crtmpserver是一个基于RTMP协议的流媒体服务器。下面比较详细的分析了它的处理过程:
1. SRAND();
它其实是一个宏定义,srand((uint32_t)time(NULL));
srand()就是给rand()提供种子seed的,如果srand每次输入的数值是一样的,那么每次运行产生的随机数也是一样的,srand(n),rand()也就是说,以一个固定的数值作为种子是一个缺点。
通常的做法是 以这样一句代码srand((unsigned) time(NULL));来取代,这样将使得种子为一个不固定的数, 这样产生的随机数就不会每次执行都一样了。
2. InitNetworking();
主要用于初始化Windows下socket资源,调用WSAStartup()接口。
3. Variant::DeserializeFromCmdLineArgs(argc, argv, gRs.commandLine)
把程序运行时所携带的命令行参数都放入变量 gRs.commandLine["arguments"]中。把命令行参数中没有带“=”号的参数都赋值为true类型值,把带“=”都按照result["arguments"][key] = value; key-value的形式存储,其中key和value都按string保存的。
4. NormalizeCommandLine(configFile);
主要是用于修正存储在gRs.commandLine["arguments"]中的命令行参数,因为第3步骤所有都是按照key类型为string,value类型也为string的模式。而实际有部分是数字格式的,所以数据类型需要转换。
5. Initialize()
用于初始化运行前的运行环境参数。
5.1 Logger::Init(); 主要用于生成一个Logger对象实例
5.2 如果需要输出到某一个log appender(附着器、输出器,比如console、具体目录下的文件),需要实例化一个基于BaseLogLocation(configuration)类的对象,设置好level,并添加到Logger对象的vector
5.3 读取配置文件,首先生成一个gRs.pConfigFile = new ConfigFile(NULL, NULL);
传递的两个NULL为:
GetApplicationFunction_t staticGetApplicationFunction
GetFactoryFunction_t staticGetFactoryFunction
另外 splitFileName(configFilePath, fileName, extension); //函数用于分割文件名和文件后缀;5.4 gRs.pConfigFile->LoadLuaFile(configFilePath, (bool)gRs.commandLine[“arguments”][“–daemon”])
用于读取配置文件crtmpserver.lua到变量Variant _configuration中并验证好。读取的时候只要带{}都认为是MAP,其余在{}外的散装则按照实际类型存储。
函数normalizePath(appDir, "");用于补全路径
5.5 gRs.pConfigFile->ConfigLogAppenders()
根据读取到的配置文件去配置系统的打印日志模块,其中configfile里面包含了
Variant _configuration;
Variant _logAppenders;
string _rootAppFolder;
Variant _applications;
map<string, string> _uniqueNames;
map<string, Module> _modules;
GetApplicationFunction_t _staticGetApplicationFunction;
GetFactoryFunction_t _staticGetFactoryFunction; 5.6 IOHandlerManager::Initialize(); 初始化FdStats _fdStats; _readFds; _writeFds; _pTimersManager _isShuttingDown
5.7 gRs.pConfigFile->ConfigModules()
遍历_applications中的每个应用模块并填充map<string, Module> _modules;变量其中Map的Module有个config变量保存着这个模块的所有配置。另外需要调用Module.load去装载每个应用的DLL,然后获取这个DLL中的接口函数指针去初始化Module下的两个函数指针变量GetApplicationFunction_t getApplication; GetFactoryFunction_t getFactory;
5.8 gRs.pProtocolFactory = new DefaultProtocolFactory();
构建类DefaultProtocolFactory的对象,其继承BaseProtocolFactory类,在这个基类的构造函数中会产生一个唯一的_id
5.9 ProtocolFactoryManager::RegisterProtocolFactory(gRs.pProtocolFactory)
把5.8创建好的默认协议工厂注册到协议工厂管理器里面进行管理,这个注册过程是比较复杂的,首先ProtocolFactoryManager维护着三个静态变量:
map<uint32_t, BaseProtocolFactory *> ProtocolFactoryManager::_factoriesById; 代表协议工厂的唯一_id标识的协议工厂;会检测注册进来的协议工厂的id是否在这个_factoriesById MAP中,如果存在就直接返回。
