文章目录
集合( collection)表示一组对象。Java SE 提供了集合框架( collections framework),是一个用于表示和操作集合的统一框架,使集合可以独立于实现细节进行操作。集合框架的主要优点如下:
- 通过提供数据结构和算法实现,使用户无需自行编写,减少编程工作。
- 通过提供数据结构和算法的高性能实现来提高性能。由于每个接口的各种实现是可互换的,因此可以通过切换实现来调整和优化程序。
- 通过提供一套标准接口来促进软件重用。
- 通过建立一种通用语言,为无关联的集合 API 之间提供互操作性。
- 减少学习成本,只须学习一些特设的集合 API。
集合框架的整体组成如下:
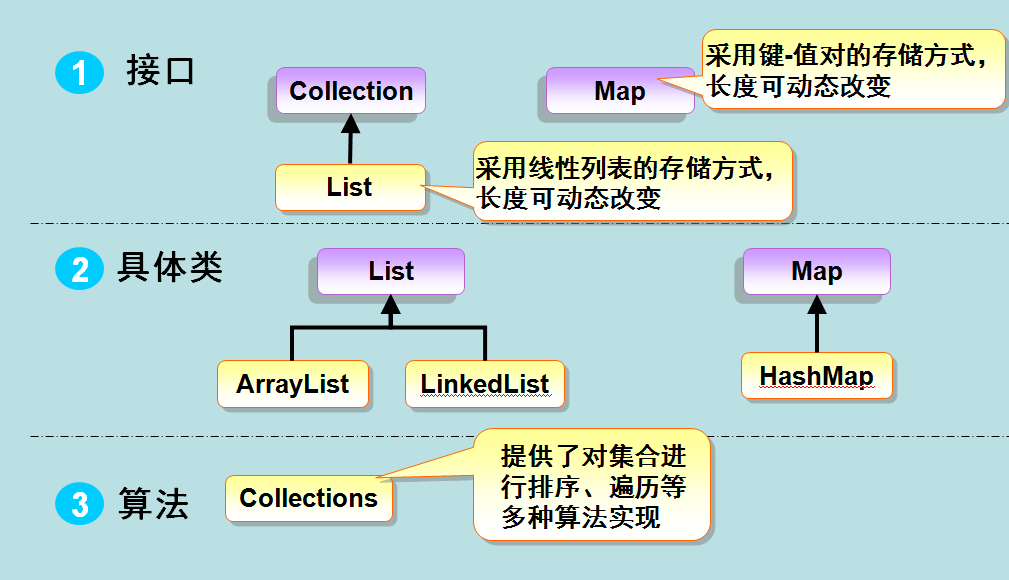
下面分别来看下各组成部分。
集合接口
集合接口分为两组:java.util.Collection 和 java.util.Map,这些接口构成了集合框架的基础:
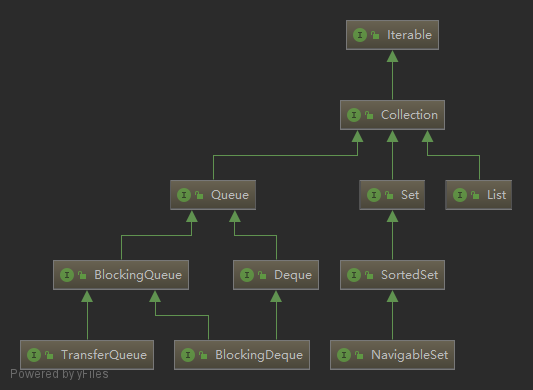
Collection
最基础的集合接口 java.util.Collection 及其子接口如下:
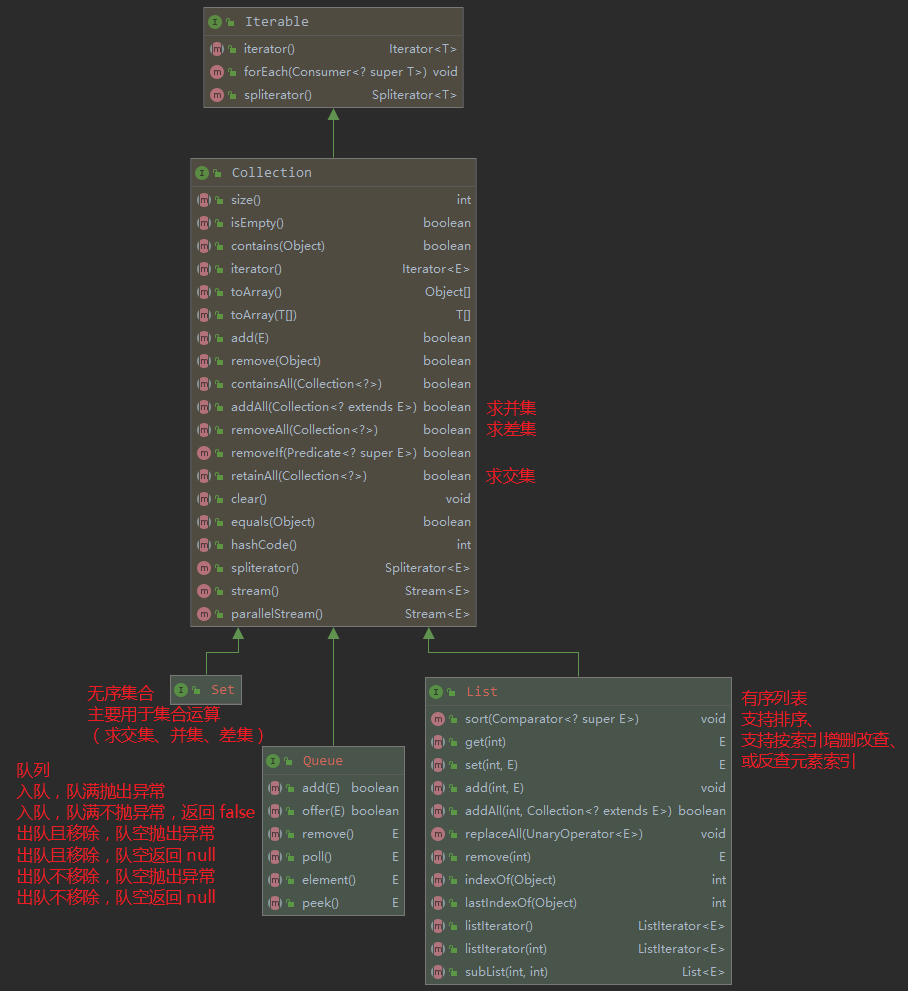
五个重点接口的方法及使用要点如下:
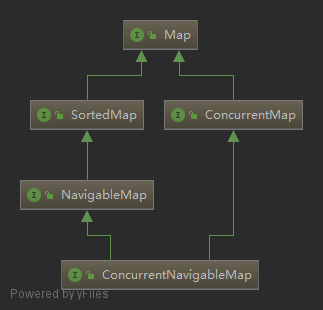
Map
其它集合接口基于 java.util.Map,不是真正的集合。但是,这些接口包含集合视图(collection-view)操作,使得它们可以作为集合进行操作。
集合实现类
抽象类实现
下列抽象类为核心集合接口提供了基本功能实现,以最小化用户自定义实现的成本。这些抽象类的 API 文档精确地描述了各个方法的实现方式,实现者能够参阅并了解哪些方法需要覆盖:
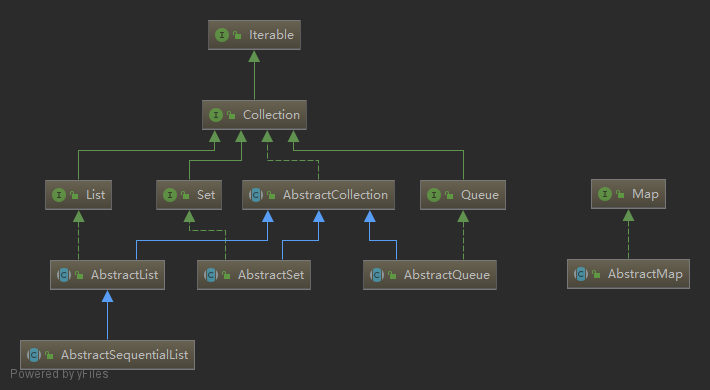
通用实现
java.util.Collection 的通用实现如下:
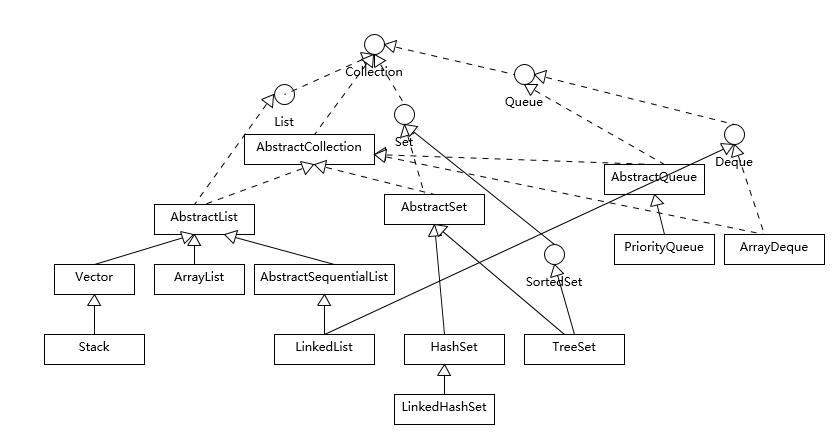
java.util.Map 的通用实现如下:
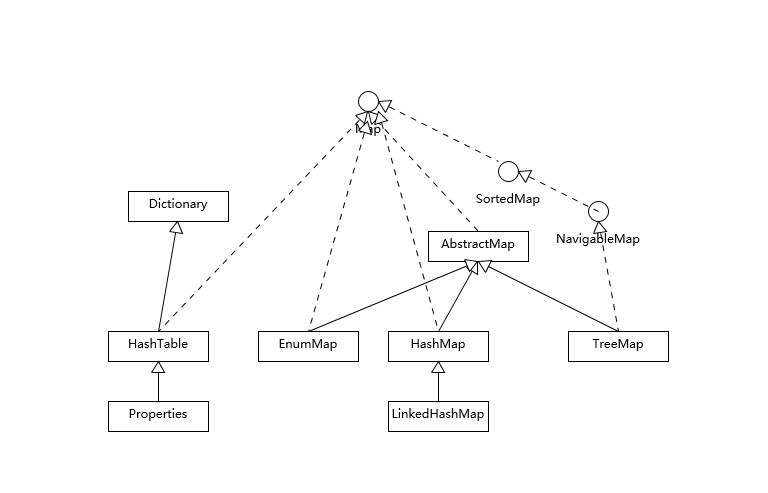
集合接口的主要实现,命名通常形如 <Implementation-style><Interface>。通用实现类汇总如下(表头为数据结构,左列为接口):
| Resizable Array | Linked List | Hash Table | Hash Table + Linked List | Balanced Tree | Heap | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
List | ArrayList | LinkedList | ||||
Queue | ArrayBlockingQueue | LinkedList LinkedBlockingQueue LinkedTransferQueue ConcurrentLinkedQueue | PriorityBlockingQueue PriorityQueue | |||
Deque | ArrayDeque | LinkedList LinkedBlockingDeque ConcurrentLinkedDeque | ||||
Set | HashSet | LinkedHashSet | TreeSet | |||
Map | HashMap | LinkedHashMap | TreeMap |
通用实现的特性如下:
- 通用实现类支持集合接口中的所有可选操作,并且对包含的元素没有限制。
- 都是非线程同步的。
Collections工具类提供了称为同步包装器(synchronization wrappers)的静态工厂方法可用于添加同步行为。 - 所有集合实现都具有快速失败的迭代器(fail-fast iterators),可以检测到无效的并发修改,然后快速失败,而不是表现异常。
遗留实现
早期版本的集合类,已被改进以实现新的集合接口:
Vector-List接口的可变长数组实现,线程同步,包含其它遗留方法。Hashtable-Map接口的散列表实现,线程同步,键和值都不允许为null,包含其它遗留方法。
并发实现
为高并发使用而设计的实现。详见另一篇《Java 并发集合总结》。
特殊实现
用于特殊情况的实现:
CopyOnWriteArrayList写时复制列表CopyOnWriteArraySet写时复制列表WeakHashMapIdentityHashMapEnumSetEnumMap
适配器实现
将某个集合接口适配成另一个:
-
根据
Map的通用实现创建一个Set的通用实现:Collections.newSetFromMap(Map) -
以后进先出(Lifo)队列的形式返回
Deque的视图:Collections.asLifoQueue(Deque)
包装器实现
用于其它集合实现的功能增强:
-
返回指定集合的不可修改视图(unmodifiable view),如果尝试修改,则会抛出
UnsupportedOperationException:Collections.unmodifiableCollection Collections.unmodifiableSet Collections.unmodifiableSortedSet Collections.unmodifiableNavigableSet Collections.unmodifiableList Collections.unmodifiableMap Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap Collections.unmodifiableNavigableMap -
返回由指定集合支持的
synchronized线程同步集合:Collections.synchronizedCollection Collections.synchronizedSet Collections.synchronizedSortedSet Collections.synchronizedNavigableSet Collections.synchronizedList Collections.synchronizedMap Collections.synchronizedSortedMap Collections.synchronizedNavigableMap -
返回指定集合的动态类型安全视图(dynamically type-safe view),如果尝试添加错误类型的元素,则会抛出
ClassCastException。泛型机制虽然提供了编译期类型检查,但可以绕过此机制。动态类型安全试图消除了这种可能性:Collections.checkedCollection Collections.checkedQueue Collections.checkedSet Collections.checkedSortedSet Collections.checkedNavigableSet Collections.checkedList Collections.checkedMap Collections.checkedSortedMap Collections.checkedNavigableMap
便利实现
集合接口的高性能版“迷你实现”:
-
返回一个不可变集合(immutable),不包含任何元素:
Collections.emptySet Collections.emptySortedSet Collections.emptyNavigableSet Collections.emptyList Collections.emptyMap Collections.emptySortedMap Collections.emptyNavigableMap -
返回一个不可变集合(immutable),仅包含一个元素:
Collections.singleton Collections.singletonList Collections.singletonMap -
返回一个不可变集合(immutable),包含指定元素的 N 个拷贝:
Collections.nCopies -
返回一个由指定数组支持的定长集合(fixed-size):
Arrays.asList
基础设施
为集合接口提供必要支持的接口。例如:
- 迭代器
Iterator、ListIterator - 排序接口
Comparable、Comparator - 运行时异常
UnsupportedOperationException、ConcurrentModificationException - 标记接口
RandomAccess
算法和工具实现
算法实现。由工具类 Collections 提供,用于集合,提供了很多静态方法例如 sort 排序、binarySearch 查找、replaceAll 替换等。这些算法体现了多态性,因为相同的方法可以在相似的接口上有着不同的实现。
数组工具。由工具类 Arrays 提供,用于基本类型和引用类型数组,提供了很多静态方法例如 sort 排序、binarySearch 查找等。严格来说,这些工具不是集合框架的一部分,此功能在集合框架引入的同时被添加到 Java 平台,并依赖于一些相同的基础设施。
集合接口中的许多修改方法都被标记为可选(optional)。实现类允许按需实现,未实现的方法需抛出运行时异常 UnsupportedOperationException。每个实现类的文档必须指明支持哪些可选操作。集合框架引入下列术语来帮助阐述本规范:
定长/变长
长度保证不变(即使元素可以更改)的列表称为 *fixed-size* 定长列表。反之则称为 *variable-size* 变长列表。
开发中接触最多的定长集合是通过 Arrays.asList() 创建的,该方法是一个适配器接口,将数组适配为定长列表,返回的对象是一个 Arrays 内部类,源码如下:
/**
* Returns a fixed-size list backed by the specified array. (Changes to
* the returned list "write through" to the array.) This method acts
* as bridge between array-based and collection-based APIs, in
