICE_NAME, mBinderService, /* allowIsolated= */ false,
DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_DEFAULT | DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL);
// 用于监控DemoManagerService是否发生死锁
Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this);
Watchdog.getInstance().addThread(mHandler);
}
@Override
public void onBootPhase(int phase) {
...
}
...
}filegroup {
name: "demo--system-service-sources",
srcs: ["DemoSystemService.java"],
}2)将services.jar模块编译依赖新增模块
修改frameworks/base/services/Android.bp,如下:
java_library {
name: "services",
...
srcs: [":services-main-sources",
":demo--system-service-sources"
],
...
}3)SystemServer.java中启动Demo服务
修改frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java, 启动DemoSystemService,如下:
public final class SystemServer implements Dumpable {
...
private void startOtherServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
t.traceBegin("StartDemoSystemService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(DemoSystemService.class);
t.traceEnd();
}
...
}4)添加selinux规则
修改system/sepolicy库,添加demo服务的标签和规则,注意添加的服务名称为demo,如下:
// system/sepolicy/private/compat/32.0/32.0.ignore.cil
vendor_vm_file
virtual_device_service
wallpaper_effects_generation_service
demo_service
// system/sepolicy/prebuilts/api/32.0/private/service_contexts
demo u:object_r:demo_service:s0
// system/sepolicy/prebuilts/api/32.0/public/service.te
type demo_service, system_server_service, service_manager_type;五、如何裁剪系统服务
所谓的系统服务裁剪,就是不让服务启动且其它获取该服务的地方有判空,避免运行时空指针报错。以printmanagerservice服务为例:
// packagemanager
public static final String FEATURE_PRINTING = "android.software.print";
private void startOtherServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
// 这类系统服务可以做裁剪,只需让hasSystemFeature方法返回false
if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_PRINTING)) {
t.traceBegin("StartPrintManager");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(PRINT_MANAGER_SERVICE_CLASS);
t.traceEnd();
}
}
...
}hasSystemFeature实现:
// 通过mAvailableFeatures得到所有的feature
public boolean hasSystemFeature(String name, int version) {
// allow instant applications
synchronized (mAvailableFeatures) {
final FeatureInfo feat = mAvailableFeatures.get(name);
if (feat == null) {
return false;
} else {
return feat.version >= version;
}
}
}
// 该方法维护mAvailableFeatures列表
private void addFeature(String name, int version) {
FeatureInfo fi = mAvailableFeatures.get(name);
if (fi == null) {
fi = new FeatureInfo();
fi.name = name;
fi.version = version;
mAvailableFeatures.put(name, fi);
} else {
fi.version = Math.max(fi.version, version);
}
}
// 系统启动时会去读取handheld_core_hardware.xml配置文件,存到mAvailableFeatures列表
SystemConfig() {
TimingsTraceLog log = new TimingsTraceLog(TAG, Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
log.traceBegin("readAllPermissions");
try {
readAllPermissions();
readPublicNativeLibrariesList();
} finally {
log.traceEnd();
}
}
// 读取handheld_core_hardware.xml配置文件
private void readPermissionsFromXml(final XmlPullParser parser, File permFile,
int permissionFlag) {
...
case "feature": {
if (allowFeatures) {
String fname = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "name");
int fversion = XmlUtils.readIntAttribute(parser, "version", 0);
boolean allowed;
if (!lowRam) {
allowed = true;
} else {
String notLowRam = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "notLowRam");
allowed = !"true".equals(notLowRam);
}
if (fname == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "<" + name + "> without name in " + permFile + " at "
+ parser.getPositionDescription());
} else if (allowed) {
addFeature(fname, fversion);
}
} else {
logNotAllowedInPartition(name, permFile, parser);
}
XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser);
} break;
...
