前置
模板 – 打印
见
CppBaseDay21
重载 <<
os是泛化的std::ostream:
- 在
operator<<函数中,os是std::ostream的引用,这意味着它可以代表任何具体的输出流,例如std::cout、std::ofstream(文件输出流)、std::ostringstream(字符串输出流)等。- 当你向
operator<<传递std::cout时,os实际上就是std::cout的引用;但你也可以将其他流传递给os,例如文件流对象或字符串流对象。
cout是特定的std::ostream实例:
std::cout是一个具体的std::ostream实例,它与标准输出(通常是终端/控制台)相关联。你可以直接用std::cout来向屏幕打印消息。cout不能替代os,因为os可以是任何输出流,而cout仅指向标准输出。
使用namespace std { }的原因
当我们对标准库模板进行特化时,必须将特化放入
std命名空间,因为这些模板是在std命名空间中定义的。如果不放在std命名空间中,编译器将无法将其视为对标准模板的特化,而是会当成一个独立的新模板。
第一种方式 – 模板的特化
类模板特化 template<> struct less<Point>
//类模板定义
template <class/typename T, ...>
class 类名{
//类定义......
};
//chatgpt给出的示例:
namespace std {
template <class T> //less<Point> 是对模板 less<T> 的特化,Point 是 T 的具体类型
struct less {
……
};
}
//代码中的写法
template <>
struct less<Point>//模板的特化
{
……
}
template<>:这是模板特化的语法,表示我们将为模板类std::less提供一个特化版本,用于处理Point类型。
struct less<Point>:我们在std::less模板中为Point类型提供特化,即定义一个新的规则用于比较Point对象。。这个特化会覆盖默认的
std::less行为–在标准库中,std::less是一个类模板,用于定义对象之间的比较操作(通常是<运算符)。它的默认实现会使用<运算符来比较对象。
struct less<Point>是对std::less这个模板类的特化,这里的Point具体化了模板参数T。
less是类名,T是一个类型参数。这个模板类可以用来创建不同类型的比较器,例如less<int>、less<double>等。
operator():这是重载的函数调用运算符,定义了less<Point>如何比较两个Point对象。在这个例子中,我们首先比较x坐标,如果x坐标相等,则比较y坐标。
为什么要末尾要加const–成为const成员函数被调用
const/非const对象 以及 const/非const函数
在 const 对象上调用成员函数:
- 只能调用
const成员函数。- 不能调用非常量成员函数。
在非常量对象上调用成员函数:
- 可以调用
const和非const成员函数(优先,没有再调用const版本)。
chatgpt例子
class MyClass {
public:
int value;
// 非 const 成员函数
void setValue(int v) {
value = v; // 修改值
}
// const 成员函数
int getValue() const {
return value; // 只读
}
};
int main() {
MyClass obj; // 非 const 对象
obj.setValue(5); // 可以调用
int val = obj.getValue(); // 可以调用
const MyClass constObj; // const 对象
// constObj.setValue(10); // 错误,不能调用非 const 成员函数
int constVal = constObj.getValue(); // 可以调用 const 成员函数
return 0;
}
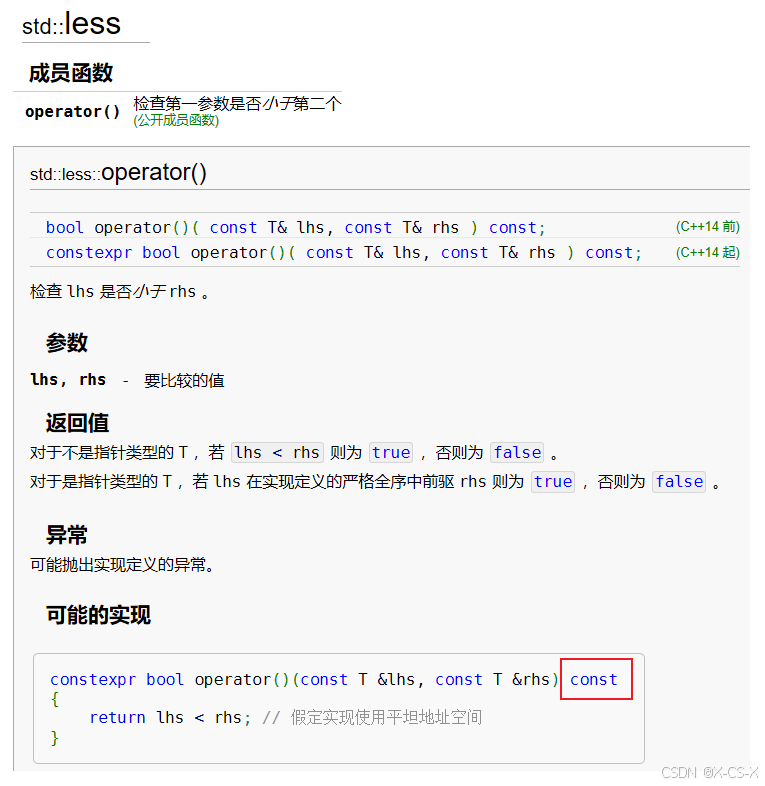
set源码中的成员函数operator()
看看吧。。。主要看图,格式就是这样要求的。。。
STL 容器(如
std::set、std::map)通常会使用传递的比较函数来比较元素。为了保证这些比较函数能够在使用时不改变容器中元素的状态,STL 要求这些函数必须是 可调用的(invocable)并且应该是const的。
以下是个人猜想。。。
set底层是const修饰的,因此set的对象只能调用const成员函数所以
bool operator()(const Point &lhs,const Point &rhs)后面要加const
//error
bool operator()(const Point &lhs,const Point &rhs) {……}
bool operator()(const Point &lhs,const Point &rhs) const {……}
//默认的模板
#if 0
namespace std
{
template <class T>
struct less
{
bool operator()(const T &lhs, const T &rhs) const
{
return lhs < rhs;
}
};
}//end of namespace std
#endif
形式
