用600样本,看XGBoost能够做到什么程度:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, GridSearchCV
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
import xgboost as xgb
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 1. 生成模拟数据(600样本,10特征)
X, y = make_regression(n_samples=600, n_features=10, noise=0.1, random_state=42)
df = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=[f'feat_{i}' for i in range(10)])
df['target'] = y
# 2. 数据预处理
X = df.drop('target', axis=1)
y = df['target']
# 划分训练集和测试集(80%训练,20%测试)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 特征标准化(对回归问题通常需要)
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_scaled = scaler.transform(X_test)
# 3. 基础模型构建(防止过拟合参数)
base_params = {
'objective': 'reg:squarederror',
'eval_metric': 'rmse',
'booster': 'gbtree',
'n_jobs': -1,
'random_state': 42,
'max_depth': 3, # 限制树深度
'learning_rate': 0.1, # 较低学习率
'subsample': 0.8, # 行采样
'colsample_bytree': 0.7, # 特征采样
'reg_alpha': 0.5, # L1正则化
'reg_lambda': 1.0 # L2正则化
}
# 4. 网格搜索调参(优化关键参数)
param_grid = {
'n_estimators': [100, 200, 300],
'max_depth': [3, 4],
'learning_rate': [0.05, 0.1],
'min_child_weight': [5, 10] # 控制叶子节点样本权重
}
# 使用5折交叉验证
grid_search = GridSearchCV(
estimator=xgb.XGBRegressor(**base_params),
param_grid=param_grid,
scoring='neg_mean_squared_error',
cv=5,
n_jobs=-1,
verbose=1
)
grid_search.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