}只要注释掉<feature name="android.software.print" />,hasSystemFeature方法返回false,printmanagerservice服务就不会启动,如下:
// frameworks/native/data/etc/handheld_core_hardware.xml
<!-- basic system services -->
<feature name="android.software.app_widgets" />
<feature name="android.software.telecom" />
<feature name="android.software.voice_recognizers" notLowRam="true" />
<feature name="android.software.backup" />
<feature name="android.software.home_screen" />
<feature name="android.software.input_methods" />
<feature name="android.software.picture_in_picture" notLowRam="true" />
<feature name="android.software.activities_on_secondary_displays" notLowRam="true" />
// <feature name="android.software.print" />
<feature name="android.software.companion_device_setup" />
<feature name="android.software.autofill" />
<feature name="android.software.credentials" />
<feature name="android.software.cant_save_state" />
<feature name="android.software.secure_lock_screen" />
<feature name="android.software.window_magnification" />
...
</permissions>PRODUCT_COPY_FILES := \ frameworks/native/data/etc/handheld_core_hardware.xml:system/etc/permissions/handheld_core_hardware.xmlapp进程或系统其它服务在使用该服务前会做空判断,避免服务获取不到引入的空指针错误:
// 服务注册
registerService(Context.PRINT_SERVICE, PrintManager.class,
new CachedServiceFetcher<PrintManager>() {
@Override
public PrintManager createService(ContextImpl ctx) throws ServiceNotFoundException {
IPrintManager service = null;
// If the feature not present, don't try to look up every time
if (ctx.getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_PRINTING)) {
service = IPrintManager.Stub.asInterface(ServiceManager
.getServiceOrThrow(Context.PRINT_SERVICE));
}
