1、原型模式基本概念
原型模式指的是,以某个对象为原型,产生一份调用该对象的某个接口方法,可以先对该对象的克隆拷贝,在Java中可以使用两种机制实现原型模式,一种是序列化机制,一种是来自Object类的clone方法。可以这么理解原型模式就是指的对象的拷贝。
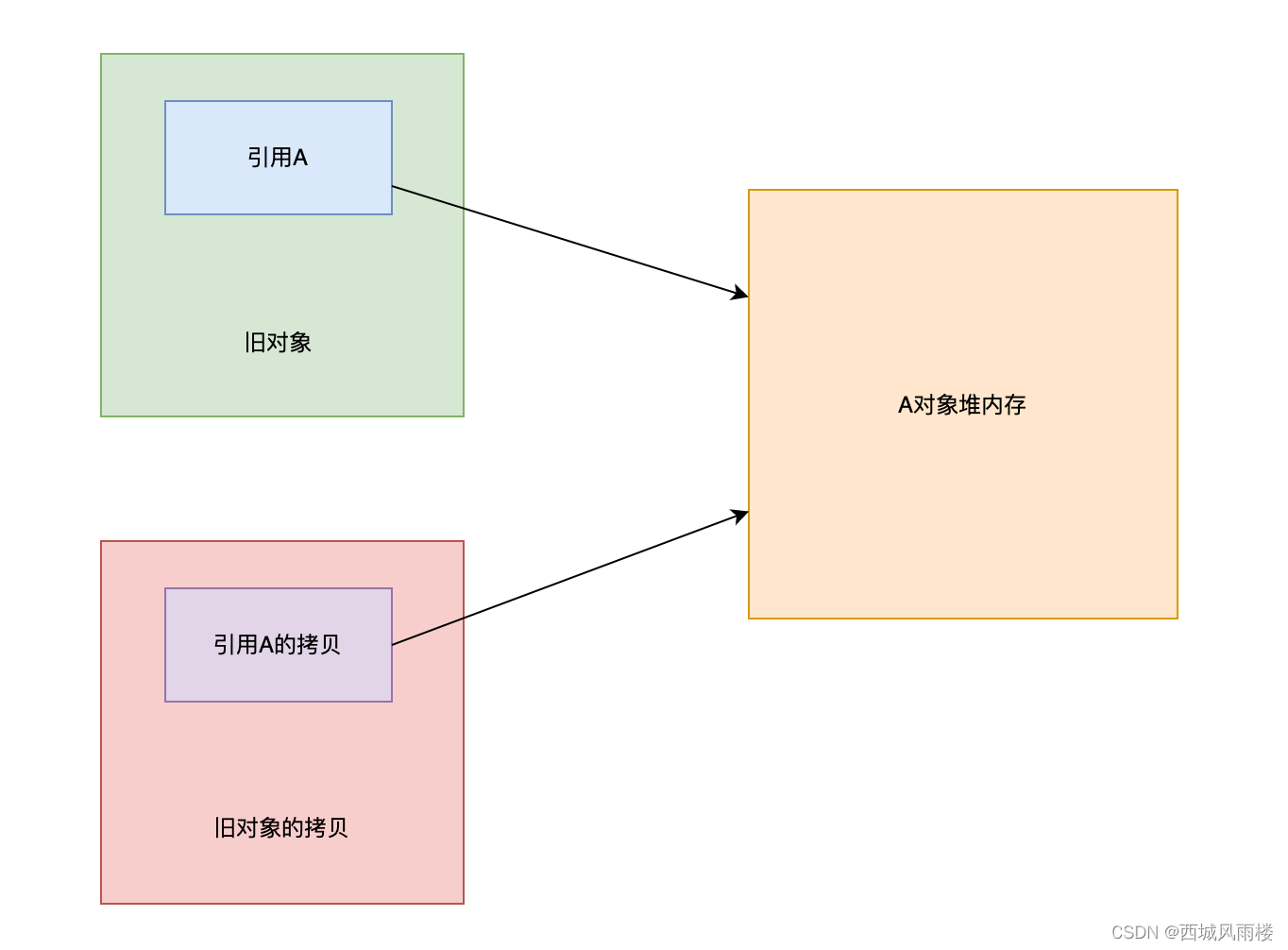
对象的拷贝又可以分为浅拷贝和深拷贝两种,所谓的浅拷贝指的是对引用类型,只是对引用本身进行了克隆,克隆的对象和以前的对象的引用指向同一块内存空间,如果该引用指向的是可变的对象,那么在某些场景下,新对象通过该引用对对象的修改,旧对象也可见,反之亦然。
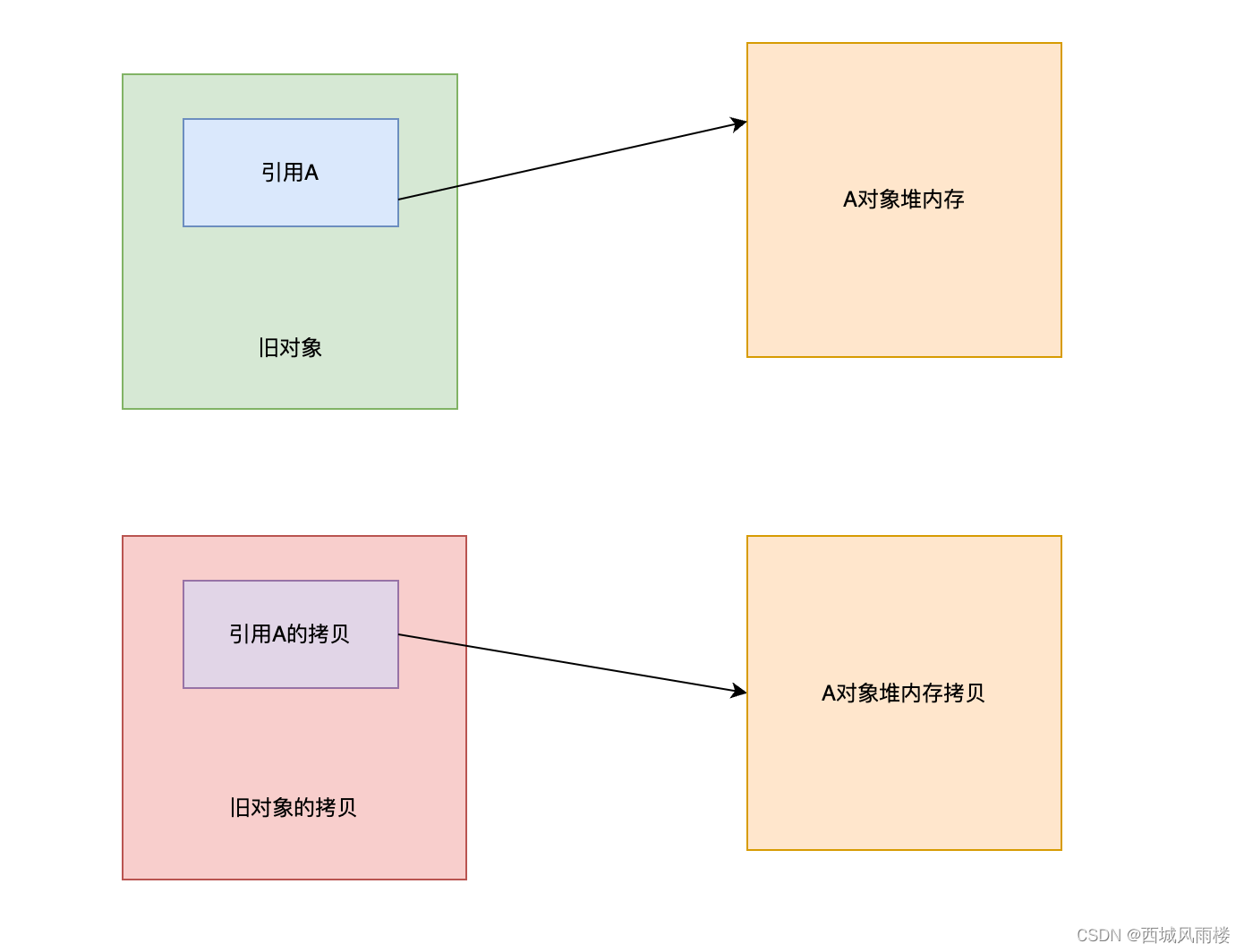
相对应的就是深拷贝,深拷贝指的是,对于引用对象,不仅仅是克隆引用本身,而是连同该引用对应的内存空间一并拷贝一份,这样新旧对象通过引用操作的就是不同的内存空间。
当然如果引用的对象是不可变对象,比如String,那么使用浅拷贝亦可。
下图是深拷贝和浅拷贝的示意图:
- 浅拷贝
- 深拷贝
2、原型模式角色
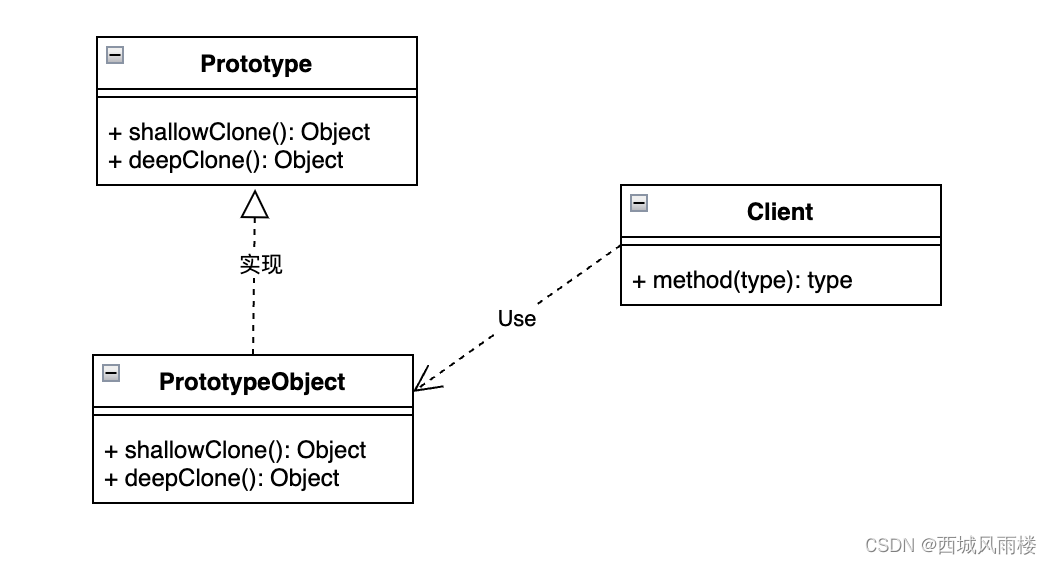
- Prototype接口,实现了该接口的对象,可以支持对象拷贝(深拷贝/浅拷贝),使用Java实现对象的拷贝的时候,该接口对应的就是Cloneable接口,如果某个类的没有实现该接口,那么调用Object的clone方法时候,将会抛出异常。
- PrototypeObject,原型对象,该对象实现了Prototype接口,表示支持克隆操作。
- Client,进行原型对象的深拷贝和浅拷贝。
3、原型模式的类图
4、原型模式的实现
原型模式的克隆在Java中可以使用两种技术实现,第一种是通过调用Object类的clone方法,第二种是通过java提供的对象序列化和反序列化机制。
并且在Java中如果要实现深度克隆,必须要求被克隆对象以及克隆对象的引用字段对象,都要实现原型接口(也就是克隆接口,并且被引用对象也要实现深度克隆才行,如果使用的是序列化机制,那么原型对象需要实现序列化接口,同时原型对象引用的其他对象也需要实现序列化接口,下面是原型模式的具体实现
- PrototypeObject
package prototype;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class PrototypeObject implements Cloneable, Serializable {
private ReferenceObject referenceObject;
private Integer id;
public PrototypeObject(ReferenceObject referenceObject, Integer id) {
this.referenceObject = referenceObject;
this.id = id;
}
