顺序存储结构实现
-
SeqString.h
#ifndef __SEQSTRING_H__ #define __SEQSTRING_H__ #define MAXSIZE 256 typedef struct { char data[MAXSIZE]; int len; }SeqString; int StrLength(char *s); int StrCat(char s1[],char s2[]); int SubStr(char* s, char t[], int i, int len); int StrCmp(char* s1, char* s2); int StrInsert(char *s,int i,char *t); #endif // !__SEQSTRING_H__ -
SeqString.cpp
#include"SeqString.h"
#include<stdio.h>
int StrLength(char* s)
{
int count = 0;
while (*s != '\0')
{
count++;
s++;
}
return count;
}
int StrCat(char s1[], char s2[])
{
int len1 = StrLength(s1);
int len2 = StrLength(s2);
if (len1 + len2 > MAXSIZE - 1)
return 0;
char* p1 = s1 + len1;
//while (*p1 != '\0')
// p1++;
char* p2 = s2;
while (*p2 != '\0')
{
*p1 = *p2;
p1++;
p2++;
}
*p1 = '\0';
return 1;
}
int SubStr(char* s, char t[], int i, int len)
{ // 用数组t返回串s中从第i个字符开始长度为len的字串
int j = 0;
int sLen = StrLength(s);
if (i<1 || i>sLen || len<0 || len>sLen - i + 1)
return 0;
while (len > 0)
{
t[j] = *(s + i + j);
len--;
}
return 1;
}
int StrCmp(char* s1, char* s2)
{
char* p1 = s1;
char* p2 = s2;
while (*p1 != '\0' && *p2 != '\0')
{
if (*p1 > *p2)
return 1;
else if (*p1 < *p2)
return -1;
else
{
p1++; p2++;
}
}
if (*p1 != '\0')
return 1;
else if (*p2 != '\0')
return -1;
}
int StrInsert(char* s, int i, char* t)
{
int sLen = StrLength(s);
int tLen = StrLength(t);
if (sLen + tLen > MAXSIZE)
{
printf("String is full\n");
return -1;
}
char* p1 = s + i;
char* p2 = p1 + tLen;
while (tLen > 0)
{
*p2 = *p1;
p1++;
p2++;
tLen--;
}
*p2 = '\0';
p1 = s + i;
while (*t != '\0')
{
*p1 = *t;
p1++;
t++;
}
return StrLength(s) + StrLength(t);
}
链式存储结构实现
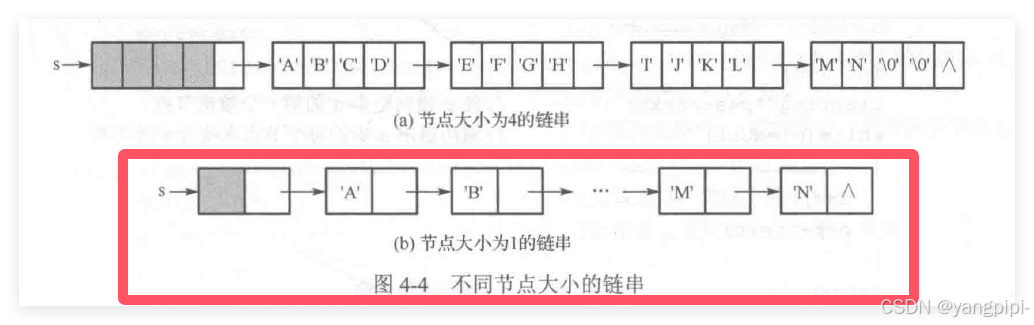
- LiString.h
#ifndef __LISTRING_H__ #define __LISTRING_H__ typedef struct snode { char data; struct snode* next; }LiString; void StringLiAssign(LiString** s, char str[]); int StrLiLength(LiString* s); void StrLiCat(LiString* s, LiString* t); void printLiStr(LiString* s); void SubLiStr(LiString* s, LiString** str, int i, int len); void StrLiInsert(LiString* s, int i, LiString* t); #endif // !__LISTRING_H__ - LiString.cpp
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #include"LiString.h" void StringLiAssign(LiString** s, char str[]) { char* p = str; LiString *head = (LiString*)malloc(sizeof(LiString)); head->next = NULL; *s = head; LiString* rear = head; while (*p != '\0') { LiString* node = (LiString*)malloc(sizeof(LiString)); node->data = *p; node->next = NULL; p++; rear->next = node; rear = rear->next; } } int StrLiLength(LiString* s) { LiString* node = s->next; int count = 0; while (node != NULL) { count++; node = node->next; } return count; } void StrLiCat(LiString* s, LiString* t) { LiString* rear = s->next; if (rear == NULL) { printf("s is empty\n"); } while (rear->next != NULL) rear = rear->next; rear->next = t->next; free(t); // 释放t的头结点 } void SubLiStr(LiString* s, LiString** str, int i, int len) { int count = 0; LiString* p = s; while (i>1) { p = p->next; i--; } LiString* Beforbegin = p; LiString *head = (LiString*)malloc(sizeof(LiString)); head->next = Beforbegin->next; while (len > 0) { p = p->next; len--; } LiString* end = p; Beforbegin->next = end->next; end->next = NULL; *str = head; } void printLiStr(LiString* s) { s = s->next; while (s) { printf("%c ",s->data); s = s->next; } printf("\n"); } // 还没有测试通过~~~~ void StrLiInsert(LiString* s, int i, LiString* t) { while (i > 1) { s = s->next; i--; } LiString* tmp = s->next; //printf("\n ----- %c %c", tmp->data, t->next->data); s->next = t->next; s = t->next; while (s->next != NULL) s = s->next; s->next = tmp; free(t); // 释放t的头结点 }
模式匹配
BF算法
- Brute-Force
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #include"BF.h" int SrtIndex_BF(char* s, char* T) { int j = 0,i=0; int flag = 0; for (i = 0; i < strlen(s); i++) { j = 0; int tmp = i; while (s[i] == T[j] && s[i] != '\0') { i++; j++; if (T[j] == '\0') { printf("Success\n"); flag = 1; break; } } if (flag == 1) break; i = tmp; } if (flag) return i - j; else return -1; }
KMP算法