* combination with {@link Collection#toArray}. The returned list is
* serializable and implements {@link RandomAccess}.
*
* <p>This method also provides a convenient way to create a fixed-size
* list initialized to contain several elements:
* <pre>
* List<String> stooges = Arrays.asList("Larry", "Moe", "Curly");
* </pre>
*
* @param <T> the class of the objects in the array
* @param a the array by which the list will be backed
* @return a list view of the specified array
*/
@SafeVarargs
@SuppressWarnings("varargs")
public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a) {
return new ArrayList<>(a);
}
private static class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements RandomAccess, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2764017481108945198L;
private final E[] a;
ArrayList(E[] array) {
a = Objects.requireNonNull(array);
}
......
}
分析发现,涉及元素增删的操作(如 add()、remove()、clear())该内部类并没有实现,而是使用了父类 AbstractList 的方法,默认抛出 UnsupportedOperationException 异常:
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E> {
public void add(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public E remove(int index) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
参考手册:

可改/不可改
不支持修改操作(例如 add、remove 和 clear)的集合称为 *unmodifiable* 不可修改集合。反之则称为 *modifiable* 可修改集合。Collections 工具类提供了一组静态工厂方法,用于包装并返回指定集合的不可修改视图(unmodifiable view),如果尝试修改,则会抛出UnsupportedOperationException:
Collections.unmodifiableCollection
Collections.unmodifiableSet
Collections.unmodifiableSortedSet
Collections.unmodifiableNavigableSet
Collections.unmodifiableList
Collections.unmodifiableMap
Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap
Collections.unmodifiableNavigableMap
从源码分析,该包装类覆盖了所有修改方法并抛出异常 UnsupportedOperationException,实现非常简单:
static class UnmodifiableCollection<E> implements Collection<E>, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1820017752578914078L;
final Collection<? extends E> c;
UnmodifiableCollection(Collection<? extends E> c) {
if (c==null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.c = c;
}
public boolean add(E e) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> coll) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> coll) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> coll) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void clear() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
......
}
可变/不可变
在 unmodifiable 的基础上,加之保证 Collection 实现类的底层数据为 final 的集合称为 *immutable* 不可变集合。反之则称为 *mutable* 可变集合。
Java 9 为 List、Set 和 Map 接口提供了新的静态工厂方法,可以创建这些集合的不可变实例,如下:
List<String> list = List.of("apple", "orange", "banana");
Set<String> set = Set.of("aggie", "alley", "steely");
Map<String, String> map = Map.of("A", "Apple", "B", "Boy", "C", "Cat");
而 Java 9 之前,要实现不可变集合只能通过第三方库,例如用 Guava 实现相同效果:
List<String> list = ImmutableList.of("apple", "orange", "banana");
Set<String> set = ImmutableSet.of("aggie", "alley", "steely");
Map<String, String> map = ImmutableMap.of("A", "Apple", "B", "Boy", "C", "Cat");
Guava 提供的不可变集合 API 如下:
ImmutableAsList
ImmutableBiMap
ImmutableClassToInstanceMap
ImmutableCollection
ImmutableEntry
ImmutableEnumMap
ImmutableEnumSet
ImmutableList
ImmutableListMultimap
ImmutableMap
ImmutableMapEntry
ImmutableMapEntrySet
ImmutableMapKeySet
ImmutableMapValues
ImmutableMultimap
ImmutableMultiset
ImmutableRangeMap
ImmutableRangeSet
ImmutableSet
ImmutableSetMultimap
ImmutableSortedAsList
ImmutableSortedMap
ImmutableSortedMapFauxverideShim
ImmutableSortedMultiset
ImmutableSortedMultisetFauxverideShim
ImmutableSortedSet
ImmutableSortedSetFauxverideShim
ImmutableTable
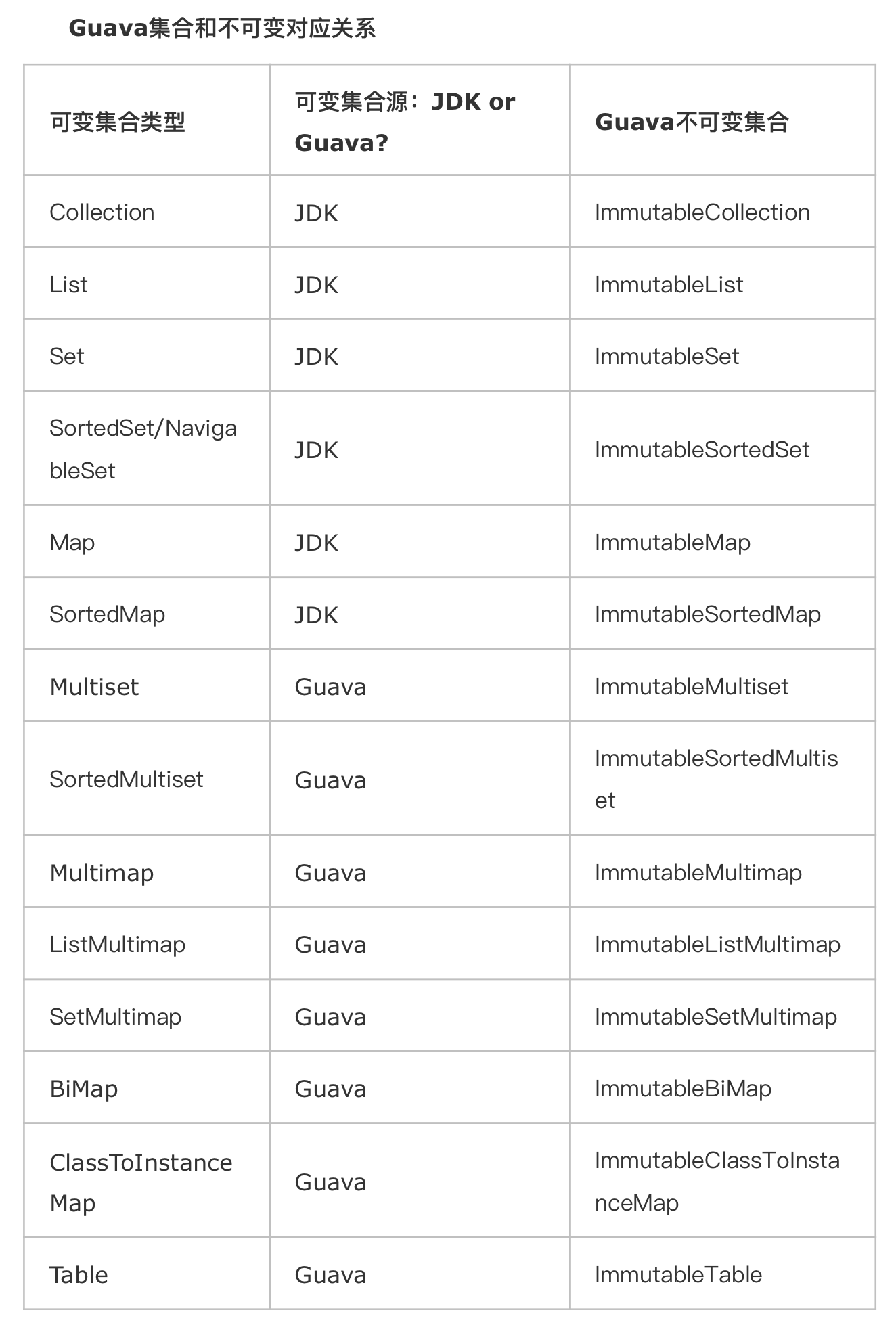
使用如下:
List<String> list = ImmutableList.of("apple", "orange", "banana");
Set<String> set = ImmutableSet.of("aggie", "alley", "steely");
Map<String, String> map = ImmutableMap.of("A", "Apple", "B", "Boy", "C", "Cat");
log.info("list={}, set={}, map={}", fruits, marbles, map); // list=[apple, orange, banana], set=[aggie, alley, steely], map={A=Apple, B=Boy, C=Cat}
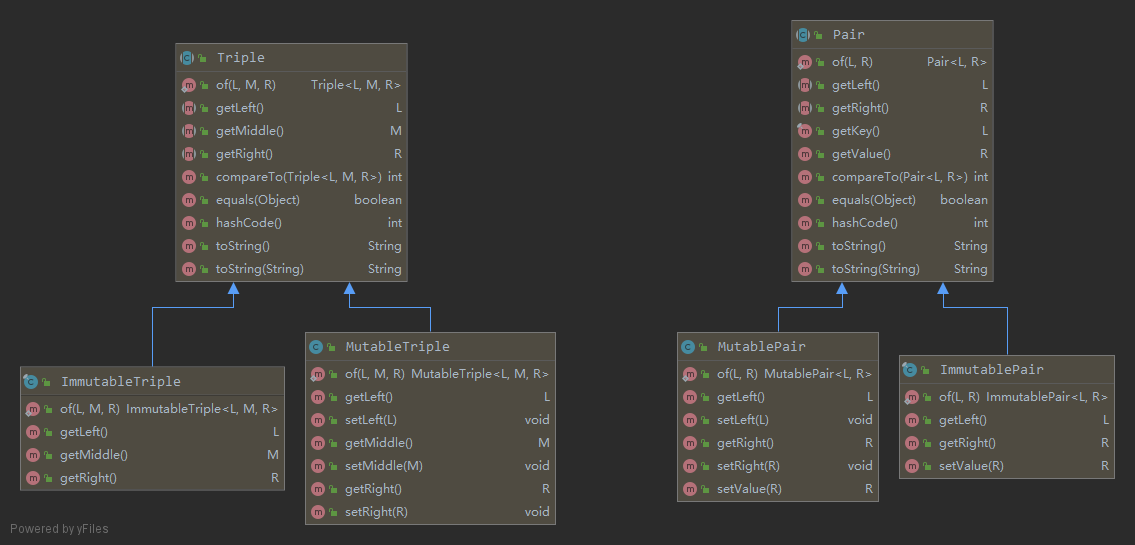
除此之外,Apache Commons Lang 也提供了两个好用的类 Pair 和 Triple,可用于存放指定个数的临时数据:
Triple.of("left", "middle", "right")
Pair.of("left", "right")
随机/顺序访问
支持根据下标索引快速(时间复杂度 0(1))访问元素的列表称为 *random access* 随机访问列表。反之则称为 *sequential access* 顺序访问列表。
标记接口 java.util.RandomAccess 用于标记列表类支持随机访问,其实现类如下:
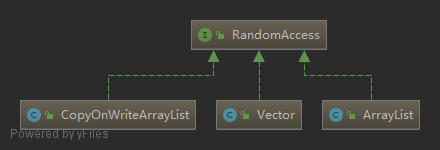
该标记接口使得 Collections 工具类中的通用算法实现能够据此更改其行为以提升性能:
binarySearchreverseshufflefillcopyrotatereplaceAllindexOfSubListlastIndexOfSubListcheckedList
以 binarySearch 为例,源码判断如下:
public static <T> int binarySearch(List<? extends Comparable<? super T>> list, T key) {
if (list instanceof RandomAccess || list.size()<BINARYSEARCH_THRESHOLD)
return Collections.indexedBinarySearch(list, key);
else
return Collections.iteratorBinarySearch(list, key);
}
元素限制
某些集合实现限制了可以存储哪些元素。可能的限制包括:
- 元素不能为
null。 - 元素必须属于特定类型。
- 元素必须匹配某些断言。
尝试添加违反集合实现限制的元素将导致运行时异常,如 ClassCastException、IllegalArgumentException 或 NullPointerException。
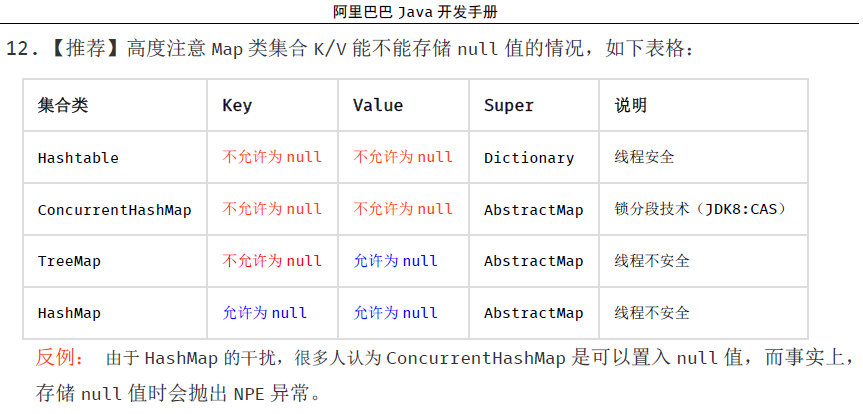
能否为 null
参考手册:
类型限制
泛型机制虽然为集合提供了编译期类型检查,但仍然可以在运行期绕过此机制(通过反射也能绕过编译期类型检查):
public void test4() {
List<Integer> intList = Lists.newArrayList(1, 2, 3);
add(intList);
// 循环到第四个元素时,报错:java.lang.ClassCastException: java.lang.String cannot be cast to java.lang.Integer
for (int item : intList) {
log.info("result is {}", item);
}
}
private void add(List list) {
list.add("4");
}
集合框架提供了一组包装器实现:
Collections.checkedCollection
Collections.checkedQueue
Collections.checkedSet
Collections.checkedSortedSet
Collections.checkedNavigableSet
Collections.checkedList
Collections.checkedMap
Collections.checkedSortedMap
Collections.checkedNavigableMap
这些包装器实现用于返回指定集合的动态类型安全视图(dynamically type-safe view),核心源码如下:
static class CheckedCollection<E> implements Collection<E>, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1578914078182001775L;
final Collection<E> c;
final Class<E> type;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E typeCheck(Object o) {
if (o != null && !type.isInstance(o))
throw new ClassCastException(badElementMsg(o));
return (E) o;
}
private String badElementMsg(Object o) {
return "Attempt to insert " + o.getClass() +
" element into collection with element type " + type;
}
CheckedCollection(Collection<E> c, Class<E> type) {
this.c = Objects.requireNonNull(c, "c");
this.type = Objects.requireNonNull(type, "type");
}
public boolean add(E e) {
return c.add(typeCheck(e));
}
......
}
以 add 方法为例,每次添加元素时,都会调用 typeCheck 私有方法进行类型检查,如果尝试添加错误类型的元素,则会抛出 ClassCastException,通过 fail fast 防止后续出错:
public void test() {
List<Integer> intList = Collections.checkedList(Lists.newArrayList(1, 2, 3), Integer.class);
add(intList);
for (int item : intList) {
log.info("result is {}", item);
}
}
private void add(List list) {
// java.lang.ClassCastException: Attempt to insert class java.lang.String element into collection with element type class java.lang.Integer
list.add("4");
}
数组转 List 方法
方法一:转两次
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c")) // from varargs
方法二:Java 8
// 包装类型
Integer [] myArray = { 1, 2, 3 };
List<Integer> myList = Arrays.stream(myArray).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 基本类型也可以实现转换(依赖 boxed 的装箱操作)
int [] myArray2 = { 1, 2, 3 };
List<Integer> myList2 = Arrays.stream(myArray2).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList());
方法三:Guava
// 不可变集合
List<String> il = ImmutableList.of("string", "elements"); // from varargs
List<String> i2 = ImmutableList.copyOf(new String[]{"string", "elements"}); // from array
// 可变集合
List<String> l0 = Lists.newLinkedList(Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c")); // from collection
List<String> l1 = Lists.newArrayList(Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c")); // from collection
List<String> l2 = Lists.newArrayList(new String[]{"string", "elements"}); // from array
List<String> l3 = Lists.newArrayList("or", "string", "elements"); // from varargs
并发编程时,集合操作必须小心谨慎。Java SE 提供了两种并发编程方法:
- 方案一:为集合通用实现添加线程同步功能。
Collections工具类提供了称为同步包装器(synchronization wrappers)的静态工厂方法可用于向许多非线程同步的集合添加同步行为。 - 方案二:使用并发集合。Java SE 提供了各种并发友好的集合接口和实现类。这些接口和类性能优于同步包装器(synchronization wrappers),提供了并发编程中经常需要的各种功能。
同步包装器
Collections 工具类提供如下静态工厂方法:
synchronizedCollection
synchronizedSet
synchronizedSortedSet
synchronizedNavigableSet
synchronizedList
synchronizedMap
synchronizedSortedMap
synchronizedNavigableMap
以 synchronizedCollection 静态方法为例,源码实现如下:
/**
* Returns a synchronized (thread-safe) collection backed by the specified
* collection. In order to guarantee serial access, it is critical that
* <strong>all</strong> access to the backing collection is accomplished
* through the returned collection.<p>
*
* It is imperative that the user manually synchronize on the returned
* collection when traversing it via {@link Iterator}, {@link Spliterator}
* or {@link Stream}:
* <pre>
* Collection c = Collections.synchronizedCollection(myCollection);
* ...
* synchronized (c) {
* Iterator i = c.iterator(); // Must be in the synchronized block
* while (i.hasNext())
* foo(i.next());
* }
* </pre>
* Failure to follow this advice may result in non-deterministic behavior.
