位运算
~ 按位非(NOT) & 按位与(AND) | 按位或(OR)
^ 按位异或(XOR) >> 右移 >>> 无符号右移 <<左移
进制转换
16进制0x 8进制0 切记是数字0
//十进制转成十六进制:Integer.toHexString(n1);
//十进制转成八进制:Integer.toOctalString(n1);
//十进制转成二进制:Integer.toBinaryString(12);
//十六进制转成十进制:Integer.valueOf("FFFF",16).toString();
//N进制转成十进制:Integer.valueOf("****",N).toString();
//16进制直接转2进制:Integer.toBinaryString(0xfdac)
Int和Byte/Byte数组互换
1.//byte 与 int 的相互转换
2.public static byte intToByte(int x) {
3. return (byte) x;
4.}
5.public static int byteToInt(byte b) {
6.Java 总是把 byte 当做有符处理;我们可以通过将其和 0xFF 进行二进制与得到它的无符值
7. return b & 0xFF;
8.}
1.//byte 数组与 int 的相互转换
2.public static int byteArrayToInt(byte[] b) {
3. return b[3] & 0xFF |
4. (b[2] & 0xFF) << 8 |
5. (b[1] & 0xFF) << 16 |
6. (b[0] & 0xFF) << 24;
7.public static byte[] intToByteArray(int a) {
8. return new byte[] {
9. (byte) ((a >> 24) & 0xFF),
10. (byte) ((a >> 16) & 0xFF),
11. (byte) ((a >> 8) & 0xFF),
12. (byte) (a & 0xFF)
Long和Byte数字互换
分配一个新的字节缓冲区,因为long的字节长度为8,所以allocate一定不能小于8buffer.putLong(0, x);
将 8 个包含给定 long 值的字节按照当前的字节顺序写入到此缓冲区的给定索引处0的位置。allocate缓冲区字节大小
1.private static ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(8);
2.//byte 数组与 long 的相互转换
3. public static byte[] longToBytes(long x) {
4. buffer.putLong(0, x);
5. return buffer.array(); //返回此缓冲区的byte数组
6. }
7. public static long bytesToLong(byte[] bytes) {
8. buffer.put(bytes); //将字节数组放入缓冲区中
9. buffer.flip();//一定要写不然报错,反转此缓冲区
10. return buffer.getLong(); //读取缓冲区8个字节组成long值
byte[] seq=new byte[4];
for(int i=0;i<seq.length;i++){
seq[i]=(byte) new Random().nextInt(127);
0到127随机整数
}
int a=0xfdac; 返回十进制64940
String binaryString = Integer.toBinaryString(a);
二进制1111110110101100
int parseInt = Integer.parseInt(a+"", 19);
0*0+4*19+9*19^2+4*19^3+6*19^4=812687
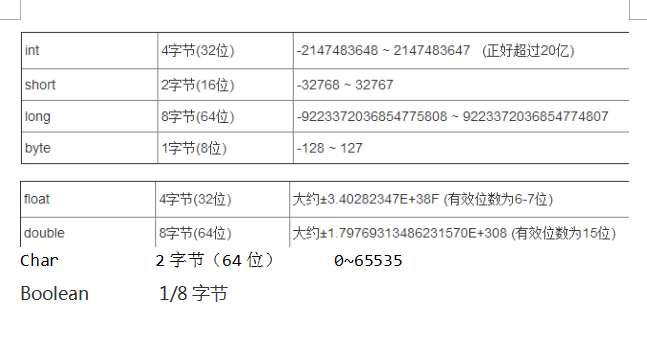
JAVA数据类型取值范围






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