final int userId = ctx.getUserId();
final int appId = UserHandle.getAppId(ctx.getApplicationInfo().uid);
return new PrintManager(ctx.getOuterContext(), service, userId, appId);
}});
public PrintManager(Context context, IPrintManager service, int userId, int appId) {
mContext = context;
mService = service;
...
}
// app进程调用服务相关接口之前会做null判断,避免服务获取失败导致空指针错误
public PrintJob getPrintJob(PrintJobId printJobId) {
if (mService == null) {
Log.w(LOG_TAG, "Feature android.software.print not available");
return null;
}
try {
PrintJobInfo printJob = mService.getPrintJobInfo(printJobId, mAppId, mUserId);
if (printJob != null) {
return new PrintJob(printJob, this);
}
} catch (RemoteException re) {
throw re.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
return null;
}
// 其它服务在调用该服务之前会做hasSystemFeature判断是否可用
@Override
public int getAvailabilityStatus() {
return mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_PRINTING)
&& mPrintManager != null
? AVAILABLE : UNSUPPORTED_ON_DEVICE;
}六、其它模块
6.1 NativeCrashListener
NativeCrashListener线程模块用于监听native crash事件,即当某个进程发生native crash时,由crash_dump64进程通过socket(ndebugsocket)方式将crash debug信息传给NativeCrashListener模块,并传给AMS服务写入dropbox.
-
流程框架
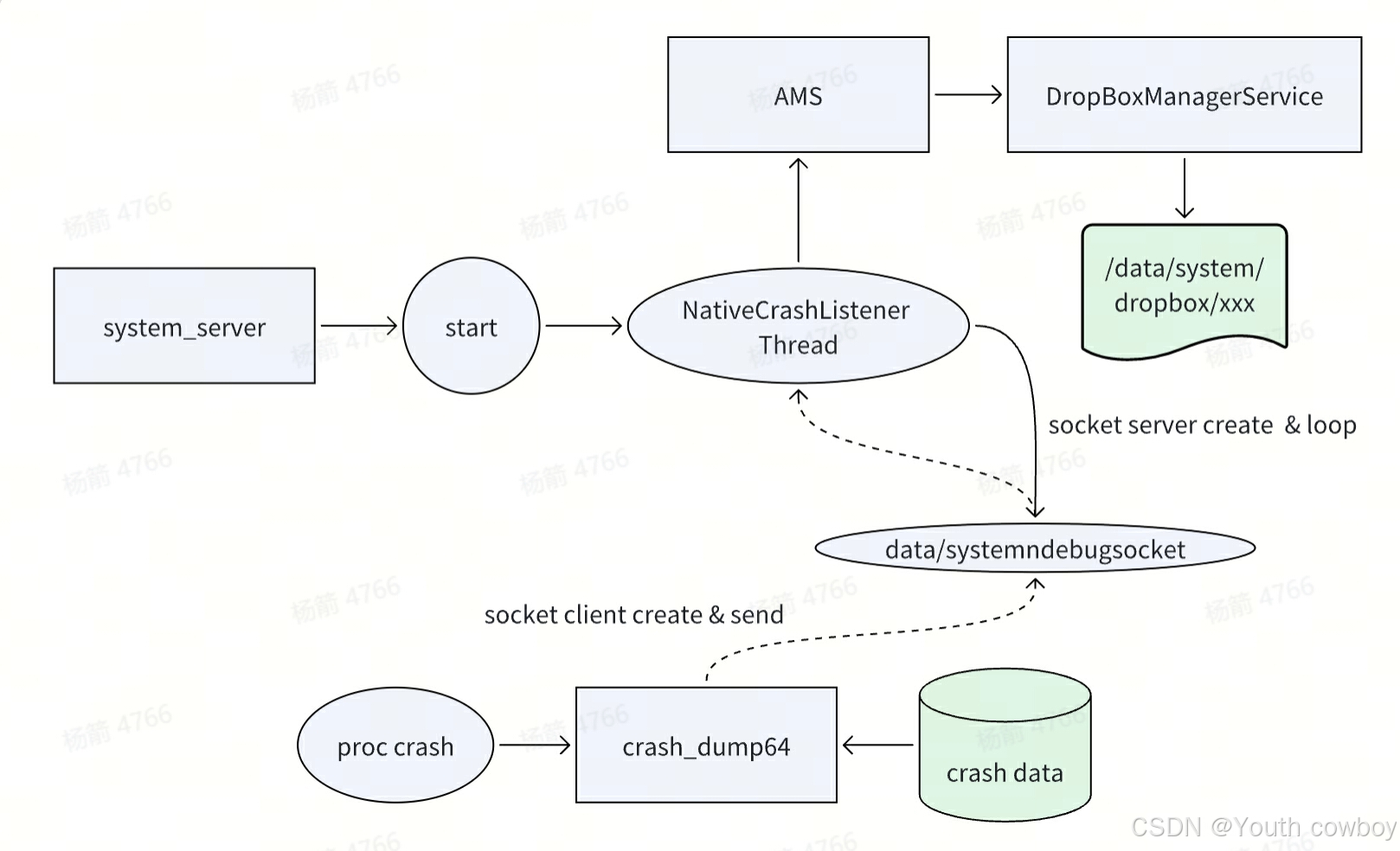
system_server进程启动的systemReady阶段创建NativeCrashListener线程,该线程创建"ndebugsocket" socket服务端,当有进程发生native crash时,crash_dump64客户端进程通过socket与system_server通信,最后将数据存到"data/system/dropbox"目录。
-
核心代码段
// frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
mActivityManagerService.systemReady(() -> {
...
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(t, SystemService.PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY);
...
mActivityManagerService.startObservingNativeCrashes();
...
