class classmate:
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def eat(self):
print ('%s is eating.'%self.name)
def drink(self):
print ('%s is drinking'%self.name)
class female(classmate):
def drink(self):
print ('%s drink orange juice'%self.name)
class male(classmate):
def drink(self):
print ('%s drink alcohol'%self.name)
class pythoner(classmate):
def occupation(self):
print ('%s is a pythoner.'%self.name)
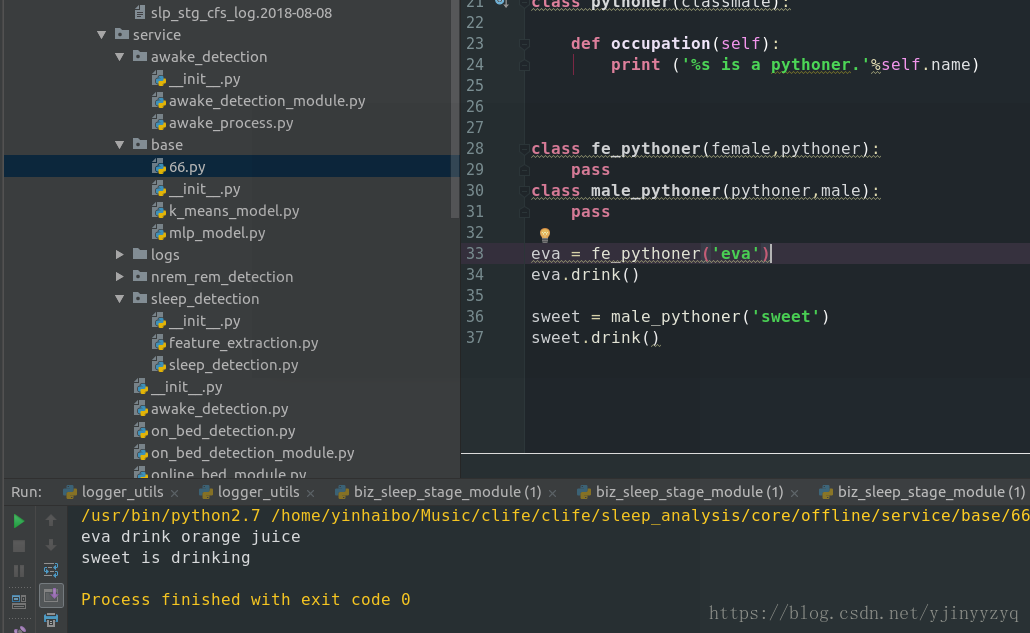
class fe_pythoner(pythoner,female):
pass
class male_pythoner(pythoner,male):
pass
eva = fe_pythoner('eva')
eva.drink()
sweet = male_pythoner('sweet')
sweet.drink()
对于这段代码若是python2输出为
eva is drinking
sweet is drinking
若是python3 输出为
eva drink orange juice
sweet drink alcohol
python2 中若要输出出相同的结果要将首行改为class classmate(object)或
将
class fe_pythoner(pythoner,female):
pass
class male_pythoner(pythoner,male):
pass
改成
class fe_pythoner(female,pythoner):
pass
class male_pythoner(male,pythoner):
pass
所以写成标准形式class classmate(object):是一个好习惯。
python2 默认深度优先





 本文通过一个简单的示例对比了Python2与Python3中多重继承的不同行为,并介绍了如何在Python2中实现与Python3相同的多重继承效果。
本文通过一个简单的示例对比了Python2与Python3中多重继承的不同行为,并介绍了如何在Python2中实现与Python3相同的多重继承效果。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