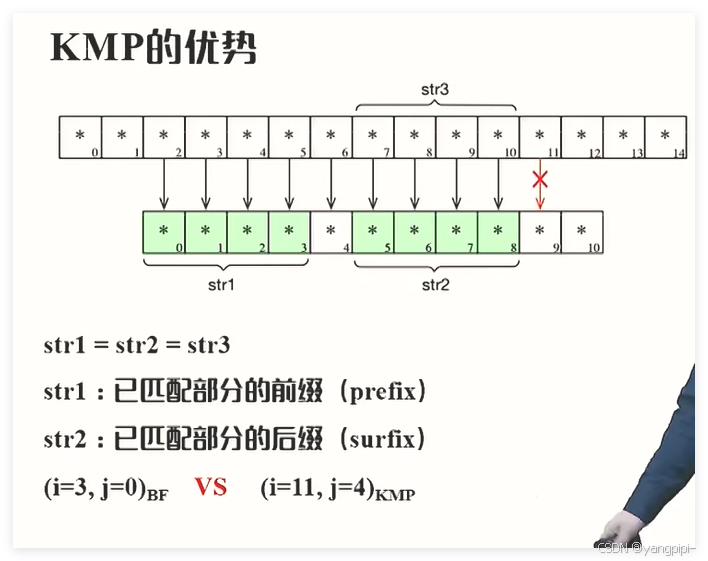
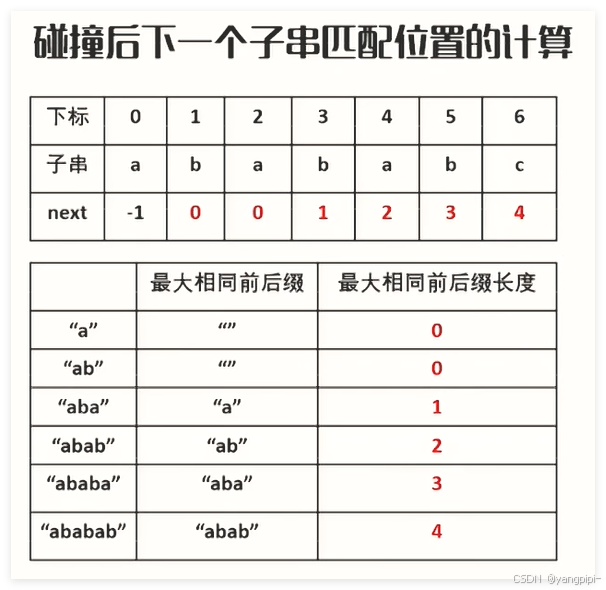
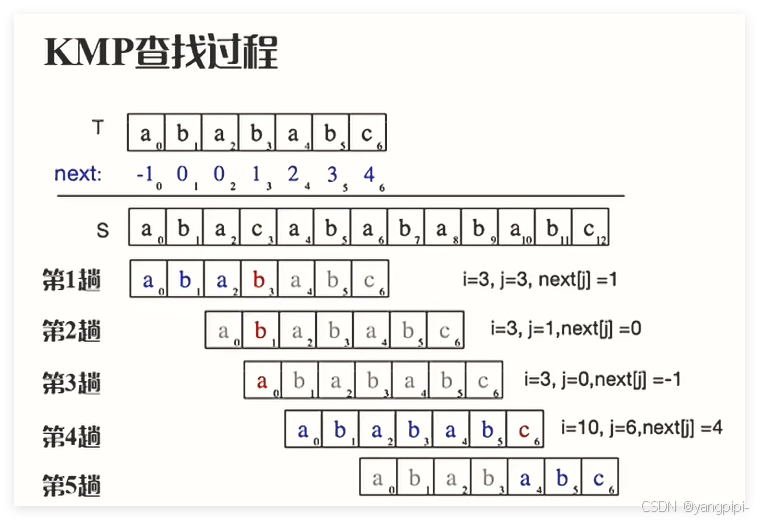