map<string, BaseProtocolFactory *> ProtocolFactoryManager::_factoriesByChainName;代表协议链名所对应的协议工厂会通过此vector<string> protocolChains = pFactory->HandledProtocolChains();去集合创建上面的协议工厂所支持的协议链名(eg. "inboundRtmp"),然后遍历这个protocolChains,查看是否有成员存在于_factoriesByChainName变量中,有就直接返回。
map<uint64_t, BaseProtocolFactory *> ProtocolFactoryManager::_factoriesByProtocolId;代表协议id所对应的协议工厂;会通过此vector<uint64_t> protocols = pFactory->HandledProtocols();函数去集合创建上面的协议工厂所支持的协议(eg. PT_TCP、PT_INBOUND_SSL)然后去遍历一下protocols向量,去查看_factoriesByProtocolId中是否存在任何一个其中的值如果有就直接返回,如果以上情况都满足的话,那么会把protocolChains包含的协议链名添加到_factoriesByChainName,并关联对应的协议工厂
FOR_VECTOR(protocolChains, i) {
_factoriesByChainName[protocolChains[i]] = pFactory;
}那么会把protocols包含的协议添加到_factoriesByProtocolId,并关联对应的协议工厂;
FOR_VECTOR(protocols, i) {
_factoriesByProtocolId[protocols[i]] = pFactory;
}那么会把pFactory添加到_factoriesById中。
_factoriesById[pFactory->GetId()] = pFactory;5.10 gRs.pConfigFile->ConfigFactories() 配置模块带入的协议工厂
遍历configfile中的map<string, Module> _modules变量,并根据GetFactoryFunction_t getFactory;函数指针变量,通过传输Module中的config作为参数来生成赋给BaseProtocolFactory *pFactory;变量的对象(也是协议工厂),然后通过ProtocolFactoryManager::RegisterProtocolFactory(pFactory)注册进ProtocolFactoryManager对象中。【实际上只有samplefactory才有新的协议工厂产生,通过GetFactory_samplefactory函数来生成。】
此协议工厂的协议类型及协议链名如下:
协议类型:
vector<uint64_t> ProtocolFactory::HandledProtocols() {
vector<uint64_t> result;
ADD_VECTOR_END(result, PT_ECHO_PROTOCOL);
ADD_VECTOR_END(result, PT_HTTP_DOWNLOAD_PROTOCOL);
return result;
}协议链名:
vector<string> ProtocolFactory::HandledProtocolChains() {
vector<string> result;
ADD_VECTOR_END(result, "echoProtocol");
ADD_VECTOR_END(result, "httpEchoProtocol");
ADD_VECTOR_END(result, "httpDownload");
return result;
}5.11 gRs.pConfigFile->ConfigAcceptors() 配置每个模块的acceptor的socket
遍历_modules中存入的每个模块,在遍历的过程中去遍历模块中的config[“acceptors”],在遍历的过程中执行Module::BindAcceptor(Variant &node) 函数,其中node就是下面这个MAP中的一个子MAP:
acceptors =
{
{
ip="0.0.0.0",
port=1935,
protocol="inboundRtmp"
},
{
ip="0.0.0.0",
port=8080,
protocol="inboundRtmpt"
},
}在这个Module::BindAcceptor(Variant &node)中需要执行更小MAP的绑定工作。
5.11.1 vector chain = ProtocolFactoryManager::ResolveProtocolChain(node[CONF_PROTOCOL]);
通过子MAP中的protocol协议链名去生成支持的协议,过程是这样的:通过链接名在_factoriesByChainName找到对应的协议工厂,然后调用协议工厂中的ResolveProtocolChain(name)函数去生成支持的协议的一个vector<uint64_t> (eg. PT_TCP PT_INBOUND_RTMP)
5.11.2 当chain[0] == PT_TCP
根据chain[0] == PT_TCP 去创建一个TCPAcceptor,它是继承自IOHandler(0, 0, IOHT_ACCEPTOR)
TCPAcceptor::TCPAcceptor(string ipAddress, uint16_t port, Variant parameters, vector<uint64_t>/*&*/ protocolChain)
TCPAcceptor *pAcceptor = new TCPAcceptor(node[CONF_IP], node[CONF_PORT], node, chain);在此构造函数中会赋值:
_pApplication = NULL; //初始化基类为BaseClientApplication的应用为NULL
/** 绑定sockaddr_in类型的socket信息*/
memset(&_address, 0, sizeof (sockaddr_in));
_address.sin_family = PF_INET;
_address.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(STR(ipAddress));
o_assert(_address.sin_addr.s_addr != INADDR_NONE);
_address.sin_port = EHTONS(port); //----MARKED-SHORT----
_protocolChain = protocolChain; //赋值协议链名
_parameters = parameters; //类型为Variant的子MAP
_enabled = false;
_acceptedCount = 0;
_droppedCount = 0;
_ipAddress = ipAddress;
_port = port;同时调用IOHandler构造函数: IOHandler(0, 0, IOHT_ACCEPTOR)
IOHandler::IOHandler(int32_t inboundFd, int32_t outboundFd, IOHandlerType type) {
_pProtocol = NULL;
_type = type;
_id = ++_idGenerator;
_inboundFd = inboundFd; //接收数据socket
_outboundFd = outboundFd; //发送数据socket
IOHandlerManager::RegisterIOHandler(this); //并把此IOHandler注册到IOHandlerManager中
}在IOHandlerManager中存在以下三个变量
map<uint32_t, IOHandler *> IOHandlerManager::_activeIOHandlers;
map<uint32_t, IOHandler *> IOHandlerManager::_deadIOHandlers;
map<int32_t, map<uint32_t, uint8_t> > IOHandlerManager::_fdState;FdStats IOHandlerManager::_fdStats; //主要用于统计fd(socket)用,_fdStats "file description statistics"存储过程是这样进行的:
首先判断传入的IOHandler是否存在于_activeIOHandlers中,如果没有就添加进去。然后调用
_fdStats.RegisterManaged(pIOHandler->GetType());此函数调用AccountManaged(type, true);此函数有以下几个步骤:
1.首先获取对应类型的管理的基类指针BaseFdStats *pFdStats = GetManaged(type);
BaseFdStats _managedTcp; //IOHT_TCP_CARRIER
BaseFdStats _managedTcpAcceptors; //IOHT_ACCEPTOR
BaseFdStats _managedTcpConnectors; //IOHT_TCP_CONNECTOR
BaseFdStats _managedUdp; //IOHT_UDP_CARRIER
BaseFdStats _managedNonTcpUdp; //IOHT_INBOUNDNAMEDPIPE_CARRIER IOHT_TIMER IOHT_STDIO:
BaseFdStats _rawUdp;2.如果AccountManaged(IOHandlerType type, bool increment)中第二个参数为true就调用第一步获得的
pFdStats->Increment()函数,否则pFdStats->Decrement(); Increment主要是执行以下三个语句:
_current++; _max = _max < _current ? _current : _max; _total++; Decrement执行_current--;执行完Increment或者Decrement后,执行以下语句:
int64_t current = Current();
_max = _max < current ? current : _max; // _max为FdStats的变量,类型int64_t其中Current()函数执行
int64_t FdStats::Current() {
return _managedTcp.Current() + _managedTcpAcceptors.Current() + _managedTcpConnectors.Current() + _managedUdp.Current() + _managedNonTcpUdp.Current() + _rawUdp.Current();
} 为计算所有BaseFdStats类型的_current变量之和,类型int64_t
创建完TCPAcceptor之后,执行Bind工作
5.11.3 pAcceptor->Bind()
这个bind其实不是严格意义上的bind动作,5.11.2节只是初始化一些关于socket的基本信息而已,这一节才是基于上节的基本信息来做socket创建绑定工作的。
1.创建socket, _inboundFd = _outboundFd = (int) socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
