C++的一个主要目标是促进代码重用。公有继承是实现这种目标的机制之一,但并不是唯一的机制。
包含对象成员的类
valarray类简介
valarray类是由头文件valarray支持的。这个类用于处理数值(或具有类似特性的类),它支持诸如将数组中所有元素的值相加以及在数组中找到最大值和最小值的操作。valarray被定义为一个模板类,以便能够处理不同的数据类型
模板特性意味着声明对象时,必须指定具体的数据类型。因此使用valarray类来声明一个对象时,需要在标识符valarray后面加上一对尖括号,并在其中包含所需的数据类型:
valarray<int> q_values; //an array of int
valarray<double> weights; //an array of double
下面是其几个构造函数的例子:
double gpa[5] = {3.1,3.5,3.8,2.9,3.3};
valarray<double> v1; //an array of double ,size 0
valarray<int>v2(8); //an array of 8 int elements
valarray<int>v3(10,8); //an array of 8 int elements, each set to 10
valarray<double> v4(gpa,4); //an array of 4 elements,
//initialized to the first 4 elements of gpa
Student类的设计
学生是什么?可以将其简化为姓名和一组考试分数,则可以使用一个包含两个成员的类来表示它:一个成员用于表示姓名——string对象,另一个成员用于表示分数——valarray<double>
你可能想以公有的方式从这两个类派生出Student类,这将是多重公有继承,语法上允许,但在这里不合适,因为学生与这些类之间的关系不是is-a模型。学生不是姓名,也不是一组考试成绩。这里的关系是has-a,学生有姓名,也有一组考试分数。通常用于建立has-a关系的C++技术是包含,即创建一个包含其他类对象的类,如可以这样声明Student类
Class Student
{
private:
string name; //use a string object for name
valarray<double> scores; //use a valarray<double> object for scores
...
}
Student类示例
#ifndef STUDENTC_H_
#define STUDENTC_H_
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<valarray>
class Student
{
private:
typedef std::valarray<double> ArrayDb;
std::string name; //contained object
ArrayDb scores; //contained object
//private method for scores output
std::ostream& arr_out(std::ostream& os)const;
public:
Student():name("Null Students"),scores(){}
explicit Student(const std::string &s):name(s),scores(){}
explicit Student(int n):name("Nully"), scores(n){}
Student(const std::string &s,int n):name(s),scores(n){}
Student(const std::string &s,const ArrayDb &a):name(s),scores(a){}
Student(const char*str,const double *pd,int n):name(str),scores(pd,n){}
~Student(){}
double Average() const;
const std::string& Name() const;
double& operator[](int i);
double operator[](int i)const;
//friends
//input
friend std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& is, Student& stu);
friend std::istream& getline(std::istream& is, Student& stu);
//output
friend std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream & os, const Student & stu);
};
#endif
为简化表示,Student类的定义中包含下述typedef:
typedef std::valarray<double> ArrayDb;
这样类方法和友元函数可以使用ArrayDb类型。将该typedef放在类定义的私有部分意味着可以在Student类的实现中使用它,但在Student类外面不能使用
前面说过,可以用一个参数调用的构造函数将用作从参数类型到类类型的隐式转换函数,但通常这样并不好,所以用explicit关闭隐式转换。——explicit防止单参数构造函数的隐式转换
#include<iostream>
#include"studentc.h"
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void set(Student& sa, int n);
const int pupils = 3;
const int quizzes = 5;
int main()
{
Student ada[pupils] =
{
Student(quizzes),Student(quizzes),Student(quizzes)
};
int i;
for (i = 0; i < pupils; ++i)
{
set(ada[i], quizzes);
}
cout << "\nStudent List:\n";
for (i = 0; i < pupils; ++i)
{
cout << ada[i].Name() << endl;
}
cout << "\nResult:";
for (i = 0; i < pupils; ++i)
{
cout << endl << ada[i];
cout << "average: " << ada[i].Average() << endl;
}
cout << "Done.\n";
return 0;
}
void set(Student& sa, int n)
{
cout << "Please enter the student's name: ";
getline(cin, sa);
cout << "Please enter " << n << " quiz scores:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> sa[i];
}
while (cin.get() != '\n')
continue;
}

私有继承
C++还有另一种实现has-a关系的途径——私有继承。 使用私有继承,基类的公有成员和保护成员都将成为派生类的私有成员。这意味着基类方法将不会成为派生类对象共有接口的一部分,但可以在派生类的成员函数中使用它们
Student类示例
要进行私有继承,需要使用private关键字而不是public来定义类(实际上,private是默认类,因此省略访问限定符也将导致私有继承)。Student类应从两个类派生而来
class Student :private std::string, private std::valarray<double>
{
public:
...