public String getReferenceObjectDescribe() {
return referenceObject.getDesctibe();
}
public void setReferenceObjectDescribe(String describe) {
referenceObject.setDescribe(describe);
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
/**
* 借助Object类的clone方法,实现深拷贝
*
* @return
* @throws CloneNotSupportedException
*/
public Object deepClone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
PrototypeObject prototypeObject = (PrototypeObject) super.clone();
prototypeObject.referenceObject = (ReferenceObject) prototypeObject.referenceObject.clone();
return prototypeObject;
}
/**
* 借助Object类的clone方法,实现浅拷贝
*
* @return
* @throws CloneNotSupportedException
*/
public Object shallowClone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
/**
* 通过序列化机制实现深度克隆
*
* @return
* @throws IOException
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
*/
public Object deepCloneBySerialize() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(this);
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
Object clone = ois.readObject();
oos.close();
bis.close();
return clone;
}
}
- ReferenceObject,该对象是为了测试深浅拷贝的区别
package prototype;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class ReferenceObject implements Cloneable, Serializable {
private String describe;
public ReferenceObject(String describe) {
this.describe = describe;
}
public String getDesctibe() {
return describe;
}
public void setDescribe(String describe) {
this.describe = describe;
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
- Client
package prototype;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
testCloneByObjectClone();
testCloneBySerialize();
}
private static void testCloneBySerialize() throws Exception {
ReferenceObject referenceObject = new ReferenceObject("reference1");
PrototypeObject prototypeObject = new PrototypeObject(referenceObject, 1);
// 深拷贝克隆一份原型对象
PrototypeObject deepClone = (PrototypeObject) prototypeObject.deepCloneBySerialize();
// 输出深拷贝克隆的原型对象的值
System.out.println("打印深拷贝对象的引用对象描述: ");
System.out.println(deepClone.getReferenceObjectDescribe());
// 改变原型对象引用对象的描述,会发现shallowClone对象对应的该值也发生了变化
System.out.println("修改原型对象的引用对象描述");
prototypeObject.setReferenceObjectDescribe("reference change");
System.out.println("再次打印深拷贝对象的引用对象描述:");
System.out.println(deepClone.getReferenceObjectDescribe());
System.out.println("打印深拷贝对象的id:");
System.out.println(deepClone.getId());
}
private static void testCloneByObjectClone() throws Exception {
ReferenceObject referenceObject = new ReferenceObject("reference1");
PrototypeObject prototypeObject = new PrototypeObject(referenceObject, 1);
// 深拷贝克隆一份原型对象