2.设置socket的属性选项,通过setFdOptions(_inboundFd, false)
bool setFdOptions(SOCKET fd, bool isUdp) {
setFdNonBlock(fd) //设置成非阻塞模式
setFdNoSIGPIPE(fd) // set no SIGPIPE
setFdKeepAlive(fd, isUdp) //set keep alive
setFdNoNagle(fd, isUdp) // disable Nagle algorithm
setFdReuseAddress(fd) // enable reuse address
}3.绑定socket的地址信息,通过bind(_inboundFd, (sockaddr *) & _address, sizeof (sockaddr)
4.监听socket listen(_inboundFd, 100) //100代表服务端socket可以同时接受客户端多少各请求,超过数量的链接就拒绝
然后把_enabled = true;使能此pAcceptor
5.11.4 ADD_VECTOR_END(acceptors, pAcceptor),
把创建好的pAcceptor添加到属于Module中一个变量的vector<IOHandler *> acceptors;中去。
5.12 gRs.pConfigFile->ConfigInstances() //创建多server的实例,win下不支持
5.13 IOHandlerManager::Start() //do nothing
5.14 gRs.pConfigFile->ConfigApplications()
遍历configfile中的每一个Module对象
5.14.1 首先调用Module中的pApplication = getApplication(config);生成基类为BaseClientApplication的应用对象,config为Module中的变量,属于每个应用模块独有的配置Variant
5.14.2 然后调用ClientApplicationManager::RegisterApplication(pApplication)把其注册到
ClientApplicationManager中这中间主要是维护ClientApplicationManager中的2个MAP变量
static map<uint32_t, BaseClientApplication *> ClientApplicationManager::_applicationsById;
static map<string, BaseClientApplication *> ClientApplicationManager::_applicationsByName;把此应用的唯一_id、应用名、应用别名(aliase)关联此应用BaseClientApplication* pApplication
并判断是否为默认应用,如果是就赋值给属于
ClientApplicationManager的static BaseClientApplication * _pDefaultApplication = pClientApplication;5.14.3 pApplication->Initialize()
AdminApplication->BaseClientApplication 应用只有两层。
首先调用实际对象的Initialize(), 例如:AdminApplication::Initialize() ,在这个函数内调用
BaseClientApplication::Initialize(),这个函数里面没有做任何事情 do nothing,然后调用
RTMPAppProtocolHandler->BaseRTMPAppProtocolHandler->BaseAppProtocolHandler 应用处理有三层
_pRTMPHandler = new RTMPAppProtocolHandler(_configuration); 此_configuration的类型为Variant,只包含与此Application有关的配置。RTMPAppProtocolHandler继承BaseRTMPAppProtocolHandler(主要在这个基类里面做了很多初始化)继承BaseAppProtocolHandler
_validateHandshake = (bool)configuration[CONF_APPLICATION_VALIDATEHANDSHAKE];
_keyframeSeek = (bool)configuration[CONF_APPLICATION_KEYFRAMESEEK];
_clientSideBuffer = (int32_t) configuration[CONF_APPLICATION_CLIENTSIDEBUFFER];
_seekGranularity = (uint32_t) ((double) configuration[CONF_APPLICATION_SEEKGRANULARITY]*1000);
_mediaFolder = (string) configuration[CONF_APPLICATION_MEDIAFOLDER];
_renameBadFiles = (bool)configuration[CONF_APPLICATION_RENAMEBADFILES];
_externSeekGenerator = (bool)configuration[CONF_APPLICATION_EXTERNSEEKGENERATOR];
_enableCheckBandwidth = false;
_enableCheckBandwidth = (bool)_configuration.GetValue("enableCheckBandwidth", false);
if (_enableCheckBandwidth) {
