前面二叉堆实现了优先队列基本的插入和删除最小元操作,但如果想要将两个堆合并的话就不太容易了,我们要把一个数组里的数据拷贝到另一个数组,如果数组1和数组2大小相同,那么合并操作的时间就是O(N)。果然合并还是需要指针呀,所以我们提出了左式堆,但是注意指针操作实际会比乘除运算更加耗费时间。
左式堆(Leftist Heap)也有结构和有序性。左式堆的有序性和二叉堆一样,父亲小于所有的儿子。它不再是用数组实现,而是采用二叉树。先定义一个零路径长(null path length,npl):npl(x)定义为从节点x到一个没有两个儿子的节点的最短路径长。左式堆在结构上要满足:对于每个节点X,其左儿子的零路径长大于等于右儿子的零路径长。这个性质让树倾向于向左偏,所以也叫左偏树。
由左式堆的结构性,我们可以得到npl(x)=min(npl(LeftChild),npl(RightChild))+1
而对任意节点,npl(LeftChild) npl(RightChild)
所以 npl(x)=npl(RightChild)+1,这个在merge合并时更新npl就可以用到了。
左式堆右边比左边浅,合并操作只涉及到右边使算法效率提高。可以证明:在右路径上有r个节点的左式树必然至少有+1个节点,进一步我们知道N个节点的左式堆有一条右路径最多含有abs(log(N+1))个节点,那么合并操作就可以被控制在O(logN)。
左式堆的合并操作:不断把最小值大的堆和最小值小的堆的右子树合并,比较左右的npl,把npl大的交换到左边,时间界为log(N)。举个例子(逆时针从左往右看)
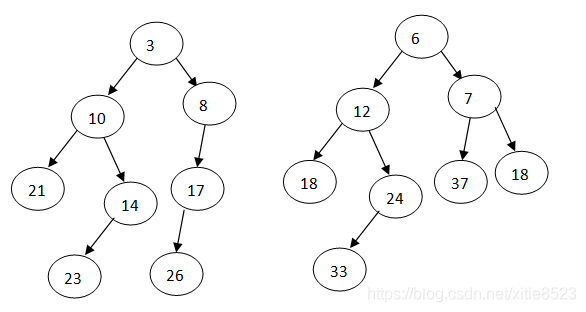
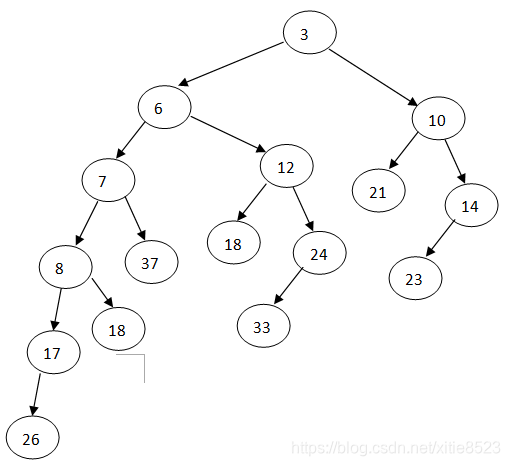
堆H1 堆H2 结果

H1->right和H2合并,放到H1->right处,以此类推
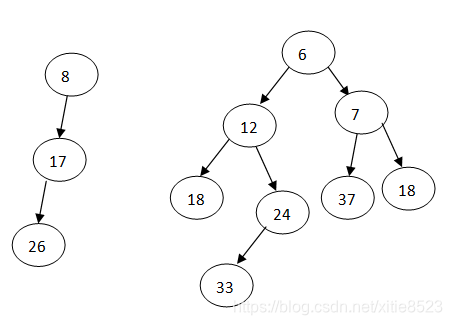
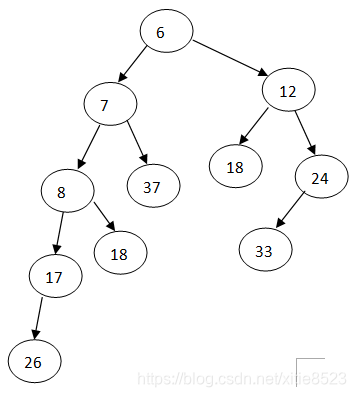