};
使用多个基类的继承被称为多重继承
使用私有继承时,只能在派生类的方法中使用基类的方法
类模板
C++的类模板为生成通用的类声明提供了一种更好的方法,模板提供参数化类型,即能够将类型名作为参数传递给接收方来建立类或函数
定义模板类
以Stack类为基础来建立模板
typedef unsigned long Item;
class Stack
{
private:
enum{MAX=10};//constant specific to class
Item items[MAX];//holds stack items
int top; //index for top stack item
public:
Stack();
bool isempty() const;
bool isfull() const;
bool push(const Item& item);
bool pop(Item& item);
};
采用模板时,将使用模板定义替换Stack声明,使用模板成员函数替换Stack的成员函数
模板类以下面的代码开头:
template<class Type>
关键字template告诉编译器,将要定义一个模板。尖括号中的内容相当于函数的参数列表。可以把关键字class看作是变量的类型名,该变量接受类型作为其值,把Type看作是该变量的名称。
这里使用class并不意味着Type必须是一个类;而只是表明Type是一个通用的类型说明符,在使用模板时,将使用实际的类型替换它。
所以使用模板后应该是:
bool Stack<Type>::push(const Type& item)
{
...
}
stacktp.h
#ifndef STACKTP_H_
#define STACKTP_H_
template <class Type>
class Stack
{
private:
enum { MAX = 10 };//constant specific to class
Type items[MAX];//holds stack items
int top; //index for top stack item
public:
Stack();
bool isempty();
bool isfull();
bool push(const Type& item);
bool pop(Type& item);
};
template<class Type>
Stack<Type>::Stack()
{
top = 0;
}
template<class Type>
bool Stack<Type>::isempty()
{
return top == 0;
}
template<class Type>
bool Stack<Type>::isfull()
{
return top == MAX;
}
template<class Type>
bool Stack<Type>::push(const Type& item)
{
if (top < MAX)
{
items[top++] = item;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
template<class Type>
bool Stack<Type>::pop(Type&item)
{
if (top > 0)
{
item = items[--top];
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
#endif
使用模板类
仅在程序包含模板并不能生成模板类,而必须实例化。为此需要声明一个类型为模板类的对象,方法是使用所需的具体类型替换泛型名。必须显式的提供所需的参数
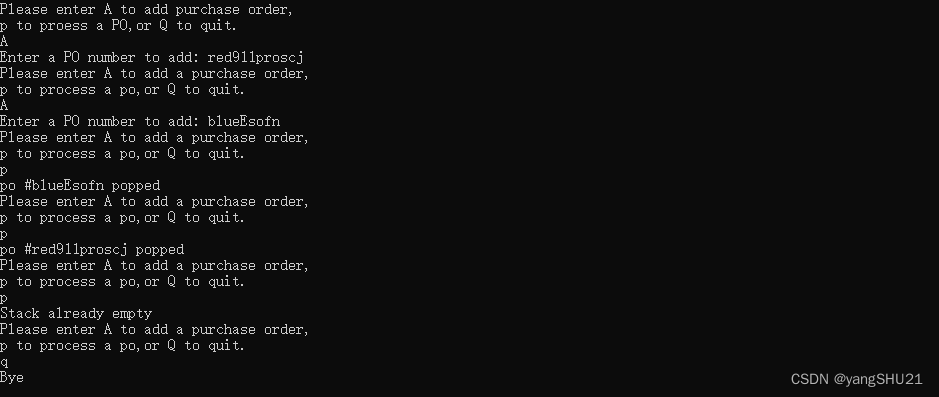
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cctype>
#include"stacktp.h"
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
int main()
{
Stack<std::string> st;
char ch;
std::string po;
cout << "Please enter A to add purchase order,\n"
<< "p to proess a PO,or Q to quit.\n";
while (cin >> ch && std::toupper(ch) != 'Q')
{
while (cin.get() != '\n')
continue;
if (!std::isalpha(ch))
{
cout << '\a';
continue;
}
switch (ch)
{
case 'A':
case 'a':
cout << "Enter a PO number to add: ";
cin >> po;
if (st.isfull())
{
cout << "Stack already full\n";
}
else
st.push(po);
break;
case'p':
case'P':
if (st.isempty())
cout << "Stack already empty\n";
else
{
st.pop(po);
cout << "po #" << po << " popped\n";
break;
}
}
cout << "Please enter A to add a purchase order,\n"
<< "p to process a po,or Q to quit.\n";
}
cout << "Bye\n";
return 0;
}





 本文介绍了C++中如何通过公有继承和valarray类实现代码重用,讨论了多重和私有继承的区别,以及类模板在创建通用类声明中的应用,以Stack类为例进行了展示。
本文介绍了C++中如何通过公有继承和valarray类实现代码重用,讨论了多重和私有继承的区别,以及类模板在创建通用类声明中的应用,以Stack类为例进行了展示。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








