Introduction
Microsoft.NET 4.0 and Visual Studio.NET 2010 ships a lot of new features in their underlying technologies. In this series of articles, I want to talk about the new features in the area of Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) in order to improve the development experience, enable more communication scenario, support new WS-* standards and provide a good integration with Windows Workflow Foundation (WF).
The new features are essentially the following: simplified configuration, standard endpoints, IIS hosting without a SVC file, support for WS-Discovery, routing service, REST improvements, enhancements for the integration with WF to support workflow services, simple byte stream encoding and ETW tracing.
In this series of article, I will illustrate each feature explaining the principles and showing some examples.
Simplified configuration
In WCF 3.x, when you specify a host for a Web service developed using WCF, you need to write or program the endpoints and behaviors. In WCF 4.0, you have new defaults for endpoints, binding and behaviors.
For our example, let's define a simple service which provides the echo functionality when it's invoked. The service contract is shown in the Listing 1.
using
System;
using
System.Collections.Generic;
using
System.Linq;
using
System.Runtime.Serialization;
using
System.ServiceModel;
using
System.Text;
namespace
WCF_NewFeatures
{
[ServiceContract ]
public interface IEchoService
{
[OperationContract ]
string Echo(String message);
}
}
Listing 1
The implementation for this service contract is shown in the Listing 2.
using
System;
using
System.Collections.Generic;
using
System.Linq;
using
System.Runtime.Serialization;
using
System.ServiceModel;
using
System.Text;
namespace
WCF_NewFeatures
{
public class EchoService : IEchoService
{
public string Echo(String message)
{
return "Called the Echo Service with message " + message;
}
}
}
Listing 2
Now let's create a ServiceHost instance for this service and bind it to a URI. When the application calls to the Open method of the ServiceHost instance, it builds the internal service description from the application configuration file along with anything the host application may have configured explicitly (see Listing 3).
using
System;
using
System.Collections.Generic;
using
System.Linq;
using
System.Text;
using
System.ServiceModel;
using
System.ServiceModel.Description;
namespace
WCF_NewFeatures
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string [] args)
{
ServiceHost serviceHost = new ServiceHost (typeof (WCF_NewFeatures.EchoService ),new Uri ("http://localhost:8080/Services/EchoService" ));
serviceHost.Open();
System.Console .WriteLine("The EchoService has started" );
foreach (ServiceEndpoint se in serviceHost.Description.Endpoints)
{
System.Console .WriteLine("Address:{0}, Binding:{1}, Contract:{2}" , se.Address, se.Binding.Name, se.Contract.Name);
}
System.Console .WriteLine("Please, press any key to finish ..." );
System.Console .ReadLine();
serviceHost.Close();
}
}
}
Listing 3
When you run this program, you will see that the IEchoService service contract can be accessed from the http://localhost:8080/Services/EchoService using BasicHttpBinding (see Figure 1). Notice that WCF uses the BasicHttpBinding as the default binding.
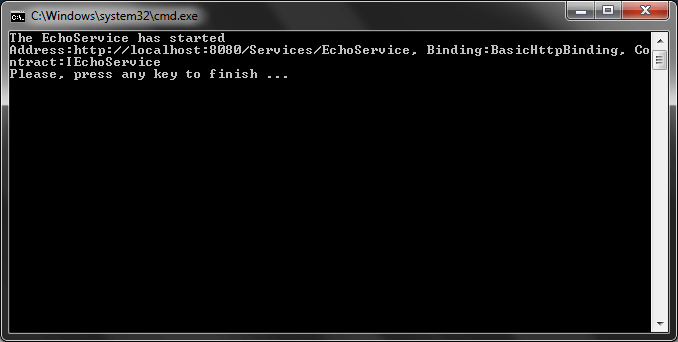
Figure 1
If you configure at least one endpoint, you will no longer see any default endpoint. Let's illustrate this by calling the AddServiceEndpoint method in the ServiceHost instance (see Listing 4).