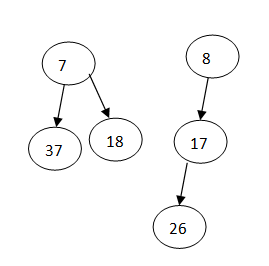
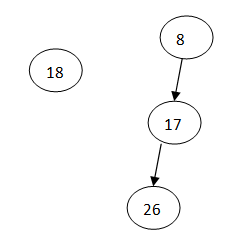 合并——》
合并——》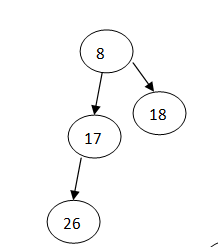
插入操作只要把插入节点看成一个堆,用合并可以完成插入的操作;删除最小元只需要删掉根节点,然后把左子树和右子树合并起来,时间界都为log(N)。buildHeap可以多次插入,这种方法比较耗时,更快速的方法是借助队列。将所有元素放入队列中,把这些节点都看成左式堆,前两个元素出队合并为一个堆再入队(放在队列最后面),依此操作下去。
代码:
LeftHeap.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int ElementType;
struct TreeNode;
typedef TreeNode *Position;
typedef Position LeftHeap;
LeftHeap initialize();
LeftHeap buildHeap(LeftHeap h);
bool isEmpty(LeftHeap h);
LeftHeap merge(LeftHeap h1, LeftHeap h2);
ElementType findMin(LeftHeap h);
#define insert(h,x) (h=insert1((h),(x)))
LeftHeap insert1(LeftHeap h, ElementType e);
LeftHeap deleteMin1(LeftHeap h);
void destory(LeftHeap h);
void printHeap(LeftHeap h);
struct TreeNode
{
ElementType element;
Position left;
Position right;
int npl;
};
LeftHeap.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "LeftHeap.h"
LeftHeap initialize()
{
return nullptr;
}
LeftHeap buildHeap(LeftHeap h)
{
ElementType input;
cout << "input: " << endl;
cin >> input;
while (input!=-1)
{
insert(h, input);
cin >> input;
}
return h;
}
bool isEmpty(LeftHeap h)
{
return h == nullptr;
}
void swapChild(LeftHeap h)
{
Position tmp = h->left;
h->left = h->right;
h->right = tmp;
}
LeftHeap merge1(LeftHeap h1, LeftHeap h2)
{
if (h1->left==nullptr)
{
h1->left = h2;
}
else
{
h1->right = merge(h1->right, h2);
if (h1->left->npl < h1->right->npl)
{
swapChild(h1);
}
h1->npl = h1->right->npl + 1;
}
return h1;
}
LeftHeap merge(LeftHeap h1, LeftHeap h2)
{
if (h1==nullptr)
{
return h2;
}
if (h2==nullptr)
{
return h1;
}
if (h1->element<h2->element)
{
return merge1(h1, h2);
}
else
{
return merge1(h2, h1);
}
}
LeftHeap insert1(LeftHeap h, ElementType e)
{
Position node = (Position)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
if (node==nullptr)
{
cerr << "out of space" << endl;
}
else
{
node->left = nullptr;
node->right = nullptr;
node->element = e;
node->npl = 0;
h = merge(h, node);
}
return h;
}
ElementType findMin(LeftHeap h)
{
if (!isEmpty(h))
{
return h->element;
}
cerr << "heap is empty" << endl;
return 0;
}
LeftHeap deleteMin1(LeftHeap h)
{
if (isEmpty(h))
{
cerr << "heap is empty" << endl;
return h;
}
LeftHeap leftchild = h->left;
LeftHeap rightchild = h->right;
free(h);
return merge(leftchild, rightchild);
}
void destory(LeftHeap h)
{
if (isEmpty(h))
{
return;
}
destory(h->left);
destory(h->right);
free(h);
h = nullptr;
}
void printHeap(LeftHeap h)
{
if (!isEmpty(h))
{
cout << h->element << " ";
printHeap(h->left);
printHeap(h->right);
}
}
test.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "LeftHeap.h"
int main()
{
LeftHeap heap = initialize();
heap = buildHeap(heap);
printHeap(heap);
cout << endl;
heap=deleteMin1(heap);
printHeap(heap);
cout << endl;
destory(heap);
return 0;
}
结果:
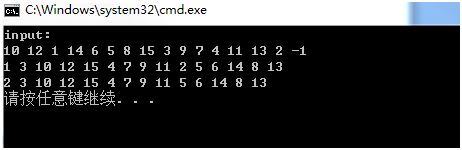





 本文介绍了一种高效的数据结构——左式堆,用于实现优先队列。左式堆通过特殊的二叉树结构和零路径长属性,使得合并操作能在O(logN)时间内完成,优于传统的二叉堆。文章详细解释了左式堆的特性、合并操作的原理及其实现代码。
本文介绍了一种高效的数据结构——左式堆,用于实现优先队列。左式堆通过特殊的二叉树结构和零路径长属性,使得合并操作能在O(logN)时间内完成,优于传统的二叉堆。文章详细解释了左式堆的特性、合并操作的原理及其实现代码。
















 2874
2874

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