*
* <p>The returned collection does <i>not</i> pass the {@code hashCode}
* and {@code equals} operations through to the backing collection, but
* relies on {@code Object}'s equals and hashCode methods. This is
* necessary to preserve the contracts of these operations in the case
* that the backing collection is a set or a list.<p>
*
* The returned collection will be serializable if the specified collection
* is serializable.
*
* @param <T> the class of the objects in the collection
* @param c the collection to be "wrapped" in a synchronized collection.
* @return a synchronized view of the specified collection.
*/
public static <T> Collection<T> synchronizedCollection(Collection<T> c) {
return new SynchronizedCollection<>(c);
}
实现就是一行代码,返回一个静态内部类 SynchronizedCollection:
static class SynchronizedCollection<E> implements Collection<E>, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3053995032091335093L;
final Collection<E> c; // Backing Collection
final Object mutex; // Object on which to synchronize
SynchronizedCollection(Collection<E> c) {
this.c = Objects.requireNonNull(c);
mutex = this;
}
SynchronizedCollection(Collection<E> c, Object mutex) {
this.c = Objects.requireNonNull(c);
this.mutex = Objects.requireNonNull(mutex);
}
public int size() {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.size();}
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.isEmpty();}
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.contains(o);}
}
public Object[] toArray() {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.toArray();}
}
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.toArray(a);}
}
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return c.iterator(); // Must be manually synched by user!
}
public boolean add(E e) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.add(e);}
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.remove(o);}
}
public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> coll) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.containsAll(coll);}
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> coll) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.addAll(coll);}
}
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> coll) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.removeAll(coll);}
}
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> coll) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.retainAll(coll);}
}
public void clear() {
synchronized (mutex) {c.clear();}
}
public String toString() {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.toString();}
}
// Override default methods in Collection
@Override
public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
synchronized (mutex) {c.forEach(consumer);}
}
@Override
public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.removeIf(filter);}
}
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return c.spliterator(); // Must be manually synched by user!
}
@Override
public Stream<E> stream() {
return c.stream(); // Must be manually synched by user!
}
@Override
public Stream<E> parallelStream() {
return c.parallelStream(); // Must be manually synched by user!
}
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException {
synchronized (mutex) {s.defaultWriteObject();}
}
}
从源码可见,其实就是返回一个包装类,内部实现使用了 synchronized 关键字加 mutex 对象作为互斥锁,对被包装集合的所有增删改查方法加锁,相当暴力。
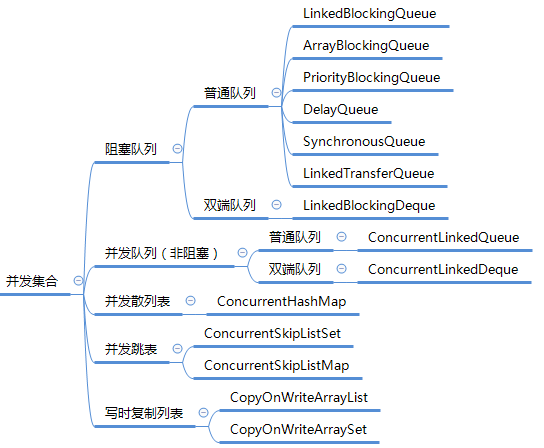
并发集合
并发集合作为 java.util.concurrent 包的一部分,提供的并发集合类如下:
队列
Queue 的常用方法差别如下:
| Throws exception | Returns special value | |
|---|---|---|
| Insert | add(e) | offer(e) |
| Remove | remove() | poll() |
| Examine | element() | peek() |
有两种并发队列实现,阻塞队列、并发队列(非阻塞式):
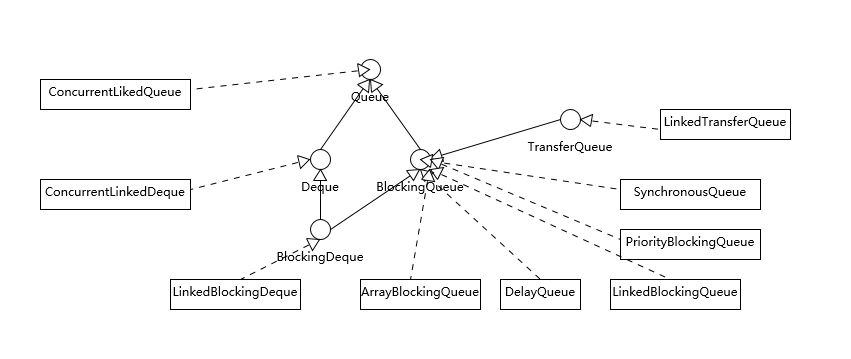
阻塞队列
BlockingQueue 扩展自 Queue 接口,主要新增了两组接口(下表后两列),其常用方法差别如下:
| Throws exception | Returns Special value | Times out | Blocks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insert | add(e) | offer(e) | offer(e, time, unit) | put(e) |
| Remove | remove() | poll() | poll(time, unit) | take() |
| Examine | element() | peek() | not applicable | not applicable |
ThreadPoolExecutor 目前使用了 BlockingQueue 的这些方法:
- 入队
offer(e) - 出队
poll(time, unit)或take()
阻塞队列 BlockingQueue 的实现如下:
- 有界队列(数组实现):
ArrayBlockingQueue,基于数组实现的有界阻塞队列。
- 无界队列(链表实现):
LinkedBlockingQueue,基于链表实现的可选无界阻塞队列。默认用于Executors.newFixedThreadPool(...)和newSingleThreadExecutor(...)。LinkedTransferQueuePriorityBlockingQueue,基于堆实现(底层是数组)的具有优先级的无界阻塞队列。DelayedQueue
- 无容量队列:
SynchronousQueue,无容量阻塞队列,每个插入操作都必须等待另一个线程的移除操作,反之亦然。默认用于Executors.newCachedThreadPool(...)。
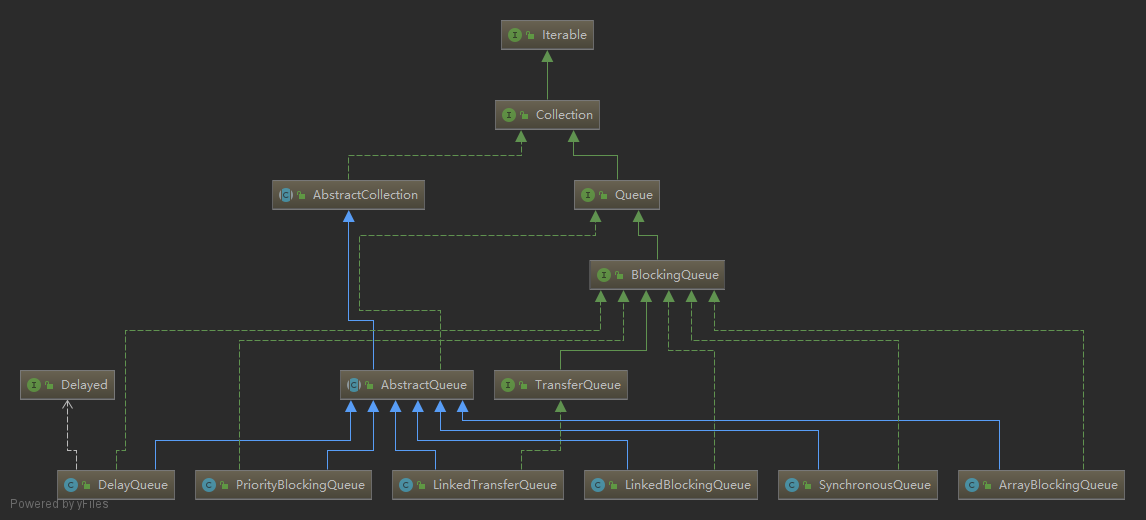
阻塞双端队列 BlockingDeque 的实现如下:
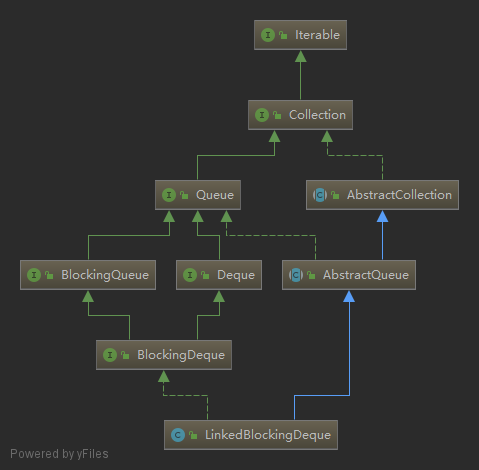
并发队列(非阻塞)
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedDeque
并发散列表
ConcurrentMap
ConcurrentHashMap
并发跳表
ConcurrentSkipListSet
ConcurrentNavigableMap
ConcurrentSkipListMap
Java 集合框架并不是一蹴而就写成的,也是经过了好多个版本迭代的演进与发展,才走到今天。本文总结下集合框架各版本的功能增强。
Java SE 9
List、Set 和 Map 接口中,新的静态工厂方法可以创建这些集合的不可变实例(immutable),如下:
List<String> list = List.of("apple", "orange", "banana");
Set<String> set = Set.of("aggie", "alley", "steely");
Map<String, String> map = Map.of("A", "Apple", "B", "Boy", "C", "Cat");
参考:https://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2017-10/147683.htm
Java SE 8
- Lambda 表达式
- Stream API,参考《Java 8 中处理集合的优雅姿势——Stream》
- 聚合操作,例如
forEach - 作为 JEP 180 提案的成果,
HashMap、LinkedHashMap、ConcurrentHashMap的性能得到提升。当出现大量散列冲突时,值将存储在红黑树而不是链表,以提升查找性能。
Java SE 7
- 新增一个集合接口:
TransferQueue,以及实现类LinkedTransferQueue。 - 为
Map及其派生实现类引入了一个性能改进的替代版散列函数(但在 Java SE 8 已被移除并取代)。
Java SE 6
新增几个集合接口:
DequeBlockingDequeNavigableSetNavigableMapConcurrentNavigableMap
新增几个集合实现类:
ArrayDequeConcurrentSkipListSetConcurrentSkipListMapLinkedBlockingDequeAbstractMap.SimpleEntryAbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry
现有实现类增强:
LinkedList实现Deque接口TreeSet实现NavigableSet接口TreeMap实现NavigableMap接口
Collections 工具类新增两个适配器方法:
newSetFromMap(Map)根据Map的通用实现创建一个Set的通用实现asLifoQueue(Deque)以后进先出(Lifo)队列的形式返回Deque的视图。
Arrays 工具类新增两个方法:
copyOfcopyOfRange
Java SE 5
三个新增的语法糖显著增强了集合框架:
-
泛型:为集合框架添加编译时类型安全,并在读取元素时不再需要做类型转换。
-
自动装箱/拆箱:往集合插入元素时自动装箱(将原始数据类型转换为对应的包装类型),读取元素时自动拆箱。
-
增强
for循环:迭代集合时不再需要显式迭代器(Iterator)。// 数组迭代 String[] strArray = {"apple", "orange", "banana"}; for (String s : strArray) { System.out.println(s); } // List 迭代 List<String> strList = Arrays.asList("apple", "orange", "banana"); for (String s : strList) { System.out.println(s); }
通用实现与并发实现:
-
新增三个集合接口:
QueueBlockingQueueConcurrentMap
-
新增几个
Queue实现类:
PriorityQueueConcurrentLinkedQueueLinkedList实现Queue接口AbstractQueue抽象类实现
-
新增五个
BlockingQueue实现类,位于
java.util.concurrent包下:
LinkedBlockingQueueArrayBlockingQueuePriorityBlockingQueueDelayQueueSynchronousQueue
-
新增一个
ConcurrentMap实现类:
ConcurrentHashMap
特殊实现:
-
新增两个特殊用途的
List和
Set实现类,用于读远大于写以及迭代无法线程同步的情况:
CopyOnWriteArrayListCopyOnWriteArraySet
-
新增两个特殊用途的
Set和
Map实现类,用于枚举:
EnumSetEnumMap
包装器实现:
- 新增一位包装器实现家族的新成员
Collections.checkedInterface,主要用于通用集合。
Collections 工具类新增三个通用算法和一个 Comparator 转换器:
frequency(Collection<?> c, Object o)计算指定元素在指定集合中出现的次数。disjoint(Collection<?> c1, Collection<?> c2)求两个集合是否不相交。addAll(Collection<? super T> c, T... a)将指定数组中的所有元素添加到指定集合的便捷方法。Comparator<T> reverseOrder(Comparator<T> cmp)反向排序。
Arrays 工具类新增下列方法:
hashCode、toStringdeepEquals、deepHashCode、deepToString用于多维数组
Java SE 1.4
-
Collections工具类新增几个新方法,例如 :
replaceAll(List list, Object oldVal, Object newVal)查找替换。
-
新增标记接口
RandomAccess。 -
新增集合实现类
LinkedHashMap、LinkedHashSet。内部使用散列表 + 双向链表(按插入顺序排序)。
本文总结下集合元素迭代的常用 API。
迭代器模式
迭代器模式(Iterator)是一种行为型设计模式,让你能在不暴露集合底层表现形式(列表、栈和树等)的情况下遍历集合中所有的元素。
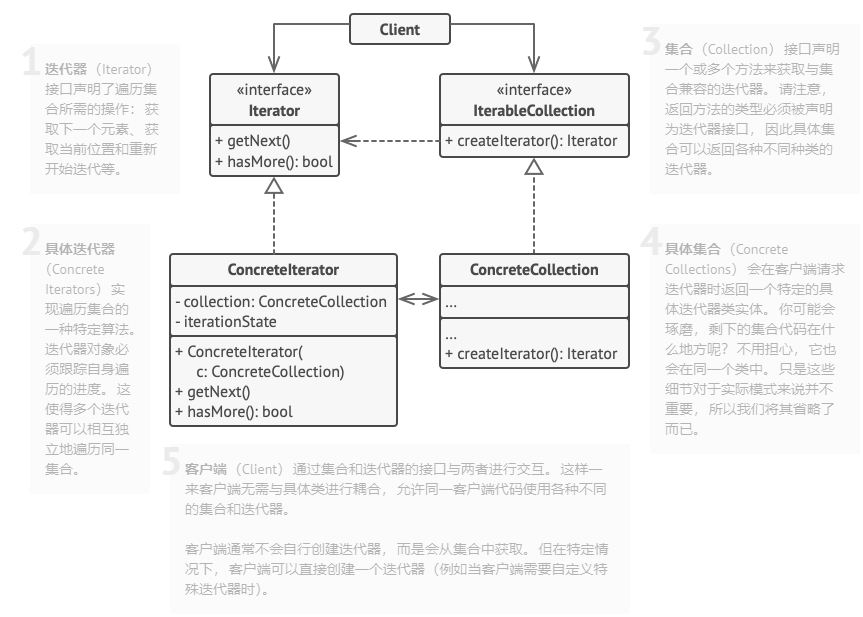
迭代器实现
在 Java 中,迭代器模式的实现有以下几种:
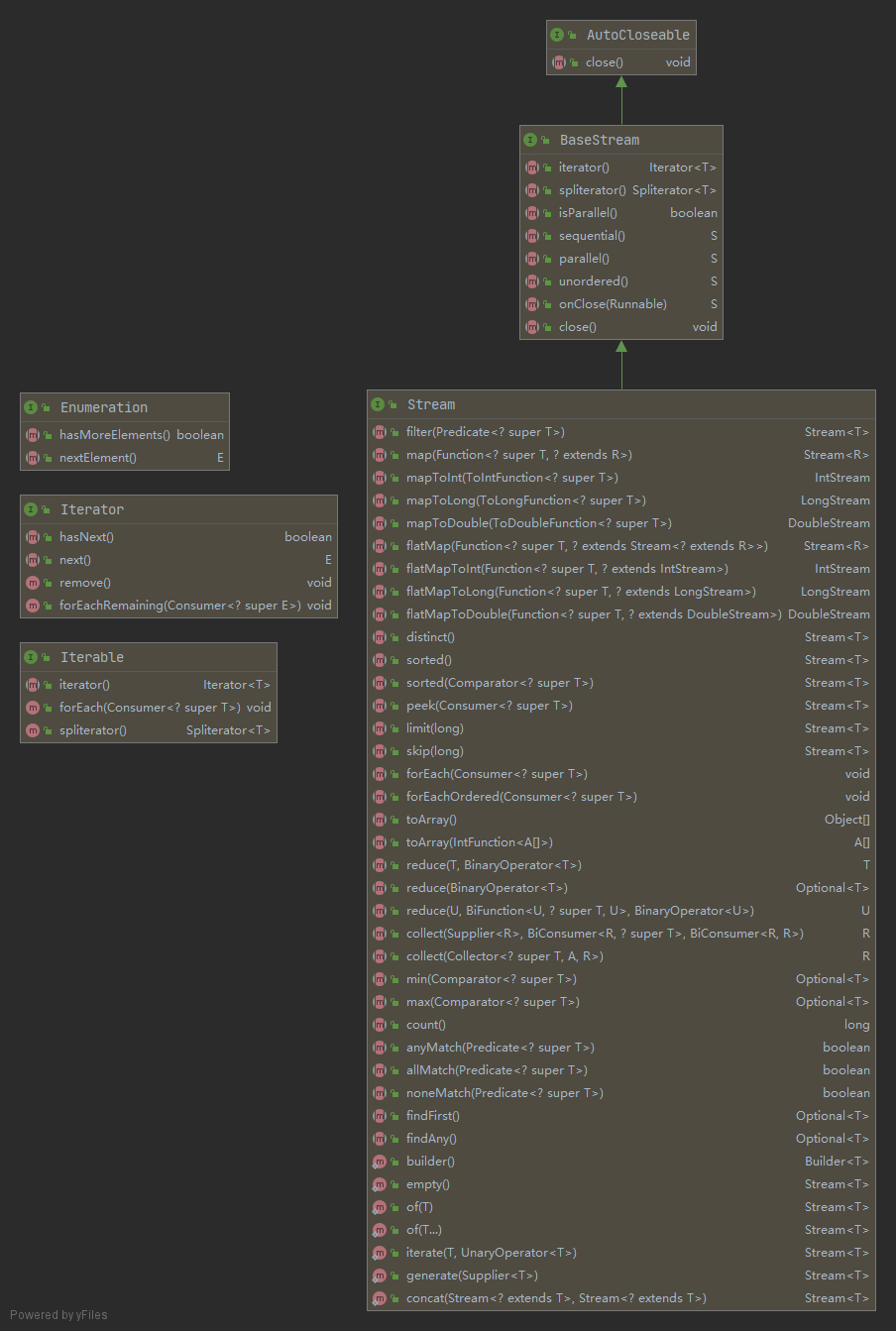
-
java.util.Enumeration:Java 1.0 引入,用于枚举集合元素。这种传统接口已被Iterator迭代器取代,虽然Enumeration还未被废弃,但在现代代码中已经被很少使用了。主要用于诸如java.util.Vector和java.util.Properties这些传统集合类。 -
java.util.Iterator<E>:Java 1.2 引入。作为
Java 集合框架
的成员,迭代器取代了枚举。迭代器与枚举有两个不同之处:
- 引入
remove方法,允许调用者在迭代期间从集合中删除元素。 - 方法名改进。
- 引入
-
java.lang.Iterable:Java 1.5 引入。For-each Loop 语法糖的底层实现,实现这个接口的对象可以用于 “For-each Loop”语句,简化迭代器繁琐的使用语法。
上述三种迭代器实现都属于命令式编程范式,即使访问值的方法仅由迭代器负责实现。但实际上,是由开发者来决定何时访问序列中的 next() 项。
与 Stream API 对比
java.util.stream.Stream:Java 8 引入,用于实现 Stream API。与迭代器的区别在于:
-