using
System;
using
System.Collections.Generic;
using
System.Linq;
using
System.Text;
using
System.ServiceModel;
using
System.ServiceModel.Description;
namespace
WCF_NewFeatures
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string [] args)
{
ServiceHost serviceHost = new ServiceHost (typeof (WCF_NewFeatures.EchoService ),new Uri ("http://localhost:8080/Services/EchoService" ));
serviceHost.AddServiceEndpoint(typeof (IEchoService ),new WSHttpBinding (),"newEndPoint" );
serviceHost.Open();
System.Console .WriteLine("The EchoService has started" );
foreach (ServiceEndpoint se in serviceHost.Description.Endpoints)
{
System.Console .WriteLine("Address:{0}, Binding:{1}, Contract:{2}" , se.Address, se.Binding.Name, se.Contract.Name);
}
System.Console .WriteLine("Please, press any key to finish ..." );
System.Console .ReadLine();
serviceHost.Close();
}
}
}
Listing 4
If you run the application, you will receive the output in the Figure 2.
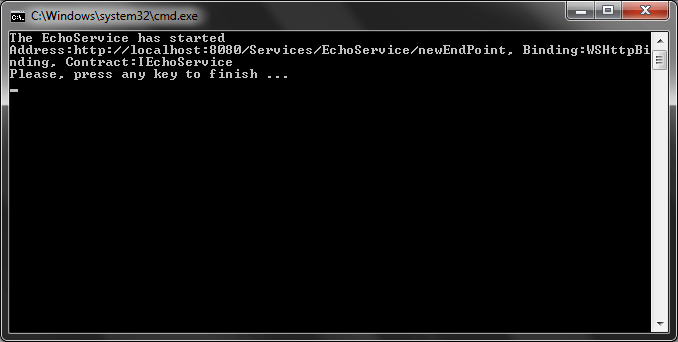
Figure 2
However you can also add the default endpoint along with your own (see Figure 2).
using
System;
using
System.Collections.Generic;
using
System.Linq;
using
System.Text;
using
System.ServiceModel;
using
System.ServiceModel.Description;
namespace
WCF_NewFeatures
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string [] args)
{
ServiceHost serviceHost = new ServiceHost (typeof (WCF_NewFeatures.EchoService ),new Uri ("http://localhost:8080/Services/EchoService" ));
serviceHost.AddServiceEndpoint(typeof (IEchoService ),new WSHttpBinding (),"newEndPoint" );
serviceHost.AddDefaultEndpoints();
serviceHost.Open();
System.Console .WriteLine("The EchoService has started" );
foreach (ServiceEndpoint se in serviceHost.Description.Endpoints)
{
System.Console .WriteLine("Address:{0}, Binding:{1}, Contract:{2}" , se.Address, se.Binding.Name, se.Contract.Name);
}
System.Console .WriteLine("Please, press any key to finish ..." );
System.Console .ReadLine();
serviceHost.Close();
}
}
}
Listing 5
And the result is shown in the Figure 3.
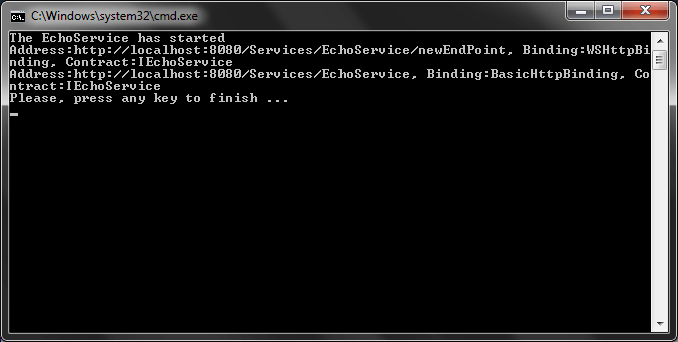
Figure 3
For bindings the default is BasicHttpBinding. With WCF 4.0, you can define default behavior configurations by omitting the name of the configuration definition in the application configuration file (see Listing 6).
<?
xml
version
=
"1.0 " encoding = "utf-8 " ?>
<
configuration
>
<
system.serviceModel
>
<
behaviors
>
<
serviceBehaviors
>
<
behavior
name
=
"">
<
serviceMetadata
httpGetEnabled
=
"true " />
</
behavior
>
</
serviceBehaviors
>
</
behaviors
>
</
system.serviceModel
>
</
configuration
>
Listing 6
In this case, we have turned on the service metadata, so you can retrieve the service definition from the WSDL document (see Figure 4).