}
// rameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
public void startObservingNativeCrashes() {
final NativeCrashListener ncl = new NativeCrashListener(this);
ncl.start();
}// frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/NativeCrashListener.java
final class NativeCrashListener extends Thread {
static final String DEBUGGERD_SOCKET_PATH = "/data/system/ndebugsocket";
static final long SOCKET_TIMEOUT_MILLIS = 10000;
final ActivityManagerService mAm;
// 内部类线程
class NativeCrashReporter extends Thread {
ProcessRecord mApp;
int mSignal;
boolean mGwpAsanRecoverableCrash;
String mCrashReport;
NativeCrashReporter(ProcessRecord app, int signal, boolean gwpAsanRecoverableCrash,
String report) {
super("NativeCrashReport");
mApp = app;
mSignal = signal;
mGwpAsanRecoverableCrash = gwpAsanRecoverableCrash;
mCrashReport = report;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
CrashInfo ci = new CrashInfo();
ci.exceptionClassName = "Native crash";
ci.exceptionMessage = Os.strsignal(mSignal);
ci.throwFileName = "unknown";
ci.throwClassName = "unknown";
ci.throwMethodName = "unknown";
ci.stackTrace = mCrashReport;
// crash数据传给AMS,由AMS写入dropbox
mAm.handleApplicationCrashInner(
mGwpAsanRecoverableCrash ? "native_recoverable_crash" : "native_crash",
mApp, mApp.processName, ci);
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "<-- handleApplicationCrash() returned");
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Unable to report native crash", e);
}
}
}
// 在system_server进程启动的systemReady阶段执行,创建socke server,进入循环监听
@Override
public void run() {
final byte[] ackSignal = new byte[1];
{
File socketFile = new File(DEBUGGERD_SOCKET_PATH);
if (socketFile.exists()) {
socketFile.delete();
}
}
try {
FileDescriptor serverFd = Os.socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
final UnixSocketAddress sockAddr = UnixSocketAddress.createFileSystem(
DEBUGGERD_SOCKET_PATH);
Os.bind(serverFd, sockAddr);
Os.listen(serverFd, 1);
Os.chmod(DEBUGGERD_SOCKET_PATH, 0777);
while (true) {
FileDescriptor peerFd = null;
try {
if (MORE_DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Waiting for debuggerd connection");
peerFd = Os.accept(serverFd, null /* peerAddress */);
if (MORE_DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Got debuggerd socket " + peerFd);
if (peerFd != null) {
// 数据客户端的信息
consumeNativeCrashData(peerFd);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Error handling connection", e);
} finally {
...
}
}
// 读取client socket数据,存到byte[] buffer
static int readExactly(FileDescriptor fd, byte[] buffer, int offset, int numBytes)
throws ErrnoException, InterruptedIOException {
int totalRead = 0;
while (numBytes > 0) {
int n = Os.read(fd, buffer, offset + totalRead, numBytes);
if (n <= 0) {
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Needed " + numBytes + " but saw " + n);
}
return -1; // premature EOF or timeout
}
numBytes -= n;
totalRead += n;
}
return totalRead;
}
// Read a crash report from the connection
void consumeNativeCrashData(FileDescriptor fd) {
final byte[] buf = new byte[4096];
final ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream(4096);
try {
StructTimeval timeout = StructTimeval.fromMillis(SOCKET_TIMEOUT_MILLIS);
Os.setsockoptTimeval(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVTIMEO, timeout);
Os.setsockoptTimeval(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDTIMEO, timeout);
int headerBytes = readExactly(fd, buf, 0, 9);
boolean gwpAsanRecoverableCrash = buf[8] != 0;
...
// byte[]转String
int bytes;
do {
// get some data
bytes = Os.read(fd, buf, 0, buf.length);
if (bytes > 0) {
if (MORE_DEBUG) {
String s = new String(buf, 0, bytes, "UTF-8");
Slog.v(TAG, "READ=" + bytes + "> " + s);
}
// did we just get the EOD null byte?
if (buf[bytes - 1] == 0) {
os.write(buf, 0, bytes - 1); // exclude the EOD token
break;
}
// no EOD, so collect it and read more
os.write(buf, 0, bytes);
}
} while (bytes > 0);
if (!gwpAsanRecoverableCrash) {
synchronized (mAm) {
synchronized (mAm.mProcLock) {
pr.mErrorState.setCrashing(true);
pr.mErrorState.setForceCrashReport(true);
}
}
}
final String reportString = new String(os.toByteArray(), "UTF-8");
(new NativeCrashReporter(pr, signal, gwpAsanRecoverableCrash, reportString)).start();
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Exception dealing with report", e);
// ugh, fail.
}
}
}
6.2 Android watchdog
Android watchdog用于监测系统服务、UI线程、动画线程等是否出现死锁或卡死,system_server进程启动时会启动watchdog线程,进入监听,系统服务启动时会加入watchdog监听。
private void startBootstrapServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
......
// Start the watchdog as early as possible so we can crash the system server// if we deadlock during early boott.traceBegin("StartWatchdog");
final Watchdog watchdog = Watchdog.getInstance(); // 对象创建
watchdog.start(); // 启动watchdong线程
mDumper.addDumpable(watchdog);
......