Variant parameters;
parameters.PushToArray(Variant());
parameters.PushToArray(generateRandomString(ONBWCHECK_SIZE));
_onBWCheckMessage = GenericMessageFactory::GetInvoke(3, 0, 0, false, 0, RM_INVOKE_FUNCTION_ONBWCHECK, parameters);
_onBWCheckStrippedMessage[RM_INVOKE][RM_INVOKE_FUNCTION] = RM_INVOKE_FUNCTION_ONBWCHECK;
}
_lastUsersFileUpdate = 0;
if ((bool)configuration[CONF_APPLICATION_GENERATE_META_FILES]) { GenerateMetaFiles(); }
RegisterAppProtocolHandler(PT_INBOUND_RTMP, _pRTMPHandler);
RegisterAppProtocolHandler(PT_OUTBOUND_RTMP, _pRTMPHandler);BaseClientApplication::RegisterAppProtocolHandler函数的执行过程主要是维护一个数据结构
map<uint64_t, BaseAppProtocolHandler *> _protocolsHandlers,首先判断此MAP里面有无PT_INBOUND_RTMP、PT_OUTBOUND_RTMP类型,如果有就返回,没有就把此类型与RTMPAppProtocolHandler通过MAP添加关联起来。然后把此RTMPAppProtocolHandler对应的应用设置为此应用,即把RTMPAppProtocolHandler中的变量BaseClientApplication *_pApplication;设置为AdminApplication应用
5.14.4 pApplication->ParseAuthentication()
这部分暂时不做解析,主要用于认证。
5.14.5 pApplication->ActivateAcceptors(acceptors) //vector<IOHandler *> acceptors
在module下调用此函数,用于激活存储在vector<IOHandler *> &acceptors中的每一个acceptor。根据acceptor的类型分为IOHT_ACCEPTOR、IOHT_UDP_CARRIER;此处分析IOHT_ACCEPTOR:
TCPAcceptor *pAcceptor = (TCPAcceptor *) pIOHandler;
pAcceptor->SetApplication(this); // 设置此acceptor的应用
pAcceptor->StartAccept(); //开始accept回到调用IOHandlerManager的IOHandlerManager::EnableAcceptConnections(this);函数,这个函数主要是更新_fdState以及_readFds,_writeFds
map<int32_t, map<uint32_t, uint8_t> > IOHandlerManager::_fdState[pIOHandler->GetInboundFd()][pIOHandler->GetId()] |= FDSTATE_READ_ENABLED;IOHandler的socket ID, IOHandler的标记ID
UpdateFdSets(pIOHandler->GetInboundFd()); 根据上面MAP的值去更新_readFds,_writeFds,如果状态无变化就通过_fdState.erase(fd);清除此socket记录。
5. 15 installQuitSignal(QuitSignalHandler);
//依据不同的平台, 如linux ,windows, android等安装不同的信号处理机;
主要调用IOHandlerManager::SignalShutdown();
6. Run()
6.1 IOHandlerManager::Pulse()
这个函数里面主要是做socket轮询工作,首先会清除_readFdsCopy、_writeFdsCopy,然后把_readFds,_writeFds分别复制给它们。通过
int32_t count = select(MAP_KEY(--_fdState.end()) + 1, &_readFdsCopy, &_writeFdsCopy, NULL, &_timeout);函数进行socket的轮询工作。
首先扫描map<uint32_t, IOHandler *> IOHandlerManager::__activeIOHandlers中的所有IOHandler,检测每个IOHandler所关联的_inboundFd,_outboundFd(其实就是socket fd),当此_inboundFd在_readFdsCopy或_outboundFd在_writeFdsCopy中时,就调用IOHandler的OnEvent()函数。
接着调用TCPAcceptor::OnConnectionAvailable(select_event &event)函数,此TCPAcceptor中存在_pApplication(在5.14.5配置好的),然后调用_pApplication->AcceptTCPConnection(this = TCPAcceptor)函数,就是调用TCPAcceptor->Accept()函数,在里面做fd = accept(_inboundFd, &address, &len); 获得链接客户端的fd(socket),并设置它的选项参数setFdOptions(fd, false)
