一、堆的实现,简单的功能:
#pragma once
# include<stdio.h>
# include<stdlib.h>
# include<assert.h>
# include<malloc.h>
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct Heap
{
DataType* _array;
int _capacity;
int _size;
}Heap;
void Swap(DataType* pLeft,DataType* pRight)
{
DataType tmp;
assert(pLeft);
assert(pRight);
tmp = *pLeft;
*pLeft = *pRight;
*pRight = tmp;
}
void _AdjustDown(Heap* hp, int parent)
{
//标记左右孩子中最小的孩子
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
int size = hp->_size;
while (child<size){
//找左右孩子中最小的孩子
if (child+1<size&&hp->_array[child] > hp->_array[child + 1])
child += 1;
if (hp->_array[parent] > hp->_array[child])
{
Swap(&hp->_array[parent], &hp->_array[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else{
return;
}
}
}
//向上调整
void _AdjustUp(Heap* hp, int child)
{
int parent = ((child - 1)) >> 1;
while (child){
if (hp->_array[parent] > hp->_array[child]){
Swap(&hp->_array[parent], &hp->_array[child]);
child = parent;
parent = ((child - 1) >> 1);
}
else
return;
}
}
//创建堆
void CreateHeap(Heap* hp, DataType* array, int size)
{
int i = 0;
int root = ((size - 2)>>2);
//给堆开辟空间
if (NULL == hp)
return;
hp->_array = (DataType*)malloc(sizeof(DataType)*size);
if (NULL == hp->_array){
assert(0);
return;
}
//将数组中的元素放到堆中
for (i = 0; i < size; ++i){
hp->_array[i] = array[i];//元素可能不满足堆的性质
}
hp->_capacity = size;
hp->_size = size;
//堆调整
for (; root >= 0; --root){
_AdjustDown(hp, root);
}
}
void _CheckCapacity(Heap* hp)
{
int i = 0;
assert(hp);
if (hp->_size == hp->_capacity)
{//开辟新空间
int NewCapacity = hp->_capacity * 2;
DataType* tmp = (DataType*)malloc(NewCapacity);
if (NULL == tmp){
assert(0);
return;
}
//申请空间成功,把元素搬移到新空间
//搬移元素
for (i=0; i < hp->_size; ++i){
tmp[i] = hp->_array[i];
}
//释放旧空间
free(hp->_array);
hp->_array = tmp;
hp->_capacity = NewCapacity;
}
}
//向堆中插入元素
void InsertHeap(Heap* hp,DataType data)
{
int child = 0;
int parent = 0;
assert(hp);
_CheckCapacity(hp);
hp->_array[hp->_size++] = data;
_AdjustUp(hp, hp->_size - 1);
child = hp->_size - 1;
}
//判空
int EmptyHeap(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return 0 == hp->_size;
}
//堆里面元素的个数
int SizeHeap(Heap *hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->_size;
}
//堆的删除:堆的删除一般删除堆顶元素,小堆删除最小值;大堆删除最大值
void DeleteHeap(Heap* hp)
{
if (EmptyHeap(hp))
{
return;
}
//堆不为空
//把最后一个元素交给堆顶
hp->_array[0] = hp->_array[hp->_size - 1];
//将元素删除
hp->_size--;
_AdjustDown(hp, 0);
}
void Test()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 5, 12, 45, 67, 8, 13, 89, 14, 56, 756 };
Heap hp;
CreateHeap(&hp, arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));
InsertHeap(&hp, 6);
DeleteHeap(&hp);
}
int main()
{
Test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2、用函数指针实现大小栈处理
typedef int (*Compare)(DataType left, DataType right);//
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct Heap
{