template <>
struct less<Point>//模板的特化
{
……
}
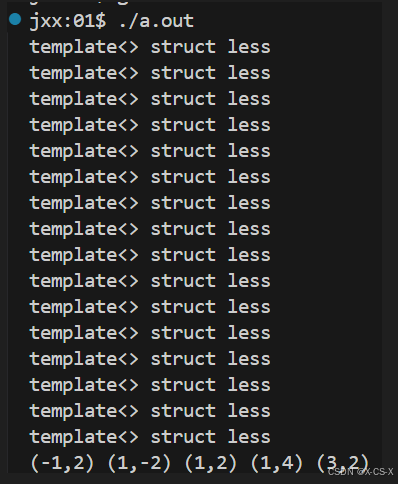
代码1
#include <math.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::set;
//模板 -- 打印
template <typename Container> //typename - class
void display(const Container & con){
for(auto & elem : con){
cout << elem << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
class Point
{
public:
Point(int ix = 0, int iy = 0)
: _ix(ix)
, _iy(iy)
{
}
//计算点到原点的距离
float getDistance() const
{
return hypot(_ix, _iy);
}
int getX() const
{
return _ix;
}
int getY() const
{
return _iy;
}
~Point()
{
}
friend std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os,const Point & rhs); //Point
private:
int _ix;
int _iy;
};
//由于是自定义模板,需要重载 <<
//同时由于需要访问Point类的私有成员,因此在Point类中需要把该函数声明为友元
std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os,const Point & rhs){
os << "(" << rhs._ix << "," << rhs._iy << ")";
return os;
}
//第一种 -- 模板的特化
namespace std
{
template <>
struct less<Point> //less是类名,T是一个类型参数。例如 less<int>、less<double> 等。
{
//比较2个Point类对象
bool operator()(const Point &lhs,const Point &rhs) const
{
cout << "template<> struct less" << endl;
// x 和 y均采用升序的方式比较大小
if(lhs.getX() < rhs.getX())
{
return true;
}else if(lhs.getX() == rhs.getX()){
if(lhs.getY() < rhs.getY()){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
else //lhs.getX() > rhs.getX()
{
return false;
}
}
};
} //end of namespace std
//第二种 -- 运算符重载
//第三种 -- 函数对象
void test0(){
set<Point> number = {
Point(1, 2),
Point(-1, 2),
Point(1, 4),
Point(1, 2),
Point(1, -2),
Point(3, 2),
};
display(number);
}
int main()
{
test0();
return 0;
}
第二种方式 – 函数对象
形式
struct ComparePoint
{
……
}
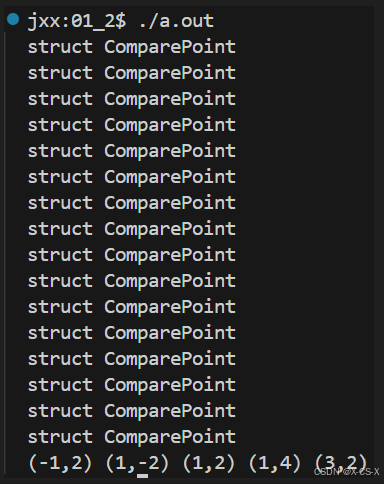
代码2
#include <math.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::set;
//模板 -- 打印
template <typename Container> //typename - class
void display(const Container & con){
for(auto & elem : con){
cout << elem << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
class Point
{
public:
Point(int ix = 0, int iy = 0)
: _ix(ix)
, _iy(iy)
{
}
//计算点到原点的距离
float getDistance() const
{
return hypot(_ix, _iy);
}
int getX() const
{
return _ix;
}
int getY() const
{
return _iy;
}
~Point()
{
}
friend std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os,const Point & rhs); //Point
//friend struct ComparePoint; //好像没将函数对象作为友元,代码运行也可以成功。。。
//因为使用了getX() 之类的函数,可以直接访问私有成员
private:
int _ix;
int _iy;
};
//由于是自定义模板,需要重载 <<