6.1.1 BaseProtocol *pProtocol = ProtocolFactoryManager::CreateProtocolChain(_protocolChain, _parameters);
这个函数主要是通过协议链创建协议对象,
BaseProtocol *ProtocolFactoryManager::CreateProtocolChain(vector<uint64_t> &chain, Variant ¶meters)
此函数逻辑过程比较复杂。函数执行过程如下:
0. 首先调用协议工厂管理器的vector<uint64_t> chain = ResolveProtocolChain(name);函数
根据协议链名去协议工厂里面查找对应的协议ID,如
_factoriesByChainName[name]->ResolveProtocolChain(name);
_factoriesByChainName[name]就是根据协议链名查找对应的协议工厂,然后调用协议工厂里面的ResolveProtocolChain(name);函数去生成协议链名对应的协议链,其中ID分别为:PT_TCP,PT_INBOUND_RTMP。
1. 根据0步得到的协议链调用协议工厂管理器的CreateProtocolChain(chain, parameters);函数
1.1. 首先遍历协议链中的每个协议是否存在_factoriesByProtocolId变量中,如果都存在才继续下一步;
1.2. 再遍历协议链中的每一个协议,,通过协议在_factoriesByProtocolId变量中对的应协议工厂,然后调用协议工厂函数BaseProtocol *DefaultProtocolFactory::SpawnProtocol(uint64_t type, Variant ¶meters) 创建协议对象,eg:
PT_TCP: pResult = new TCPProtocol(); PT_INBOUND_RTMP: pResult = new InboundRTMPProtocol();
TCPProtocol-> BaseProtocol
InboundRTMPProtocol -> BaseRTMPProtocol -> BaseProtocol1.3. 生成两个协议对象后,需要交织它们的关联关系,
TCPProtocol->SetNearProtocol(InboundRTMPProtocol)把TCPProtocol的近点协议设置为InboundRTMPProtocol;
TCPProtocol的远点协议没有设置就是自己本身。
同样地,InboundRTMPProtocol->SetFarProtocol(TCPProtocol)把InboundRTMPProtocol的远点协议设置为TCPProtocol;InboundRTMPProtocol近点协议没有设置就是自己本身
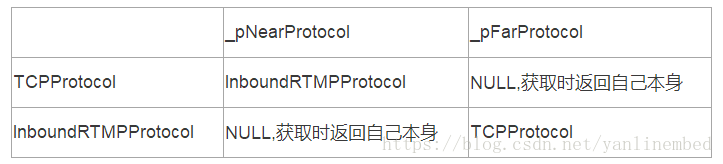
1.4. 但BaseProtocol *ProtocolFactoryManager::CreateProtocolChain(vector<uint64_t> &chain, Variant ¶meters)返回的依然是InboundRTMPProtocol协议
6.1.2 根据accept接口返回的客户端fd(其实是个socket) 生成一个TCPCarrier *pTCPCarrier = new TCPCarrier(fd);对象
6.1.3 pTCPCarrier->SetProtocol(pProtocol->GetFarEndpoint());
设置TCPCarrier携带的协议,即_pProtocol = InboundRTMPProtocol的远点协议TCPProtocol
6.1.4 pProtocol->GetFarEndpoint()->SetIOHandler(pTCPCarrier);
设置InboundRTMPProtocol的远点协议(其实是TCPProtocol)的IOHandler为TCPCarrier
6.1.5 设置协议对应的应用,代码如下:
if (_pApplication != NULL) {
pProtocol = pProtocol->GetNearEndpoint();
pProtocol->SetApplication(_pApplication);
}由于TCPAcceptor 的_pApplication 不为NULL,首先把pProtocol 协议置为近点协议即InboundRTMPProtocol,然后设置它的应用_pApplication = pApplication;
这一步骤的具体过程如下:
由于InboundRTMPProtocol没有重写SetApplication接口,所以会调用BaseRTMPProtocol::SetApplication()接口
首先调用BaseProtocol::SetApplication(pApplication); 函数体执行过程如下:
//1. Get the old and the new application name and id
string oldAppName = "(none)";
uint32_t oldAppId = 0;
string newAppName = "(none)";
uint32_t newAppId = 0;
if (_pApplication != NULL) { oldAppName = _pApplication->GetName(); oldAppId = _pApplication->GetId(); }
if (pApplication != NULL) { newAppName = pApplication->GetName(); newAppId = pApplication->GetId(); }
//2. Are we landing on the same application?
