全文6k字,带你速通西浦CPT101课程精要。为确保结构紧凑,本文最早于word中排版为8页,转录至网页版本不免出现格式问题,笔者在此提供pdf版链接方便同学们阅读,本文遵循CC BY-NC-SA 4.0协议,请勿商用喵
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1U7PrAddSE7HdNemW9adNow
提取码:2333 PS:下载完点赞收藏再走嘛(;´Д`)
正文
L1-计算机发展史
一、计算机类型(Types of Computers)
• 大型机Mainframe computers (1960s) • 巨型机Supercomputers (1970s) • 工作站Workstations (1980s)
• 微型机Microcomputers (1980s) • 个人电脑 Personal computers (1980s) • 微控制器 Microcontrollers (1980s) (嵌入式或专用计算机,如计算器) • 服务器 Servers (1980s) (通过network/cloud可用) • 单片机 Chip computer
随着计算机的发展,性能增长,体积减小(Increased performance & downsizing)。
二、计算机的四个世代(Computer Generations)
第一代:(1944 ~1958)电子管vacuum tube
第二代:(1959 ~1963)晶体管transistor
第三代:(1964 ~ 1970)集成电路IC(integrated circuit)
第四代:(1971 ~ now) 超大规模集成电路VLSI(Very Large Scale Integration)
三、五种计算机硬件(Hardware)
Input-输入,processing-处理,output-输出,storage-储存,communications-通信
四、计算机软件(Software)
系统软件:与硬件交互(communication),资源管理,便于应用程序之间通信(facilitates communication)
应用软件(Applications software):便利/辅助用户
五、向后兼容(Backward / Downward Compatibility)
新的版本的软/硬件可以使用老版本的软/硬件产生的数据。
六、VHDL(Very-High-Speed Integrated Circuit Hardware Description Language)硬件描述语言-集成电路设计
七、计算机系统层次结构(hierarchy of systems)
Hardware (CPU, Graphics, Sound)>Software [Operating Systems (O/S kernel, Win32 API)> User code (e.g. myPrograme.c)]
操作系统的优势:硬件系统的功能由OS提供给用户,用户也以此交互硬件。易于编程,保护系统与其他用户,提高系统资源使用的效率与公平性。
八、摩尔定律(Moore's Law)
The amount of circuitry (number of transistors) which can be placed on a given chip area approximately doubles every two years. ->A circuit designed 24 months ago can now be shrunk to fit into an area of half the size.
可以放置在给定芯片区域上的电路数量(晶体管数量)大约每两年翻一番
九、软硬件交互发展
1.Windowing interfaces –WIMPs. 视窗-Window、图标-Icon、菜单-Menu、鼠标-Pointing device
2. Internet-Netscape网景浏览器
L2-计算机架构
〇、以下两种架构的基本组件:
硬件(CPU(Central Processing Unit), memory, secondary storage(hard disk, CDs), keyboard, screen),软件,数据(Data that is being manipulated)
一、机器指令 (Machine instructions)
CPU执行机器指令, 每个CPU都有自己的指令集(instruction set),通常为100-200条指令,没有标准指令集。
分类:
• Input-output: IN, OUT
• Data transfer and manipulations: MOV, ADD, MUL, AND, OR
• Transfer of program control: JMP, JC,
• Machine control: can halt processing, reset the hardware, INT, HLT
二、HLL高级编程语言(High Level Programming Language)( : FORTRAN, C, C++, Java, Perl…)
比机器指令更适合编程,但程序仍需翻译为机器代码(硬件只能处理机器指令)。
三、输入-处理-输出模型(Input-Process-Output Model)
是冯诺依曼模型的基本方案(essential scheme)
处理过程由一个特殊的、定制的程序控制。The process is to be controlled by a special, custom-made program.