Iterator外部迭代,使用命令式编程范式,完全由用户来决定”做什么“和”怎么做“,例如:@Test public void iterator() { List<String> example = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C"); List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(example.size()); // 怎么做(通过 Iterator API 遍历 List) Iterator<String> iterator = example.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { // 做什么(把大写转成小写) result.add(iterator.next().toLowerCase()); } } @Test public void iterable() { List<String> example = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C"); List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(example.size()); // 怎么做(通过 For-each Loop 遍历 List) for (String s : example) { // 做什么(把大写转成小写) result.add(s.toLowerCase()); } }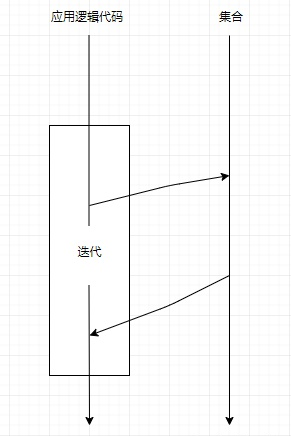
-
Stream内部迭代,使用声明式编程范式 > 函数式编程,用户仅需要决定“做什么”,而把“怎么做”的任务交给 JVM:@Test public void streamApi() { List<String> result = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C") // 这里遍历方式由 Stream API 实现,用户仅调用相应 API,数据量小可以用串行,数据量大可以用并行,怎么做、怎么实现用户并不用关心 .stream() // 做什么(把大写转成小写) .map(String::toLowerCase) // 这里转成线性表由 Stream API 实现,用户仅调用相应 API,也可以转成集合、散列表,怎么实现用户并不关心。 .collect(Collectors.toList()); }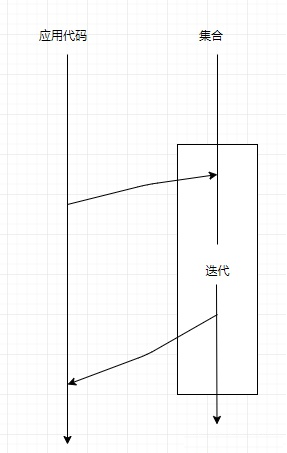
使用内部迭代的优势在于:
- 用户只需要关注问题本身,无需关注如何解决问题的细节。
- Java 可以利用短路、并行等对性能进行优化,用户无需关心。
与 Reactive Stream 对比
响应式编程范式通常在面向对象语言中作为观察者模式的扩展出现。可以将其与大家熟知的迭代器模式作对比,主要区别在于:
- 迭代器、Stream API 基于拉模式(PULL)
- 响应式流基于推模式(PUSH)
参考:响应式编程总结
集合元素排序的常用 API:
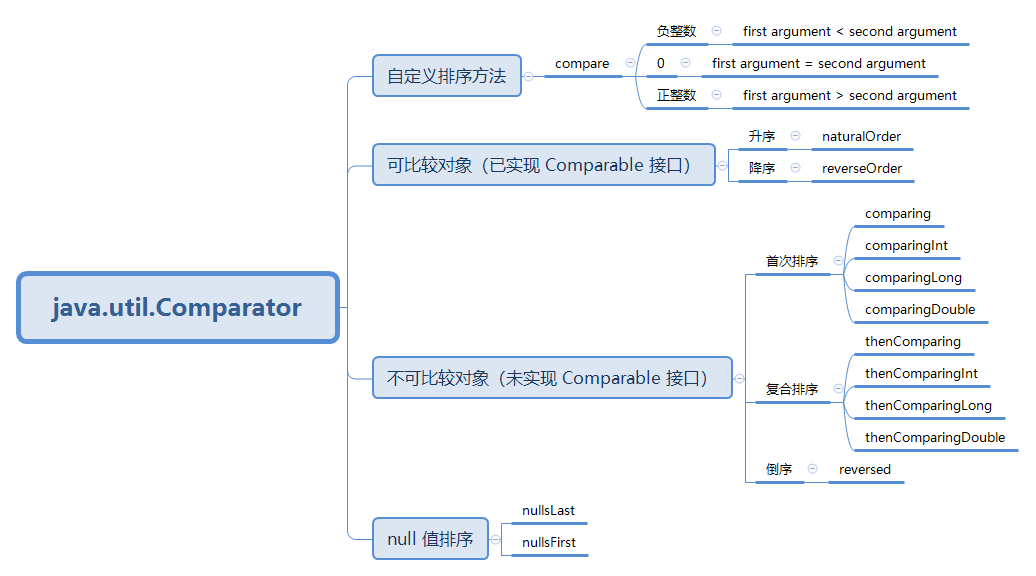
基于可比较对象排序
如果集合元素已实现 Comparable 接口,可以直接使用 naturalOrder、reverseOrder 方法进行排序:
List<Integer> integers = Arrays.asList(3, 1, 2, 4);
// 升序
// [1, 2, 3, 4]
integers.sort(Comparator.naturalOrder());
// 降序
// [4, 3, 2, 1]
integers.sort(Comparator.reverseOrder());
上述排序不支持 null 值(会抛 NPE 异常),如果自定义实现的话,代码比较冗余,容易出错:
List<Integer> integers = Arrays.asList(3, 1, null, 2, 4);
// [null, 1, 2, 3, 4]
integers.sort((o1, o2) -> {
// 写法1:
if (o1 != null && o2 != null) {
return o1.compareTo(o2);
} else {
return o1 == null ? -1 : 1;
}
// 写法2:
// return o1 == null ? -1 : (o2 == null ? 1 : o1.compareTo(o2));
});
// [4, 3, 2, 1, null]
integers.sort((o1, o2) -> {
// 写法1:
if (o1 != null && o2 != null) {
return o2.compareTo(o1);
} else {
return o1 == null ? 1 : -1;
}
// 写法2:
// return o1 == null ? 1 : (o2 == null ? -1 : o2.compareTo(o1));
});
可采用 nullsFirst、nullsLast 方法兼容 null 值情况:
List<Integer> integers = Arrays.asList(3, 1, null, 2, 4);
// null 值在前
// [null, 1, 2, 3, 4]
integers.sort(Comparator.nullsFirst(Comparator.naturalOrder()));
// null 值在后
// [4, 3, 2, 1, null]
integers.sort(Comparator.nullsLast(Comparator.reverseOrder()));
基于不可比较对象排序
例子:
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class IdName {
private Integer id;
private String name;
}
如果集合元素未实现 Comparable 接口,需要抽取关键字(关键字需实现 Comparable 接口)排序:
List<IdName> idNames = Arrays.asList(
new IdName(3, "Pete"),
new IdName(1, "Tom"),
new IdName(2, "Ben"),
new IdName(2, "Allen"));
// 根据 ID 升序
// [IdName(id=1, name=Tom), IdName(id=2, name=Ben), IdName(id=2, name=Allen), IdName(id=3, name=Pete)]
idNames.sort(Comparator.comparing(IdName::getId));
// 根据 ID、Name 复合排序(升序)
// [IdName(id=1, name=Tom), IdName(id=2, name=Allen), IdName(id=2, name=Ben), IdName(id=3, name=Pete)]
idNames.sort(Comparator.comparing(IdName::getId)
.thenComparing(IdName::getName));
// 根据 ID、Name 复合排序(降序)
// [IdName(id=3, name=Pete), IdName(id=2, name=Ben), IdName(id=2, name=Allen), IdName(id=1, name=Tom)]
idNames.sort(Comparator.comparing(IdName::getId)
.thenComparing(IdName::getName)
.reversed());
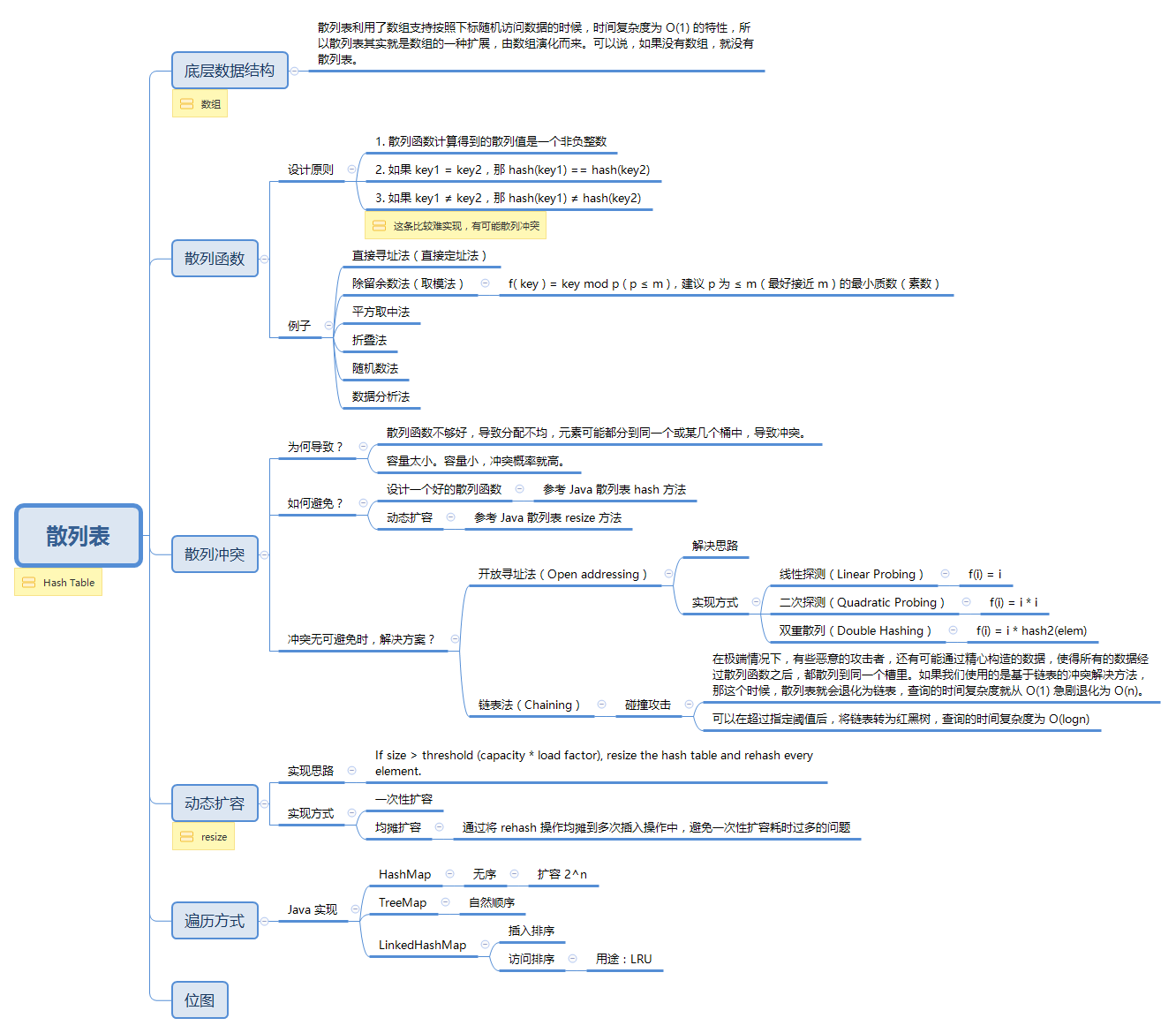
散列表是一种通过散列函数可以快速定位数据的数据结构。散列表利用了数组支持按照下标随机访问数据的时候,时间复杂度为 O(1) 的特性,所以散列表其实就是数组的一种扩展,由数组演化而来。可以说,如果没有数组,就没有散列表。
散列表的要点总结如下:
内部类
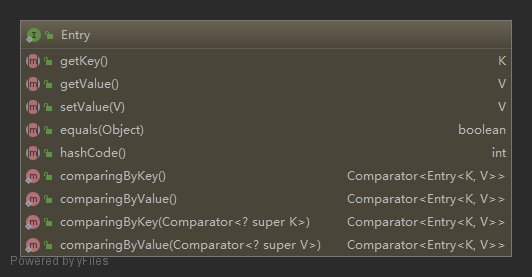
Entry 接口设计
java.util.Map 接口中的内部接口 Entry 如下,其中 getKey、getValue、setValue、equals、hashCode 五个方法待实现:
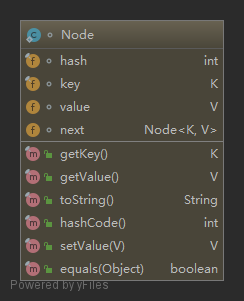
单链表节点实现
/**
* Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for
* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.)
*/
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) && Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
}
单链表节点的散列表结构如下,下图体现了单链表节点 key 和 next 属性:
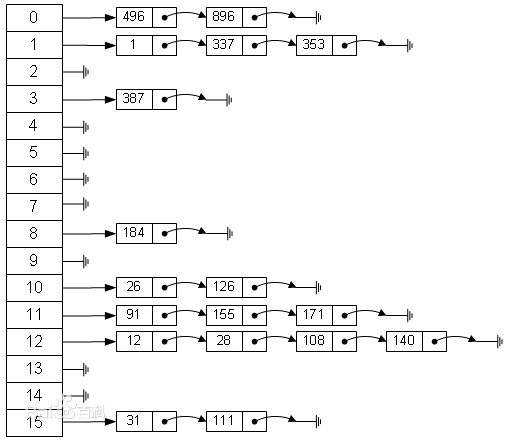
红黑树节点实现
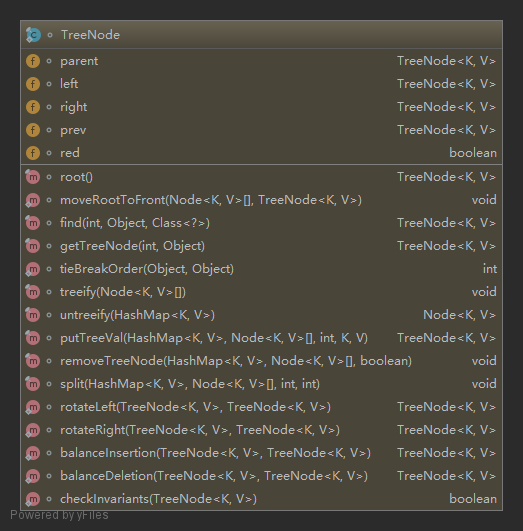
/**
* Entry for Tree bins. Extends LinkedHashMap.Entry (which in turn
* extends Node) so can be used as extension of either regular or
* linked node.