//同时由于需要访问Point类的私有成员,因此在Point类中需要把该函数声明为友元
std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os,const Point & rhs){
os << "(" << rhs._ix << "," << rhs._iy << ")";
return os;
}
//第一种 -- 模板的特化
//第二种 -- 函数对象
struct ComparePoint
{
//比较2个Point类对象
bool operator()(const Point &lhs,const Point &rhs) const
{
cout << "struct ComparePoint" << endl;
// x 和 y均采用升序的方式比较大小
if(lhs.getX() < rhs.getX())
{
return true;
}else if(lhs.getX() == rhs.getX()){
if(lhs.getY() < rhs.getY()){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
else //lhs.getX() > rhs.getX()
{
return false;
}
}
};
//第三种 -- 运算符重载
void test0(){
set<Point,ComparePoint> number = {
Point(1, 2),
Point(-1, 2),
Point(1, 4),
Point(1, 2),
Point(1, -2),
Point(3, 2),
};
display(number);
}
int main()
{
test0();
return 0;
}
第三种方式 – 运算符重载
形式
bool operator<(const Point & lhs,const Point & rhs)
{
……
}
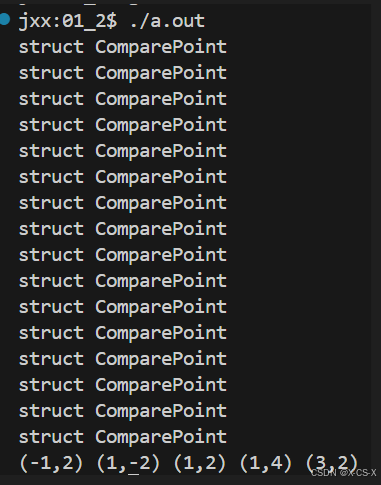
代码
#include <math.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::set;
//模板 -- 打印
template <typename Container> //typename - class
void display(const Container & con){
for(auto & elem : con){
cout << elem << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
class Point
{
public:
Point(int ix = 0, int iy = 0)
: _ix(ix)
, _iy(iy)
{
}
//计算点到原点的距离
float getDistance() const
{
return hypot(_ix, _iy);
}
int getX() const
{
return _ix;
}
int getY() const
{
return _iy;
}
~Point()
{
}
friend std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os,const Point & rhs); //Point
friend bool operator<(const Point &lhs, const Point &rhs); // < 运算符重载
private:
int _ix;
int _iy;
};
//由于是自定义模板,需要重载 <<
//同时由于需要访问Point类的私有成员,因此在Point类中需要把该函数声明为友元
std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os,const Point & rhs){
os << "(" << rhs._ix << "," << rhs._iy << ")";
return os;
}
//第一种 -- 模板的特化
//第二种 -- 函数对象
//第三种 -- 运算符重载
bool operator<(const Point & lhs,const Point & rhs){
cout << "bool operator<" << endl;
if(lhs.getX() < rhs.getX())
{
return true;
}else if(lhs.getX() == rhs.getX()){
if(lhs.getY() < rhs.getY()){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
else //lhs.getX() > rhs.getX()
{
return false;
}
}
void test0(){
set<Point> number = {
Point(1, 2),
Point(-1, 2),
Point(1, 4),
Point(1, 2),
Point(1, -2),
Point(3, 2),
};
display(number);
}
int main()
{
test0();
return 0;
}
补充
如果模板的特化 和 运算符重载同时存在
优先调用 模板的特化
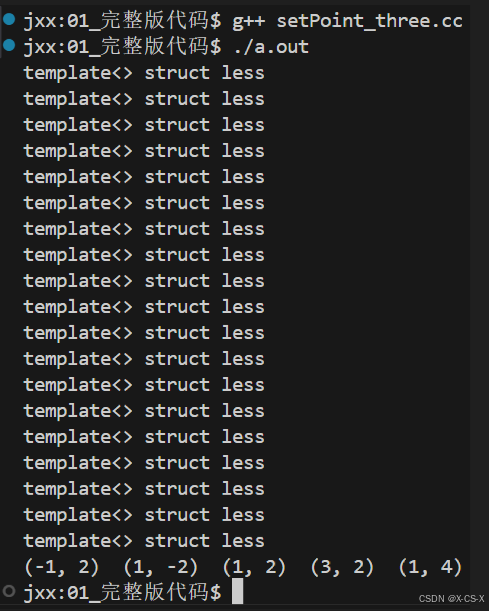
完整版代码
//setPoint_three.cc
#include <math.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::set;