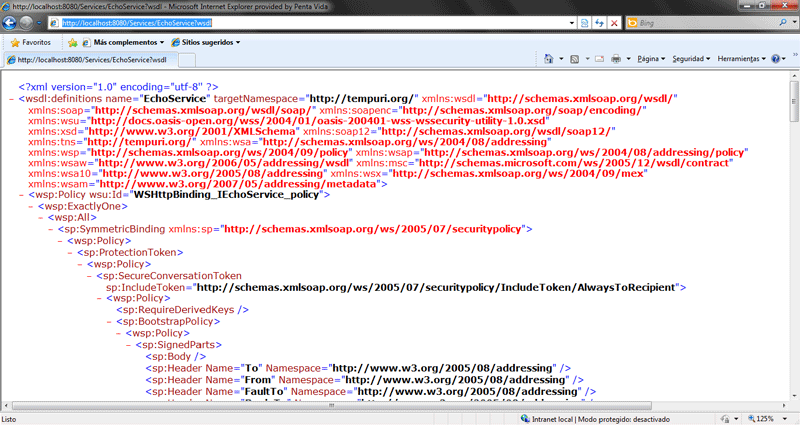
Figure 4
Standard Endpoint
Standard Endpoints are pre-configured endpoint definitions built into the WCF 4.0 framework without the need to define them. These endpoints are defined using the <Kind> attribute. The standard endpoints are: mexEndpoint, dynamicEndpoint, discoveryEndpoint, udpEndpoint, announcementEndpoint, udpAnnouncementEndpoint, workflowControlEndpoint, webHttpEndpoint, webScriptEndpoint.
The mexEndpoint endpoint defines an endpoint for MEX configured with IMetadataExchange for the service contract.
The dynamicEndpoint configures an endpoint with WS-Discovery support within the a WCF client application.
The discoveryEndpoint configures the discovery operations within a client application.
The udpDiscoveryEndpoint defines an endpoint for discovery operations within a client application using UDP binding at a multicast address.
The announcementEndpoint defines an endpoint for announcement features of discovery.
The udpAnnouncementEndpoint defines an endpoint for announcement features of discovery using the UDP protocol.
The workflowControlEndpoint defines an endpoint for controlling the execution of workflow instances.
The webHttpEndpoint defines an endpoint using WebHttpBinding and WebHttpBehavior to expose REST services.
The webScriptEndpoint defines an endpoint using WebHttpBinding and WebHttpBehavior to expose Ajax services.
IIS hosting without a SVC file
In WCF 4.0, you can define virtual service activation endpoints in the Web.config file order to activate a WCF service without the need of .svc file (see Listing 7).
<
configuration
>
<
system.serviceModel
>
<
serviceHostingEnvironment
>
<
serviceActivations
>
<
add
relativeAddress
=
"EchoService.svc " service = "EchoService "/>
</
serviceActivations
>
</
serviceHostingEnvironment
>
</
system.serviceModel
>
</
configuration
>
Listing 7
With this configuration, you can activate the EchoService using the relative address EchoService.svc. If you create a Web application in your IIS named EchoApp and copy the EchoService service definitions and set up the service configuration as shown in the Listing 7, you can browse to the service following the URI
http://localhost/EchoApp/EchoService.svc without having a physical EchoService.svc file with the service activation definition.
Conclusion
In this series of article, I've explained the new features of WCF 4.0 through concepts and examples.
Further Readings
New Features of WCF 4.0: Part II
New Features of WCF 4.0: Part III
New Features of WCF 4.0: Part IV
New Features of WCF 4.0: Part V
Further Readings
New Features of WCF 4.0: Part II
New Features of WCF 4.0: Part III
New Features of WCF 4.0: Part IV
New Features of WCF 4.0: Part V





 本文介绍了 Microsoft .NET 4.0 和 Visual Studio 2010 中 Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) 的新特性,包括简化配置、标准端点、IIS 托管、WS-Discovery 支持等,旨在改善开发体验并支持更多通信场景。
本文介绍了 Microsoft .NET 4.0 和 Visual Studio 2010 中 Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) 的新特性,包括简化配置、标准端点、IIS 托管、WS-Discovery 支持等,旨在改善开发体验并支持更多通信场景。
















 129
129

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








