Solr allows you to create multiple search indexes, each of which is represented by a Solr core. It is possible to partition your content across multiple Solr indexes (called sharding), as well as to create multiple copies of any partition of the data (called replication).
Choosing to shard
Sharding can be useful if you have too many documents to comfortably handle on a single server.
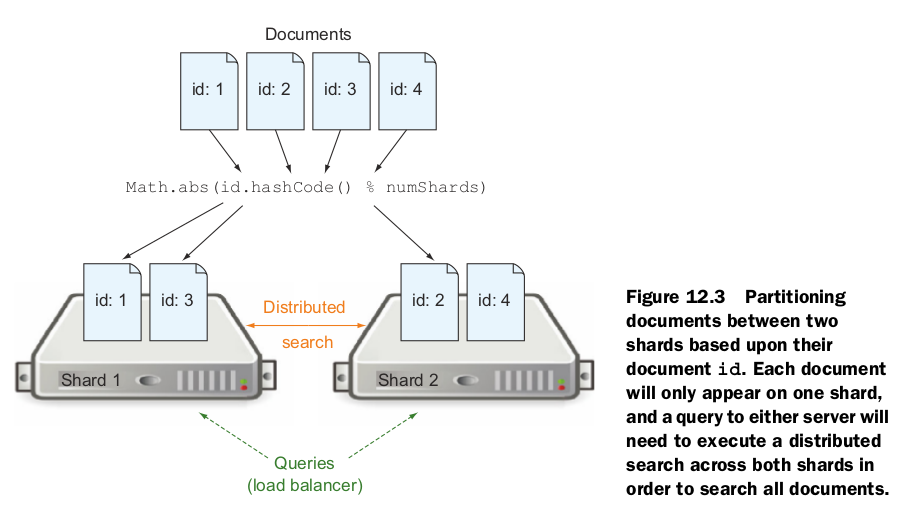
The number of shards has nothing to do with fault tolerance. It is strictly to help scale as the size of your collection of documents grows.In general, there are five primary factors you need to consider when decid-
ing on how many shards you need:
- Total number of documents
- Document size
- Required indexing throughput
- Query complexity
- Expected growth
Choosing to replicate
If your Solr cluster can handle 100 queries per second but your application needs to support 150 queries per second, you have a problem. Rather than breaking your index into additional partitions (adding shards), you would want to create multiple identical copies of your index and load balance traffic across each of the copies.

Master server’s solrconfig.xml
(http://masterserver:8983/solr/core1) <requestHandler name="/replication" class="solr.ReplicationHandler"> <lst name="master"> <str name="enable">true</str> <str name="replicateAfter">commit</str> <str name="replicateAfter">optimize</str> <str name="replicateAfter">startup</str> </lst> </requestHandler>
Slave server’s solrconfig.xml
(http://slaveserver:8983/solr/core1) <requestHandler name="/replication" class="solr.ReplicationHandler"> <lst name="slave"> <str name="enable">true</str> <str name="masterUrl"> http://masterserver:8983/solr/core1/replication </str> <str name="pollInterval">00:00:15</str> </lst> </requestHandler>
COMBINING SHARDING AND REPLICATION
At this point you know how to scale Solr to handle either more content (by sharding) or more query load (by replicating). If you are lucky enough to have both a large dataset and a large number of users trying to query your data, however, you may need to set up a cluster utilizing both sharding and replication. If you often have a large amount of indexing going, you may also want to separate your indexing operation and your query operation onto separate servers.
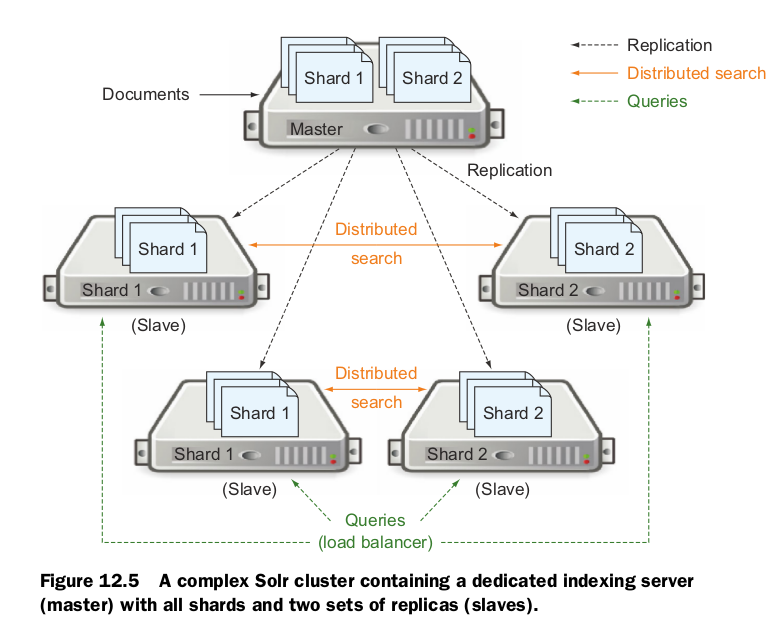
As you can tell from figure 12.5, setting up a Solr cluster to handle both sharding and replication can quickly become a maintenance nightmare. Querying load balancing between multiple manually defined Solr cores and ensuring replication is configured and enabled between each Solr core on the slave servers and the associated Solr core on the master server can become complex quickly. If you ever have a failure in one of your nodes, it can cause multiple nodes in the cluster to fail. If the single master server in figure 12.5 fails, for example, the entire cluster will stop receiving updates. Likewise, if one slave fails, any other slaves trying to run a distributed search dependent upon the failed slave will also fail their queries.
Thankfully, SolrCloud was created to take over management of these kinds of complexities for you.





 本文深入探讨了Solr中分片和复制技术的应用,包括如何选择分片数量以应对大量文档,以及如何通过创建复制副本以支持更高的查询负载。详细解释了设置sharding和replication的步骤,并强调了结合使用这两种技术以同时处理大量内容和高查询流量的重要性。同时,讨论了在构建包含分片和复制的Solr集群时面临的挑战,以及SolrCloud如何简化这些复杂性的管理。
本文深入探讨了Solr中分片和复制技术的应用,包括如何选择分片数量以应对大量文档,以及如何通过创建复制副本以支持更高的查询负载。详细解释了设置sharding和replication的步骤,并强调了结合使用这两种技术以同时处理大量内容和高查询流量的重要性。同时,讨论了在构建包含分片和复制的Solr集群时面临的挑战,以及SolrCloud如何简化这些复杂性的管理。
















 1226
1226

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