DataType* _array;
int _capacity;
int _size;
Compare _com;
}Heap;
int Less(DataType left,DataType right)
{
return left < right;
}
int Greater(DataType left, DataType right)
{
return left>right;
}
void Swap(DataType* pLeft, DataType* pRight)
{
DataType tmp;
assert(pLeft);
assert(pRight);
tmp = *pLeft;
*pLeft = *pRight;
*pRight = tmp;
}
void _AdjustDown(Heap* hp, int parent)
{
//标记左右孩子中最小的孩子
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
int size = hp->_size;
while (child<size){
//找左右孩子中最小的孩子
if (child + 1<size&&hp->_com(hp->_array[child+1] , hp->_array[child]))
child += 1;
if (hp->_com(hp->_array[child] , hp->_array[parent]))
{
Swap(&hp->_array[parent], &hp->_array[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else{
return;
}
}
}
//向上调整
void _AdjustUp(Heap* hp, int child)
{
int parent = ((child - 1)) >> 1;
while (child){
if (hp->_com(hp->_array[child] , hp->_array[parent])){
Swap(&hp->_array[parent], &hp->_array[child]);
child = parent;
parent = ((child - 1) >> 1);
}
else
return;
}
}
void InitHeap(Heap* hp,Compare com)
{
//给堆开辟空间
hp->_array = (DataType*)malloc(sizeof(DataType)*3);
if (NULL == hp->_array){
assert(0);
return;
}
hp->_capacity = 3;
hp->_size = 0;
hp->_com = com;
}
//创建堆
void CreateHeap(Heap* hp, DataType* array, int size,Compare com)
{
int i = 0;
int root = ((size - 2) >> 2);
//给堆开辟空间
if (NULL == hp)
return;
hp->_array = (DataType*)malloc(sizeof(DataType)*size);
if (NULL == hp->_array){
assert(0);
return;
}
//将数组中的元素放到堆中
for (i = 0; i < size; ++i){
hp->_array[i] = array[i];//元素可能不满足堆的性质
}
hp->_capacity = size;
hp->_size = size;
hp->_com = com;
//堆调整
for (; root >= 0; --root){
_AdjustDown(hp, root);
}
}
void _CheckCapacity(Heap* hp)
{
int i = 0;
assert(hp);
if (hp->_size == hp->_capacity)
{//开辟新空间
int NewCapacity = hp->_capacity * 2;
DataType* tmp = (DataType*)malloc(NewCapacity);
if (NULL == tmp){
assert(0);
return;
}
//申请空间成功,把元素搬移到新空间
//搬移元素
for (i = 0; i < hp->_size; ++i){
tmp[i] = hp->_array[i];
}
//释放旧空间
free(hp->_array);
hp->_array = tmp;
hp->_capacity = NewCapacity;
}
}
//向堆中插入元素
void InsertHeap(Heap* hp, DataType data)
{
int child = 0;
int parent = 0;
assert(hp);
_CheckCapacity(hp);
hp->_array[hp->_size++] = data;
_AdjustUp(hp, hp->_size - 1);
child = hp->_size - 1;
}
//判空
int EmptyHeap(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return 0 == hp->_size;
}
//获取堆定元素
DataType TopHeap(Heap* hp)
{
assert(!EmptyHeap(&hp));
return hp->_array[0];
}
//堆里面元素的个数
int SizeHeap(Heap *hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->_size;
}
//堆的删除:堆的删除一般删除堆顶元素,小堆删除最小值;大堆删除最大值
void DeleteHeap(Heap* hp)
{
if (EmptyHeap(hp))
{
return;
}
//堆不为空
//把最后一个元素交给堆顶
hp->_array[0] = hp->_array[hp->_size - 1];
//将元素删除
hp->_size--;
_AdjustDown(hp, 0);
}
void Test()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 5, 12, 45, 67, 8, 13, 89, 14, 56, 756 };
Heap hp;