if (oldAppId == newAppId) { return; }
//3. If the application is the same, return. Otherwise, unregister
if (_pApplication != NULL) { _pApplication->UnRegisterProtocol(this); _pApplication = NULL; }this的基类为BaseProtocol,UnRegisterProtocol()函数首先检查协议有无存在
map<uint64_t, BaseAppProtocolHandler *> _protocolsHandlers;中然后调用
_streamsManager.UnRegisterStreams(pProtocol->GetId());函数,在这个函数中的执行过程如下:
通过调用map<uint32_t, BaseStream *> streams = FindByProtocolId(protocolId);在
map<uint32_t, map<uint32_t, BaseStream *> > _streamsByProtocolId;查找
map<uint32_t, BaseStream *> streams,然后遍历它,即:
FOR_MAP(streams, uint32_t, BaseStream *, i) { UnRegisterStream(MAP_VAL(i)); }调用StreamsManager::UnRegisterStream(BaseStream *pStream)函数,其实就是一些擦除操作,如下:
map<uint32_t, BaseStream *> _streamsByUniqueId;
map<uint32_t, map<uint32_t, BaseStream *> > _streamsByProtocolId;
map<uint64_t, map<uint32_t, BaseStream * > > _streamsByType;
map<string, map<uint32_t, BaseStream * > > _streamsByName;此函数map<uint64_t, BaseAppProtocolHandler *> _protocolsHandlers[pProtocol->GetType()]->UnRegisterProtocol(pProtocol);也是调用一些擦除操作
SOManager _soManager.UnRegisterProtocol((BaseRTMPProtocol*) pProtocol); //一些杂项(版本,persistent)管理操作
if (!MAP_HAS1(_connections, pProtocol->GetId())) { return; }
_connections.erase(pProtocol->GetId());
_nextInvokeId.erase(pProtocol->GetId());
_resultMessageTracking.erase(pProtocol->GetId());
//4. Setup the new application
_pApplication = pApplication;
//5. Register to it
if (_pApplication != NULL) { _pApplication->RegisterProtocol(this); } //this 其实是协议对象
---> void BaseClientApplication::RegisterProtocol(BaseProtocol *pProtocol)
---> map<uint64_t, BaseAppProtocolHandler *> _protocolsHandlers[pProtocol->GetType()]->RegisterProtocol(pProtocol)实际调用void BaseRTMPAppProtocolHandler::RegisterProtocol(BaseProtocol *pProtocol)函数,动作:
if (MAP_HAS1(_connections, pProtocol->GetId())) return;
map<uint32_t, BaseRTMPProtocol *> _connections[pProtocol->GetId()] = (BaseRTMPProtocol *) pProtocol;
map<uint32_t, uint32_t> _nextInvokeId[pProtocol->GetId()] = 1;6.1.6 _pProtocolHandler = (BaseRTMPAppProtocolHandler *)pApplication->GetProtocolHandler(this);
6.1.7 if(pProtocol->GetNearEndpoint()->GetOutputBuffer() != NULL)// IOBuffer BaseRTMPProtocol::_outputBuffer
pProtocol->GetNearEndpoint()->EnqueueForOutbound();
//BaseProtocol::EnqueueForOutbound() ---> _pFarProtocol->EnqueueForOutbound() --->
//TCPProtocol::EnqueueForOutbound() ---> _pCarrier->SignalOutputData() --->
//TCPCarrier::SignalOutputData() ---> ENABLE_WRITE_DATA ---> return true;6.2 TCPCarrier::OnEvent(select_event &event)
轮询的时候用于数据收发处理。
IOBuffer *pInputBuffer = _pProtocol->GetInputBuffer();
//调用 TCPProtocol::GetInputBuffer() 返回 变量IOBuffer _inputBuffer;
pInputBuffer->ReadFromTCPFd(_inboundFd, _recvBufferSize, _ioAmount)
_rx += _ioAmount;
ADD_IN_BYTES_MANAGED(_type, _ioAmount);
return _pProtocol->SignalInputData(_ioAmount);
//TCPProtocol::SignalInputData ---> _pNearProtocol->SignalInputData(_inputBuffer); --->
//BaseRTMPProtocol::SignalInputData(IOBuffer &buffer)







 本文详细剖析了CRtmpServer流媒体服务器的启动过程,包括随机数生成、网络初始化、命令行参数处理、配置文件加载、协议工厂注册、Acceptor绑定、应用初始化等多个关键步骤。
本文详细剖析了CRtmpServer流媒体服务器的启动过程,包括随机数生成、网络初始化、命令行参数处理、配置文件加载、协议工厂注册、Acceptor绑定、应用初始化等多个关键步骤。

















 2539
2539

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








