场景
数组在语法中用于访问连续的同类型对象,一般数组的声明和使用如下:
int a[10];
for(int i= 0; i< 10;i++)
a[i]=i;数组的使用需要预先分配空间,这种方式对于确定的数组没有任何问题,但换一种场景如下:
- 数组的跨度弹性很大
- 数组内同一时刻有效对象个数不固定
这种场景下一次为所有可能的对象分配所有空间不是一个很优的方案。那如何能兼顾空间和使用效率,这就需要用到xarray工具类了。
原理
一个很大的数组必然可以由一个个小数组拼接而成,若定义一个最小粒度的数组长度,比如长度4,那么从宏观上看一个大数组就由一个个长度为4的小数组排队而成
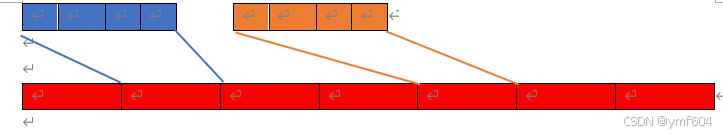 对于未使用到的小数组不申请空间,这样只需设计一种方法将这些非连续的小数组在一个数据结构中组织在一起即可,对于这个数组结构需要具有结构紧凑并且能够快速定位到对应的小数组段上,这时候树形结构上场了
对于未使用到的小数组不申请空间,这样只需设计一种方法将这些非连续的小数组在一个数据结构中组织在一起即可,对于这个数组结构需要具有结构紧凑并且能够快速定位到对应的小数组段上,这时候树形结构上场了
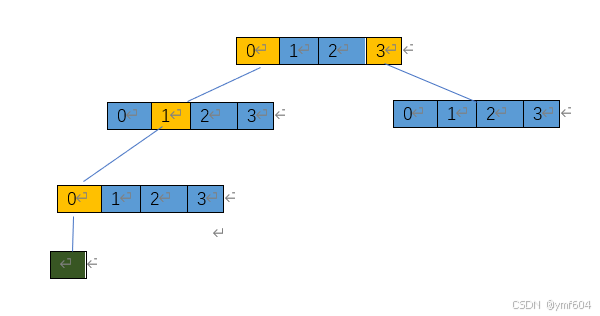
上图中只有三层,上两层为节点,每一个节点可以分出四个叉,黄色为该位置向下存在分叉,蓝色为不存在分叉。第三层节点直接与绿色的值绑定,若需要像数组一样通过下标访问绿色的值对象那么需要给每一个节点进行编码,这样通过根节点即可访问到具体的对象。当前每一个节点中有四个分叉,那么只需要两bit即可覆盖一个节点,对于绿色的值其位置编码即可定义如下:
00.01.00
综上所述,若需要描述一个这样的数据结构,需要以下信息:
- 一个节点结构
- 该节点结构在树形结构中第几层
- 该节点用于存放的是具体值还是指向下一层节点
数据结构
节点
/*
* @count is the count of every non-NULL element in the ->slots array
* whether that is a value entry, a retry entry, a user pointer,
* a sibling entry or a pointer to the next level of the tree.
* @nr_values is the count of every element in ->slots which is
* either a value entry or a sibling of a value entry.
*/
struct xa_node {
// 当前节点的偏移,可用于在下标的处理
unsigned char shift; /* Bits remaining in each slot */
//在父节点的数组(即slots数据)中的位置
unsigned char offset; /* Slot offset in parent */
unsigned char count; /* Total entry count */
unsigned char nr_values; /* Value entry count */
//父节点指针
struct xa_node __rcu *parent; /* NULL at top of tree */
//该节点属于哪个数组对象
struct xarray *array; /* The array we belong to */
union {
struct list_head private_list; /* For tree user */
struct rcu_head rcu_head; /* Used when freeing node */
};
//存放下层节点或者数值
void __rcu *slots[XA_CHUNK_SIZE];
//一些特殊属性数组
union {
unsigned long tags[XA_MAX_MARKS][XA_MARK_LONGS];
unsigned long marks[XA_MAX_MARKS][XA_MARK_LONGS];
};
};数组
/**
* struct xarray - The anchor of the XArray.
* @xa_lock: Lock that protects the contents of the XArray.
*
* To use the xarray, define it statically or embed it in your data structure.
* It is a very small data structure, so it does not usually make sense to
* allocate it separately and keep a pointer to it in your data structure.
*
* You may use the xa_lock to protect your own data structures as well.
*/
/*
* If all of the entries in the array are NULL, @xa_head is a NULL pointer.
* If the only non-NULL entry in the array is at index 0, @xa_head is that
* entry. If any other entry in the array is non-NULL, @xa_head points
* to an @xa_node.
*/
struct xarray {
//锁对象
spinlock_t xa_lock;
/* private: The rest of the data structure is not to be used directly. */
gfp_t xa_flags;
//指针指向根节点或者当数组中只有一个值时指向对应的值
void __rcu * xa_head;
};迭代器
/*
* The xa_state is opaque to its users. It contains various different pieces
* of state involved in the current operation on the XArray. It should be
* declared on the stack and passed between the various internal routines.
* The various elements in it should not be accessed directly, but only
* through the provided accessor functions. The below documentation is for
* the benefit of those working on the code, not for users of the XArray.
*
* @xa_node usually points to the xa_node containing the slot we're operating
* on (and @xa_offset is the offset in the slots array). If there is a
* single entry in the array at index 0, there are no allocated xa_nodes to
* point to, and so we store %NULL in @xa_node. @xa_node is set to
* the value %XAS_RESTART if the xa_state is not walked to the correct
* position in the tree of nodes for this operation. If an error occurs
* during an operation, it is set to an %XAS_ERROR value. If we run off the
* end of the allocated nodes, it is set to %XAS_BOUNDS.
*/
struct xa_state {
//数组对象
struct xarray *xa;
//搜索对象的索引
unsigned long xa_index;
unsigned char xa_shift;
unsigned char xa_sibs;
unsigned char xa_offset;
unsigned char xa_pad; /* Helps gcc generate better code */
//当前搜索到的节点对象
struct xa_node *xa_node;
//扩展数组时新分配节点的缓存
struct xa_node *xa_alloc;
xa_update_node_t xa_update;
struct list_lru *xa_lru;
};代码逻辑
辅助函数
/*
* The bottom two bits of the entry determine how the XArray interprets
* the contents:
*
* 00: Pointer entry
* 10: Internal entry
* x1: Value entry or tagged pointer
*
* Attempting to store internal entries in the XArray is a bug.
*
* Most internal entries are pointers to the next node in the tree.
* The following internal entries have a special meaning:
*
* 0-62: Sibling entries
* 256: Retry entry
* 257: Zero entry
*
* Errors are also represented as internal entries, but use the negative
* space (-4094 to -2). They're never stored in the slots array; only
* returned by the normal API.
*/
/**
* xa_mk_value() - Create an XArray entry from an integer.
* @v: Value to store in XArray.
*
* Context: Any context.
* Return: An entry suitable for storing in the XArray.
*/
static inline void *xa_mk_value(unsigned long v)
{
WARN_ON((long)v < 0);
return (void *)((v << 1) | 1);
}
/**
* xa_to_value() - Get value stored in an XArray entry.
* @entry: XArray entry.
*
* Context: Any context.
* Return: The value stored in the XArray entry.
*/
static inline unsigned long xa_to_value(const void *entry)
{
return (unsigned long)entry >> 1;
}
/*
*




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1843
1843

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