# 输出最佳参数
print(f"Best parameters: {grid_search.best_params_}")
print(f"Best CV RMSE: {-grid_search.best_score_:.4f}")
# 5. 最终模型训练
best_model = grid_search.best_estimator_
eval_set = [(X_train_scaled, y_train), (X_test_scaled, y_test)]
best_model.fit(
X_train_scaled,
y_train,
eval_set=eval_set,
verbose=False)
# 6. 模型评估
y_pred = best_model.predict(X_test_scaled)
# 计算RMSE(手动计算平方根)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
rmse = np.sqrt(mse)
r2 = r2_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Test RMSE: {rmse:.4f}")
print(f"Test R²: {r2:.4f}")
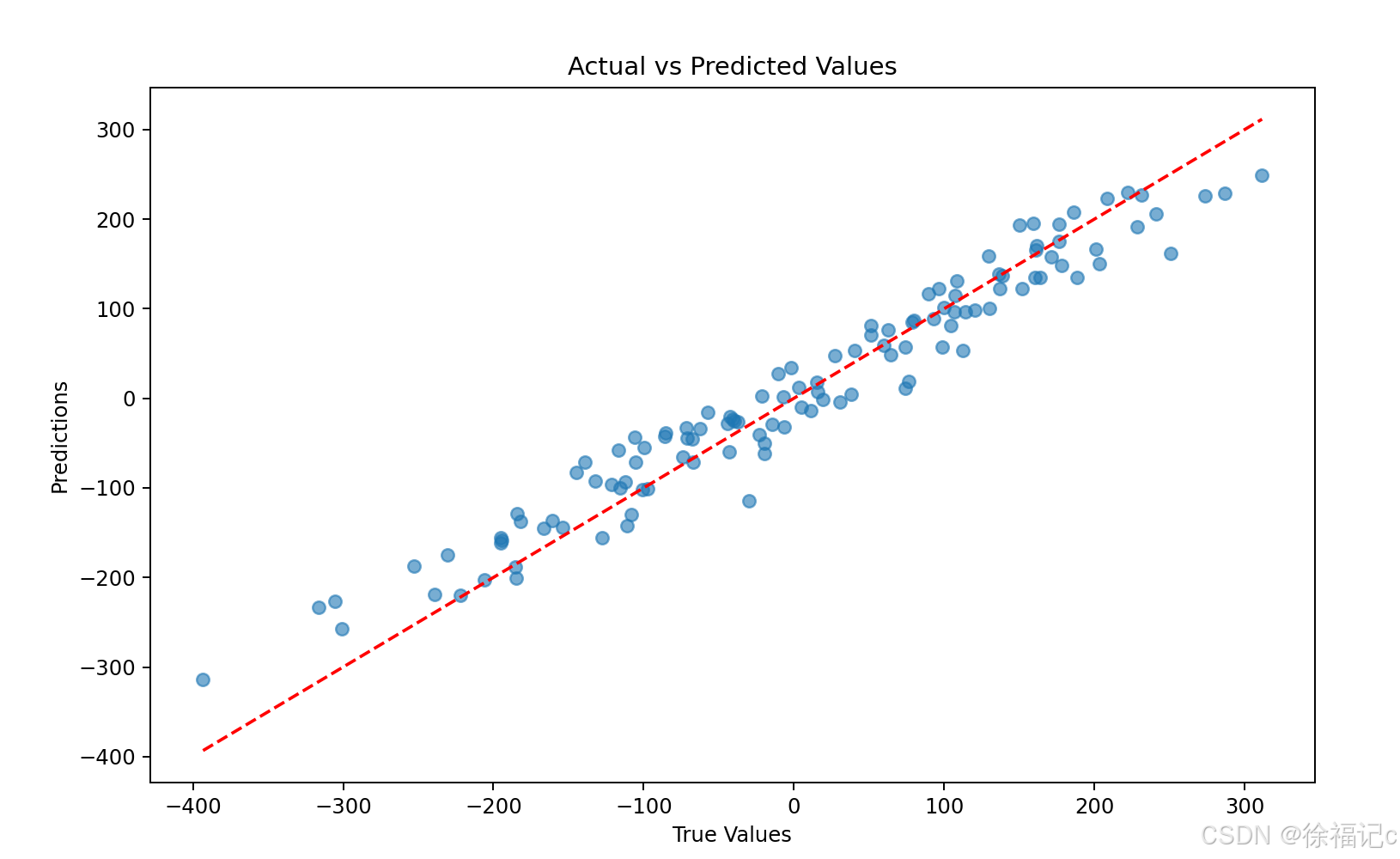
# 7. 可视化预测结果
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.scatter(y_test, y_pred, alpha=0.6)
plt.plot([y_test.min(), y_test.max()], [y_test.min(), y_test.max()], 'r--')
plt.xlabel('True Values')
plt.ylabel('Predictions')
plt.title('Actual vs Predicted Values')
plt.show()
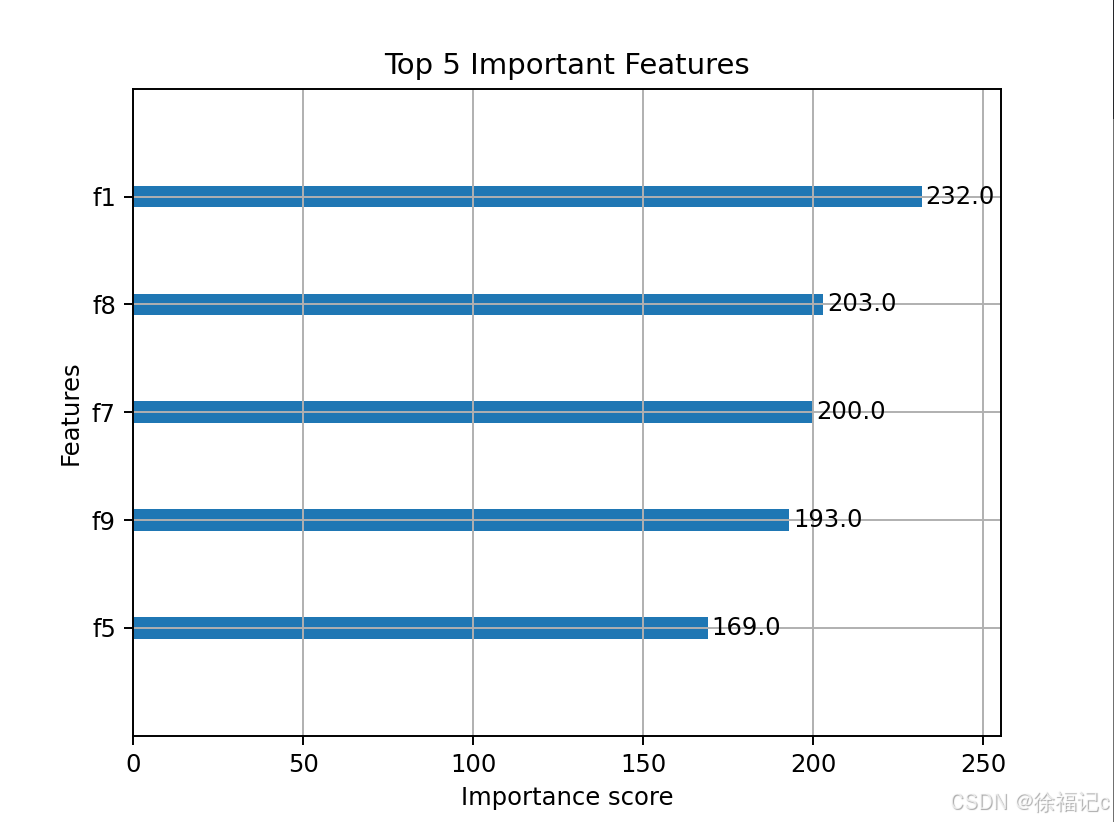
# 8. 特征重要性分析
xgb.plot_importance(best_model, max_num_features=5)
plt.title('Top 5 Important Features')
plt.show()
运行之后:
Fitting 5 folds for each of 24 candidates, totalling 120 fits
Best parameters: {'learning_rate': 0.1, 'max_depth': 3, 'min_child_weight': 5, 'n_estimators': 300}
Best CV RMSE: 1627.6646
Test RMSE: 35.1356
Test R²: 0.9429






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