#include"BF.h"
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
void Next(char* T, int next[], int n)
{
int j = 0, k = -1;
next[0] = -1;
while (j < n)
{
if (k == -1 || T[j] == T[k])
{
j++;
k++;
next[j] = k;
}
else
k = next[k];
}
}
int KMP(char* S, char* T, int m, int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
int* next = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);
memset(next,0,sizeof(next)*n);
Next(T,next,n);
while (i < m && j < n)
{
if (j == -1 || S[i] == T[j])
{
i++;
j++;
}
else
j = next[j];
}
if (j == n)
return i - n;
else
return -1;
}
next数组
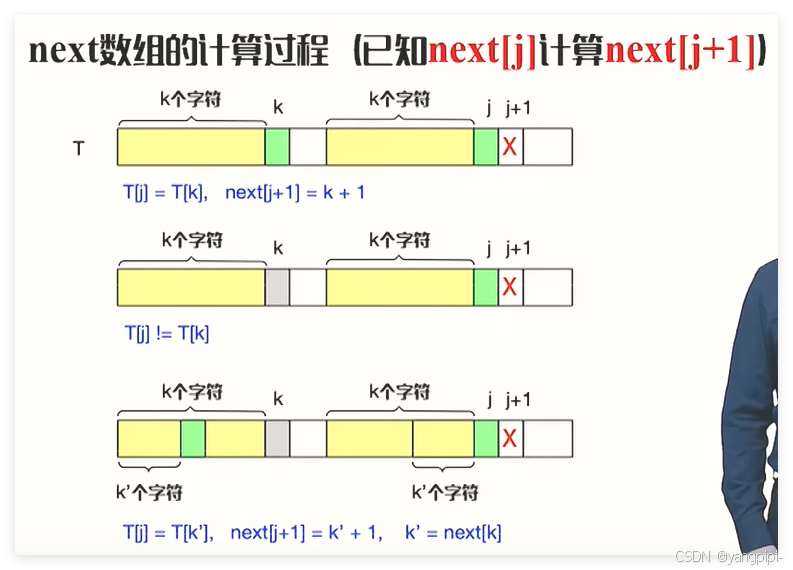
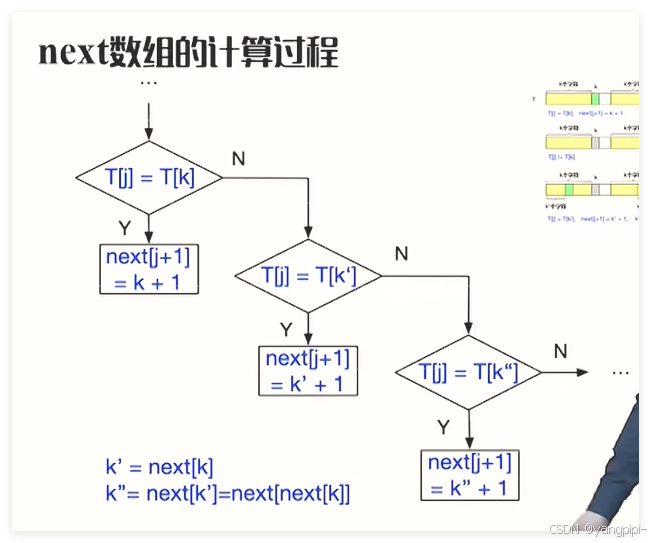

课后题
查找字串出现的次数

BP算法

KMP算法
int Soll6(char* str, char* T, int strSize, int Tsize)
{
int lenStr = strSize;
int res = 0,count=0;
char* p = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*(strSize+1));
strcpy(p,str); // 会将str中的\0复制过去
while (res != -1)
{
/*
char str[] = "123456123456123";
char T[] = "123";
*/
res = KMP(p, T, lenStr - res-Tsize, Tsize);
if (res == -1) // 没有找到
break;
count++;
p = p + res+Tsize;
}
return count;
}
思路:利用KMP算法,从上次找到的位置之后继续使用KMP算法进行查找
回文字符判断

- 见代码随想录
等值子串

int Sol9(char* str)
{
char* p = str;
int count = 1,max=0;
int endInex = 0;
int i = 0;
while (*(p+i) != '\0') //121234566666
{
if (*(p+i) == *(p +i+1))
count++;
else
{
if (max < count)
{
max = count;
count = 1;
endInex = i;
}
}
i++;
}
if(max<=0)
return -1;
else
{
printf("%s最长的等值子串为:",str);
for (int i = 0; i < max; i++)
printf("%c",*(str+ endInex-max+1+i));
printf("\n长度为%d\n",max);
return max;
}
}






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








