Since Sonya has just learned the basics of matrices, she decided to play with them a little bit.
Sonya imagined a new type of matrices that she called rhombic matrices. These matrices have exactly one zero, while all other cells have the Manhattan distance to the cell containing the zero. The cells with equal numbers have the form of a rhombus, that is why Sonya called this type so.
The Manhattan distance between two cells (x1x1, y1y1) and (x2x2, y2y2) is defined as |x1−x2|+|y1−y2||x1−x2|+|y1−y2|. For example, the Manhattan distance between the cells (5,2)(5,2) and (7,1)(7,1) equals to |5−7|+|2−1|=3|5−7|+|2−1|=3.
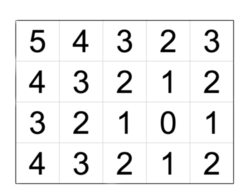 Example of a rhombic matrix.
Example of a rhombic matrix.Note that rhombic matrices are uniquely defined by nn, mm, and the coordinates of the cell containing the zero.
She drew a n×mn×m rhombic matrix. She believes that you can not recreate the matrix if she gives you only the elements of this matrix in some arbitrary order (i.e., the sequence of n⋅mn⋅m numbers). Note that Sonya will not give you nn and mm, so only the sequence of numbers in this matrix will be at your disposal.
Write a program that finds such an n×mn×m rhombic matrix whose elements are the same as the elements in the sequence in some order.
The first line contains a single integer tt (1≤t≤1061≤t≤106) — the number of cells in the matrix.
The second line contains tt integers a1,a2,…,ata1,a2,…,at (0≤ai<t0≤ai<t) — the values in the cells in arbitrary order.
In the first line, print two positive integers nn and mm (n×m=tn×m=t) — the size of the matrix.
In the second line, print two integers xx and yy (1≤x≤n1≤x≤n, 1≤y≤m1≤y≤m) — the row number and the column number where the cell with 00 is located.
If there are multiple possible answers, print any of them. If there is no solution, print the single integer −1−1.
20 1 0 2 3 5 3 2 1 3 2 3 1 4 2 1 4 2 3 2 4
4 5 2 2
18 2 2 3 2 4 3 3 3 0 2 4 2 1 3 2 1 1 1
3 6 2 3
6 2 1 0 2 1 2
-1
You can see the solution to the first example in the legend. You also can choose the cell (2,2)(2,2) for the cell where 00 is located. You also can choose a 5×45×4 matrix with zero at (4,2)(4,2).
In the second example, there is a 3×63×6 matrix, where the zero is located at (2,3)(2,3) there.
In the third example, a solution does not exist.
思路:
设 0的坐标为(x,y),矩阵的大小为(m,n),矩阵第一行第一列为(1,1)(在这里我们要把矩阵翻过来看);设 a=x-1+y-1 , b=m-x +n-y;
则a表示0到(1,1)的距离,b表示0到m,n的距离,这里注意,很容易知道b的值就是输入数中最大的那一个,因为最大的那个数距离0是最远的。
将a=x-1+y-1 , b=m-x +n-y合并得 a=m+n-2-b;代入a=x-1+y-1中得到y=n+m-b-x; 如果 a[i] != 4*i,x=i;
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+10;
int a[N],d[N];
int t;
int n,m;
int x,y;
int b;///矩阵角落到"0"的最大距离
///y=n+m-b-x
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d",&t)!=EOF){
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
b=0;
for(int i=1;i<=t;i++){
int num;
scanf("%d",&num);
a[num]++; //这样a[i]=n 就代表数i有n个
b=max(b,num);//找最大的那个数
}
x=1;///x需要初始化为1,因为x的最小值为1,我们可能在下面的循环中,找不到这样的x
///从而导致x的值不确定.eg:1 0这一组数据。
for(int i=1;i<b;i++)
if(a[i]!=4*i){ //这个找求x的过程建议结合图理解
x=i;
break;
}
int flag2=1;
for(n=1;n<=t;n++){
if(t%n==0){ //因为m*n=t;n首先得满足是t的因数
m=t/n;
y=n+m-b-x;
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ //因为距离就是数的大小,所以我们验证在当前m,n,x,y下各个坐标到0的距离,即数的大小和个数保存在d中,和原数组做比较。
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
int temp=abs(i-x)+abs(j-y);
d[temp]++;
}
}
int flag=1;
for(int i=0;i<=b;i++){///这里i要从0开始比较,因为有可能出现多个"0"的情况.
if(a[i]!=d[i]){
flag=0;
break;
}
}
if(flag){
printf("%d %d\n",n,m);
printf("%d %d\n",x,y);
flag2=0;
break;
}
}
}
if(flag2)printf("-1\n");
}
return 0;
}




 本文介绍了一种特殊的矩阵——菱形矩阵,该矩阵仅包含一个零元素,其余元素为各自到零元素的曼哈顿距离。文章提供了一个算法,通过输入矩阵元素的无序列表来重建菱形矩阵的大小及其零元素的位置。
本文介绍了一种特殊的矩阵——菱形矩阵,该矩阵仅包含一个零元素,其余元素为各自到零元素的曼哈顿距离。文章提供了一个算法,通过输入矩阵元素的无序列表来重建菱形矩阵的大小及其零元素的位置。
















 266
266

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