CreateHeap(&hp, arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]),Less);
InsertHeap(&hp, 6);
DeleteHeap(&hp);
}
a、创建堆的时间复杂度:一个节点调整时间复杂度为:lgN,n个节点调整的时间复杂度为n*lgN;创建堆:n*调整堆次数+n
所以为O(n*lgN)
b、堆删除的时间复杂度,只需要调整一次为:O(lgN)
c、插入的时间复杂度:调整的也为树的高度,所以时间复杂度为:O(lgN)
d、不使用向下调整是否可以创建堆:先对元素排序,序列排好后(小堆:升序;大堆:降序),还原成树。
二、堆的应用:
1、优先级队列:队列中的元素存在优先级,优先级高的元素先出(创建大堆,让大堆作为优先级队列的结构,堆顶的元素最大,出队列时,删除堆顶元素)
typedef struct PriorityQueue
{
//底层封装一个堆
Heap _hp;
}PriorityQueue;
//初始化
void PriorityQueueInit(PriorityQueue* q,Compare com)
{
InitHeap(&q->_hp,com);
}
void PriorityQueuePush(PriorityQueue* q, DataType data)
{
InsertHeap(&q->_hp,data);
}
//移除元素,删除堆顶元素
void PriorityQueuePop(PriorityQueue* q)
{
DeleteHeap(&q->_hp);
}
//优先级队列有多少元素
int PriorityQueueSize(PriorityQueue* q)
{
return SizeHeap(&q->_hp);
}
//判断优先级队列是否为空
int PriorityQueueEmpty(PriorityQueue* q)
{
return EmptyHeap(&q->_hp);
}
//判断优先级的高低
DataType PriorityQueueTop(PriorityQueue* q)
{
return TopHeap(&q->_hp);
}
void Test()
{
PriorityQueue p;
PriorityQueueInit(&p,Greater);
PriorityQueuePush(&p, 3);
PriorityQueuePush(&p, 5);
PriorityQueuePush(&p, 7);
PriorityQueuePush(&p, 2);
printf("size=%d\n", PriorityQueueSize(&p));
printf("top=%d\n", PriorityQueueTop(&p));
PriorityQueuePop(&p);
PriorityQueuePop(&p);
printf("size=%d\n", PriorityQueueSize(&p));
printf("top=%d\n", PriorityQueueTop(&p));
}2、100亿个数中找出最大的前k个数(海量数据top k问题)
一个数据占4个字节,100亿个数据则占400亿个字节。400亿/1024/1024/1024~=40G的空间。大量的时间花费到了操作磁盘上去了,详细说明参见海量数据存储那篇博客。https://mp.youkuaiyun.com/postedit/80453175
也可以使用小堆存储的方式:建立一个K个元素大小的小堆,用剩余的(n-k)个元素和小堆中的元素进行比较,将大的那个元素替换到小堆中,比较完毕后剩下的小堆中的k个元素就是最大的前k个数。
3、堆排序
//堆调整
void HeapAdjust(int arr[], int size, int parent)
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < size){
//找左右孩子中最大的孩子,升序:大堆
if (child + 1 < size&&arr[child + 1] > arr[child])
child += 1;
//双亲是否比最大的孩子小
if (arr[parent] < arr[child])
{
Swap(&arr[parent], arr[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2;
}
else{
return;
}
}
}
//堆排序
void HeapSort(int array[], int size)
{
//1、建堆
//倒数第一个非叶子节点的位置一直调整到根节点
int root = (size - 2)>>2;
int end = size - 1;
for (; root >= 0; --root){
HeapAdjust(array, size, root);
}
//2、进行堆排序---堆删除
//交换堆顶元素和最后一个元素
while (end)
{
Swap(&array[end], &array[0]);
HeapAdjust(array, end,0);
--end;
}
}
void TestHeapSort()
{
int arr[] = { 4, 4, 1, 3, 6,9, 0, 5, 3, 1 };
HeapSort(arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));
}查找:
1、序列----数据杂乱---顺序查找----O(n)
2、有序----二分查找----O(lgN)
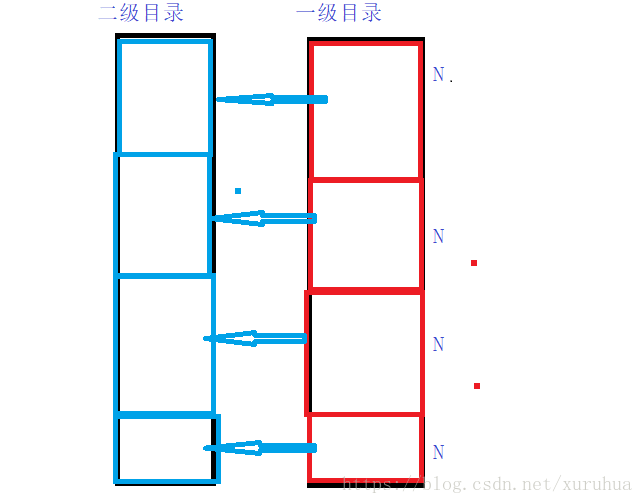
3、建立索引:把有序的数据分为n段,最后一段可以小于前面的数据,前面的数据大小是相等的,在每一段中提取出一个最大或者最小的数据,相当于得到一个一级目录,得到目录后,在里面查找数据按照目录里面的数据进行比较,数据在哪个段里,就在哪个段里面查找数据。因为数据是有序的,时间复杂度为O(lgN),速度非常快。还可以继续划分目录,使速度更快。
4、将数据中比中间数据小的放到最左边,比中间数据大的放到最右边。根节点大于所有左子树中的数据,小于右子树中的数据。左右子树都满足此性质,称这种树为二叉搜索树(二叉排序树)。二叉搜索树按照中序遍历的顺序,可以得到一个有序的序列。





















 30万+
30万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