template <typename Container>
void display(const Container &con)
{
for(auto &elem : con)
{
cout << elem << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
class Point
{
public:
Point(int ix = 0, int iy = 0)
: _ix(ix)
, _iy(iy)
{
}
//计算点到原点的距离
float getDistance() const
{
return hypot(_ix, _iy);
}
int getX() const
{
return _ix;
}
int getY() const
{
return _iy;
}
~Point()
{
}
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Point &rhs);
friend bool operator<(const Point &lhs, const Point &rhs);
friend struct ComparePoint;
private:
int _ix;
int _iy;
};
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Point &rhs)
{
os << "(" << rhs._ix
<< ", " << rhs._iy
<< ")";
return os;
}
bool operator<(const Point &lhs, const Point &rhs)
{
cout << "bool operator<" << endl;
if(lhs.getDistance() < rhs.getDistance())
{
return true;
}
else if(lhs.getDistance() == rhs.getDistance())
{
if(lhs._ix < rhs._ix)
{
return true;
}
else if(lhs._ix == rhs._ix)
{
if(lhs._iy < rhs._iy)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
struct ComparePoint
{
bool operator()(const Point &lhs, const Point &rhs) const
{
cout << "struct ComparePoint" << endl;
if(lhs.getDistance() < rhs.getDistance())
{
return true;
}
else if(lhs.getDistance() == rhs.getDistance())
{
if(lhs._ix < rhs._ix)
{
return true;
}
else if(lhs._ix == rhs._ix)
{
if(lhs._iy < rhs._iy)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
};
#if 0
namespace std
{
template <class T>
struct less
{
bool operator()(const T &lhs, const T &rhs) const
{
return lhs < rhs;
}
};
}//end of namespace std
#endif
//命名空间的扩展
namespace std
{
template <>
struct less<Point>//模板的特化
{
bool operator()(const Point &lhs, const Point &rhs) const
{
cout << "template<> struct less" << endl;
if(lhs.getDistance() < rhs.getDistance())
{
return true;
}
else if(lhs.getDistance() == rhs.getDistance())
{
if(lhs.getX() < rhs.getX())
{
return true;
}
else if(lhs.getX() == rhs.getX())
{
if(lhs.getY() < rhs.getY())
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
};
}//end of namespace std
void test()
{
set<Point> number = {
/* set<Point, ComparePoint> number = { */
Point(1, 2),
Point(-1, 2),
Point(1, 4),
Point(1, 2),
Point(1, -2),
Point(3, 2),
};
display(number);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
test();
return 0;
}





















 1133
1133

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