PrototypeObject deepClone = (PrototypeObject) prototypeObject.deepClone();
// 浅拷贝克隆一份原型对象
PrototypeObject shallowClone = (PrototypeObject) prototypeObject.shallowClone();
// 输出浅拷贝克隆的原型对象的值
System.out.println("打印浅拷贝对象的引用对象描述: ");
System.out.println(shallowClone.getReferenceObjectDescribe());
// 改变原型对象引用对象的描述,会发现shallowClone对象对应的该值也发生了变化
System.out.println("修改原型对象的引用对象描述");
prototypeObject.setReferenceObjectDescribe("reference change");
System.out.println("再次打印浅拷贝对象的引用对象描述:");
System.out.println(shallowClone.getReferenceObjectDescribe());
System.out.println("打印浅拷贝对象的id:");
System.out.println(shallowClone.getId());
// 输出深拷贝克隆的原型对象的值
System.out.println("打印深拷贝对象的引用对象描述: ");
System.out.println(deepClone.getReferenceObjectDescribe());
// 改变原型对象引用对象的描述,会发现shallowClone对象对应的该值也发生了变化
System.out.println("修改原型对象的引用对象描述");
prototypeObject.setReferenceObjectDescribe("reference change");
System.out.println("再次打印深拷贝对象的引用对象描述:");
System.out.println(deepClone.getReferenceObjectDescribe());
System.out.println("打印深拷贝对象的id:");
System.out.println(deepClone.getId());
}
}
 原型模式与对象拷贝
原型模式与对象拷贝





 本文介绍了原型模式的基本概念及其实现方式,包括浅拷贝和深拷贝的区别,并通过Java代码示例展示了如何实现这两种拷贝。
本文介绍了原型模式的基本概念及其实现方式,包括浅拷贝和深拷贝的区别,并通过Java代码示例展示了如何实现这两种拷贝。
















 2465
2465

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