*/
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links
TreeNode<K,V> left;
TreeNode<K,V> right;
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
}
......
}
常量及字段
常量值
/**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
* 数组默认初始容量为 16,必须是 2 的 n 次幂
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
/**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
*
* 数组最大容量,,必须是 2 的 n 次幂,且小于等于 2^30
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
* 默认装载因子
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a
* bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a
* bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater
* than 2 and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in
* tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon
* shrinkage.
*
* 桶树化时的阈值
*/
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
/**
* The bin count threshold for untreeifying a (split) bin during a
* resize operation. Should be less than TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, and at
* most 6 to mesh with shrinkage detection under removal.
*
* 桶非树化时的阈值
*/
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
/**
* The smallest table capacity for which bins may be treeified.
* (Otherwise the table is resized if too many nodes in a bin.)
* Should be at least 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD to avoid conflicts
* between resizing and treeification thresholds.
*
* 树化时数组最小容量
*/
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
字段
/**
* The table, initialized on first use, and resized as
* necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two.
* (We also tolerate length zero in some operations to allow
* bootstrapping mechanics that are currently not needed.)
*
* 底层数组
*/
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
/**
* Holds cached entrySet(). Note that AbstractMap fields are used
* for keySet() and values().
*/
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
/**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
*
* 实际存储的键值对数量
*/
transient int size;
/**
* The number of times this HashMap has been structurally modified
* Structural modifications are those that change the number of mappings in
* the HashMap or otherwise modify its internal structure (e.g.,
* rehash). This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of
* the HashMap fail-fast. (See ConcurrentModificationException).
*
* 修改次数
*/
transient int modCount;
/**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
*
* resize 操作的阈值(capacity * load factor)
*/
int threshold;
/**
* The load factor for the hash table.
*
* 装载因子
*/
final float loadFactor;
关键的几个字段:
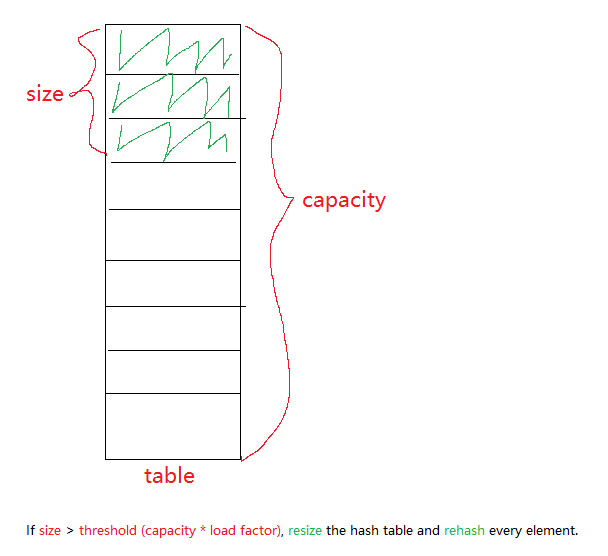
table散列表的底层数据结构为数组,其容量用capacity表示。此外,Java 通过链表法解决散列冲突的问题,因此数组类型为Node<K,V>[]节点数组。loadFactor散列表的装载因子。当散列表中空闲位置不多的时候,散列冲突的概率就会大大提高。为了尽可能保证散列表的操作效率,一般情况下,会尽可能保证散列表中有一定比例的空闲槽位。我们用装载因子来表示散列表满的程度,默认值是0.75f,也就是说默认情况下,当散列表中元素个数达到了容量的 3/4 时就会进行扩容。threshold散列表的扩容阈值,计算公式:threshold = capacity * load factor,即默认配置下的扩容阈值为:12=16*0.75。size散列表实际存储的键值对数量,如果size > threshold则对 hashtable进行双倍扩容(resize),并对原数组每个元素进行重新散列(rehash)。modCount修改次数。
构造方法
构造方法的参数主要用于指定数组的初始容量 initialCapacity、装载因子 loadFactor,并计算扩容阈值 threshold。
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial
* capacity and load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
// 参数校验及默认值设置
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor);
// 装载因子及扩容阈值赋值
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial
* capacity and the default load factor (0.75).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative.
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity
* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
/**
* Constructs a new <tt>HashMap</tt> with the same mappings as the
* specified <tt>Map</tt>. The <tt>HashMap</tt> is created with
* default load factor (0.75) and an initial capacity sufficient to
* hold the mappings in the specified <tt>Map</tt>.
*
* @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}
初始容量
在集合初始化时,建议指定 initialCapacity 初始容量:

如果不想手工计算初始容量 initialCapacity,可以使用 Guava 的静态工厂方法 Maps.newHashMapWithExpectedSize,源码如下:
/**
* Creates a {@code HashMap} instance, with a high enough "initial capacity"
* that it <i>should</i> hold {@code expectedSize} elements without growth.
* This behavior cannot be broadly guaranteed, but it is observed to be true
* for OpenJDK 1.7. It also can't be guaranteed that the method isn't
* inadvertently <i>oversizing</i> the returned map.
*
* @param expectedSize the number of entries you expect to add to the
* returned map
* @return a new, empty {@code HashMap} with enough capacity to hold {@code
* expectedSize} entries without resizing
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code expectedSize} is negative
*/
public static <K, V> HashMap<K, V> newHashMapWithExpectedSize(int expectedSize) {
return new HashMap<K, V>(capacity(expectedSize));
}
/**
* Returns a capacity that is sufficient to keep the map from being resized as
* long as it grows no larger than expectedSize and the load factor is >= its
* default (0.75).
*/
static int capacity(int expectedSize) {
if (expectedSize < 3) {
checkNonnegative(expectedSize, "expectedSize");
return expectedSize + 1;
}
if (expectedSize < Ints.MAX_POWER_OF_TWO) {
// This is the calculation used in JDK8 to resize when a putAll
// happens; it seems to be the most conservative calculation we
// can make. 0.75 is the default load factor.
return (int) ((float) expectedSize / 0.75F + 1.0F);
}
return Integer.MAX_VALUE; // any large value
}
不管是通过手工指定还是通过 Guava 的静态工厂方法,计算出来的初始容量都只是一个参考值。因为在随后 resize 会重新计算。
扩容阈值
第一个构造方法中调用了 tableSizeFor 方法,用于产生一个大于等于 initialCapacity 的最小的 2 的整数次幂。做法是通过右移操作让每一位都变为 1,最后 +1 变成 2 的 n 次幂:
/**
* Returns a power of two size for the given target capacity.
*/
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
关键私有方法
hash
在 HashMap 源码中,散列函数是分三步走的:
第一步,获取 hashcode。hashCode 需要遵循以下规则:

第二步,hash 值的计算,源码如下:
/**
* Computes key.hashCode() and spreads (XORs) higher bits of hash
* to lower. Because the table uses power-of-two masking, sets of
* hashes that vary only in bits above the current mask will
* always collide. (Among known examples are sets of Float keys
* holding consecutive whole numbers in small tables.) So we
* apply a transform that spreads the impact of higher bits
* downward. There is a tradeoff between speed, utility, and
* quality of bit-spreading. Because many common sets of hashes
* are already reasonably distributed (so don't benefit from
* spreading), and because we use trees to handle large sets of
* collisions in bins, we just XOR some shifted bits in the
* cheapest possible way to reduce systematic lossage, as well as
* to incorporate impact of the highest bits that would otherwise
* never be used in index calculations because of table bounds.
*/
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
该函数也叫扰动函数:先获取 32 位长度的 hashCode,再进行高 16 位与低 16 位异或,在低位加入高位特征,目的是减少碰撞冲突的概率。
第三步,在更新、插入或删除的时候,计算 Key 被映射到的桶的位置:
// capacity 表示 table.length
int index = hash(key) & (capacity - 1)
该按位与运算相当于通过**取模法(除留余数法)**计算存放的数组下标。
总结:
JDK HashMap 中 hash 函数的设计,确实很巧妙:
首先 hashcode 本身是个 32 位整型值,在系统中,这个值对于不同的对象必须保证唯一(JAVA 规范),这也是大家常说的,重写 equals 必须重写 hashcode 的重要原因。
获取对象的 hashcode 以后,先进行移位运算,然后再和自己做异或运算,即:hashcode ^ (hashcode >>> 16),这一步甚是巧妙,是将高 16 位移到低 16 位,这样计算出来的整型值将“具有”高位和低位的性质。
最后,用 hash 表当前的容量减去一,再和刚刚计算出来的整型值做位与运算。进行位与运算,很好理解,是为了计算出数组中的位置。但这里有个问题:
为什么要用容量减去一?
因为 A % B = A & (B - 1),注意这个公式只有当 B 为 2 的幂次方时才有效,所以 HashMap 中的数组容量要求必须是 2 的幂次方。
最后,(h ^ (h >>> 16)) & (capitity -1) = (h ^ (h >>> 16)) % capitity,可以看出这里本质上是使用了「除留余数法」
综上,可以看出,hashcode 的随机性,加上移位异或算法,得到一个非常随机的 hash 值,再通过「除留余数法」,得到 index。
整个散列函数的整体过程如下:
int hash(Object key) {
int h = key.hashCode();
h = h ^ (h >>> 16);
return h & (capitity - 1); //capicity 表示散列表的大小
}
resize
用于初始化或扩容散列表。
/**
* Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in
* accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold.
* Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the
* elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move
* with a power of two offset in the new table.
*
* @return the table
*/
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
...