四、冯·诺依曼模型(The von Neumann Model)
general-purpose machine controlled by an executable program
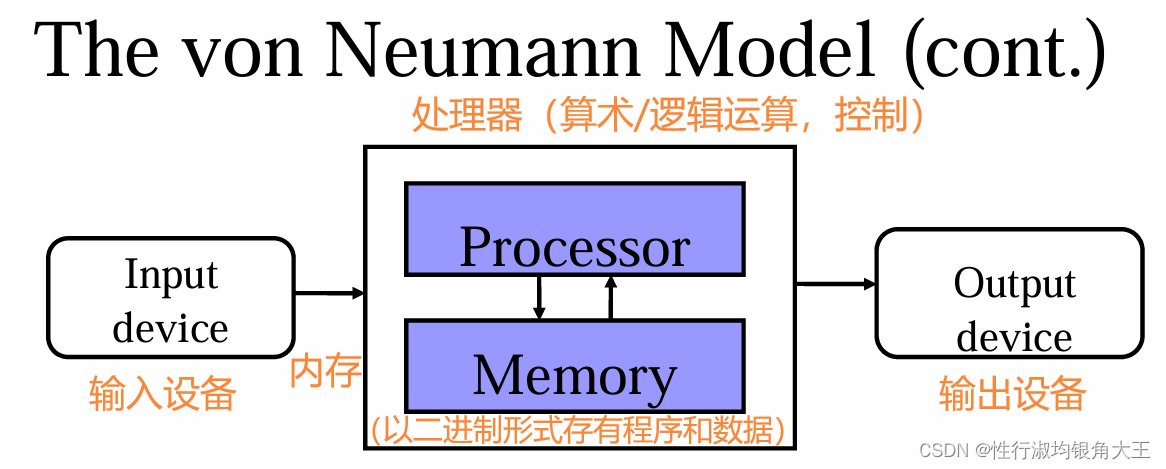 (late 1940s)
(late 1940s)
程序-a list of instructions used to direct a task.
处理器-an active part that executes the program instructions.
数据和指令都存储在内存中不同的区域,将某个内存地址开始的字节全部当作指令,将某个内存地址开始的字节全部当作数据。(使计算机可以区分数据和指令)
冯诺依曼瓶颈:CPU速度快,内存速度慢,CPU大部分时间需要等待数据和指令从内存读出/写入
五、哈佛架构(Harvard architecture)
Program Memory <->CPU<-> Data Memory(速度快高吞吐-嵌入式/CPU内)
程序指令存储和数据存储分开的存储器结构,当取指使用程序空间,执指使用数据空间时,可以同时处理。
L3-编译原理(Fundamentals of Compiling)
一、语义鸿沟(Semantic gap)
自然语言与电脑指令处理数据方式的巨大差异。
二、三种翻译方式(translation)
1. 编译器 (Compilers): 在运行前将高级语言编写的源程序翻译成机器语言(sequence of instructions)。
2. 汇编器 (Assemblers): 将汇编语言(助记符如MOV等)编写的源程序翻译成二进制代码。
3. 解释器 (Interpreters): 在运行时转换高级语言的源程序为机器码,不生成目标文件(on-the-fly)。
三、编译(Compiling)*
-[编辑]>源文件(HLL source file) –[编译]>二进制文件(Binary object file+ Library File) –[link]>可执行文件(Executable file)-[加载Load]>加载(时报错) └编译时报错(根据错误信息在源文件中修改) └连接时报错
四、连接(Linking)
编译器无法解析对其他模块的引用,连接器将所有二进制部分连接,找不到引用则报错。
五、库文件(library file .dll)仅当被使用时加入程序,为程序提供许多功能
六、解释器(interpreters) 接受指令,一次一个,翻译和执行交错进行。
C源代码→编译器(程序)→汇编语言→汇编器→机器码→linking & loading→可执行文件
Java源代码→编译器→Java字节码byte code→Java解释器(JVM虚拟机)
七、代码共享和重用(Code sharing and reuse) 源文件(Edit)->Compile(macros)->link(Obj libraries)->Build(Dyna libs)








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 4880
4880

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