}
-
实现原理
以PMS服务为例,
1)PMS服务实现Watchdog.Monitor接口,服务启动时,将PMS服务对象加入到watchdong的Monitor列表
2)system_server进程启动时,会启动watchdog线程,每隔30s会启动monitor线程调用monitor列表中的PMS对象加锁的monitor方法,如果超过30s没有返回,说明一直在等待锁,即PMS服务卡死。
// PowerManagerService.java
public final class PowerManagerService extends SystemService
implements Watchdog.Monitor {
...
@Override
public void onStart() {
// 加入watchdog监听
Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this); // pms服务实现了Watchdog.Monitor接口
...
}
// 在watch dog中调用,超过30s没有返回,说明一直在等待锁,即服务卡死
@Override
public void monitor() {
// Grab and release lock for watchdog monitor to detect deadlocks.
synchronized (mLock) {
}
}
...
}
// frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/Watchdog.java
public class Watchdog implements Dumpable {
...
private final Thread mThread;
private final HandlerChecker mMonitorChecker;
private Watchdog() {
// 创建watchdog线程
mThread = new Thread(this::run, "watchdog");
// 创建monitor线程
mMonitorChecker = new HandlerChecker(new Handler(t.getLooper()), "monitor thread");
...
}
public void start() {
// 启动watchdog线程,执行Watchdog类中的run方法
mThread.start();
}
public void addMonitor(Monitor monitor) {
synchronized (mLock) {
mMonitorChecker.addMonitorLocked(monitor);
}
}
private void run() {
boolean waitedHalf = false;
while (true) {
List<HandlerChecker> blockedCheckers = Collections.emptyList();
String subject = "";
boolean allowRestart = true;
int debuggerWasConnected = 0;
boolean doWaitedHalfDump = false;
final long watchdogTimeoutMillis = mWatchdogTimeoutMillis;
final long checkIntervalMillis = watchdogTimeoutMillis / 2;
final ArrayList<Integer> pids;
synchronized (mLock) {
long timeout = checkIntervalMillis;
for (int i=0; i<mHandlerCheckers.size(); i++) {
HandlerCheckerAndTimeout hc = mHandlerCheckers.get(i);
// 执行内部类HandlerChecker中的scheduleCheckLocked方法
hc.checker().scheduleCheckLocked(hc.customTimeoutMillis()
.orElse(watchdogTimeoutMillis * Build.HW_TIMEOUT_MULTIPLIER));
}
...
}
public final class HandlerChecker implements Runnable {
...
private Monitor mCurrentMonitor;
private final ArrayList<Monitor> mMonitors = new ArrayList<Monitor>();
private final ArrayList<Monitor> mMonitorQueue = new ArrayList<Monitor>();
HandlerChecker(Handler handler, String name) {
mHandler = handler;
mName = name;
mCompleted = true;
}
void addMonitorLocked(Monitor monitor) {
mMonitorQueue.add(monitor);
}
public void scheduleCheckLocked(long handlerCheckerTimeoutMillis) {
mWaitMaxMillis = handlerCheckerTimeoutMillis;
if (mCompleted) {
// Safe to update monitors in queue, Handler is not in the middle of work
mMonitors.addAll(mMonitorQueue);
mMonitorQueue.clear();
}
if ((mMonitors.size() == 0 && mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().isPolling())
|| (mPauseCount > 0)) {
mCompleted = true;
return;
}
if (!mCompleted) {
// we already have a check in flight, so no need
return;
}
mCompleted = false;
mCurrentMonitor = null;
mStartTimeMillis = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
// 发送消息,插入消息队列最开头,执行下面的run()方法
mHandler.postAtFrontOfQueue(this);
}
@Override
public void run() {
final int size = mMonitors.size();
for (int i = 0 ; i < size ; i++) {
synchronized (mLock) {
mCurrentMonitor = mMonitors.get(i);
}
// 开始监测服务是否出现死锁或卡死
mCurrentMonitor.monitor();
}
synchronized (mLock) {
mCompleted = true;
mCurrentMonitor = null;
}
}
...
} // HandlerChecker内部类
...
} // Watchdog 























 352
352

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