}
putVal
putVal 的核心流程如下:
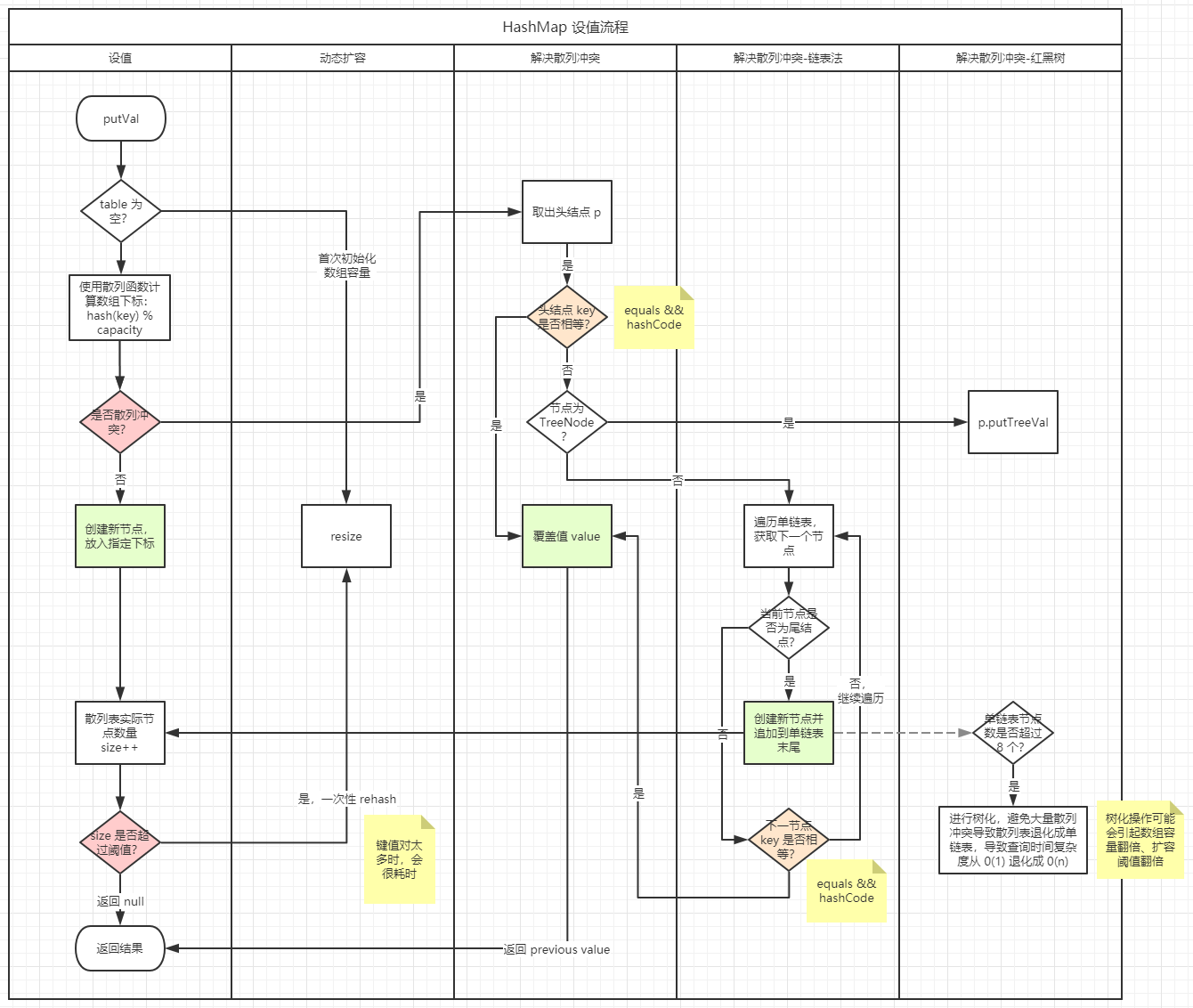
一些关键代码分析:
- 散列表只在首次设值时,才初始化;
- 散列函数:
(n - 1) & hash,通过取模法计算存放的数组下标。通过该散列函数将元素的键值(key)映射为数组下标,然后将数据存储在数组中对应的下标位置。当我们按照键值查询元素时,用同样的散列函数,将键值转化为数组下标,从对应的数组下标的位置取数据。因此散列函数在散列表中起着非常关键的作用。 - 为了避免散列值冲突,除了对比散列值是否相等之外,还需要对比
key是否相等; - 散列冲突解决方法:链表法。同时为了避免链表过长及散列表碰撞攻击,如果节点数超过 8 个,则进行树化
treeifyBin,避免大量散列冲突导致散列表退化成单链表,导致查询时间复杂度从 0(1) 退化成 0(n); - 如果实际映射数量超过阈值,则进行
resize扩容。
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
// tab 表示底层数组
// p 表示头结点
// n 表示数组长度
// i 表示数组下标
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// 节点数组为空,则首次初始化
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 计算数组下标,并获取指定下标元素,如果为空,表示无散列冲突,则创建节点并放入指定下标对应的桶
// 无散列冲突情况:
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 有散列冲突情况:
else {
// e 表示当前节点
Node<K,V> e; K k;
// 判断头结点是否为重复键,如果是则后续覆盖值
if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
// 如果是根节点是树节点类型,则进行相关操作
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
// 否则就是单链表节点
else {
// 遍历单链表
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
// 找到尾结点
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
// 创建新节点并追加到单链表末尾
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 如果节点数超过 8 个,则进行树化,避免大量散列冲突导致散列表退化成单链表,导致查询时间复杂度从 0(1) 退化成 0(n)
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
// 树化操作可能会引起数组容量翻倍、扩容阈值翻倍
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// 如果桶中的节点有重复键,则后续覆盖值
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 如果存在重复键,则覆盖值
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
// 实际数量加一。同时如果超过阈值,则进行扩容
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
树化前,会先判断数组容量是否达到阈值 MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64,如果是则将指定散列值对应数组下标的桶中所有链表节点都替换为红黑树节点,否则进行 resize 扩容操作:
/**
* Replaces all linked nodes in bin at index for given hash unless
* table is too small, in which case resizes instead.
*/
final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index; Node<K,V> e;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
resize();
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
do {
TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl;
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
hd.treeify(tab);
}
}
getNode
关键的 getNode 查找节点方法:
/**
* Implements Map.get and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
// 判断散列表是否为空,且散列值对应头节点是否为空
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
// 头节点散列值、键值匹配,则返回该节点
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
// 否则遍历下一个节点
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
// 树节点
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
// 顺序遍历单链表,查找匹配结果
do {
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
removeNode
关键的 removeNode 删除节点方法:
/**
* Implements Map.remove and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to match if matchValue, else ignored
* @param matchValue if true only remove if value is equal
* @param movable if false do not move other nodes while removing
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
do {
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value || (value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)
tab[index] = node.next;
else
p.next = node.next;
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
常用方法
设值
主要使用到了关键的 hash、putVal、resize 方法:
@Override
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
@Override
public V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, true, true);
}
/**
* Copies all of the mappings from the specified map to this map.
* These mappings will replace any mappings that this map had for
* any of the keys currently in the specified map.
*
* @param m mappings to be stored in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
@Override
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
putMapEntries(m, true);
}
/**
* Implements Map.putAll and Map constructor
*
* @param m the map
* @param evict false when initially constructing this map, else
* true (relayed to method afterNodeInsertion).
*/
final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict) {
int s = m.size();
if (s > 0) {
if (table == null) { // pre-size
float ft = ((float)s / loadFactor) + 1.0F;
int t = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
if (t > threshold)
threshold = tableSizeFor(t);
}
else if (s > threshold)
resize();
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) {
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, evict);
}
}
}
查找和替换
下面这组方法都使用到了关键的 getNode 方法查找指定节点:
@Override
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
@Override
public V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? defaultValue : e.value;
}
@Override
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getNode(hash(key), key) != null;
}
@Override
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; V v;
if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if ((v = e.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {
Node<K,V> e; V v;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) != null &&
((v = e.value) == oldValue || (v != null && v.equals(oldValue)))) {
e.value = newValue;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public V replace(K key, V value) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) != null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
return null;
}
删除节点
@Override
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
@Override
public boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {
return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null;
}
清空 map
@Override
public void clear() {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
modCount++;
// 内部数组不为空,则遍历并清空所有元素
if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) {
size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i)
tab[i] = null;
}
}
迭代
外部循环:
// key 迭代
for (String key : map.keySet()) {}
// value 迭代
for (String value : map.values()) {}
// entry 显式迭代器
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> entry = it.next();
}
// foreach 循环增强,不再需要显式迭代器,简化迭代集合操作
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {}
内部循环:
map.forEach((key, value) -> {});

Java 8 新增方法
Java 8 为 Map 接口引入了一组新的 default 默认方法,如下:
java.util.Map#forEach
java.util.Map#remove(java.lang.Object, java.lang.Object)
java.util.Map#replace
java.util.Map#replaceAll
java.util.Map#getOrDefault
java.util.Map#putIfAbsent
java.util.Map#computeIfAbsent
java.util.Map#computeIfPresent
java.util.Map#compute
java.util.Map#merge
我们重点看下其中几个,
putIfAbsent 和 computeIfAbsent:
Map<Integer, Integer> ipStats = new HashMap<>();
// previousValue is null
Integer previousValue = ipStats.putIfAbsent(100000000, 1);
// currentValue is 1
Integer currentValue = ipStats.computeIfAbsent(200000000, key -> {
// key = 200000000
log.info("key = {}", key);
return 1;
});
computeIfPresent :
// newValue is 2
Integer newValue = ipStats.computeIfPresent(200000000, (key, oldValue) -> {
// key = 200000000, oldValue = 1
log.info("key = {}, oldValue = {}", key, oldValue);
return oldValue += 1;
});
使用 compute 实现类似 Redis 散列表的原子递增命令 HINCRBY key field increment 的效果:
// newValue2 is 1
Integer newValue2 = ipStats.compute(300000000, (key, oldValue) -> {
if (oldValue == null) {
return 1;
} else {
return oldValue += 1;
}
});
最终结果:
// result is {300000000=1, 100000000=1, 200000000=2}
log.info("result is {}", ipStats.toString());
使用 Guava 快速创建 Map
创建不可变的 Map:
Map<String, String> map = ImmutableMap.of("A", "Apple", "B", "Boy", "C", "Cat");
创建指定 initialCapacity 初始容量的 Map:
Maps.newHashMapWithExpectedSize(10);
Guava 的 Maps 还提供了更多的 API,可以自行研究使用。








 本文详细介绍了Java集合框架,包括Collection和Map接口,以及它们的实现类、抽象类、通用实现、遗留实现、并发实现和特殊实现。讨论了适配器实现、包装器实现、便利实现、基础设施、算法和工具。还深入探讨了集合的迭代器模式、元素排序、内部类设计,如单链表节点和红黑树节点实现,以及关键的构造方法、resize方法、putVal方法、resize方法和removeNode方法。文章还对比了迭代器、Stream API和Reactive Stream,并展示了Java不同版本的集合框架变化。最后,提到了Java 8新增的Map方法和Guava库在创建Map方面的便利性。
本文详细介绍了Java集合框架,包括Collection和Map接口,以及它们的实现类、抽象类、通用实现、遗留实现、并发实现和特殊实现。讨论了适配器实现、包装器实现、便利实现、基础设施、算法和工具。还深入探讨了集合的迭代器模式、元素排序、内部类设计,如单链表节点和红黑树节点实现,以及关键的构造方法、resize方法、putVal方法、resize方法和removeNode方法。文章还对比了迭代器、Stream API和Reactive Stream,并展示了Java不同版本的集合框架变化。最后,提到了Java 8新增的Map方法和Guava库在创建Map方面的便利性。


















 22万+
22万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










